How to Enhance Biocompatibility in Carboxylic Acid Applications?
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carboxylic Acid Biocompatibility Background and Objectives
Carboxylic acids play a crucial role in various biological processes and have extensive applications in pharmaceuticals, biomaterials, and medical devices. However, their inherent acidity and potential for reactivity pose challenges in terms of biocompatibility. Enhancing the biocompatibility of carboxylic acid applications has become a critical focus in the fields of biomedicine and materials science.
The development of carboxylic acid-based materials and their applications has seen significant progress over the past few decades. From early uses in simple drug formulations to advanced biomaterials and tissue engineering scaffolds, the versatility of carboxylic acids has been increasingly recognized. However, as applications have become more sophisticated, so too have the demands for improved biocompatibility.
Biocompatibility refers to the ability of a material to perform with an appropriate host response in a specific application. In the context of carboxylic acids, this involves minimizing adverse reactions, reducing inflammation, and ensuring proper integration with biological systems. The challenge lies in maintaining the desired functional properties of carboxylic acids while mitigating their potential negative impacts on living tissues.
Recent technological advancements have opened up new possibilities for enhancing biocompatibility. These include novel surface modification techniques, the development of smart polymers, and the integration of carboxylic acids into composite materials. Additionally, the emergence of nanotechnology has provided tools for precise control over material properties at the molecular level.
The objectives of current research in this field are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a drive to develop carboxylic acid-based materials with improved biocompatibility profiles, capable of interfacing seamlessly with biological systems. Secondly, researchers aim to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of biocompatibility, including the interactions between carboxylic acids and various biological components such as proteins, cells, and tissues.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on creating adaptive and responsive carboxylic acid systems that can dynamically adjust their properties in response to biological cues. This approach holds promise for applications in drug delivery, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine, where materials need to evolve in concert with biological processes.
As we look to the future, the goal is to push the boundaries of what is possible with carboxylic acid applications in biological settings. This includes developing materials with unprecedented levels of biocompatibility, expanding the range of applications, and creating innovative solutions to long-standing challenges in healthcare and biotechnology. The path forward involves interdisciplinary collaboration, combining insights from chemistry, materials science, biology, and medicine to drive progress in this critical area of research.
The development of carboxylic acid-based materials and their applications has seen significant progress over the past few decades. From early uses in simple drug formulations to advanced biomaterials and tissue engineering scaffolds, the versatility of carboxylic acids has been increasingly recognized. However, as applications have become more sophisticated, so too have the demands for improved biocompatibility.
Biocompatibility refers to the ability of a material to perform with an appropriate host response in a specific application. In the context of carboxylic acids, this involves minimizing adverse reactions, reducing inflammation, and ensuring proper integration with biological systems. The challenge lies in maintaining the desired functional properties of carboxylic acids while mitigating their potential negative impacts on living tissues.
Recent technological advancements have opened up new possibilities for enhancing biocompatibility. These include novel surface modification techniques, the development of smart polymers, and the integration of carboxylic acids into composite materials. Additionally, the emergence of nanotechnology has provided tools for precise control over material properties at the molecular level.
The objectives of current research in this field are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a drive to develop carboxylic acid-based materials with improved biocompatibility profiles, capable of interfacing seamlessly with biological systems. Secondly, researchers aim to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of biocompatibility, including the interactions between carboxylic acids and various biological components such as proteins, cells, and tissues.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on creating adaptive and responsive carboxylic acid systems that can dynamically adjust their properties in response to biological cues. This approach holds promise for applications in drug delivery, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine, where materials need to evolve in concert with biological processes.
As we look to the future, the goal is to push the boundaries of what is possible with carboxylic acid applications in biological settings. This includes developing materials with unprecedented levels of biocompatibility, expanding the range of applications, and creating innovative solutions to long-standing challenges in healthcare and biotechnology. The path forward involves interdisciplinary collaboration, combining insights from chemistry, materials science, biology, and medicine to drive progress in this critical area of research.
Market Analysis for Biocompatible Carboxylic Acid Products
The market for biocompatible carboxylic acid products has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand in various industries, particularly in healthcare and biomaterials. The global market size for these products is expected to expand substantially over the next decade, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) outpacing many other segments in the specialty chemicals sector.
Healthcare applications dominate the market, accounting for the largest share of biocompatible carboxylic acid product usage. This is primarily due to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing aging population, which has led to increased demand for medical devices, implants, and drug delivery systems that require biocompatible materials. The pharmaceutical industry also contributes significantly to market growth, utilizing these products in drug formulations and as excipients.
The biomaterials sector represents another key market segment, with applications in tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, and advanced wound care products. As research in these fields progresses, the demand for biocompatible carboxylic acid products is expected to surge, opening new avenues for market expansion.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and robust research and development activities. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a lucrative market, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of advanced medical technologies.
Key factors influencing market growth include technological advancements in material science, increasing investments in healthcare research, and stringent regulations promoting the use of biocompatible materials. The trend towards personalized medicine and the development of smart implants are also expected to fuel demand for these products.
Challenges in the market include the high cost of research and development, regulatory hurdles, and the need for extensive clinical trials to prove long-term biocompatibility. Additionally, concerns about the environmental impact of synthetic carboxylic acids have led to a growing interest in bio-based alternatives, which could reshape the market landscape in the coming years.
Looking ahead, the market is poised for further expansion, with opportunities arising from the integration of nanotechnology in biocompatible materials and the development of multifunctional carboxylic acid derivatives. As the focus on patient safety and comfort intensifies, manufacturers are likely to invest more in enhancing the biocompatibility of their products, driving innovation and market growth.
Healthcare applications dominate the market, accounting for the largest share of biocompatible carboxylic acid product usage. This is primarily due to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing aging population, which has led to increased demand for medical devices, implants, and drug delivery systems that require biocompatible materials. The pharmaceutical industry also contributes significantly to market growth, utilizing these products in drug formulations and as excipients.
The biomaterials sector represents another key market segment, with applications in tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, and advanced wound care products. As research in these fields progresses, the demand for biocompatible carboxylic acid products is expected to surge, opening new avenues for market expansion.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and robust research and development activities. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a lucrative market, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of advanced medical technologies.
Key factors influencing market growth include technological advancements in material science, increasing investments in healthcare research, and stringent regulations promoting the use of biocompatible materials. The trend towards personalized medicine and the development of smart implants are also expected to fuel demand for these products.
Challenges in the market include the high cost of research and development, regulatory hurdles, and the need for extensive clinical trials to prove long-term biocompatibility. Additionally, concerns about the environmental impact of synthetic carboxylic acids have led to a growing interest in bio-based alternatives, which could reshape the market landscape in the coming years.
Looking ahead, the market is poised for further expansion, with opportunities arising from the integration of nanotechnology in biocompatible materials and the development of multifunctional carboxylic acid derivatives. As the focus on patient safety and comfort intensifies, manufacturers are likely to invest more in enhancing the biocompatibility of their products, driving innovation and market growth.
Current Challenges in Carboxylic Acid Biocompatibility
Despite the widespread use of carboxylic acids in various biomedical applications, several challenges persist in enhancing their biocompatibility. One of the primary issues is the inherent acidity of these compounds, which can lead to local pH changes in biological environments. This alteration in pH can potentially disrupt cellular functions, damage tissues, and trigger inflammatory responses, limiting the long-term efficacy and safety of carboxylic acid-based interventions.
Another significant challenge lies in the surface interactions between carboxylic acid-containing materials and biological entities. The negatively charged carboxyl groups can non-specifically adsorb proteins and other biomolecules, leading to undesired biological responses such as thrombosis or immune system activation. This protein adsorption can also alter the intended functionality of the material, reducing its effectiveness in the target application.
The hydrophobic nature of many carboxylic acid derivatives poses additional biocompatibility concerns. While this property can be advantageous for certain applications, such as drug delivery systems, it can also lead to poor solubility and distribution in aqueous biological environments. This limited solubility may result in reduced bioavailability and efficacy of carboxylic acid-based therapeutics.
Furthermore, the potential for carboxylic acids to form hydrogen bonds with surrounding molecules can interfere with critical biological processes. This interaction may disrupt cell membrane integrity, alter protein conformations, or interfere with enzyme activities, leading to unintended physiological effects and compromised biocompatibility.
The metabolic fate of carboxylic acids in biological systems presents another challenge. While many carboxylic acids are naturally occurring and can be metabolized, some synthetic derivatives may accumulate in tissues or organs, potentially leading to long-term toxicity or adverse effects. Understanding and controlling the biodegradation pathways of these compounds is crucial for ensuring their safe use in biomedical applications.
Lastly, the scalability and reproducibility of carboxylic acid modifications for enhanced biocompatibility remain significant hurdles. Developing consistent and cost-effective methods for surface functionalization or encapsulation of carboxylic acids, while maintaining their desired properties, is essential for their widespread adoption in biomedical devices and therapeutics.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from chemistry, materials science, biology, and bioengineering. Innovative strategies such as surface modification techniques, controlled release systems, and novel molecular designs are being explored to overcome these biocompatibility issues and unlock the full potential of carboxylic acids in biomedical applications.
Another significant challenge lies in the surface interactions between carboxylic acid-containing materials and biological entities. The negatively charged carboxyl groups can non-specifically adsorb proteins and other biomolecules, leading to undesired biological responses such as thrombosis or immune system activation. This protein adsorption can also alter the intended functionality of the material, reducing its effectiveness in the target application.
The hydrophobic nature of many carboxylic acid derivatives poses additional biocompatibility concerns. While this property can be advantageous for certain applications, such as drug delivery systems, it can also lead to poor solubility and distribution in aqueous biological environments. This limited solubility may result in reduced bioavailability and efficacy of carboxylic acid-based therapeutics.
Furthermore, the potential for carboxylic acids to form hydrogen bonds with surrounding molecules can interfere with critical biological processes. This interaction may disrupt cell membrane integrity, alter protein conformations, or interfere with enzyme activities, leading to unintended physiological effects and compromised biocompatibility.
The metabolic fate of carboxylic acids in biological systems presents another challenge. While many carboxylic acids are naturally occurring and can be metabolized, some synthetic derivatives may accumulate in tissues or organs, potentially leading to long-term toxicity or adverse effects. Understanding and controlling the biodegradation pathways of these compounds is crucial for ensuring their safe use in biomedical applications.
Lastly, the scalability and reproducibility of carboxylic acid modifications for enhanced biocompatibility remain significant hurdles. Developing consistent and cost-effective methods for surface functionalization or encapsulation of carboxylic acids, while maintaining their desired properties, is essential for their widespread adoption in biomedical devices and therapeutics.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from chemistry, materials science, biology, and bioengineering. Innovative strategies such as surface modification techniques, controlled release systems, and novel molecular designs are being explored to overcome these biocompatibility issues and unlock the full potential of carboxylic acids in biomedical applications.
Existing Biocompatibility Enhancement Strategies
01 Biocompatible carboxylic acid derivatives
Development of biocompatible carboxylic acid derivatives for various applications in medicine and biotechnology. These compounds are designed to have improved compatibility with biological systems while maintaining the desired functional properties of carboxylic acids.- Biocompatible carboxylic acid derivatives: Development of biocompatible carboxylic acid derivatives for various applications in medicine and biotechnology. These compounds are designed to have improved compatibility with biological systems while maintaining the desired functional properties of carboxylic acids.
- Carboxylic acid-based polymers for biomedical applications: Creation of biocompatible polymers containing carboxylic acid groups for use in medical devices, drug delivery systems, and tissue engineering. These polymers offer improved biocompatibility and can be tailored for specific biomedical applications.
- Carboxylic acid modifications for enhanced biocompatibility: Methods for modifying carboxylic acids to improve their biocompatibility, including functionalization, conjugation with biocompatible molecules, and incorporation into nanostructures. These modifications aim to reduce potential adverse effects while maintaining the desired properties of carboxylic acids.
- Biocompatible carboxylic acid-based coatings: Development of biocompatible coatings containing carboxylic acid groups for medical implants and devices. These coatings improve the integration of implants with biological tissues and reduce the risk of adverse reactions.
- Carboxylic acid-based drug delivery systems: Design of biocompatible drug delivery systems utilizing carboxylic acid-containing compounds or polymers. These systems aim to improve drug solubility, stability, and targeted delivery while maintaining biocompatibility and reducing side effects.
02 Carboxylic acid-based polymers for biomedical applications
Creation of biocompatible polymers containing carboxylic acid groups for use in medical devices, drug delivery systems, and tissue engineering. These polymers offer improved biocompatibility and can be tailored for specific biomedical applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Carboxylic acid modifications for enhanced biocompatibility
Methods for modifying carboxylic acids to improve their biocompatibility, including functionalization, conjugation with biocompatible molecules, or incorporation into larger structures. These modifications aim to reduce potential adverse effects while maintaining the desired properties of the carboxylic acids.Expand Specific Solutions04 Biocompatible carboxylic acid-based materials for implants
Development of biocompatible materials incorporating carboxylic acids for use in medical implants, such as orthopedic devices, dental implants, or cardiovascular stents. These materials are designed to minimize immune responses and promote integration with surrounding tissues.Expand Specific Solutions05 Carboxylic acid-based drug delivery systems
Creation of biocompatible drug delivery systems utilizing carboxylic acids as key components. These systems aim to improve drug solubility, stability, and targeted delivery while maintaining biocompatibility and minimizing potential side effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Biocompatible Carboxylic Acid Research
The biocompatibility enhancement of carboxylic acid applications is in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by expanding uses in medical devices, drug delivery systems, and biomaterials. The technology's maturity is advancing, but still evolving. Key players like Evonik Operations GmbH, LANXESS Deutschland GmbH, and Dow Silicones Corp. are leading innovation, leveraging their expertise in specialty chemicals and materials science. Academic institutions such as Jiangnan University and South China University of Technology are contributing to fundamental research. Pharmaceutical companies like Takeda and Boehringer Ingelheim are exploring applications in drug formulations, while smaller specialized firms like Noxelis SAS and Falgagen SAS focus on niche biomedical applications.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed a novel approach to enhance biocompatibility in carboxylic acid applications through their RESOMER® platform. This technology utilizes biodegradable polymers based on lactic and glycolic acids to create biocompatible materials for medical devices and drug delivery systems. The company has implemented surface modification techniques, such as plasma treatment and chemical grafting, to introduce carboxylic acid groups onto the polymer surface, improving cell adhesion and protein adsorption [1][3]. Additionally, Evonik has explored the use of block copolymers containing both hydrophobic and hydrophilic segments, with carboxylic acid functionalities strategically placed to enhance biocompatibility while maintaining desired mechanical properties [2].
Strengths: Versatile polymer platform, customizable surface properties, and established presence in the medical device industry. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in long-term stability and cost-effectiveness for large-scale applications.
LANXESS Deutschland GmbH
Technical Solution: LANXESS has developed a range of specialty chemicals and polymers to address biocompatibility challenges in carboxylic acid applications. Their approach focuses on the synthesis of carboxylic acid-functionalized polymers with controlled molecular weight and distribution. These polymers are designed to form stable hydrogels or coatings that can be applied to various substrates, enhancing their biocompatibility [4]. LANXESS has also explored the incorporation of zwitterionic moieties alongside carboxylic acid groups to create materials with excellent anti-fouling properties and reduced protein adsorption [5]. Furthermore, the company has invested in developing biodegradable alternatives to traditional polymers, utilizing renewable resources and green chemistry principles to produce biocompatible materials with reduced environmental impact [6].
Strengths: Diverse product portfolio, strong focus on sustainability, and expertise in polymer chemistry. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up production of highly specialized materials and meeting regulatory requirements for medical applications.
Innovative Approaches in Carboxylic Acid Biocompatibility
Prostacyclin derivatives
PatentWO2008079383A1
Innovation
- Development of novel prostacyclin derivatives with enhanced stability and prolonged action, allowing for less frequent dosing and improved therapeutic coverage, including specific isotopic enrichment and formulation strategies to enhance bioavailability and reduce side effects.
Carboxylic ester compound
PatentWO1994007865A1
Innovation
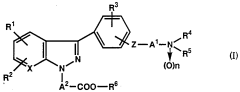
- A novel carboxylic acid ester compound with a specific general formula, including various substituents and functional groups, is developed to enhance oral absorption and bioavailability, which is represented by compounds like 3-(4-(2-dimethylamino-1-methylethoxy)phenyl)-1H-pyrazo[3,4-b]pyridine-1-acetate and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
Regulatory Landscape for Biocompatible Materials
The regulatory landscape for biocompatible materials in carboxylic acid applications is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental agencies and international organizations. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating biocompatible materials, particularly those used in medical devices and pharmaceuticals. The FDA's Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) oversees the safety and effectiveness of medical devices, including those incorporating carboxylic acid-based materials.
Internationally, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards relevant to biocompatibility, such as ISO 10993, which provides a framework for biological evaluation of medical devices. This standard is widely recognized and adopted by regulatory bodies worldwide, including the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
The European Union's regulatory framework for biocompatible materials is governed by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR). These regulations set stringent requirements for manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and performance of their products, including the biocompatibility of materials used in medical applications.
In Japan, the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) oversees the regulation of biocompatible materials. The PMDA follows guidelines similar to those of the FDA and EMA but may have additional requirements specific to the Japanese market.
Regulatory bodies typically require manufacturers to conduct extensive biocompatibility testing to assess the potential risks associated with the use of carboxylic acid-based materials in medical applications. These tests often include cytotoxicity, sensitization, irritation, and systemic toxicity studies, among others.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses environmental considerations, particularly for the disposal of biocompatible materials containing carboxylic acids. Agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in the EU have established guidelines for the safe handling and disposal of these materials.
As the field of biocompatible materials continues to evolve, regulatory agencies are adapting their frameworks to address emerging technologies and applications. This includes the development of new guidance documents and the revision of existing standards to ensure the safety and efficacy of novel biocompatible materials incorporating carboxylic acids.
Manufacturers and researchers working with carboxylic acid-based biocompatible materials must navigate this complex regulatory landscape to ensure compliance and market access. This often requires a comprehensive understanding of the relevant regulations, standards, and testing requirements across different jurisdictions, as well as ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes and updates in this rapidly evolving field.
Internationally, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards relevant to biocompatibility, such as ISO 10993, which provides a framework for biological evaluation of medical devices. This standard is widely recognized and adopted by regulatory bodies worldwide, including the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
The European Union's regulatory framework for biocompatible materials is governed by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR). These regulations set stringent requirements for manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and performance of their products, including the biocompatibility of materials used in medical applications.
In Japan, the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) oversees the regulation of biocompatible materials. The PMDA follows guidelines similar to those of the FDA and EMA but may have additional requirements specific to the Japanese market.
Regulatory bodies typically require manufacturers to conduct extensive biocompatibility testing to assess the potential risks associated with the use of carboxylic acid-based materials in medical applications. These tests often include cytotoxicity, sensitization, irritation, and systemic toxicity studies, among others.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses environmental considerations, particularly for the disposal of biocompatible materials containing carboxylic acids. Agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in the EU have established guidelines for the safe handling and disposal of these materials.
As the field of biocompatible materials continues to evolve, regulatory agencies are adapting their frameworks to address emerging technologies and applications. This includes the development of new guidance documents and the revision of existing standards to ensure the safety and efficacy of novel biocompatible materials incorporating carboxylic acids.
Manufacturers and researchers working with carboxylic acid-based biocompatible materials must navigate this complex regulatory landscape to ensure compliance and market access. This often requires a comprehensive understanding of the relevant regulations, standards, and testing requirements across different jurisdictions, as well as ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes and updates in this rapidly evolving field.
Environmental Impact of Biocompatible Carboxylic Acids
The environmental impact of biocompatible carboxylic acids is a crucial consideration in their application and development. These compounds, while essential for various industries, can have both positive and negative effects on ecosystems and human health.
Biocompatible carboxylic acids, by definition, are designed to be less harmful to living organisms and the environment. This inherent property contributes to reduced ecological risks compared to their non-biocompatible counterparts. When released into the environment, these acids are more likely to degrade naturally, minimizing long-term accumulation in soil and water systems.
One of the primary environmental benefits of biocompatible carboxylic acids is their potential to replace more toxic chemicals in various applications. For instance, in the field of agriculture, these compounds can serve as eco-friendly alternatives to conventional pesticides and herbicides. This substitution can lead to decreased soil and water pollution, as well as reduced harm to non-target organisms.
However, the environmental impact is not entirely benign. Even biocompatible carboxylic acids, when present in high concentrations, can alter the pH of aquatic environments. This change can disrupt ecosystems, affecting the growth and survival of various aquatic species. Therefore, proper management and controlled release of these compounds are essential to mitigate potential negative impacts.
In industrial applications, the use of biocompatible carboxylic acids can contribute to greener manufacturing processes. These acids often require less energy for production and processing, resulting in a lower carbon footprint. Additionally, their biodegradability reduces the burden on waste management systems and decreases the risk of long-term environmental contamination.
The impact on air quality is another important aspect to consider. Volatile carboxylic acids can contribute to the formation of secondary organic aerosols, which are a component of particulate matter pollution. However, biocompatible variants typically have lower volatility, potentially reducing their contribution to air pollution compared to traditional carboxylic acids.
Research into the lifecycle assessment of biocompatible carboxylic acids is ongoing. Studies aim to quantify their overall environmental impact from production to disposal, considering factors such as resource consumption, emissions, and end-of-life scenarios. This comprehensive approach helps in making informed decisions about their use and development.
As the demand for sustainable solutions grows, the development of even more environmentally friendly carboxylic acids continues. Researchers are exploring novel synthesis methods using renewable resources and investigating ways to enhance the biodegradability of these compounds without compromising their functionality.
Biocompatible carboxylic acids, by definition, are designed to be less harmful to living organisms and the environment. This inherent property contributes to reduced ecological risks compared to their non-biocompatible counterparts. When released into the environment, these acids are more likely to degrade naturally, minimizing long-term accumulation in soil and water systems.
One of the primary environmental benefits of biocompatible carboxylic acids is their potential to replace more toxic chemicals in various applications. For instance, in the field of agriculture, these compounds can serve as eco-friendly alternatives to conventional pesticides and herbicides. This substitution can lead to decreased soil and water pollution, as well as reduced harm to non-target organisms.
However, the environmental impact is not entirely benign. Even biocompatible carboxylic acids, when present in high concentrations, can alter the pH of aquatic environments. This change can disrupt ecosystems, affecting the growth and survival of various aquatic species. Therefore, proper management and controlled release of these compounds are essential to mitigate potential negative impacts.
In industrial applications, the use of biocompatible carboxylic acids can contribute to greener manufacturing processes. These acids often require less energy for production and processing, resulting in a lower carbon footprint. Additionally, their biodegradability reduces the burden on waste management systems and decreases the risk of long-term environmental contamination.
The impact on air quality is another important aspect to consider. Volatile carboxylic acids can contribute to the formation of secondary organic aerosols, which are a component of particulate matter pollution. However, biocompatible variants typically have lower volatility, potentially reducing their contribution to air pollution compared to traditional carboxylic acids.
Research into the lifecycle assessment of biocompatible carboxylic acids is ongoing. Studies aim to quantify their overall environmental impact from production to disposal, considering factors such as resource consumption, emissions, and end-of-life scenarios. This comprehensive approach helps in making informed decisions about their use and development.
As the demand for sustainable solutions grows, the development of even more environmentally friendly carboxylic acids continues. Researchers are exploring novel synthesis methods using renewable resources and investigating ways to enhance the biodegradability of these compounds without compromising their functionality.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!