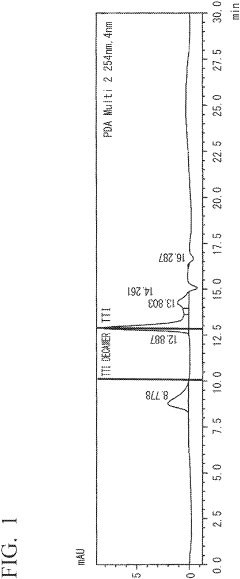
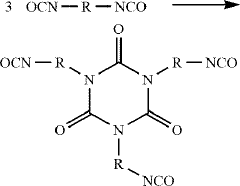
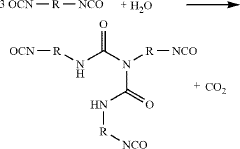
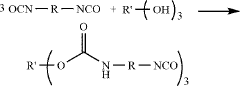
How to Leverage Isocyanates in High-Performance Polymers?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Polymer Evolution and Objectives
Isocyanates have played a pivotal role in the evolution of high-performance polymers since their discovery in the early 20th century. The journey of isocyanate-based polymers began with Otto Bayer's groundbreaking work in 1937, which led to the development of polyurethanes. This innovation marked the beginning of a new era in polymer science, opening up possibilities for creating materials with tailored properties and diverse applications.
Over the decades, the utilization of isocyanates in polymer chemistry has expanded significantly. The versatility of isocyanate chemistry has enabled the creation of a wide range of polymers with exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. From flexible foams to rigid structural materials, isocyanates have become indispensable in various industries, including automotive, construction, electronics, and healthcare.
The evolution of isocyanate-based polymers has been driven by the continuous pursuit of enhanced performance and sustainability. Researchers and industry professionals have focused on developing new isocyanate chemistries, optimizing reaction conditions, and exploring novel catalysts to improve the efficiency and properties of the resulting polymers. This ongoing research has led to the creation of high-performance materials with superior strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors.
In recent years, the objectives for leveraging isocyanates in high-performance polymers have shifted towards addressing global challenges. Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have pushed the industry to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly isocyanate-based polymers. This includes efforts to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, increase the use of bio-based raw materials, and improve the recyclability and biodegradability of isocyanate-derived products.
Another key objective in the evolution of isocyanate polymers is the development of smart and responsive materials. Researchers are exploring ways to incorporate stimuli-responsive properties into isocyanate-based polymers, enabling the creation of materials that can adapt to changing environmental conditions or external stimuli. This opens up new possibilities for applications in areas such as self-healing materials, shape-memory polymers, and adaptive structures.
The future objectives for leveraging isocyanates in high-performance polymers are focused on pushing the boundaries of material properties and functionality. This includes developing polymers with enhanced thermal stability, improved chemical resistance, and advanced mechanical properties. Additionally, there is a growing interest in exploring the potential of isocyanates in emerging fields such as 3D printing, nanotechnology, and biomedical applications.
Over the decades, the utilization of isocyanates in polymer chemistry has expanded significantly. The versatility of isocyanate chemistry has enabled the creation of a wide range of polymers with exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. From flexible foams to rigid structural materials, isocyanates have become indispensable in various industries, including automotive, construction, electronics, and healthcare.
The evolution of isocyanate-based polymers has been driven by the continuous pursuit of enhanced performance and sustainability. Researchers and industry professionals have focused on developing new isocyanate chemistries, optimizing reaction conditions, and exploring novel catalysts to improve the efficiency and properties of the resulting polymers. This ongoing research has led to the creation of high-performance materials with superior strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors.
In recent years, the objectives for leveraging isocyanates in high-performance polymers have shifted towards addressing global challenges. Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have pushed the industry to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly isocyanate-based polymers. This includes efforts to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, increase the use of bio-based raw materials, and improve the recyclability and biodegradability of isocyanate-derived products.
Another key objective in the evolution of isocyanate polymers is the development of smart and responsive materials. Researchers are exploring ways to incorporate stimuli-responsive properties into isocyanate-based polymers, enabling the creation of materials that can adapt to changing environmental conditions or external stimuli. This opens up new possibilities for applications in areas such as self-healing materials, shape-memory polymers, and adaptive structures.
The future objectives for leveraging isocyanates in high-performance polymers are focused on pushing the boundaries of material properties and functionality. This includes developing polymers with enhanced thermal stability, improved chemical resistance, and advanced mechanical properties. Additionally, there is a growing interest in exploring the potential of isocyanates in emerging fields such as 3D printing, nanotechnology, and biomedical applications.
Market Analysis for High-Performance Polymers
The high-performance polymers market has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and healthcare. These advanced materials offer superior mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties compared to conventional polymers, making them ideal for demanding applications.
In recent years, the global high-performance polymers market has shown a steady increase, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 6%. This growth is expected to continue as industries seek innovative materials to meet evolving performance requirements and regulatory standards.
The automotive sector represents a major market for high-performance polymers, particularly in light-weighting applications to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. As electric vehicles gain popularity, the demand for high-performance polymers in battery components and structural parts is also rising.
Aerospace and defense industries are another significant consumer of high-performance polymers, utilizing these materials in aircraft interiors, structural components, and advanced composites. The ongoing trend towards more fuel-efficient and lighter aircraft is driving the adoption of these advanced materials.
In the electronics industry, high-performance polymers are increasingly used in semiconductor packaging, printed circuit boards, and connectors due to their excellent electrical properties and heat resistance. The rapid growth of 5G technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) is further boosting demand in this sector.
The healthcare industry is also a key market for high-performance polymers, with applications in medical devices, implants, and drug delivery systems. The aging population and increasing focus on personalized medicine are driving growth in this segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest markets for high-performance polymers. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing automotive production, and growing electronics manufacturing in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Key players in the high-performance polymers market include BASF, DuPont, Solvay, Arkema, and Evonik Industries. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create new formulations and expand their product portfolios to meet evolving market demands.
The integration of isocyanates in high-performance polymers presents significant opportunities for market growth. Isocyanates are crucial in the production of polyurethanes, which offer excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and versatility. As industries seek materials with enhanced performance characteristics, the demand for isocyanate-based high-performance polymers is expected to increase, particularly in applications requiring superior durability, flexibility, and thermal stability.
In recent years, the global high-performance polymers market has shown a steady increase, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 6%. This growth is expected to continue as industries seek innovative materials to meet evolving performance requirements and regulatory standards.
The automotive sector represents a major market for high-performance polymers, particularly in light-weighting applications to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. As electric vehicles gain popularity, the demand for high-performance polymers in battery components and structural parts is also rising.
Aerospace and defense industries are another significant consumer of high-performance polymers, utilizing these materials in aircraft interiors, structural components, and advanced composites. The ongoing trend towards more fuel-efficient and lighter aircraft is driving the adoption of these advanced materials.
In the electronics industry, high-performance polymers are increasingly used in semiconductor packaging, printed circuit boards, and connectors due to their excellent electrical properties and heat resistance. The rapid growth of 5G technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) is further boosting demand in this sector.
The healthcare industry is also a key market for high-performance polymers, with applications in medical devices, implants, and drug delivery systems. The aging population and increasing focus on personalized medicine are driving growth in this segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest markets for high-performance polymers. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing automotive production, and growing electronics manufacturing in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Key players in the high-performance polymers market include BASF, DuPont, Solvay, Arkema, and Evonik Industries. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create new formulations and expand their product portfolios to meet evolving market demands.
The integration of isocyanates in high-performance polymers presents significant opportunities for market growth. Isocyanates are crucial in the production of polyurethanes, which offer excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and versatility. As industries seek materials with enhanced performance characteristics, the demand for isocyanate-based high-performance polymers is expected to increase, particularly in applications requiring superior durability, flexibility, and thermal stability.
Isocyanate Technology: Current State and Challenges
Isocyanates have become a cornerstone in the development of high-performance polymers, playing a crucial role in various industries. However, the current state of isocyanate technology faces several challenges that need to be addressed to fully leverage its potential in advanced polymer applications.
One of the primary challenges is the toxicity associated with isocyanates, particularly during the manufacturing process. Exposure to isocyanates can cause respiratory issues and skin irritation, necessitating stringent safety measures and protective equipment. This has led to increased production costs and regulatory scrutiny, prompting researchers to explore safer alternatives or improved handling methods.
Another significant challenge lies in the environmental impact of isocyanate-based polymers. Many traditional isocyanate-derived products, such as polyurethanes, are not easily biodegradable, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. The industry is under pressure to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly isocyanate formulations that maintain high performance while reducing environmental footprint.
The volatility of raw material prices, particularly for key isocyanate precursors like toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), poses a challenge to consistent production and pricing of high-performance polymers. This volatility can impact the overall cost-effectiveness and market competitiveness of isocyanate-based products.
Technical limitations in isocyanate chemistry also present ongoing challenges. For instance, achieving precise control over reaction kinetics and crosslinking density in polyurethane synthesis remains difficult, affecting the final properties of the polymer. Researchers are working on developing new catalysts and reaction mechanisms to overcome these limitations and enhance polymer performance.
The demand for customized and specialized high-performance polymers is growing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. This requires continuous innovation in isocyanate technology to meet specific performance requirements, such as improved heat resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength. Balancing these diverse property demands while maintaining processability and cost-effectiveness is a significant challenge.
Lastly, the global shift towards renewable and bio-based materials is challenging the traditional petroleum-based isocyanate industry. Developing bio-based isocyanates or finding renewable alternatives that can match the performance of conventional isocyanates is a major focus of current research efforts. This transition is essential for long-term sustainability but presents technical and economic hurdles that need to be overcome.
One of the primary challenges is the toxicity associated with isocyanates, particularly during the manufacturing process. Exposure to isocyanates can cause respiratory issues and skin irritation, necessitating stringent safety measures and protective equipment. This has led to increased production costs and regulatory scrutiny, prompting researchers to explore safer alternatives or improved handling methods.
Another significant challenge lies in the environmental impact of isocyanate-based polymers. Many traditional isocyanate-derived products, such as polyurethanes, are not easily biodegradable, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. The industry is under pressure to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly isocyanate formulations that maintain high performance while reducing environmental footprint.
The volatility of raw material prices, particularly for key isocyanate precursors like toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), poses a challenge to consistent production and pricing of high-performance polymers. This volatility can impact the overall cost-effectiveness and market competitiveness of isocyanate-based products.
Technical limitations in isocyanate chemistry also present ongoing challenges. For instance, achieving precise control over reaction kinetics and crosslinking density in polyurethane synthesis remains difficult, affecting the final properties of the polymer. Researchers are working on developing new catalysts and reaction mechanisms to overcome these limitations and enhance polymer performance.
The demand for customized and specialized high-performance polymers is growing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. This requires continuous innovation in isocyanate technology to meet specific performance requirements, such as improved heat resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength. Balancing these diverse property demands while maintaining processability and cost-effectiveness is a significant challenge.
Lastly, the global shift towards renewable and bio-based materials is challenging the traditional petroleum-based isocyanate industry. Developing bio-based isocyanates or finding renewable alternatives that can match the performance of conventional isocyanates is a major focus of current research efforts. This transition is essential for long-term sustainability but presents technical and economic hurdles that need to be overcome.
Current Isocyanate Utilization Strategies
01 Synthesis and production of isocyanates
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel reaction pathways, catalysts, and production techniques to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate manufacturing.- Synthesis and production of isocyanates: Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel reaction pathways, catalysts, and production techniques to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate manufacturing.
- Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry: Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents discuss various applications, including foam production, coatings, adhesives, and elastomers, as well as novel polymer formulations incorporating isocyanates.
- Isocyanate-based coating technologies: Several patents focus on coating technologies utilizing isocyanates. These include developments in water-based coatings, high-performance protective coatings, and specialized coatings for various industrial applications.
- Safety and handling of isocyanates: Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, patents address safety concerns and handling procedures. This includes methods for reducing toxicity, improving storage stability, and developing safer alternatives or modified isocyanates with reduced health risks.
- Isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes: Some patents explore alternatives to traditional isocyanates, addressing environmental and health concerns. These include bio-based substitutes, non-isocyanate polyurethanes, and alternative chemistries that can replace isocyanates in certain applications.
02 Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry
Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents discuss various applications, including coatings, adhesives, foams, and elastomers, as well as novel formulations and processing techniques.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate-based catalysts and reaction modifiers
Several patents focus on the use of isocyanates as catalysts or reaction modifiers in various chemical processes. This includes their role in polymerization reactions, cross-linking agents, and as components in complex catalyst systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety and handling of isocyanates
Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, patents address safety concerns and handling procedures. This includes methods for reducing toxicity, improving storage stability, and developing safer alternatives or modified forms of isocyanates for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes
Some patents explore alternatives to traditional isocyanates, addressing environmental and health concerns. This includes the development of isocyanate-free polymers, alternative cross-linking agents, and novel chemistries that mimic the properties of isocyanate-based systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isocyanate-Based Polymer Industry
The market for high-performance polymers leveraging isocyanates is in a mature growth phase, with a global market size estimated to exceed $30 billion by 2025. The technology has reached a high level of maturity, with major players like BASF, Covestro, and Wanhua Chemical Group leading innovation. These companies have established strong R&D capabilities and extensive product portfolios. Emerging trends include bio-based isocyanates and sustainable polyurethane formulations. The competitive landscape is characterized by intense rivalry among multinational chemical corporations, with increasing focus on developing eco-friendly solutions and expanding applications in automotive, construction, and electronics industries.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF leverages isocyanates in high-performance polymers through their innovative Elastollan® thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) technology. This advanced material combines the durability of rubber with the processability of thermoplastics. BASF's approach involves carefully controlling the reaction between diisocyanates and polyols to create customizable polymer chains[1]. The company has developed a range of isocyanate-based products, including aliphatic and aromatic variants, to suit different application needs. Their process allows for fine-tuning of properties such as hardness, elasticity, and chemical resistance[2]. BASF also focuses on sustainable solutions, incorporating bio-based and recycled content into their isocyanate-based polymers to address environmental concerns[3].
Strengths: Wide range of customizable properties, established market presence, focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Potential health and environmental concerns associated with isocyanates, dependency on petrochemical feedstocks.
Bayer AG
Technical Solution: Bayer AG utilizes isocyanates in high-performance polymers through their Desmodur® and Desmophen® product lines. Their approach focuses on developing novel polyisocyanates and polyols to create advanced polyurethane systems. Bayer's technology allows for the creation of both flexible and rigid foams, as well as high-performance coatings and adhesives[1]. They have developed low-emission isocyanate technologies to address environmental and health concerns[2]. Bayer's research also extends to non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) as a sustainable alternative, demonstrating their commitment to innovation in this field[3]. The company's expertise in catalyst systems enables precise control over reaction kinetics, resulting in improved polymer performance and processing efficiency.
Strengths: Diverse product portfolio, strong R&D capabilities, focus on low-emission technologies. Weaknesses: Regulatory challenges associated with isocyanates, competition from alternative technologies.
Innovative Isocyanate Chemistry Breakthroughs
Isocyanate composition and method for producing isocyanate polymer
PatentPendingUS20230114799A1
Innovation
- An isocyanate composition containing a trifunctional or more-functional isocyanate compound, along with specific additives such as compounds with unsaturated bonds, sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid esters, and inert compounds, which improve storage stability by suppressing viscosity increase and gelation.
(BLOCK) polyisocyanate composition and coating composition using same
PatentWO2005082966A1
Innovation
- A (block) polyisocyanate composition is developed with a specific mass ratio of aliphatic and alicyclic diisocyanates and a polyol, featuring allophanate linkages, isocyanurate bonds, and a controlled glass transition temperature, which enhances curability and drying properties, and is used in a coating composition that can achieve high coating film hardness.
Environmental Impact of Isocyanate-Based Polymers
The environmental impact of isocyanate-based polymers is a critical consideration in the development and application of high-performance materials. These polymers, while offering exceptional mechanical properties and versatility, pose significant challenges to environmental sustainability throughout their lifecycle.
During production, isocyanates are highly reactive compounds that can release toxic fumes and vapors. This necessitates stringent safety measures and emission control systems in manufacturing facilities. The production process often involves the use of solvents and catalysts, which can contribute to air and water pollution if not properly managed. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of polymer synthesis contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint concerns.
In their use phase, isocyanate-based polymers generally exhibit good durability and resistance to degradation, which can be both an advantage and a drawback from an environmental perspective. While their longevity reduces the need for frequent replacement, it also means these materials persist in the environment for extended periods when discarded.
End-of-life management of isocyanate-based polymers presents significant challenges. Many of these materials are thermoset polymers, which are difficult to recycle due to their cross-linked structure. Incineration, a common disposal method, can release toxic compounds if not conducted under controlled conditions. Landfilling is also problematic, as these polymers do not biodegrade readily and may leach harmful substances into soil and groundwater over time.
Recent research has focused on developing more environmentally friendly alternatives and improving the sustainability of isocyanate-based polymers. Efforts include the use of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, the development of recyclable or biodegradable formulations, and the implementation of more efficient production processes that reduce waste and energy consumption.
The automotive and construction industries, major consumers of these polymers, are increasingly adopting life cycle assessment approaches to evaluate and mitigate the environmental impact of their products. This holistic view considers factors such as raw material sourcing, manufacturing efficiency, product lifespan, and end-of-life disposal options.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter guidelines for the production, use, and disposal of isocyanate-based polymers. These regulations aim to minimize environmental risks, protect worker health, and promote the development of more sustainable alternatives. Compliance with these evolving standards is driving innovation in the polymer industry, pushing manufacturers to explore greener chemistries and production methods.
During production, isocyanates are highly reactive compounds that can release toxic fumes and vapors. This necessitates stringent safety measures and emission control systems in manufacturing facilities. The production process often involves the use of solvents and catalysts, which can contribute to air and water pollution if not properly managed. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of polymer synthesis contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint concerns.
In their use phase, isocyanate-based polymers generally exhibit good durability and resistance to degradation, which can be both an advantage and a drawback from an environmental perspective. While their longevity reduces the need for frequent replacement, it also means these materials persist in the environment for extended periods when discarded.
End-of-life management of isocyanate-based polymers presents significant challenges. Many of these materials are thermoset polymers, which are difficult to recycle due to their cross-linked structure. Incineration, a common disposal method, can release toxic compounds if not conducted under controlled conditions. Landfilling is also problematic, as these polymers do not biodegrade readily and may leach harmful substances into soil and groundwater over time.
Recent research has focused on developing more environmentally friendly alternatives and improving the sustainability of isocyanate-based polymers. Efforts include the use of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, the development of recyclable or biodegradable formulations, and the implementation of more efficient production processes that reduce waste and energy consumption.
The automotive and construction industries, major consumers of these polymers, are increasingly adopting life cycle assessment approaches to evaluate and mitigate the environmental impact of their products. This holistic view considers factors such as raw material sourcing, manufacturing efficiency, product lifespan, and end-of-life disposal options.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter guidelines for the production, use, and disposal of isocyanate-based polymers. These regulations aim to minimize environmental risks, protect worker health, and promote the development of more sustainable alternatives. Compliance with these evolving standards is driving innovation in the polymer industry, pushing manufacturers to explore greener chemistries and production methods.
Safety Regulations for Isocyanate Handling and Use
The safe handling and use of isocyanates in high-performance polymer production is governed by stringent regulations due to their potential health and environmental hazards. Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) have established comprehensive guidelines to ensure worker safety and environmental protection.
These regulations typically mandate the implementation of engineering controls, including closed systems and local exhaust ventilation, to minimize worker exposure to isocyanate vapors and aerosols. Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements are also specified, often including impervious gloves, chemical-resistant clothing, and respiratory protection with supplied air or self-contained breathing apparatus.
Workplace monitoring is a crucial aspect of safety regulations, with employers required to conduct regular air sampling and medical surveillance of workers exposed to isocyanates. Exposure limits are set by regulatory agencies, such as OSHA's Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) of 0.02 ppm for most common isocyanates, which must be strictly adhered to in industrial settings.
Training and education form a significant component of safety regulations. Workers must receive comprehensive instruction on the hazards of isocyanates, proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the correct use of PPE. This training must be documented and regularly updated to reflect changes in regulations or workplace practices.
Storage and transportation of isocyanates are subject to specific requirements to prevent accidental releases. These include using appropriate containers, maintaining proper temperature and humidity conditions, and implementing spill containment measures. Regulations often dictate the need for secondary containment systems and specific labeling requirements for isocyanate containers.
Emergency response planning is mandated by safety regulations, requiring facilities to have detailed procedures in place for handling spills, fires, or other incidents involving isocyanates. This includes the provision of appropriate fire suppression systems, eyewash stations, and safety showers in areas where isocyanates are handled or stored.
Waste management and disposal of isocyanate-containing materials are also regulated to prevent environmental contamination. Proper disposal methods, such as incineration or chemical treatment, must be employed in accordance with local and national environmental regulations.
Compliance with these safety regulations is typically enforced through regular inspections by regulatory agencies. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, including fines and potential shutdown of operations. As such, companies working with isocyanates in high-performance polymer production must maintain robust safety management systems to ensure ongoing compliance and worker protection.
These regulations typically mandate the implementation of engineering controls, including closed systems and local exhaust ventilation, to minimize worker exposure to isocyanate vapors and aerosols. Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements are also specified, often including impervious gloves, chemical-resistant clothing, and respiratory protection with supplied air or self-contained breathing apparatus.
Workplace monitoring is a crucial aspect of safety regulations, with employers required to conduct regular air sampling and medical surveillance of workers exposed to isocyanates. Exposure limits are set by regulatory agencies, such as OSHA's Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) of 0.02 ppm for most common isocyanates, which must be strictly adhered to in industrial settings.
Training and education form a significant component of safety regulations. Workers must receive comprehensive instruction on the hazards of isocyanates, proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the correct use of PPE. This training must be documented and regularly updated to reflect changes in regulations or workplace practices.
Storage and transportation of isocyanates are subject to specific requirements to prevent accidental releases. These include using appropriate containers, maintaining proper temperature and humidity conditions, and implementing spill containment measures. Regulations often dictate the need for secondary containment systems and specific labeling requirements for isocyanate containers.
Emergency response planning is mandated by safety regulations, requiring facilities to have detailed procedures in place for handling spills, fires, or other incidents involving isocyanates. This includes the provision of appropriate fire suppression systems, eyewash stations, and safety showers in areas where isocyanates are handled or stored.
Waste management and disposal of isocyanate-containing materials are also regulated to prevent environmental contamination. Proper disposal methods, such as incineration or chemical treatment, must be employed in accordance with local and national environmental regulations.
Compliance with these safety regulations is typically enforced through regular inspections by regulatory agencies. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, including fines and potential shutdown of operations. As such, companies working with isocyanates in high-performance polymer production must maintain robust safety management systems to ensure ongoing compliance and worker protection.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!