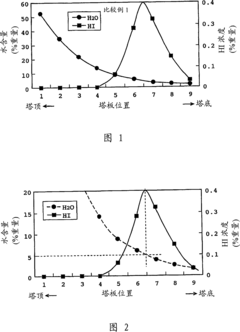
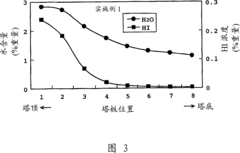
How to Reduce Contaminants in Lithium Acetate Production
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Acetate Purification Background and Objectives
Lithium acetate has emerged as a critical compound in various high-tech applications, including pharmaceuticals, organic synthesis, and most prominently, lithium-ion battery production. The evolution of this technology has been marked by increasing demands for higher purity levels as downstream applications become more sophisticated and quality-sensitive. Historical production methods dating back to the 1950s primarily focused on yield rather than purity, resulting in products containing significant levels of sodium, potassium, calcium, and heavy metal contaminants.
The global shift toward electrification and renewable energy storage has dramatically accelerated demand for high-purity lithium compounds, with lithium acetate serving as an important precursor in several manufacturing processes. Market projections indicate a compound annual growth rate of 8.7% for lithium acetate through 2030, driven primarily by battery technology advancements and pharmaceutical applications requiring ultra-pure reagents.
Current purification technologies have evolved from simple recrystallization methods to more sophisticated approaches including selective precipitation, ion exchange, and membrane filtration. However, these methods often struggle to achieve the increasingly stringent purity requirements (>99.95%) while maintaining economic viability at industrial scales. The presence of even trace contaminants can significantly impact downstream product performance, particularly in battery applications where metal impurities contribute to reduced cycle life and safety concerns.
The primary technical objective of this research is to develop cost-effective purification methodologies capable of reducing contaminant levels in lithium acetate to below 50 ppm for critical impurities while maintaining scalability for industrial production. Secondary objectives include minimizing environmental impact through reduced solvent usage, decreasing energy consumption in purification processes, and establishing robust analytical protocols for impurity detection at sub-ppm levels.
Recent technological breakthroughs in selective chelation chemistry and advanced membrane technologies present promising avenues for investigation. Additionally, emerging electrochemical purification methods have demonstrated potential for selective removal of metal contaminants without introducing additional chemical reagents into the process stream.
The geographical distribution of lithium acetate production technology development shows concentration in China, South Korea, and North America, with European research institutions making significant contributions to analytical methodology. This global research landscape provides diverse approaches to addressing the fundamental challenge of contaminant reduction while highlighting the universal importance of this technical objective across the lithium value chain.
The global shift toward electrification and renewable energy storage has dramatically accelerated demand for high-purity lithium compounds, with lithium acetate serving as an important precursor in several manufacturing processes. Market projections indicate a compound annual growth rate of 8.7% for lithium acetate through 2030, driven primarily by battery technology advancements and pharmaceutical applications requiring ultra-pure reagents.
Current purification technologies have evolved from simple recrystallization methods to more sophisticated approaches including selective precipitation, ion exchange, and membrane filtration. However, these methods often struggle to achieve the increasingly stringent purity requirements (>99.95%) while maintaining economic viability at industrial scales. The presence of even trace contaminants can significantly impact downstream product performance, particularly in battery applications where metal impurities contribute to reduced cycle life and safety concerns.
The primary technical objective of this research is to develop cost-effective purification methodologies capable of reducing contaminant levels in lithium acetate to below 50 ppm for critical impurities while maintaining scalability for industrial production. Secondary objectives include minimizing environmental impact through reduced solvent usage, decreasing energy consumption in purification processes, and establishing robust analytical protocols for impurity detection at sub-ppm levels.
Recent technological breakthroughs in selective chelation chemistry and advanced membrane technologies present promising avenues for investigation. Additionally, emerging electrochemical purification methods have demonstrated potential for selective removal of metal contaminants without introducing additional chemical reagents into the process stream.
The geographical distribution of lithium acetate production technology development shows concentration in China, South Korea, and North America, with European research institutions making significant contributions to analytical methodology. This global research landscape provides diverse approaches to addressing the fundamental challenge of contaminant reduction while highlighting the universal importance of this technical objective across the lithium value chain.
Market Demand Analysis for High-Purity Lithium Acetate
The global market for high-purity lithium acetate has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by the expanding applications in pharmaceuticals, battery technologies, and specialty chemicals. The demand for lithium acetate with reduced contaminant levels has become particularly pronounced as industries require increasingly pure materials for advanced applications.
In the pharmaceutical sector, high-purity lithium acetate serves as a critical ingredient in the synthesis of various medications, particularly those used in treating bipolar disorder and other psychiatric conditions. The pharmaceutical grade requires contaminant levels below 10 ppm for heavy metals and other impurities, creating a premium market segment with stringent quality requirements.
The battery industry represents another major demand driver, with lithium acetate being utilized as a precursor in the production of lithium-ion battery cathode materials. As electric vehicle adoption accelerates globally, the demand for high-purity battery materials has surged. Market research indicates that the battery materials sector is growing at a compound annual growth rate of 22% through 2028, directly impacting the demand for high-purity lithium compounds.
Laboratory applications constitute a smaller but significant market segment, where ultra-high purity lithium acetate (99.999%) commands premium pricing. This segment is particularly sensitive to metal contaminants that can interfere with research outcomes and analytical procedures.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the consumption of high-purity lithium acetate, accounting for approximately 65% of global demand. This concentration aligns with the region's manufacturing strength in electronics and battery production. North America and Europe follow with growing demand driven by pharmaceutical applications and emerging energy storage technologies.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across application segments. While pharmaceutical applications prioritize purity over cost considerations, industrial applications maintain a stronger focus on cost-effectiveness while meeting minimum purity requirements. This market dynamic has created distinct tiers within the high-purity lithium acetate market.
Future market projections indicate continued growth, with particular emphasis on ultra-high purity grades. The trend toward miniaturization in electronics and increased energy density in batteries will likely accelerate demand for lithium acetate with contaminant levels below 5 ppm. Additionally, emerging applications in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing processes are expected to create new market opportunities.
Supply chain considerations have become increasingly important, with end-users seeking reliable sources of consistently high-purity materials. This has led to vertical integration strategies among major players and long-term supply agreements to secure access to premium-grade lithium acetate.
In the pharmaceutical sector, high-purity lithium acetate serves as a critical ingredient in the synthesis of various medications, particularly those used in treating bipolar disorder and other psychiatric conditions. The pharmaceutical grade requires contaminant levels below 10 ppm for heavy metals and other impurities, creating a premium market segment with stringent quality requirements.
The battery industry represents another major demand driver, with lithium acetate being utilized as a precursor in the production of lithium-ion battery cathode materials. As electric vehicle adoption accelerates globally, the demand for high-purity battery materials has surged. Market research indicates that the battery materials sector is growing at a compound annual growth rate of 22% through 2028, directly impacting the demand for high-purity lithium compounds.
Laboratory applications constitute a smaller but significant market segment, where ultra-high purity lithium acetate (99.999%) commands premium pricing. This segment is particularly sensitive to metal contaminants that can interfere with research outcomes and analytical procedures.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the consumption of high-purity lithium acetate, accounting for approximately 65% of global demand. This concentration aligns with the region's manufacturing strength in electronics and battery production. North America and Europe follow with growing demand driven by pharmaceutical applications and emerging energy storage technologies.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across application segments. While pharmaceutical applications prioritize purity over cost considerations, industrial applications maintain a stronger focus on cost-effectiveness while meeting minimum purity requirements. This market dynamic has created distinct tiers within the high-purity lithium acetate market.
Future market projections indicate continued growth, with particular emphasis on ultra-high purity grades. The trend toward miniaturization in electronics and increased energy density in batteries will likely accelerate demand for lithium acetate with contaminant levels below 5 ppm. Additionally, emerging applications in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing processes are expected to create new market opportunities.
Supply chain considerations have become increasingly important, with end-users seeking reliable sources of consistently high-purity materials. This has led to vertical integration strategies among major players and long-term supply agreements to secure access to premium-grade lithium acetate.
Current Contamination Challenges in Production Processes
Lithium acetate production processes currently face significant contamination challenges that impact product quality, yield, and downstream applications. The primary contaminants include metal ions (particularly sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium), organic impurities, and particulate matter that enter the production stream through various pathways.
Raw material quality represents a fundamental contamination source, with lithium carbonate or hydroxide precursors often containing trace metal impurities that persist throughout the production process. Commercial-grade acetic acid similarly introduces organic contaminants that can be difficult to separate from the final product. Water quality used in dissolution and crystallization steps further compounds these issues, as inadequate water purification systems allow minerals and microorganisms to enter the production stream.
Equipment-related contamination presents another significant challenge. Metal leaching from reaction vessels, pipelines, and storage tanks occurs particularly under acidic conditions present during acetate formation. Corrosion products, including iron oxides and other metal compounds, contaminate batches and catalyze unwanted side reactions. Additionally, inadequate cleaning protocols between production runs result in cross-batch contamination, especially in facilities producing multiple lithium compounds.
Process-specific contamination mechanisms include incomplete reaction conversion, leaving unreacted precursors as contaminants. Side reactions during neutralization generate byproducts such as lithium formate and propionate that are difficult to separate due to similar solubility profiles. The crystallization process itself introduces challenges, as rapid crystallization can trap impurities within crystal structures, while slow crystallization allows time for oxidation reactions that generate colored impurities.
Environmental factors further exacerbate contamination issues. Airborne particulates in production facilities deposit directly into open vessels and solutions. Humidity fluctuations affect crystallization dynamics and can introduce moisture-borne contaminants. Temperature variations across production equipment create "cold spots" where undesired precipitation occurs, forming nucleation sites for impurities.
Current quality control methods often fail to detect contamination until late production stages. Traditional analytical techniques lack sensitivity for detecting trace impurities at early process points, while real-time monitoring systems remain limited in their implementation across the industry. This delayed detection results in significant material waste and production inefficiencies when contaminated batches must be rejected or reprocessed.
These contamination challenges have become increasingly critical as high-purity lithium acetate demand grows for applications in pharmaceuticals, battery technologies, and specialty ceramics, where even trace contaminants can significantly impact performance characteristics and safety profiles.
Raw material quality represents a fundamental contamination source, with lithium carbonate or hydroxide precursors often containing trace metal impurities that persist throughout the production process. Commercial-grade acetic acid similarly introduces organic contaminants that can be difficult to separate from the final product. Water quality used in dissolution and crystallization steps further compounds these issues, as inadequate water purification systems allow minerals and microorganisms to enter the production stream.
Equipment-related contamination presents another significant challenge. Metal leaching from reaction vessels, pipelines, and storage tanks occurs particularly under acidic conditions present during acetate formation. Corrosion products, including iron oxides and other metal compounds, contaminate batches and catalyze unwanted side reactions. Additionally, inadequate cleaning protocols between production runs result in cross-batch contamination, especially in facilities producing multiple lithium compounds.
Process-specific contamination mechanisms include incomplete reaction conversion, leaving unreacted precursors as contaminants. Side reactions during neutralization generate byproducts such as lithium formate and propionate that are difficult to separate due to similar solubility profiles. The crystallization process itself introduces challenges, as rapid crystallization can trap impurities within crystal structures, while slow crystallization allows time for oxidation reactions that generate colored impurities.
Environmental factors further exacerbate contamination issues. Airborne particulates in production facilities deposit directly into open vessels and solutions. Humidity fluctuations affect crystallization dynamics and can introduce moisture-borne contaminants. Temperature variations across production equipment create "cold spots" where undesired precipitation occurs, forming nucleation sites for impurities.
Current quality control methods often fail to detect contamination until late production stages. Traditional analytical techniques lack sensitivity for detecting trace impurities at early process points, while real-time monitoring systems remain limited in their implementation across the industry. This delayed detection results in significant material waste and production inefficiencies when contaminated batches must be rejected or reprocessed.
These contamination challenges have become increasingly critical as high-purity lithium acetate demand grows for applications in pharmaceuticals, battery technologies, and specialty ceramics, where even trace contaminants can significantly impact performance characteristics and safety profiles.
Current Contaminant Reduction Methodologies
01 Purification methods for lithium acetate
Various purification methods can be employed to remove contaminants from lithium acetate. These include crystallization, filtration, and chemical treatments to eliminate impurities such as heavy metals, organic compounds, and other salts. Advanced purification techniques may involve ion exchange resins, selective precipitation, or multi-stage crystallization processes to achieve high-purity lithium acetate suitable for pharmaceutical or battery applications.- Purification methods for lithium acetate: Various purification methods can be employed to remove contaminants from lithium acetate. These methods include crystallization, filtration, and chemical treatments that target specific impurities. Advanced purification techniques help to achieve high-purity lithium acetate by removing metal ions, organic compounds, and other unwanted substances that could affect its performance in applications such as battery production and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Detection and analysis of contaminants in lithium acetate: Analytical techniques are essential for identifying and quantifying contaminants in lithium acetate. Methods such as spectroscopy, chromatography, and electrochemical analysis can be used to detect impurities at trace levels. These techniques allow for the monitoring of contaminant profiles, ensuring that lithium acetate meets quality standards for specific applications. Regular testing helps maintain consistency in product quality and performance.
- Impact of contaminants on lithium-ion battery performance: Contaminants in lithium acetate can significantly affect the performance and safety of lithium-ion batteries. Impurities such as heavy metals, moisture, and organic compounds can lead to reduced capacity, shortened battery life, increased internal resistance, and safety hazards. Understanding the relationship between specific contaminants and battery degradation mechanisms is crucial for developing high-performance energy storage systems with improved stability and longevity.
- Environmental and health concerns related to lithium acetate contaminants: Contaminants in lithium acetate can pose environmental and health risks that require careful management. Heavy metals and toxic compounds present as impurities may lead to environmental pollution during production, use, or disposal. Exposure to these contaminants can cause health issues ranging from skin irritation to more serious conditions. Regulatory standards and safety protocols are established to minimize these risks and ensure safe handling of lithium acetate in various applications.
- Contaminant control in lithium acetate manufacturing processes: Controlling contaminants during the manufacturing of lithium acetate involves implementing strict quality control measures throughout the production process. This includes selecting high-purity raw materials, optimizing reaction conditions, using appropriate equipment materials, and implementing in-process testing. Advanced manufacturing technologies and closed-loop systems help minimize the introduction of impurities, ensuring consistent product quality that meets industry specifications for applications in pharmaceuticals, batteries, and other fields.
02 Detection and analysis of lithium acetate contaminants
Analytical methods for identifying and quantifying contaminants in lithium acetate include spectroscopic techniques, chromatography, and electrochemical analysis. These methods can detect trace amounts of impurities such as other metal ions, organic compounds, and moisture. Quality control protocols often involve multiple analytical techniques to ensure comprehensive contaminant profiling and verification of lithium acetate purity for various industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Impact of contaminants on lithium-ion battery performance
Contaminants in lithium acetate can significantly affect the performance and safety of lithium-ion batteries. Impurities may interfere with electrode reactions, reduce capacity, increase internal resistance, or accelerate degradation mechanisms. Trace metal contaminants can catalyze unwanted side reactions, while moisture and organic impurities may affect electrolyte stability. Controlling contaminant levels is crucial for ensuring battery longevity, safety, and consistent performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and health concerns related to lithium acetate contaminants
Contaminants in lithium acetate may pose environmental and health risks that require careful management. Heavy metal impurities can be toxic if released into the environment, while certain organic contaminants may have adverse health effects. Regulatory frameworks often specify maximum allowable contaminant levels for different applications. Proper handling, disposal, and treatment protocols are necessary to mitigate potential risks associated with lithium acetate contaminants in industrial processes and consumer products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Manufacturing processes to minimize contaminants
Specialized manufacturing processes have been developed to minimize contaminant introduction during lithium acetate production. These include controlled reaction environments, high-purity raw materials selection, and contamination prevention protocols. Advanced production techniques may involve continuous monitoring systems, clean room facilities, or automated processes that reduce human handling. Implementing good manufacturing practices specifically designed for lithium compounds can significantly reduce contaminant levels in the final product.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The lithium acetate production contaminant reduction landscape is evolving within the rapidly growing lithium battery materials market, currently in its growth phase with increasing demand driven by electric vehicle adoption. The market is projected to expand significantly as companies like Ganfeng Lithium, Tianqi Lithium, and BASF develop advanced purification technologies. Technical maturity varies across players, with established chemical manufacturers such as Sumitomo Metal Mining, Daicel, and Johnson Matthey leveraging their expertise in chemical processing to develop proprietary contaminant reduction methods. Emerging specialists like Group14 Technologies and Energy Material Technology are introducing innovative approaches, while academic institutions including Guilin University of Technology contribute fundamental research to address persistent technical challenges in achieving high-purity lithium acetate production.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has pioneered a membrane filtration technology specifically designed for lithium acetate production. Their system employs a series of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes with precisely controlled pore sizes to selectively remove contaminants while retaining lithium acetate molecules. The process operates at lower temperatures (60-70°C) than traditional methods, reducing energy consumption by approximately 25%. Celanese's approach incorporates a proprietary pre-treatment step using activated carbon to adsorb organic impurities before membrane filtration. Their system features automated backwashing and cleaning cycles that extend membrane life by preventing fouling. The technology achieves consistent purity levels exceeding 99.8% while maintaining production throughput comparable to conventional methods.
Strengths: Energy-efficient operation; minimal chemical additives required; highly automated process with reduced labor requirements. Weaknesses: Membrane replacement costs can be significant; potential for membrane fouling in high-impurity environments; limited effectiveness against certain organic contaminants without additional treatment steps.
Daicel Corp.
Technical Solution: Daicel has developed a chromatographic separation technology specifically optimized for lithium acetate purification. Their system utilizes specialized stationary phases with high selectivity for common contaminants in lithium acetate production. The process employs a continuous simulated moving bed (SMB) chromatography approach that allows for uninterrupted production while achieving high purity. Daicel's technology incorporates a preliminary crystallization step that removes bulk impurities before the more precise chromatographic separation. Their system can process solutions with varying impurity profiles by adjusting mobile phase composition and flow parameters. The technology achieves purity levels up to 99.95% while maintaining high recovery rates of lithium acetate, typically exceeding 95% yield.
Strengths: Exceptional purity levels suitable for electronic and pharmaceutical applications; adaptable to varying feedstock quality; continuous operation capability. Weaknesses: Higher operational complexity requiring specialized expertise; greater initial capital investment; higher solvent consumption compared to some alternative methods.
Critical Patents and Research in Purification Techniques
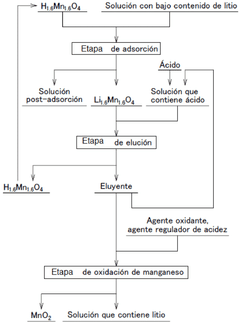
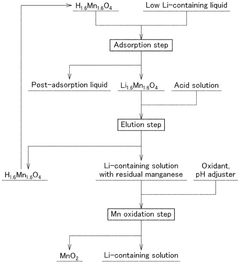
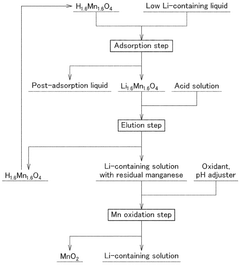
Method of producing a lithium-containing solution and oxidation of the eluted manganese.
PatentUndeterminedCL202300842A1
Innovation
- A method involving an adsorption stage using manganese acid lithium as an adsorbent, followed by an elution stage with controlled acid concentration and repeated reuse of the eluent, and a manganese oxidation stage to enhance lithium concentration and reduce eluent usage.
Distillation method
PatentActiveCN101072744A
Innovation
- Keep the water content in the distillation system no more than 5%. Distill the mixture containing hydrogen iodide and water, and introduce components such as methyl acetate and alkali metal hydroxide to ensure that the hydrogen iodide is not concentrated and reduces the bottom or side of the tower. Hydrogen iodide contamination of streaming solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of lithium acetate production represents a critical concern for the industry, particularly regarding contaminant management. Traditional production methods generate significant wastewater containing heavy metals, organic solvents, and unreacted materials that pose substantial ecological risks when improperly treated. These contaminants can lead to soil degradation, water pollution, and adverse effects on aquatic ecosystems, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable production approaches.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly imposing stricter environmental compliance requirements on lithium compound manufacturers. The European Union's REACH regulations, China's strengthened environmental protection laws, and the United States EPA guidelines all mandate comprehensive contaminant management strategies. Companies failing to meet these standards face not only legal penalties but also reputational damage in an increasingly environmentally conscious market.
Implementing closed-loop production systems offers a promising pathway toward sustainability in lithium acetate manufacturing. These systems capture and recycle process water, recover solvents, and reprocess waste materials, significantly reducing the environmental footprint. Several leading manufacturers have reported 60-80% reductions in wastewater discharge and up to 40% decreases in freshwater consumption through such implementations.
Energy consumption represents another significant environmental consideration. Conventional purification methods for contaminant removal, particularly multiple recrystallization steps, are energy-intensive processes that contribute to carbon emissions. Advanced technologies such as membrane filtration and selective adsorption not only reduce contaminant levels but also decrease energy requirements by 30-50% compared to traditional methods, offering dual environmental and economic benefits.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that addressing contaminants early in the production process yields greater sustainability benefits than end-of-pipe treatments. Preventive approaches that modify reaction conditions to minimize by-product formation have demonstrated superior environmental performance compared to remedial purification steps. Companies adopting such preventive strategies have reported reduced chemical consumption and improved product quality alongside environmental benefits.
The growing demand for battery-grade lithium compounds for electric vehicles has intensified scrutiny of production sustainability. Major automotive manufacturers and battery producers increasingly require suppliers to demonstrate environmentally responsible production practices, including contaminant management protocols. This market pressure is accelerating industry adoption of greener production technologies and transparent environmental reporting practices.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly imposing stricter environmental compliance requirements on lithium compound manufacturers. The European Union's REACH regulations, China's strengthened environmental protection laws, and the United States EPA guidelines all mandate comprehensive contaminant management strategies. Companies failing to meet these standards face not only legal penalties but also reputational damage in an increasingly environmentally conscious market.
Implementing closed-loop production systems offers a promising pathway toward sustainability in lithium acetate manufacturing. These systems capture and recycle process water, recover solvents, and reprocess waste materials, significantly reducing the environmental footprint. Several leading manufacturers have reported 60-80% reductions in wastewater discharge and up to 40% decreases in freshwater consumption through such implementations.
Energy consumption represents another significant environmental consideration. Conventional purification methods for contaminant removal, particularly multiple recrystallization steps, are energy-intensive processes that contribute to carbon emissions. Advanced technologies such as membrane filtration and selective adsorption not only reduce contaminant levels but also decrease energy requirements by 30-50% compared to traditional methods, offering dual environmental and economic benefits.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that addressing contaminants early in the production process yields greater sustainability benefits than end-of-pipe treatments. Preventive approaches that modify reaction conditions to minimize by-product formation have demonstrated superior environmental performance compared to remedial purification steps. Companies adopting such preventive strategies have reported reduced chemical consumption and improved product quality alongside environmental benefits.
The growing demand for battery-grade lithium compounds for electric vehicles has intensified scrutiny of production sustainability. Major automotive manufacturers and battery producers increasingly require suppliers to demonstrate environmentally responsible production practices, including contaminant management protocols. This market pressure is accelerating industry adoption of greener production technologies and transparent environmental reporting practices.
Quality Control and Testing Protocols
Comprehensive quality control and testing protocols are essential for ensuring the purity of lithium acetate production. The industry has established several standardized testing methods that focus on detecting and quantifying various contaminants. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) and Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) serve as primary analytical techniques for detecting metallic impurities with detection limits in the parts-per-billion range. These methods can accurately identify trace amounts of iron, copper, nickel, and other metal contaminants that significantly impact lithium acetate quality.
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Gas Chromatography (GC) are employed for organic contaminant detection, particularly residual solvents and organic byproducts from synthesis reactions. These chromatographic techniques provide detailed separation and quantification of organic impurities that may affect downstream applications of lithium acetate.
In-process testing represents a critical component of contamination reduction strategies. Continuous monitoring systems equipped with real-time sensors can detect pH fluctuations, conductivity changes, and turbidity variations that often indicate contamination events. Implementing statistical process control (SPC) charts enables manufacturers to identify trends and address process deviations before they result in significant contamination issues.
Automated sampling systems have revolutionized quality control in lithium acetate production. These systems collect samples at predetermined intervals throughout the production process, minimizing human handling and reducing the risk of sample contamination. When coupled with laboratory information management systems (LIMS), they create a comprehensive data trail that facilitates traceability and regulatory compliance.
Validation protocols for testing methods must be rigorously established and regularly reviewed. This includes determining method specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, detection limits, and quantification limits for each contaminant of interest. Cross-validation between different analytical techniques enhances confidence in test results and provides redundancy in quality assurance.
The implementation of risk-based testing approaches has gained traction in recent years. This methodology allocates testing resources based on the criticality of specific contaminants and their potential impact on product quality. Critical control points are identified throughout the production process, with more intensive testing focused on stages with higher contamination risks.
Documentation and record-keeping systems form the backbone of effective quality control programs. Electronic batch records, certificate of analysis (CoA) generation, and deviation management systems ensure that all testing data is properly captured, reviewed, and archived for regulatory purposes and continuous improvement initiatives.
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Gas Chromatography (GC) are employed for organic contaminant detection, particularly residual solvents and organic byproducts from synthesis reactions. These chromatographic techniques provide detailed separation and quantification of organic impurities that may affect downstream applications of lithium acetate.
In-process testing represents a critical component of contamination reduction strategies. Continuous monitoring systems equipped with real-time sensors can detect pH fluctuations, conductivity changes, and turbidity variations that often indicate contamination events. Implementing statistical process control (SPC) charts enables manufacturers to identify trends and address process deviations before they result in significant contamination issues.
Automated sampling systems have revolutionized quality control in lithium acetate production. These systems collect samples at predetermined intervals throughout the production process, minimizing human handling and reducing the risk of sample contamination. When coupled with laboratory information management systems (LIMS), they create a comprehensive data trail that facilitates traceability and regulatory compliance.
Validation protocols for testing methods must be rigorously established and regularly reviewed. This includes determining method specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, detection limits, and quantification limits for each contaminant of interest. Cross-validation between different analytical techniques enhances confidence in test results and provides redundancy in quality assurance.
The implementation of risk-based testing approaches has gained traction in recent years. This methodology allocates testing resources based on the criticality of specific contaminants and their potential impact on product quality. Critical control points are identified throughout the production process, with more intensive testing focused on stages with higher contamination risks.
Documentation and record-keeping systems form the backbone of effective quality control programs. Electronic batch records, certificate of analysis (CoA) generation, and deviation management systems ensure that all testing data is properly captured, reviewed, and archived for regulatory purposes and continuous improvement initiatives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!