How to Optimize Carboxylic Acid Solvent Systems for Purity?
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carboxylic Acid Purification Background and Objectives
Carboxylic acids are essential compounds in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food production, and chemical manufacturing. The purification of these acids is crucial for ensuring product quality and meeting regulatory standards. Over the years, the development of efficient purification methods has been a key focus in the field of organic chemistry and chemical engineering.
The evolution of carboxylic acid purification techniques has been driven by the increasing demand for high-purity products and the need for more sustainable and cost-effective processes. Traditional methods such as distillation and crystallization have been complemented by advanced techniques like chromatography and membrane separation. The optimization of solvent systems plays a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of these purification processes.
The primary objective of optimizing carboxylic acid solvent systems for purity is to achieve maximum separation of the target acid from impurities while minimizing solvent consumption and energy requirements. This involves a comprehensive understanding of the physicochemical properties of both the carboxylic acids and the solvents, as well as their interactions under various conditions.
Key factors influencing the optimization process include solubility, polarity, boiling point differences, and the formation of azeotropes. The selection of appropriate solvents or solvent mixtures is critical, as it directly impacts the partition coefficients and separation factors. Additionally, considerations such as environmental impact, toxicity, and recyclability of solvents have become increasingly important in recent years.
The technological advancements in this field have led to the development of novel solvent systems, including ionic liquids, deep eutectic solvents, and supercritical fluids. These innovative approaches offer unique properties that can enhance selectivity and efficiency in carboxylic acid purification. Furthermore, the integration of computational modeling and machine learning techniques has enabled more precise prediction of solvent-solute interactions and optimization of process parameters.
As the industry continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on developing green and sustainable purification methods. This includes the use of bio-based solvents, solvent-free techniques, and the implementation of process intensification strategies. The ultimate goal is to create purification processes that not only yield high-purity carboxylic acids but also align with the principles of green chemistry and circular economy.
The evolution of carboxylic acid purification techniques has been driven by the increasing demand for high-purity products and the need for more sustainable and cost-effective processes. Traditional methods such as distillation and crystallization have been complemented by advanced techniques like chromatography and membrane separation. The optimization of solvent systems plays a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of these purification processes.
The primary objective of optimizing carboxylic acid solvent systems for purity is to achieve maximum separation of the target acid from impurities while minimizing solvent consumption and energy requirements. This involves a comprehensive understanding of the physicochemical properties of both the carboxylic acids and the solvents, as well as their interactions under various conditions.
Key factors influencing the optimization process include solubility, polarity, boiling point differences, and the formation of azeotropes. The selection of appropriate solvents or solvent mixtures is critical, as it directly impacts the partition coefficients and separation factors. Additionally, considerations such as environmental impact, toxicity, and recyclability of solvents have become increasingly important in recent years.
The technological advancements in this field have led to the development of novel solvent systems, including ionic liquids, deep eutectic solvents, and supercritical fluids. These innovative approaches offer unique properties that can enhance selectivity and efficiency in carboxylic acid purification. Furthermore, the integration of computational modeling and machine learning techniques has enabled more precise prediction of solvent-solute interactions and optimization of process parameters.
As the industry continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on developing green and sustainable purification methods. This includes the use of bio-based solvents, solvent-free techniques, and the implementation of process intensification strategies. The ultimate goal is to create purification processes that not only yield high-purity carboxylic acids but also align with the principles of green chemistry and circular economy.
Market Demand for High-Purity Carboxylic Acids
The market demand for high-purity carboxylic acids has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by their diverse applications and the growing emphasis on product quality and performance. In the pharmaceutical sector, high-purity carboxylic acids are crucial for the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates. The stringent regulatory requirements for drug manufacturing necessitate the use of ultra-pure carboxylic acids to ensure product safety and efficacy.
The food and beverage industry also contributes significantly to the demand for high-purity carboxylic acids. These compounds are widely used as preservatives, flavor enhancers, and acidulants in a range of products. As consumers become more health-conscious and demand cleaner labels, the need for high-purity food-grade carboxylic acids has intensified.
In the personal care and cosmetics sector, the trend towards natural and organic products has fueled the demand for high-purity carboxylic acids derived from sustainable sources. These acids are utilized in formulations for skincare, haircare, and other personal care products, where purity is essential for product stability and efficacy.
The industrial sector, particularly in the production of polymers, lubricants, and specialty chemicals, represents another significant market for high-purity carboxylic acids. The performance of these end products is directly influenced by the purity of the carboxylic acids used in their manufacture, driving the demand for higher quality raw materials.
The global market for high-purity carboxylic acids is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5-7% over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the expanding applications in emerging economies, technological advancements in purification processes, and the increasing adoption of green chemistry principles in industrial processes.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for high-purity carboxylic acids, owing to their well-established pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and growing awareness of product quality in countries like China and India.
The demand for specific high-purity carboxylic acids varies based on their applications. For instance, acetic acid, propionic acid, and butyric acid are seeing robust growth in the food and beverage sector, while longer-chain fatty acids are in high demand for personal care and cosmetic applications. The pharmaceutical industry continues to drive demand for a wide range of high-purity carboxylic acids, including both common and specialty compounds.
The food and beverage industry also contributes significantly to the demand for high-purity carboxylic acids. These compounds are widely used as preservatives, flavor enhancers, and acidulants in a range of products. As consumers become more health-conscious and demand cleaner labels, the need for high-purity food-grade carboxylic acids has intensified.
In the personal care and cosmetics sector, the trend towards natural and organic products has fueled the demand for high-purity carboxylic acids derived from sustainable sources. These acids are utilized in formulations for skincare, haircare, and other personal care products, where purity is essential for product stability and efficacy.
The industrial sector, particularly in the production of polymers, lubricants, and specialty chemicals, represents another significant market for high-purity carboxylic acids. The performance of these end products is directly influenced by the purity of the carboxylic acids used in their manufacture, driving the demand for higher quality raw materials.
The global market for high-purity carboxylic acids is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5-7% over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the expanding applications in emerging economies, technological advancements in purification processes, and the increasing adoption of green chemistry principles in industrial processes.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for high-purity carboxylic acids, owing to their well-established pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and growing awareness of product quality in countries like China and India.
The demand for specific high-purity carboxylic acids varies based on their applications. For instance, acetic acid, propionic acid, and butyric acid are seeing robust growth in the food and beverage sector, while longer-chain fatty acids are in high demand for personal care and cosmetic applications. The pharmaceutical industry continues to drive demand for a wide range of high-purity carboxylic acids, including both common and specialty compounds.
Current Challenges in Carboxylic Acid Solvent Systems
The optimization of carboxylic acid solvent systems for purity faces several significant challenges in the current landscape. One of the primary issues is the inherent complexity of carboxylic acid mixtures, which often contain multiple components with varying physical and chemical properties. This complexity makes it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all approach to purification and optimization.
Another challenge lies in the strong hydrogen bonding capabilities of carboxylic acids, which can lead to the formation of dimers and other aggregates in solution. These interactions can significantly affect the solubility, reactivity, and separation behavior of the acids, complicating efforts to achieve high purity levels.
The presence of impurities, such as aldehydes, ketones, and other organic compounds, poses a substantial challenge in carboxylic acid purification. These impurities often have similar physical properties to the target acids, making their removal through conventional separation techniques like distillation or crystallization particularly challenging.
Furthermore, the corrosive nature of many carboxylic acids presents material compatibility issues in solvent systems and purification equipment. This corrosivity can lead to contamination of the product and degradation of processing equipment, necessitating the use of specialized, often expensive, materials and coatings.
Temperature sensitivity is another critical challenge in optimizing carboxylic acid solvent systems. Many carboxylic acids are thermally unstable or prone to decomposition at elevated temperatures, limiting the range of purification techniques that can be employed without risking product degradation or unwanted side reactions.
The environmental impact of solvent systems used in carboxylic acid purification is an increasingly important consideration. Traditional organic solvents often pose environmental and health risks, driving the need for more sustainable and green alternatives. However, finding eco-friendly solvents that maintain or improve purification efficiency remains a significant challenge.
Scalability of purification processes from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. Techniques that work well at small scales may not be economically viable or technically feasible when scaled up to production levels, necessitating the development of novel approaches that can maintain efficiency and purity at larger scales.
Lastly, the energy intensity of many purification processes, particularly those involving multiple distillation steps or extensive solvent recovery operations, poses both economic and environmental challenges. Developing energy-efficient purification methods that can achieve high purity levels while minimizing energy consumption is a critical area of focus in the optimization of carboxylic acid solvent systems.
Another challenge lies in the strong hydrogen bonding capabilities of carboxylic acids, which can lead to the formation of dimers and other aggregates in solution. These interactions can significantly affect the solubility, reactivity, and separation behavior of the acids, complicating efforts to achieve high purity levels.
The presence of impurities, such as aldehydes, ketones, and other organic compounds, poses a substantial challenge in carboxylic acid purification. These impurities often have similar physical properties to the target acids, making their removal through conventional separation techniques like distillation or crystallization particularly challenging.
Furthermore, the corrosive nature of many carboxylic acids presents material compatibility issues in solvent systems and purification equipment. This corrosivity can lead to contamination of the product and degradation of processing equipment, necessitating the use of specialized, often expensive, materials and coatings.
Temperature sensitivity is another critical challenge in optimizing carboxylic acid solvent systems. Many carboxylic acids are thermally unstable or prone to decomposition at elevated temperatures, limiting the range of purification techniques that can be employed without risking product degradation or unwanted side reactions.
The environmental impact of solvent systems used in carboxylic acid purification is an increasingly important consideration. Traditional organic solvents often pose environmental and health risks, driving the need for more sustainable and green alternatives. However, finding eco-friendly solvents that maintain or improve purification efficiency remains a significant challenge.
Scalability of purification processes from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. Techniques that work well at small scales may not be economically viable or technically feasible when scaled up to production levels, necessitating the development of novel approaches that can maintain efficiency and purity at larger scales.
Lastly, the energy intensity of many purification processes, particularly those involving multiple distillation steps or extensive solvent recovery operations, poses both economic and environmental challenges. Developing energy-efficient purification methods that can achieve high purity levels while minimizing energy consumption is a critical area of focus in the optimization of carboxylic acid solvent systems.
Existing Solvent System Optimization Approaches
01 Purification of carboxylic acids using solvent systems
Various solvent systems are employed to purify carboxylic acids. These systems often involve a combination of organic solvents and water, which can effectively separate the desired carboxylic acid from impurities. The choice of solvents depends on the specific carboxylic acid and the nature of the impurities present.- Purification of carboxylic acids using solvent systems: Various solvent systems are employed to purify carboxylic acids. These systems often involve a combination of organic solvents and water, which can effectively separate the desired carboxylic acid from impurities. The choice of solvents and their ratios can be optimized to achieve high purity levels.
- Crystallization techniques for carboxylic acid purification: Crystallization is a widely used method for purifying carboxylic acids. This process involves dissolving the impure acid in a suitable solvent, then carefully controlling temperature and other conditions to promote the formation of pure crystals. Multiple crystallization steps may be employed to achieve higher purity levels.
- Extraction methods for carboxylic acid purification: Liquid-liquid extraction techniques are utilized to separate carboxylic acids from impurities. This method involves using immiscible solvents to selectively extract the desired acid from a mixture. The choice of extraction solvents and pH conditions can significantly impact the efficiency and purity of the separation process.
- Use of ionic liquids in carboxylic acid purification: Ionic liquids have emerged as novel solvents for carboxylic acid purification. These non-volatile, thermally stable compounds can selectively dissolve carboxylic acids, allowing for efficient separation from impurities. The unique properties of ionic liquids can lead to improved purity and yield in acid purification processes.
- Membrane-based separation for carboxylic acid purification: Membrane technology is applied in the purification of carboxylic acids. This method uses selective membranes to separate the desired acid from impurities based on molecular size or charge. Various types of membranes, including nanofiltration and pervaporation membranes, can be employed to achieve high purity levels in carboxylic acid production.
02 Crystallization techniques for enhancing purity
Crystallization is a widely used method for purifying carboxylic acids. By carefully controlling temperature, solvent composition, and cooling rates, high-purity crystals of the desired carboxylic acid can be obtained. This technique is particularly effective for separating structurally similar compounds.Expand Specific Solutions03 Extraction and liquid-liquid separation methods
Liquid-liquid extraction techniques are employed to separate carboxylic acids from impurities. These methods often involve the use of immiscible solvents with different polarities to selectively extract the desired carboxylic acid. Multiple extraction stages may be used to improve purity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use of ionic liquids in carboxylic acid purification
Ionic liquids have emerged as novel solvents for the purification of carboxylic acids. These non-volatile, highly polar solvents can selectively dissolve carboxylic acids, allowing for efficient separation from impurities. The unique properties of ionic liquids often result in improved purification compared to conventional organic solvents.Expand Specific Solutions05 Distillation and fractional distillation for high purity
Distillation and fractional distillation techniques are used to separate carboxylic acids based on their boiling points. These methods are particularly useful for volatile carboxylic acids or when dealing with mixtures of acids with significantly different boiling points. Careful control of temperature and pressure can yield high-purity products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Carboxylic Acid Purification Industry
The optimization of carboxylic acid solvent systems for purity is a mature field with ongoing research and development. The market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for high-purity chemicals in various industries. Key players like FUJIFILM Electronic Materials, Eastman Chemical, and Mitsubishi Gas Chemical are investing in advanced technologies to improve solvent purity and efficiency. The market size is expanding, with a focus on developing eco-friendly and cost-effective solutions. Companies such as Daicel Corp. and Air Liquide SA are leveraging their expertise in chemical processing to gain a competitive edge. As the industry progresses, collaboration between academic institutions and corporations is likely to accelerate innovation in this field.
Eastman Chemical Co.
Technical Solution: Eastman Chemical Co. has developed advanced solvent systems for optimizing carboxylic acid purification. Their approach involves using a combination of ester solvents and co-solvents to enhance selectivity and efficiency. The process utilizes a multi-stage extraction system with carefully controlled temperature and pressure conditions. This method allows for the separation of target carboxylic acids from impurities with high purity levels, often exceeding 99.5%[1]. Additionally, Eastman has implemented innovative recycling techniques to minimize solvent loss and reduce environmental impact, achieving a solvent recovery rate of up to 98%[2].
Strengths: High purity levels, efficient solvent recovery, environmentally friendly. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment, potentially higher initial costs.
Air Liquide SA
Technical Solution: Air Liquide has developed a cryogenic distillation process for high-purity carboxylic acid production. This method utilizes extremely low temperatures to exploit differences in volatility between the target acid and impurities. The process involves a series of cryogenic columns operating at different pressure and temperature conditions, allowing for precise fractionation. Air Liquide's technology can achieve purities of up to 99.99% for certain carboxylic acids[5]. The company has also integrated heat recovery systems to improve overall energy efficiency, reducing energy consumption by up to 25% compared to conventional distillation processes[6].
Strengths: Extremely high purity levels, suitable for specialty chemicals. Weaknesses: High energy requirements, limited to certain types of carboxylic acids.
Innovative Solvent System Design for Carboxylic Acids
Systems and methods for purifying solvents
PatentActiveUS11786841B2
Innovation
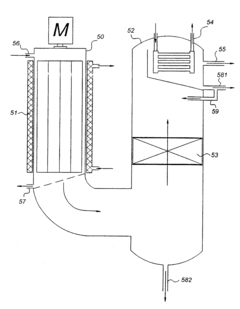
- A purification system and method utilizing a combination of anionic and cationic ion exchange filters with positively and negatively charged ion exchange resins, respectively, to significantly reduce metal impurities in organic solvents, ensuring the solvent meets predetermined purity standards without introducing unwanted substances.
Purification of aqueous solutions of organic acids
PatentInactiveUS20080257710A1
Innovation
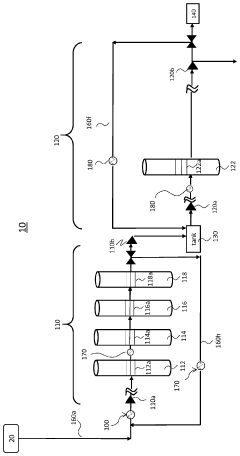
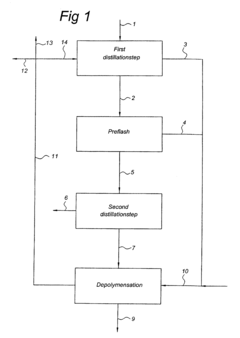
- A method involving two distillation steps using falling film or thin film evaporators followed by distillation columns, with a preflash step to remove residual water and gases, and a second vacuum distillation step to achieve high purity, along with a depolymerization step for residual components, to produce a high-purity organic acid.
Environmental Impact of Solvent Systems
The environmental impact of solvent systems used in carboxylic acid purification is a critical consideration in the optimization process. Traditional solvent systems often involve volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can contribute to air pollution and pose health risks to workers. These solvents may also lead to soil and water contamination if not properly managed. As industries strive for more sustainable practices, there is a growing emphasis on developing environmentally friendly solvent systems.
One approach to mitigating environmental impact is the use of green solvents, such as bio-based solvents derived from renewable resources. These alternatives often have lower toxicity and reduced carbon footprints compared to petroleum-based solvents. For instance, ethyl lactate and 2-methyltetrahydrofuran have shown promise as more sustainable options in various chemical processes, including carboxylic acid purification.
Water-based solvent systems are another environmentally friendly alternative, although they may present challenges in terms of efficiency for certain carboxylic acids. Supercritical fluid extraction, particularly using supercritical CO2, offers a potentially cleaner approach with minimal environmental impact. This method allows for easy solvent recovery and recycling, reducing waste generation.
The concept of solvent recycling plays a crucial role in minimizing environmental impact. Implementing efficient recovery and purification systems for solvents can significantly reduce the overall consumption and disposal of these chemicals. This not only decreases the environmental footprint but also improves the economic viability of the purification process.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) has become an essential tool in evaluating the environmental impact of solvent systems. By considering factors such as resource depletion, energy consumption, and emissions throughout the entire life cycle of the solvent, researchers can make more informed decisions about solvent selection and process optimization.
Emerging technologies, such as membrane-based separations and ionic liquids, offer promising avenues for developing more environmentally friendly solvent systems. These technologies can potentially reduce energy consumption and minimize waste generation in carboxylic acid purification processes.
Regulatory frameworks and industry standards increasingly emphasize the importance of environmental considerations in chemical processes. This has led to the development of green chemistry metrics that can be applied to solvent selection and process optimization, ensuring that environmental impact is a key factor in decision-making.
As research in this area continues, it is likely that new, innovative solvent systems will emerge, balancing the need for high purity carboxylic acids with reduced environmental impact. This ongoing evolution in solvent technology will play a crucial role in the sustainable development of chemical industries and related sectors.
One approach to mitigating environmental impact is the use of green solvents, such as bio-based solvents derived from renewable resources. These alternatives often have lower toxicity and reduced carbon footprints compared to petroleum-based solvents. For instance, ethyl lactate and 2-methyltetrahydrofuran have shown promise as more sustainable options in various chemical processes, including carboxylic acid purification.
Water-based solvent systems are another environmentally friendly alternative, although they may present challenges in terms of efficiency for certain carboxylic acids. Supercritical fluid extraction, particularly using supercritical CO2, offers a potentially cleaner approach with minimal environmental impact. This method allows for easy solvent recovery and recycling, reducing waste generation.
The concept of solvent recycling plays a crucial role in minimizing environmental impact. Implementing efficient recovery and purification systems for solvents can significantly reduce the overall consumption and disposal of these chemicals. This not only decreases the environmental footprint but also improves the economic viability of the purification process.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) has become an essential tool in evaluating the environmental impact of solvent systems. By considering factors such as resource depletion, energy consumption, and emissions throughout the entire life cycle of the solvent, researchers can make more informed decisions about solvent selection and process optimization.
Emerging technologies, such as membrane-based separations and ionic liquids, offer promising avenues for developing more environmentally friendly solvent systems. These technologies can potentially reduce energy consumption and minimize waste generation in carboxylic acid purification processes.
Regulatory frameworks and industry standards increasingly emphasize the importance of environmental considerations in chemical processes. This has led to the development of green chemistry metrics that can be applied to solvent selection and process optimization, ensuring that environmental impact is a key factor in decision-making.
As research in this area continues, it is likely that new, innovative solvent systems will emerge, balancing the need for high purity carboxylic acids with reduced environmental impact. This ongoing evolution in solvent technology will play a crucial role in the sustainable development of chemical industries and related sectors.
Analytical Methods for Purity Assessment
Analytical methods play a crucial role in assessing the purity of carboxylic acid solvent systems. These techniques are essential for optimizing the systems and ensuring high-quality products. One of the primary methods used is high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), which offers excellent separation and quantification of carboxylic acids and their impurities. HPLC can be coupled with various detectors, such as UV-Vis or mass spectrometry, to enhance sensitivity and specificity.
Gas chromatography (GC) is another valuable technique, particularly for volatile carboxylic acids and their derivatives. GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry) provides both separation and identification capabilities, making it ideal for complex mixtures. For non-volatile compounds, derivatization techniques can be employed to improve GC analysis.
Spectroscopic methods, including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), offer complementary information about the structure and purity of carboxylic acids. NMR can provide detailed structural information and quantitative analysis, while FTIR is useful for identifying functional groups and detecting impurities.
Titration techniques, such as potentiometric titration and Karl Fischer titration, are widely used for determining the acid content and water content, respectively. These methods are particularly important for assessing the purity of carboxylic acid solvents, as water is a common impurity that can significantly affect their performance.
Thermal analysis methods, including differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), can provide information about the thermal stability and composition of carboxylic acid solvent systems. These techniques are valuable for detecting impurities that may not be easily identified by other methods.
Elemental analysis is another important tool for assessing purity, particularly for detecting inorganic impurities. Techniques such as inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) or atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) can provide precise measurements of trace metal contaminants.
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of purity assessments, it is crucial to develop and validate analytical methods specific to the carboxylic acid solvent system under investigation. This process typically involves optimizing parameters such as sample preparation, instrument settings, and data analysis procedures. Additionally, the use of certified reference materials and participation in interlaboratory comparisons can help maintain the quality of analytical results.
Gas chromatography (GC) is another valuable technique, particularly for volatile carboxylic acids and their derivatives. GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry) provides both separation and identification capabilities, making it ideal for complex mixtures. For non-volatile compounds, derivatization techniques can be employed to improve GC analysis.
Spectroscopic methods, including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), offer complementary information about the structure and purity of carboxylic acids. NMR can provide detailed structural information and quantitative analysis, while FTIR is useful for identifying functional groups and detecting impurities.
Titration techniques, such as potentiometric titration and Karl Fischer titration, are widely used for determining the acid content and water content, respectively. These methods are particularly important for assessing the purity of carboxylic acid solvents, as water is a common impurity that can significantly affect their performance.
Thermal analysis methods, including differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), can provide information about the thermal stability and composition of carboxylic acid solvent systems. These techniques are valuable for detecting impurities that may not be easily identified by other methods.
Elemental analysis is another important tool for assessing purity, particularly for detecting inorganic impurities. Techniques such as inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) or atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) can provide precise measurements of trace metal contaminants.
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of purity assessments, it is crucial to develop and validate analytical methods specific to the carboxylic acid solvent system under investigation. This process typically involves optimizing parameters such as sample preparation, instrument settings, and data analysis procedures. Additionally, the use of certified reference materials and participation in interlaboratory comparisons can help maintain the quality of analytical results.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!