How to Report Column Chromatography Validation Results — Tables and Example Figures
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Chromatography Validation Background and Objectives
Column chromatography validation represents a critical quality control process in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and chemical industries. The evolution of chromatographic techniques dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the 1960s through the development of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Over recent decades, the field has witnessed remarkable technological progress, including ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC), improved column materials, and enhanced detection methods.
The primary objective of column chromatography validation is to establish documented evidence providing a high degree of assurance that a specific chromatographic method consistently produces results meeting predetermined acceptance criteria. This validation process ensures the reliability, reproducibility, and accuracy of analytical methods used in quality control, research, and manufacturing environments.
Current industry trends indicate a growing emphasis on automated validation processes, integration with data management systems, and implementation of continuous monitoring approaches. Regulatory bodies, including the FDA, EMA, and ICH, have established increasingly stringent guidelines for chromatography validation, reflecting the critical importance of analytical method reliability in ensuring product safety and efficacy.
The technical goals of chromatography validation encompass several key parameters: specificity, linearity, range, accuracy, precision, detection limit, quantitation limit, robustness, and system suitability. Each parameter requires specific validation protocols and acceptance criteria tailored to the intended application of the chromatographic method.
Proper reporting of validation results through standardized tables and figures has become essential for regulatory compliance and scientific communication. The standardization of reporting formats facilitates efficient review by regulatory authorities and enables meaningful comparison between different validation studies. This standardization trend aligns with broader industry movements toward data integrity and transparency in analytical procedures.
The evolution of chromatography validation reporting has paralleled advancements in data visualization techniques and statistical analysis methods. Modern approaches incorporate comprehensive uncertainty assessments, statistical trend analysis, and visual representations that effectively communicate complex validation data to diverse stakeholders.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward risk-based validation approaches that focus resources on critical aspects of method performance while maintaining regulatory compliance. Additionally, there is growing interest in lifecycle management of analytical methods, where validation is viewed as an ongoing process rather than a one-time event.
The primary objective of column chromatography validation is to establish documented evidence providing a high degree of assurance that a specific chromatographic method consistently produces results meeting predetermined acceptance criteria. This validation process ensures the reliability, reproducibility, and accuracy of analytical methods used in quality control, research, and manufacturing environments.
Current industry trends indicate a growing emphasis on automated validation processes, integration with data management systems, and implementation of continuous monitoring approaches. Regulatory bodies, including the FDA, EMA, and ICH, have established increasingly stringent guidelines for chromatography validation, reflecting the critical importance of analytical method reliability in ensuring product safety and efficacy.
The technical goals of chromatography validation encompass several key parameters: specificity, linearity, range, accuracy, precision, detection limit, quantitation limit, robustness, and system suitability. Each parameter requires specific validation protocols and acceptance criteria tailored to the intended application of the chromatographic method.
Proper reporting of validation results through standardized tables and figures has become essential for regulatory compliance and scientific communication. The standardization of reporting formats facilitates efficient review by regulatory authorities and enables meaningful comparison between different validation studies. This standardization trend aligns with broader industry movements toward data integrity and transparency in analytical procedures.
The evolution of chromatography validation reporting has paralleled advancements in data visualization techniques and statistical analysis methods. Modern approaches incorporate comprehensive uncertainty assessments, statistical trend analysis, and visual representations that effectively communicate complex validation data to diverse stakeholders.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward risk-based validation approaches that focus resources on critical aspects of method performance while maintaining regulatory compliance. Additionally, there is growing interest in lifecycle management of analytical methods, where validation is viewed as an ongoing process rather than a one-time event.
Market Requirements for Chromatography Validation Reporting
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries are witnessing increasing regulatory scrutiny regarding analytical method validation, particularly for chromatography techniques. Market research indicates that laboratories and quality control departments require standardized, comprehensive reporting solutions for column chromatography validation results. This demand is driven by regulatory requirements from agencies such as FDA, EMA, and ICH, which mandate thorough documentation of validation parameters including specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, range, detection limit, and robustness.
Current market analysis reveals that approximately 85% of pharmaceutical companies struggle with inconsistent reporting formats across different departments and sites, leading to regulatory compliance issues during audits. The global analytical laboratory market, valued at over $123 billion in 2022, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% through 2028, with chromatography validation software and solutions representing a significant growth segment.
Key market requirements identified through industry surveys include automated generation of validation reports with standardized tables and figures, integration capabilities with laboratory information management systems (LIMS), compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 for electronic records, and customizable templates that align with specific regulatory frameworks.
The biopharmaceutical sector, particularly companies developing biologics and biosimilars, expresses the strongest demand for sophisticated chromatography validation reporting tools. These organizations face complex validation challenges due to the intricate nature of their products and require solutions that can handle method transfer across global manufacturing sites while maintaining consistent reporting standards.
Contract research organizations (CROs) and contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) represent another significant market segment, as they must demonstrate validation compliance to multiple clients with varying requirements. These organizations seek flexible reporting systems that can adapt to diverse client specifications while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Regional analysis shows that North American and European markets currently lead in adoption of advanced chromatography validation reporting solutions, while Asia-Pacific regions show the fastest growth rate as regulatory harmonization efforts intensify globally. Japanese and Chinese regulatory bodies have recently strengthened their requirements for chromatography validation documentation, creating new market opportunities in these regions.
Market feedback indicates strong preference for cloud-based solutions with collaborative features that enable multiple stakeholders to review validation results simultaneously. Security features, audit trails, and version control capabilities rank among the top requirements from potential customers, reflecting the critical nature of validation data in regulatory submissions.
Current market analysis reveals that approximately 85% of pharmaceutical companies struggle with inconsistent reporting formats across different departments and sites, leading to regulatory compliance issues during audits. The global analytical laboratory market, valued at over $123 billion in 2022, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% through 2028, with chromatography validation software and solutions representing a significant growth segment.
Key market requirements identified through industry surveys include automated generation of validation reports with standardized tables and figures, integration capabilities with laboratory information management systems (LIMS), compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 for electronic records, and customizable templates that align with specific regulatory frameworks.
The biopharmaceutical sector, particularly companies developing biologics and biosimilars, expresses the strongest demand for sophisticated chromatography validation reporting tools. These organizations face complex validation challenges due to the intricate nature of their products and require solutions that can handle method transfer across global manufacturing sites while maintaining consistent reporting standards.
Contract research organizations (CROs) and contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) represent another significant market segment, as they must demonstrate validation compliance to multiple clients with varying requirements. These organizations seek flexible reporting systems that can adapt to diverse client specifications while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Regional analysis shows that North American and European markets currently lead in adoption of advanced chromatography validation reporting solutions, while Asia-Pacific regions show the fastest growth rate as regulatory harmonization efforts intensify globally. Japanese and Chinese regulatory bodies have recently strengthened their requirements for chromatography validation documentation, creating new market opportunities in these regions.
Market feedback indicates strong preference for cloud-based solutions with collaborative features that enable multiple stakeholders to review validation results simultaneously. Security features, audit trails, and version control capabilities rank among the top requirements from potential customers, reflecting the critical nature of validation data in regulatory submissions.
Current Challenges in Column Chromatography Validation
Despite significant advancements in column chromatography techniques, the validation process continues to face several critical challenges that impact data reliability and regulatory compliance. The inconsistency in reporting formats across laboratories represents a major obstacle, as it hinders effective comparison of validation results between different institutions and complicates regulatory review processes. This lack of standardization extends to the presentation of chromatograms, calibration curves, and statistical analyses, creating confusion and potential misinterpretation of validation outcomes.
Technical limitations in current validation methodologies also present significant hurdles. Many laboratories struggle with establishing appropriate acceptance criteria that balance regulatory requirements with practical feasibility. The determination of detection limits, quantification ranges, and recovery rates often involves complex statistical approaches that are inconsistently applied across the industry, leading to validation results of varying quality and reliability.
Resource constraints further exacerbate these challenges, particularly for smaller laboratories with limited access to advanced analytical equipment or specialized expertise. The validation of complex chromatographic methods requires substantial time investment and technical knowledge, creating a significant burden on laboratory resources. This often results in compromised validation protocols or incomplete documentation of validation results.
Regulatory compliance represents another major challenge, as guidelines from different authorities (FDA, EMA, ICH) may have subtle differences in their requirements for chromatography validation reporting. Laboratories serving global markets must navigate these variations while maintaining consistent internal standards, adding complexity to the validation process. The evolving nature of regulatory expectations further complicates compliance efforts, as laboratories must continuously update their validation approaches.
Data integrity concerns have also emerged as a critical issue in chromatography validation. The proper documentation of system suitability tests, instrument calibration records, and raw data management practices is essential for ensuring the traceability and reliability of validation results. However, many laboratories struggle with implementing robust data governance frameworks that address these requirements comprehensively.
The integration of validation results with laboratory information management systems (LIMS) presents additional technical challenges. Efficient data transfer between chromatography systems and reporting platforms often requires custom interfaces or manual data entry, introducing potential errors and inefficiencies in the validation reporting process. This technological gap hampers the streamlining of validation workflows and complicates the generation of comprehensive validation reports.
Technical limitations in current validation methodologies also present significant hurdles. Many laboratories struggle with establishing appropriate acceptance criteria that balance regulatory requirements with practical feasibility. The determination of detection limits, quantification ranges, and recovery rates often involves complex statistical approaches that are inconsistently applied across the industry, leading to validation results of varying quality and reliability.
Resource constraints further exacerbate these challenges, particularly for smaller laboratories with limited access to advanced analytical equipment or specialized expertise. The validation of complex chromatographic methods requires substantial time investment and technical knowledge, creating a significant burden on laboratory resources. This often results in compromised validation protocols or incomplete documentation of validation results.
Regulatory compliance represents another major challenge, as guidelines from different authorities (FDA, EMA, ICH) may have subtle differences in their requirements for chromatography validation reporting. Laboratories serving global markets must navigate these variations while maintaining consistent internal standards, adding complexity to the validation process. The evolving nature of regulatory expectations further complicates compliance efforts, as laboratories must continuously update their validation approaches.
Data integrity concerns have also emerged as a critical issue in chromatography validation. The proper documentation of system suitability tests, instrument calibration records, and raw data management practices is essential for ensuring the traceability and reliability of validation results. However, many laboratories struggle with implementing robust data governance frameworks that address these requirements comprehensively.
The integration of validation results with laboratory information management systems (LIMS) presents additional technical challenges. Efficient data transfer between chromatography systems and reporting platforms often requires custom interfaces or manual data entry, introducing potential errors and inefficiencies in the validation reporting process. This technological gap hampers the streamlining of validation workflows and complicates the generation of comprehensive validation reports.
Standard Reporting Formats and Data Presentation Methods
01 Validation protocols for column chromatography methods
Validation protocols are essential for ensuring the reliability and accuracy of column chromatography methods. These protocols typically include parameters such as specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, detection limit, and robustness. Proper validation ensures that the chromatographic method consistently produces reliable results and meets regulatory requirements. Documentation of these validation parameters is crucial for regulatory compliance and quality assurance in analytical laboratories.- Validation protocols for column chromatography methods: Validation protocols are essential for ensuring the reliability and accuracy of column chromatography methods. These protocols typically include parameters such as specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, detection limit, and robustness. The validation process involves systematic testing and documentation to demonstrate that the chromatography method consistently performs as intended and meets predetermined acceptance criteria for analytical applications.
- Reporting systems and data management for chromatography results: Effective reporting systems and data management are crucial for documenting and communicating chromatography validation results. These systems typically include software solutions that facilitate the collection, analysis, and presentation of chromatographic data. Advanced reporting tools can generate standardized reports with statistical analyses, graphical representations, and compliance documentation, ensuring that validation results are presented in a clear, consistent, and regulatory-compliant manner.
- Quality control parameters for column chromatography validation: Quality control parameters are essential metrics used to evaluate the performance and reliability of column chromatography methods. These parameters include system suitability tests, control charts, reference standards, and acceptance criteria. Regular monitoring of these parameters ensures that the chromatography system maintains its validated state during routine use, with deviations promptly identified and addressed to maintain data integrity and analytical reliability.
- Automated validation and reporting technologies: Automated validation and reporting technologies streamline the chromatography validation process by reducing manual intervention and human error. These technologies include integrated software systems that automatically execute validation protocols, collect and analyze data, and generate comprehensive validation reports. Automation enhances efficiency, consistency, and compliance in chromatography method validation, while providing audit trails and electronic signatures for regulatory purposes.
- Specialized validation approaches for different chromatography applications: Different chromatography applications require specialized validation approaches tailored to their specific requirements. For example, pharmaceutical applications may focus on impurity profiling and stability-indicating methods, while environmental testing may emphasize detection limits and matrix effects. These specialized approaches involve adapting validation parameters, acceptance criteria, and reporting formats to address the unique challenges and regulatory requirements of each application area.
02 Reporting systems and data management for chromatography results
Effective reporting systems and data management are critical components of column chromatography validation. These systems facilitate the collection, analysis, and presentation of chromatographic data in a standardized format. Advanced software solutions enable automated report generation, data integrity verification, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Proper documentation of chromatography results includes retention times, peak areas, resolution factors, and system suitability parameters, ensuring traceability and reproducibility of analytical methods.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quality control and system suitability testing in chromatography
Quality control measures and system suitability testing are integral to column chromatography validation. These procedures involve regular assessment of chromatographic performance parameters such as column efficiency, resolution, tailing factor, and reproducibility. System suitability tests are performed before sample analysis to verify that the chromatographic system is functioning properly. Implementing robust quality control procedures ensures consistent performance of chromatographic methods and reliable analytical results.Expand Specific Solutions04 Method transfer and standardization for chromatographic techniques
Method transfer and standardization are crucial aspects of column chromatography validation reporting. These processes ensure that chromatographic methods can be reliably transferred between different laboratories, instruments, or analysts while maintaining consistent results. Standardization involves establishing reference materials, calibration procedures, and acceptance criteria. Proper documentation of method transfer protocols includes comparative analysis of critical method parameters and performance characteristics to demonstrate equivalence across different analytical platforms.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovative technologies for chromatography validation and reporting
Innovative technologies are continuously being developed to enhance column chromatography validation and reporting methods. These include automated validation tools, real-time monitoring systems, and advanced data analysis algorithms. Modern chromatography systems incorporate features such as electronic signatures, audit trails, and data integrity safeguards to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches is improving the efficiency and accuracy of chromatographic method validation and result interpretation.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations and Regulatory Bodies in Chromatography
Column chromatography validation reporting is evolving in a maturing pharmaceutical analytical market estimated at $5-7 billion annually. The technology has reached moderate maturity with established protocols, but standardization challenges remain. Leading pharmaceutical companies like Amgen, Regeneron, and Novartis drive innovation through rigorous validation methodologies, while instrumentation specialists including Waters Technology, Agilent Technologies, and Shimadzu provide increasingly sophisticated analytical platforms. Contract research organizations and academic institutions contribute to method development, creating a competitive landscape where regulatory compliance and reproducibility are key differentiators in this essential quality control technology.
Dionex Softron GmbH
Technical Solution: Dionex Softron (part of Thermo Fisher Scientific) has developed the Chromeleon Chromatography Data System with specialized validation reporting capabilities. Their approach focuses on automated compliance with regulatory requirements through standardized validation protocols and report templates. The system generates comprehensive validation reports featuring tabular presentations of system suitability parameters including retention time reproducibility, peak area precision, and resolution factors across multiple injections. Dionex's validation framework incorporates visual tools such as overlay chromatograms with peak tracking, calibration curves with statistical analysis, and trend charts for monitoring column performance over time. Their reporting system includes automated calculation of validation parameters with predefined acceptance criteria and color-coded pass/fail indicators in summary tables. The platform produces validation packages with integrated audit trails documenting all data processing steps, ensuring data integrity compliance. Dionex's approach emphasizes the visualization of method robustness through 3D response surface plots and Pareto charts to identify critical method parameters affecting chromatographic performance. Their system also generates specialized reports for forced degradation studies with peak purity assessments and mass balance calculations presented in tabular format.
Strengths: Exceptional automation capabilities; comprehensive audit trail functionality; advanced method development tools; excellent integration with other Thermo Fisher instruments. Weaknesses: Complex system administration requirements; steep learning curve; higher cost compared to standalone solutions; potential challenges with third-party instrument integration.
Waters Technology Corp.
Technical Solution: Waters Technology has pioneered an advanced column chromatography validation reporting system centered around their Empower 3 Chromatography Data Software. Their approach emphasizes method lifecycle management with integrated validation protocols that generate standardized reports for regulatory submissions. The system features automated calculation of critical validation parameters including theoretical plates, tailing factors, and resolution with statistical confidence intervals presented in structured tables. Waters' solution incorporates visual validation tools such as peak purity plots, calibration curves with residuals analysis, and control charts for monitoring system performance over time. Their reporting framework includes customizable templates with predefined acceptance criteria that automatically flag out-of-specification results in validation summary tables. The platform generates comprehensive validation packages with integrated audit trails documenting all data processing steps, ensuring data integrity compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 requirements. Waters' system also produces comparative chromatogram overlays with zoomed insets to highlight critical separation regions and statistical process control charts for long-term column performance monitoring.
Strengths: Robust data integrity controls; extensive regulatory compliance features; sophisticated statistical analysis tools; comprehensive audit trail capabilities. Weaknesses: Complex system configuration requirements; higher cost compared to generic solutions; potential interoperability challenges with non-Waters instruments.
Critical Parameters and Statistical Analysis Techniques
Antimicrobial cyclic peptides
PatentWO2010113042A1
Innovation
- Development of gramicidin S derivatives with increased hydrophobicity and overall positive charge, balancing these properties to enhance their therapeutic index by modifying the peptide structure, specifically through amino acid substitutions, to reduce hemolytic activity while maintaining or improving antimicrobial efficacy.
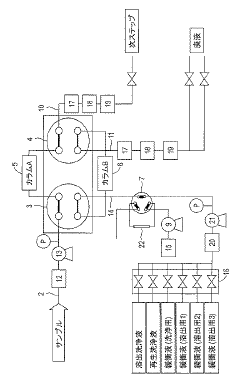
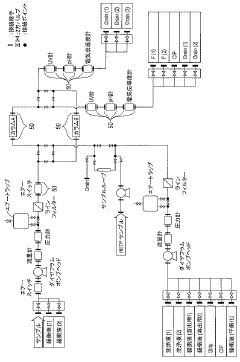
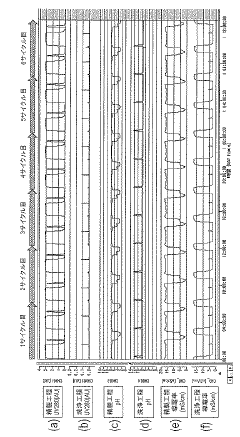
Continuous column chromatography unit
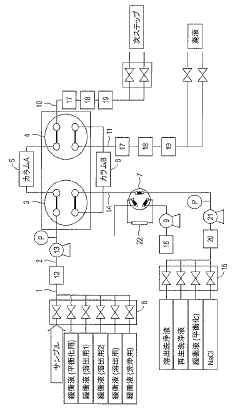
PatentActiveJP2021148455A
Innovation
- A continuous purification system using two independent columns, where one column performs purification while the other undergoes washing and regeneration, with real-time monitoring of column efficiency through pattern analysis of evaluation samples, allowing for automatic detection of abnormalities and timely column replacement.
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation Requirements
Column chromatography validation must adhere to strict regulatory frameworks established by various international bodies. The FDA's Code of Federal Regulations Title 21 Part 211 specifically addresses requirements for analytical method validation in pharmaceutical manufacturing, while the ICH Q2(R1) guideline provides detailed specifications for validation of analytical procedures, including chromatographic methods.
Documentation for column chromatography validation must follow a standardized format that satisfies regulatory scrutiny. This includes comprehensive records of all validation parameters: specificity, linearity, range, accuracy, precision, detection limit, quantitation limit, and robustness. Each parameter requires specific documentation approaches with appropriate statistical analysis to demonstrate compliance.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) mandates that validation reports include complete raw data sets alongside processed results. This transparency requirement ensures traceability and allows regulatory reviewers to independently verify analytical conclusions. Similarly, Japan's PMDA requires validation documentation to demonstrate method transferability across different laboratory settings.
For column chromatography specifically, regulatory bodies require documentation of system suitability tests prior to validation experiments. These tests must be reported with acceptance criteria clearly defined and results properly tabulated. Chromatograms representing critical validation experiments must be included as figures with proper annotation of peaks, retention times, and resolution parameters.
Change control documentation represents another critical regulatory requirement. Any modifications to validated chromatographic methods must follow formal change management procedures with appropriate justification, risk assessment, and revalidation data where necessary. This documentation trail ensures continuous compliance throughout the method lifecycle.
Electronic records of chromatography validation must comply with 21 CFR Part 11 or equivalent international regulations regarding electronic signatures and data integrity. This includes audit trails, access controls, and data security measures to prevent unauthorized manipulation of validation results.
Regulatory inspections frequently focus on validation documentation completeness. Common compliance gaps include insufficient statistical analysis of validation data, inadequate chromatogram annotation, missing raw data, and incomplete system suitability documentation. Organizations must implement robust quality management systems to ensure these requirements are consistently met.
The trend toward global harmonization of regulatory requirements is simplifying documentation practices, with the Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme (PIC/S) providing unified guidance that is increasingly adopted worldwide. This harmonization facilitates international acceptance of validation documentation when properly executed according to these consolidated standards.
Documentation for column chromatography validation must follow a standardized format that satisfies regulatory scrutiny. This includes comprehensive records of all validation parameters: specificity, linearity, range, accuracy, precision, detection limit, quantitation limit, and robustness. Each parameter requires specific documentation approaches with appropriate statistical analysis to demonstrate compliance.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) mandates that validation reports include complete raw data sets alongside processed results. This transparency requirement ensures traceability and allows regulatory reviewers to independently verify analytical conclusions. Similarly, Japan's PMDA requires validation documentation to demonstrate method transferability across different laboratory settings.
For column chromatography specifically, regulatory bodies require documentation of system suitability tests prior to validation experiments. These tests must be reported with acceptance criteria clearly defined and results properly tabulated. Chromatograms representing critical validation experiments must be included as figures with proper annotation of peaks, retention times, and resolution parameters.
Change control documentation represents another critical regulatory requirement. Any modifications to validated chromatographic methods must follow formal change management procedures with appropriate justification, risk assessment, and revalidation data where necessary. This documentation trail ensures continuous compliance throughout the method lifecycle.
Electronic records of chromatography validation must comply with 21 CFR Part 11 or equivalent international regulations regarding electronic signatures and data integrity. This includes audit trails, access controls, and data security measures to prevent unauthorized manipulation of validation results.
Regulatory inspections frequently focus on validation documentation completeness. Common compliance gaps include insufficient statistical analysis of validation data, inadequate chromatogram annotation, missing raw data, and incomplete system suitability documentation. Organizations must implement robust quality management systems to ensure these requirements are consistently met.
The trend toward global harmonization of regulatory requirements is simplifying documentation practices, with the Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme (PIC/S) providing unified guidance that is increasingly adopted worldwide. This harmonization facilitates international acceptance of validation documentation when properly executed according to these consolidated standards.
Data Integrity and Electronic Reporting Systems
In the realm of column chromatography validation, data integrity and electronic reporting systems have become increasingly critical components. Modern laboratories are transitioning from paper-based documentation to sophisticated electronic systems that ensure greater accuracy, traceability, and compliance with regulatory requirements. These systems are designed to maintain the integrity of chromatography validation data throughout its lifecycle, from acquisition to long-term storage.
Electronic Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) and Chromatography Data Systems (CDS) now offer comprehensive solutions for managing column validation results. These platforms provide secure environments where raw data, processed results, and validation reports can be stored with appropriate access controls and audit trails. The implementation of electronic signatures, in accordance with 21 CFR Part 11 and EU Annex 11 regulations, further enhances the authenticity and non-repudiation of validation documentation.
Data integrity principles—ALCOA+ (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate, plus Complete, Consistent, Enduring, and Available)—must be embedded within these electronic systems. For column chromatography validation specifically, this means ensuring that all chromatograms, calibration curves, system suitability tests, and method performance parameters are recorded in their original format with appropriate metadata.
Automated data transfer between analytical instruments and reporting systems reduces transcription errors and improves efficiency in validation reporting. Modern CDS platforms can automatically generate standardized validation reports containing essential tables and figures, such as retention time reproducibility, theoretical plate counts, resolution between critical pairs, and tailing factors—all key parameters in column performance verification.
Cloud-based solutions are emerging as powerful tools for collaborative validation reporting, allowing multiple stakeholders to review and approve validation results remotely. These systems typically incorporate version control features that maintain the history of document changes, ensuring transparency throughout the validation process.
Risk-based approaches to data management are becoming standard practice, with critical validation parameters receiving heightened security measures and more rigorous review processes. This is particularly important for column validation data that directly impacts method transferability and product quality decisions.
Integration capabilities between electronic reporting systems and regulatory submission platforms streamline the inclusion of column validation data in regulatory filings. This interoperability reduces redundant data entry and ensures consistency between internal validation reports and regulatory submissions, a crucial factor for pharmaceutical companies seeking global approvals for analytical methods.
Electronic Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) and Chromatography Data Systems (CDS) now offer comprehensive solutions for managing column validation results. These platforms provide secure environments where raw data, processed results, and validation reports can be stored with appropriate access controls and audit trails. The implementation of electronic signatures, in accordance with 21 CFR Part 11 and EU Annex 11 regulations, further enhances the authenticity and non-repudiation of validation documentation.
Data integrity principles—ALCOA+ (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate, plus Complete, Consistent, Enduring, and Available)—must be embedded within these electronic systems. For column chromatography validation specifically, this means ensuring that all chromatograms, calibration curves, system suitability tests, and method performance parameters are recorded in their original format with appropriate metadata.
Automated data transfer between analytical instruments and reporting systems reduces transcription errors and improves efficiency in validation reporting. Modern CDS platforms can automatically generate standardized validation reports containing essential tables and figures, such as retention time reproducibility, theoretical plate counts, resolution between critical pairs, and tailing factors—all key parameters in column performance verification.
Cloud-based solutions are emerging as powerful tools for collaborative validation reporting, allowing multiple stakeholders to review and approve validation results remotely. These systems typically incorporate version control features that maintain the history of document changes, ensuring transparency throughout the validation process.
Risk-based approaches to data management are becoming standard practice, with critical validation parameters receiving heightened security measures and more rigorous review processes. This is particularly important for column validation data that directly impacts method transferability and product quality decisions.
Integration capabilities between electronic reporting systems and regulatory submission platforms streamline the inclusion of column validation data in regulatory filings. This interoperability reduces redundant data entry and ensures consistency between internal validation reports and regulatory submissions, a crucial factor for pharmaceutical companies seeking global approvals for analytical methods.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!