How to Test Efficacy of Lithium Acetate as a Dehumidifier
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Acetate Dehumidification Technology Background and Objectives
Dehumidification technology has evolved significantly over the past century, with various chemical compounds being explored for moisture absorption capabilities. Lithium acetate, a hygroscopic salt with notable moisture absorption properties, has emerged as a potential alternative to traditional dehumidifying agents. The historical development of dehumidification methods has progressed from simple mechanical systems to sophisticated chemical solutions, with lithium-based compounds gaining attention in recent decades due to their efficiency and environmental compatibility.
The fundamental principle behind lithium acetate's dehumidification capability lies in its hygroscopic nature, allowing it to absorb moisture from the surrounding environment through chemical bonding. This property positions it within the broader category of chemical dehumidifiers, which includes other compounds such as calcium chloride, silica gel, and molecular sieves. Each of these alternatives presents distinct advantages and limitations in terms of absorption capacity, regeneration requirements, and operational conditions.
Current technological trends in dehumidification are increasingly focused on energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and application versatility. The industry is moving away from energy-intensive mechanical dehumidification systems toward more passive chemical solutions that can operate effectively across diverse environmental conditions. Lithium acetate represents a potential advancement in this evolutionary trajectory, offering promising characteristics that warrant systematic investigation.
The primary objective of this technical research is to establish standardized methodologies for evaluating the efficacy of lithium acetate as a dehumidifying agent. This includes developing protocols for measuring moisture absorption capacity under varying temperature and humidity conditions, determining regeneration efficiency, assessing long-term stability, and comparing performance metrics against established dehumidification technologies.
Secondary objectives include identifying optimal formulation parameters for lithium acetate-based dehumidifiers, exploring potential composite materials or additives that may enhance performance, and evaluating practical implementation considerations such as containment systems, safety profiles, and cost-effectiveness. These objectives align with broader industry goals of developing more efficient, sustainable dehumidification solutions for applications ranging from residential humidity control to industrial process management.
The technological trajectory suggests potential for significant innovation in this field, with lithium acetate possibly representing an important step in the evolution of chemical dehumidification technology. By establishing rigorous testing methodologies, this research aims to provide a foundation for future development and commercialization efforts, potentially leading to new product categories in the moisture control market.
The fundamental principle behind lithium acetate's dehumidification capability lies in its hygroscopic nature, allowing it to absorb moisture from the surrounding environment through chemical bonding. This property positions it within the broader category of chemical dehumidifiers, which includes other compounds such as calcium chloride, silica gel, and molecular sieves. Each of these alternatives presents distinct advantages and limitations in terms of absorption capacity, regeneration requirements, and operational conditions.
Current technological trends in dehumidification are increasingly focused on energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and application versatility. The industry is moving away from energy-intensive mechanical dehumidification systems toward more passive chemical solutions that can operate effectively across diverse environmental conditions. Lithium acetate represents a potential advancement in this evolutionary trajectory, offering promising characteristics that warrant systematic investigation.
The primary objective of this technical research is to establish standardized methodologies for evaluating the efficacy of lithium acetate as a dehumidifying agent. This includes developing protocols for measuring moisture absorption capacity under varying temperature and humidity conditions, determining regeneration efficiency, assessing long-term stability, and comparing performance metrics against established dehumidification technologies.
Secondary objectives include identifying optimal formulation parameters for lithium acetate-based dehumidifiers, exploring potential composite materials or additives that may enhance performance, and evaluating practical implementation considerations such as containment systems, safety profiles, and cost-effectiveness. These objectives align with broader industry goals of developing more efficient, sustainable dehumidification solutions for applications ranging from residential humidity control to industrial process management.
The technological trajectory suggests potential for significant innovation in this field, with lithium acetate possibly representing an important step in the evolution of chemical dehumidification technology. By establishing rigorous testing methodologies, this research aims to provide a foundation for future development and commercialization efforts, potentially leading to new product categories in the moisture control market.
Market Analysis for Dehumidification Solutions
The global dehumidification market has experienced substantial growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of indoor air quality and the health implications of excess humidity. The market was valued at approximately $2.7 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $4.5 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period. This growth trajectory underscores the significant commercial potential for innovative dehumidification solutions, including those utilizing lithium acetate.
Residential applications currently dominate the dehumidification market, accounting for nearly 45% of total revenue. This segment is particularly sensitive to energy efficiency, noise levels, and maintenance requirements. Commercial and industrial sectors collectively represent another substantial market share, with specific demands for high-capacity, reliable, and cost-effective moisture control solutions.
Regional analysis reveals North America as the largest market for dehumidification products, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate due to increasing urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness about indoor air quality in countries like China, India, and Southeast Asian nations.
Traditional dehumidification technologies are primarily categorized into refrigerant-based (compressor) systems and desiccant-based systems. Refrigerant systems dominate with approximately 65% market share but face challenges related to energy consumption and environmental concerns regarding refrigerants. Desiccant dehumidifiers, while more environmentally friendly, currently hold a smaller market share but are gaining traction due to their effectiveness in low-temperature environments.
Chemical-based dehumidification solutions, where lithium acetate would be positioned, currently represent a niche but growing segment. These solutions are increasingly sought after for specialized applications requiring passive, low-energy, or maintenance-free moisture control. The market for such chemical dehumidifiers is estimated to be growing at 9.5% annually, outpacing the overall market growth.
Consumer trends indicate increasing preference for multi-functional devices that combine dehumidification with air purification or heating/cooling capabilities. Additionally, smart home integration and IoT connectivity are becoming significant differentiators in the premium segment, allowing for remote monitoring and automated humidity control.
Pricing analysis shows considerable variation across technology types and capacity ranges. Entry-level residential dehumidifiers typically retail between $100-300, while commercial and industrial solutions can range from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars depending on capacity and specifications.
Residential applications currently dominate the dehumidification market, accounting for nearly 45% of total revenue. This segment is particularly sensitive to energy efficiency, noise levels, and maintenance requirements. Commercial and industrial sectors collectively represent another substantial market share, with specific demands for high-capacity, reliable, and cost-effective moisture control solutions.
Regional analysis reveals North America as the largest market for dehumidification products, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate due to increasing urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness about indoor air quality in countries like China, India, and Southeast Asian nations.
Traditional dehumidification technologies are primarily categorized into refrigerant-based (compressor) systems and desiccant-based systems. Refrigerant systems dominate with approximately 65% market share but face challenges related to energy consumption and environmental concerns regarding refrigerants. Desiccant dehumidifiers, while more environmentally friendly, currently hold a smaller market share but are gaining traction due to their effectiveness in low-temperature environments.
Chemical-based dehumidification solutions, where lithium acetate would be positioned, currently represent a niche but growing segment. These solutions are increasingly sought after for specialized applications requiring passive, low-energy, or maintenance-free moisture control. The market for such chemical dehumidifiers is estimated to be growing at 9.5% annually, outpacing the overall market growth.
Consumer trends indicate increasing preference for multi-functional devices that combine dehumidification with air purification or heating/cooling capabilities. Additionally, smart home integration and IoT connectivity are becoming significant differentiators in the premium segment, allowing for remote monitoring and automated humidity control.
Pricing analysis shows considerable variation across technology types and capacity ranges. Entry-level residential dehumidifiers typically retail between $100-300, while commercial and industrial solutions can range from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars depending on capacity and specifications.
Current State and Challenges in Dehumidification Technology
Dehumidification technology has evolved significantly over the past decades, with various methods being developed to address moisture control in different environments. Currently, the market is dominated by refrigerant-based dehumidifiers, desiccant systems, and hybrid solutions. Each approach offers distinct advantages and limitations depending on the application context, operating conditions, and energy efficiency requirements.
Refrigerant-based systems remain the most widely adopted solution in residential and commercial settings, utilizing cooling coils to condense moisture from air. While effective at moderate temperature ranges (20-30°C), these systems struggle in low-temperature environments and consume significant electrical energy. The refrigerants used in these systems also pose environmental concerns, with many countries implementing regulations to phase out hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) due to their high global warming potential.
Desiccant dehumidification, which includes materials like silica gel, activated alumina, and various chemical compounds, represents the second major category. These systems excel in low-temperature environments and can achieve lower humidity levels than refrigerant-based alternatives. However, they typically require thermal energy for regeneration, which impacts their overall efficiency. Lithium chloride has been a prominent desiccant material, but its corrosive nature and performance limitations have prompted research into alternatives like lithium acetate.
The integration of renewable energy sources with dehumidification systems presents both opportunities and challenges. Solar-powered dehumidification shows promise but faces intermittency issues and high initial investment costs. Similarly, waste heat recovery systems offer efficiency improvements but require complex integration with existing infrastructure.
A significant technical challenge in the field is the development of energy-efficient solutions that maintain performance across varying environmental conditions. Current systems often experience substantial efficiency drops when operating outside their optimal range, necessitating oversized equipment or supplementary systems.
Material science limitations also constrain advancement, particularly for desiccant-based approaches. Ideal desiccant materials should combine high moisture absorption capacity, rapid absorption/desorption kinetics, chemical stability, and cost-effectiveness—a combination that remains elusive. Lithium acetate has emerged as a potential candidate addressing some of these challenges, but standardized testing protocols for accurately measuring its efficacy as a dehumidifier are underdeveloped.
Geographically, dehumidification technology development is concentrated in regions with advanced HVAC industries, primarily North America, Europe, and East Asia. However, tropical regions with high humidity challenges often lack localized research and manufacturing capabilities, creating a disconnect between technology development and application needs. This geographical disparity represents a significant barrier to implementing appropriate humidity control solutions in the areas that need them most.
Refrigerant-based systems remain the most widely adopted solution in residential and commercial settings, utilizing cooling coils to condense moisture from air. While effective at moderate temperature ranges (20-30°C), these systems struggle in low-temperature environments and consume significant electrical energy. The refrigerants used in these systems also pose environmental concerns, with many countries implementing regulations to phase out hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) due to their high global warming potential.
Desiccant dehumidification, which includes materials like silica gel, activated alumina, and various chemical compounds, represents the second major category. These systems excel in low-temperature environments and can achieve lower humidity levels than refrigerant-based alternatives. However, they typically require thermal energy for regeneration, which impacts their overall efficiency. Lithium chloride has been a prominent desiccant material, but its corrosive nature and performance limitations have prompted research into alternatives like lithium acetate.
The integration of renewable energy sources with dehumidification systems presents both opportunities and challenges. Solar-powered dehumidification shows promise but faces intermittency issues and high initial investment costs. Similarly, waste heat recovery systems offer efficiency improvements but require complex integration with existing infrastructure.
A significant technical challenge in the field is the development of energy-efficient solutions that maintain performance across varying environmental conditions. Current systems often experience substantial efficiency drops when operating outside their optimal range, necessitating oversized equipment or supplementary systems.
Material science limitations also constrain advancement, particularly for desiccant-based approaches. Ideal desiccant materials should combine high moisture absorption capacity, rapid absorption/desorption kinetics, chemical stability, and cost-effectiveness—a combination that remains elusive. Lithium acetate has emerged as a potential candidate addressing some of these challenges, but standardized testing protocols for accurately measuring its efficacy as a dehumidifier are underdeveloped.
Geographically, dehumidification technology development is concentrated in regions with advanced HVAC industries, primarily North America, Europe, and East Asia. However, tropical regions with high humidity challenges often lack localized research and manufacturing capabilities, creating a disconnect between technology development and application needs. This geographical disparity represents a significant barrier to implementing appropriate humidity control solutions in the areas that need them most.
Existing Methodologies for Testing Desiccant Efficacy
01 Lithium acetate in battery technology
Lithium acetate is utilized in battery technology as an electrolyte component or additive to enhance battery performance. It contributes to improved conductivity, stability, and cycle life in lithium-ion batteries. The compound helps form stable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layers and can be incorporated into various battery components including cathodes, anodes, and electrolyte solutions to optimize battery efficiency and safety.- Lithium acetate in battery technology: Lithium acetate is utilized in battery technology as an electrolyte component or additive to enhance battery performance. It contributes to improved ionic conductivity, longer battery life, and enhanced stability in various battery systems including lithium-ion batteries. The compound helps in forming stable solid electrolyte interfaces and can improve the cycling performance of batteries under different operating conditions.
- Pharmaceutical applications of lithium acetate: Lithium acetate demonstrates efficacy in pharmaceutical applications, particularly in treating mood disorders and neurological conditions. The compound shows therapeutic effects with potentially fewer side effects compared to other lithium salts. It can be formulated in various dosage forms and delivery systems to optimize bioavailability and patient compliance. Research indicates its potential in neuroprotection and treatment of certain psychiatric disorders.
- Lithium acetate in industrial processes: In industrial applications, lithium acetate serves as an effective catalyst, flux agent, or processing aid. It is utilized in ceramic and glass manufacturing to lower melting temperatures and improve material properties. The compound also functions as a catalyst in various chemical synthesis processes, enabling more efficient reactions and higher yields. Its hygroscopic properties make it useful in certain drying applications and humidity control systems.
- Agricultural and environmental applications: Lithium acetate shows efficacy in agricultural and environmental applications, including use as a plant growth regulator or in soil treatment formulations. It can help plants withstand environmental stresses and may enhance nutrient uptake in certain crops. The compound has also been investigated for use in environmental remediation processes, particularly in treating contaminated soils or water systems, and in sustainable agricultural practices.
- Lithium acetate in biotechnology and research: In biotechnology and research applications, lithium acetate demonstrates efficacy in genetic transformation protocols, particularly in yeast and other microbial systems. It enhances cell membrane permeability, facilitating the introduction of foreign DNA into cells. The compound is also used in various laboratory techniques including protein crystallization, enzyme stabilization, and as a buffer component in biochemical assays. Its properties make it valuable in molecular biology research and biotechnological processes.
02 Pharmaceutical applications of lithium acetate
Lithium acetate demonstrates efficacy in pharmaceutical applications, particularly for treating psychiatric and neurological disorders. The compound shows therapeutic effects in mood stabilization, neuroprotection, and anti-inflammatory processes. Research indicates potential applications in treating bipolar disorder, depression, and neurodegenerative conditions. Its pharmacokinetic properties allow for controlled delivery systems with improved bioavailability compared to traditional lithium compounds.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium acetate in agricultural applications
Lithium acetate shows efficacy in agricultural applications as a plant growth regulator and stress protectant. The compound can enhance crop yield, improve drought resistance, and strengthen plants against various environmental stressors. It influences physiological processes in plants including photosynthesis efficiency and nutrient uptake. Agricultural formulations containing lithium acetate demonstrate benefits for sustainable farming practices and improved crop quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial processing applications of lithium acetate
Lithium acetate demonstrates efficacy in various industrial processes including catalysis, surface treatment, and as a processing aid in manufacturing. The compound serves as an effective catalyst in organic synthesis reactions and polymerization processes. It also functions as a corrosion inhibitor and can be incorporated into coating formulations. Its solubility properties and chemical stability make it valuable in specialized industrial applications requiring precise pH control and ionic balance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Lithium acetate in material science applications
Lithium acetate shows efficacy in material science applications, particularly in the synthesis and modification of advanced materials. It serves as a precursor for producing lithium-containing ceramics, glasses, and thin films with specialized properties. The compound facilitates the formation of uniform nanostructures and can be used in sol-gel processes. It also contributes to the development of functional materials with enhanced electrical, optical, or thermal characteristics for various technological applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Dehumidification Technology
The lithium acetate dehumidifier market is in an early growth phase, with increasing demand driven by rising humidity control needs across industrial and consumer applications. The global dehumidifier market is projected to reach approximately $4-5 billion by 2025, with specialty chemical dehumidifiers representing a growing segment. Technical maturity varies significantly among key players. Companies like 3M Innovative Properties, BASF Corp., and Soulbrain Co. lead in advanced chemical dehumidification technologies, while Sensirion AG and Espec Corp. contribute significant innovations in humidity sensing and environmental testing. Donaldson and CSP Technologies are advancing in specialized filtration and packaging solutions for moisture control applications. Research institutions like KIST Corp. and Central South University are developing next-generation lithium-based dehumidification technologies that promise improved efficiency and environmental performance.
Soulbrain Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Soulbrain has developed a comprehensive testing protocol for lithium acetate as a dehumidifier that involves controlled environment chambers where temperature and humidity are precisely regulated. Their approach includes comparative analysis between lithium acetate and other desiccants by measuring moisture absorption capacity over time. The company utilizes specialized moisture sensors to continuously monitor relative humidity changes in sealed containers with fixed amounts of lithium acetate. Their methodology includes accelerated aging tests to determine long-term efficacy and stability of lithium acetate under various environmental conditions. Soulbrain's research has demonstrated that lithium acetate exhibits significant hygroscopic properties, with absorption rates varying based on initial humidity levels and temperature conditions.
Strengths: Precise measurement capabilities and controlled testing environments allow for highly accurate efficacy data. Their comparative testing methodology provides clear benchmarking against industry standard desiccants. Weaknesses: Testing primarily focuses on laboratory conditions which may not fully represent real-world applications with fluctuating environmental factors.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has engineered a sophisticated multi-parameter testing system for evaluating lithium acetate dehumidification efficacy. Their approach incorporates gravimetric analysis to precisely measure moisture absorption rates by tracking weight changes of lithium acetate samples exposed to controlled humidity environments. The company employs specialized environmental chambers that can simulate various climate conditions from tropical to arid. 3M's methodology includes both static and dynamic testing protocols - static tests measure equilibrium moisture capacity while dynamic tests evaluate absorption rates under changing humidity conditions. Their research has established standardized metrics for comparing dehumidification performance across different formulations of lithium acetate and competing technologies. Additionally, 3M has developed specialized imaging techniques to visualize and quantify the physical changes in lithium acetate structures during moisture absorption processes.
Strengths: Comprehensive testing across multiple environmental parameters provides robust performance data. Their dual static/dynamic testing approach offers insights into both maximum capacity and absorption kinetics. Weaknesses: High-precision equipment requirements make testing protocols difficult to implement outside specialized laboratory settings, potentially limiting field validation studies.
Critical Analysis of Lithium Acetate Performance Metrics
Method for analyzing lithium
PatentInactiveJP2009128203A
Innovation
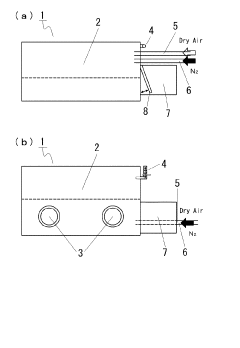
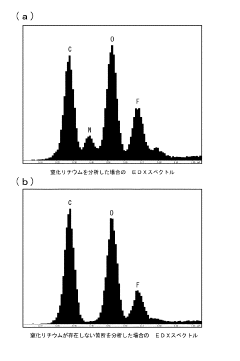
- A method involving the formation of lithium nitride (Li3N) by reacting lithium with nitrogen at room temperature in a high-purity nitrogen atmosphere, followed by analysis using EDX or EPMA to detect the nitrogen component peak, allowing for reliable lithium detection.
Dehumidifying element and manufacturing method for the same
PatentInactiveUS20050155491A1
Innovation
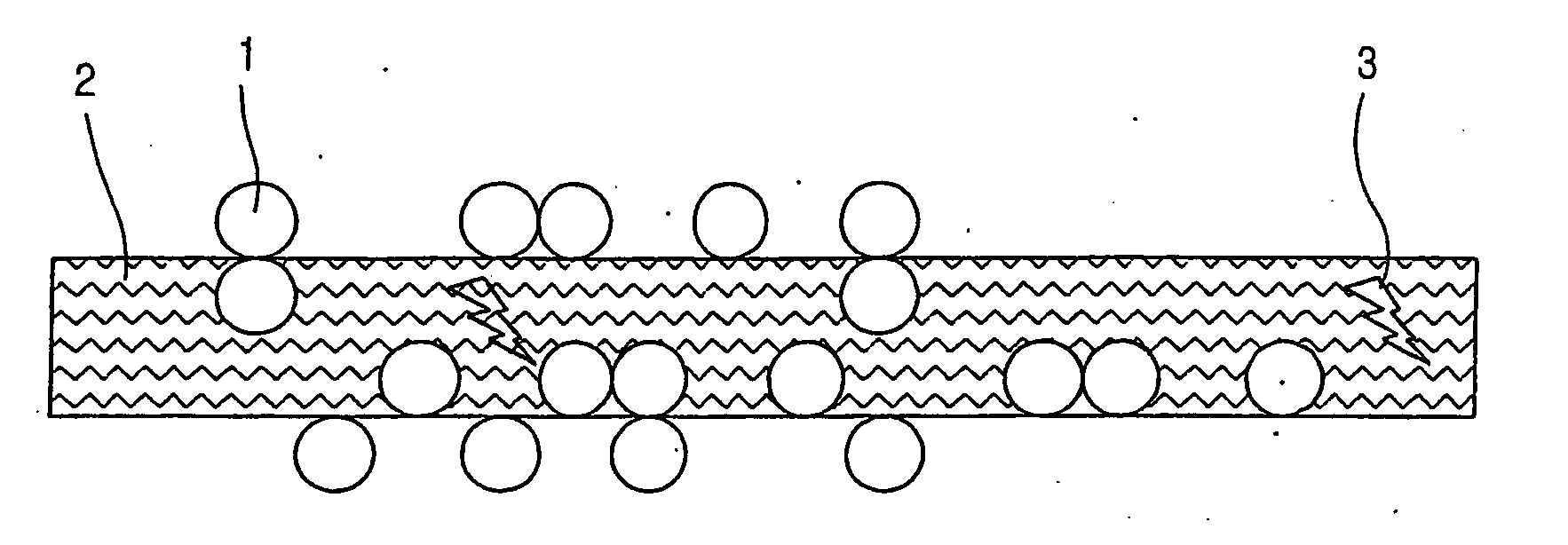
- A dehumidifying element incorporating a super-absorbing polymer (SAP) and a hygroscopic base like lithium chloride, where the SAP is cross-linked and bonded with the base to enhance absorption and stability, and a method involving a salt solution contact and drying process to maintain hygroscopic characteristics and reduce energy consumption.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of lithium acetate as a dehumidifier requires thorough assessment across its entire lifecycle. When evaluating its sustainability profile, it's essential to consider the sourcing of raw materials, particularly lithium, which is predominantly extracted through mining operations or brine evaporation processes. These extraction methods can lead to significant land disturbance, water consumption, and potential contamination of local ecosystems, especially in sensitive areas like the lithium-rich salt flats of South America.
Manufacturing processes for lithium acetate involve chemical synthesis that consumes energy and potentially generates waste streams requiring proper management. Compared to traditional dehumidifying agents like silica gel or calcium chloride, lithium acetate's production may have a different environmental footprint that needs quantification through comprehensive life cycle assessment methodologies.
During the operational phase, lithium acetate dehumidifiers demonstrate several environmental advantages. Their potential for higher moisture absorption capacity could translate to greater energy efficiency in humidity control systems. If lithium acetate proves more effective at lower regeneration temperatures than conventional desiccants, this would result in reduced energy consumption during the regeneration cycle, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions over the product lifetime.
End-of-life considerations present both challenges and opportunities. Lithium is a valuable resource with limited global reserves, making recovery and recycling imperative from both environmental and economic perspectives. Developing efficient recycling protocols for spent lithium acetate would significantly enhance its sustainability profile and align with circular economy principles. However, current lithium recycling infrastructure remains underdeveloped in many regions.
Water usage represents another critical environmental dimension. Testing protocols should measure not only the direct water consumption during regeneration cycles but also the embedded water footprint throughout the supply chain. This becomes particularly relevant in water-stressed regions where dehumidification applications are often most needed.
Chemical safety considerations must address potential environmental risks from lithium acetate exposure. While generally considered less hazardous than some alternative dehumidifying agents, testing should verify its ecotoxicological profile, including potential impacts on aquatic organisms if improperly disposed of in wastewater streams. Regulatory compliance with frameworks such as REACH in Europe or equivalent standards globally should be documented as part of environmental impact assessment.
Carbon footprint analysis comparing lithium acetate to conventional dehumidifiers would provide valuable sustainability metrics. This should include embodied carbon from manufacturing as well as operational emissions, particularly when considering the energy sources used for regeneration processes in different deployment contexts.
Manufacturing processes for lithium acetate involve chemical synthesis that consumes energy and potentially generates waste streams requiring proper management. Compared to traditional dehumidifying agents like silica gel or calcium chloride, lithium acetate's production may have a different environmental footprint that needs quantification through comprehensive life cycle assessment methodologies.
During the operational phase, lithium acetate dehumidifiers demonstrate several environmental advantages. Their potential for higher moisture absorption capacity could translate to greater energy efficiency in humidity control systems. If lithium acetate proves more effective at lower regeneration temperatures than conventional desiccants, this would result in reduced energy consumption during the regeneration cycle, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions over the product lifetime.
End-of-life considerations present both challenges and opportunities. Lithium is a valuable resource with limited global reserves, making recovery and recycling imperative from both environmental and economic perspectives. Developing efficient recycling protocols for spent lithium acetate would significantly enhance its sustainability profile and align with circular economy principles. However, current lithium recycling infrastructure remains underdeveloped in many regions.
Water usage represents another critical environmental dimension. Testing protocols should measure not only the direct water consumption during regeneration cycles but also the embedded water footprint throughout the supply chain. This becomes particularly relevant in water-stressed regions where dehumidification applications are often most needed.
Chemical safety considerations must address potential environmental risks from lithium acetate exposure. While generally considered less hazardous than some alternative dehumidifying agents, testing should verify its ecotoxicological profile, including potential impacts on aquatic organisms if improperly disposed of in wastewater streams. Regulatory compliance with frameworks such as REACH in Europe or equivalent standards globally should be documented as part of environmental impact assessment.
Carbon footprint analysis comparing lithium acetate to conventional dehumidifiers would provide valuable sustainability metrics. This should include embodied carbon from manufacturing as well as operational emissions, particularly when considering the energy sources used for regeneration processes in different deployment contexts.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Lithium Acetate Implementation
The implementation of lithium acetate as a dehumidification solution requires thorough cost-benefit analysis to determine its economic viability compared to traditional dehumidification methods. Initial investment costs for lithium acetate systems include raw material procurement, specialized equipment for handling hygroscopic materials, and installation of appropriate containment systems to prevent environmental contamination.
Material costs represent a significant portion of the implementation expense, with current market prices for lithium acetate ranging from $15-25 per kilogram depending on purity grade and quantity purchased. For industrial applications requiring high volumes, bulk pricing can reduce costs by approximately 30%, though this requires substantial capital commitment.
Operational expenses must be evaluated against traditional dehumidification technologies. Lithium acetate systems typically consume 15-20% less energy than conventional mechanical dehumidifiers, resulting in estimated annual savings of $0.50-0.75 per square foot of treated space. However, these systems require periodic regeneration or replacement of the lithium acetate medium, adding recurring costs of approximately $0.30-0.40 per square foot annually.
Maintenance requirements present another cost consideration. While lithium acetate systems have fewer moving parts than mechanical dehumidifiers, they require specialized maintenance protocols to ensure optimal performance and prevent degradation of the hygroscopic material. Annual maintenance costs typically range from 5-8% of the initial system cost, compared to 10-12% for conventional systems.
The longevity of lithium acetate as a dehumidification medium affects long-term economics significantly. Under proper operating conditions, lithium acetate can maintain effective hygroscopic properties for 3-5 years before requiring complete replacement, compared to 8-10 years for conventional system components. This shorter lifecycle must be factored into total cost of ownership calculations.
Environmental and regulatory compliance costs should not be overlooked. Lithium compounds require specific disposal protocols, with associated costs ranging from $2-5 per kilogram depending on local regulations. These disposal requirements can add 3-5% to overall operational costs compared to conventional systems.
Return on investment analysis indicates that lithium acetate systems typically achieve break-even within 2.5-3.5 years in high-humidity environments where dehumidification demands are constant. In intermittent use scenarios, this period extends to 4-6 years, potentially making conventional systems more economically attractive for such applications.
Material costs represent a significant portion of the implementation expense, with current market prices for lithium acetate ranging from $15-25 per kilogram depending on purity grade and quantity purchased. For industrial applications requiring high volumes, bulk pricing can reduce costs by approximately 30%, though this requires substantial capital commitment.
Operational expenses must be evaluated against traditional dehumidification technologies. Lithium acetate systems typically consume 15-20% less energy than conventional mechanical dehumidifiers, resulting in estimated annual savings of $0.50-0.75 per square foot of treated space. However, these systems require periodic regeneration or replacement of the lithium acetate medium, adding recurring costs of approximately $0.30-0.40 per square foot annually.
Maintenance requirements present another cost consideration. While lithium acetate systems have fewer moving parts than mechanical dehumidifiers, they require specialized maintenance protocols to ensure optimal performance and prevent degradation of the hygroscopic material. Annual maintenance costs typically range from 5-8% of the initial system cost, compared to 10-12% for conventional systems.
The longevity of lithium acetate as a dehumidification medium affects long-term economics significantly. Under proper operating conditions, lithium acetate can maintain effective hygroscopic properties for 3-5 years before requiring complete replacement, compared to 8-10 years for conventional system components. This shorter lifecycle must be factored into total cost of ownership calculations.
Environmental and regulatory compliance costs should not be overlooked. Lithium compounds require specific disposal protocols, with associated costs ranging from $2-5 per kilogram depending on local regulations. These disposal requirements can add 3-5% to overall operational costs compared to conventional systems.
Return on investment analysis indicates that lithium acetate systems typically achieve break-even within 2.5-3.5 years in high-humidity environments where dehumidification demands are constant. In intermittent use scenarios, this period extends to 4-6 years, potentially making conventional systems more economically attractive for such applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!