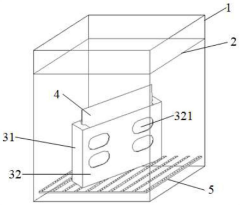
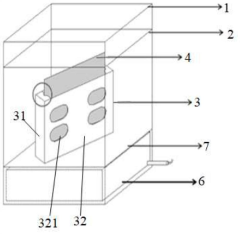
Industrial Supplier Evaluation Checklist For Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG) In Flexible Displays
AUG 26, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
UTG Technology Background and Objectives
Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG) technology represents a significant advancement in display materials, evolving from traditional glass manufacturing techniques to meet the demanding requirements of flexible display applications. The development of UTG can be traced back to the early 2010s when display manufacturers began seeking alternatives to plastic substrates that could offer better scratch resistance and optical clarity while maintaining flexibility. This technological evolution has been driven by the growing consumer demand for foldable smartphones, rollable displays, and other form factors that require durable yet flexible screen materials.
The progression of UTG technology has followed a trajectory of continuous thickness reduction, from early iterations measuring approximately 100 micrometers to current cutting-edge solutions achieving thicknesses below 30 micrometers. This remarkable thinning process has been accompanied by significant improvements in mechanical properties, particularly in terms of bend radius capabilities and folding endurance.
Industry objectives for UTG technology center around several key parameters that suppliers must address. Primary among these is achieving the optimal balance between flexibility and durability - UTG must be thin enough to bend repeatedly without fracturing while maintaining sufficient hardness to resist scratches and impacts. Optical performance represents another critical objective, with requirements for high transparency (>90%), minimal haze (<0.5%), and excellent color reproduction characteristics.
Manufacturing scalability constitutes a significant technological goal, as suppliers must demonstrate the ability to produce UTG in volumes sufficient to meet growing market demand while maintaining strict quality control standards. Current production challenges include yield management, handling of extremely thin substrates, and consistent application of functional coatings.
Cost-effectiveness remains a persistent objective in UTG development, with manufacturers seeking to reduce production expenses to enable broader adoption across various price segments of the flexible display market. This includes optimization of raw materials, processing techniques, and manufacturing workflows.
Looking forward, the technological roadmap for UTG includes objectives for further thickness reduction (targeting sub-20 micrometer solutions), enhanced folding durability (exceeding 200,000 fold cycles), improved impact resistance, and integration with advanced touch and sensing technologies. Suppliers are also exploring environmentally sustainable production methods and materials to align with growing industry commitments to reduced environmental impact.
The evaluation of industrial suppliers for UTG must therefore consider not only their current technical capabilities but also their research trajectory and commitment to advancing these critical objectives that will define the next generation of flexible display technologies.
The progression of UTG technology has followed a trajectory of continuous thickness reduction, from early iterations measuring approximately 100 micrometers to current cutting-edge solutions achieving thicknesses below 30 micrometers. This remarkable thinning process has been accompanied by significant improvements in mechanical properties, particularly in terms of bend radius capabilities and folding endurance.
Industry objectives for UTG technology center around several key parameters that suppliers must address. Primary among these is achieving the optimal balance between flexibility and durability - UTG must be thin enough to bend repeatedly without fracturing while maintaining sufficient hardness to resist scratches and impacts. Optical performance represents another critical objective, with requirements for high transparency (>90%), minimal haze (<0.5%), and excellent color reproduction characteristics.
Manufacturing scalability constitutes a significant technological goal, as suppliers must demonstrate the ability to produce UTG in volumes sufficient to meet growing market demand while maintaining strict quality control standards. Current production challenges include yield management, handling of extremely thin substrates, and consistent application of functional coatings.
Cost-effectiveness remains a persistent objective in UTG development, with manufacturers seeking to reduce production expenses to enable broader adoption across various price segments of the flexible display market. This includes optimization of raw materials, processing techniques, and manufacturing workflows.
Looking forward, the technological roadmap for UTG includes objectives for further thickness reduction (targeting sub-20 micrometer solutions), enhanced folding durability (exceeding 200,000 fold cycles), improved impact resistance, and integration with advanced touch and sensing technologies. Suppliers are also exploring environmentally sustainable production methods and materials to align with growing industry commitments to reduced environmental impact.
The evaluation of industrial suppliers for UTG must therefore consider not only their current technical capabilities but also their research trajectory and commitment to advancing these critical objectives that will define the next generation of flexible display technologies.
Market Demand Analysis for Flexible Display UTG
The flexible display market has witnessed exponential growth in recent years, with Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG) emerging as a critical component driving this expansion. Market research indicates that the global flexible display market is projected to reach $87.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 28.1% from 2021. UTG specifically has become a focal point within this ecosystem due to its superior optical properties, enhanced durability, and improved scratch resistance compared to alternative materials like polyimide films.
Consumer electronics represents the largest application segment for UTG-based flexible displays, with smartphones accounting for approximately 65% of the total market share. Major smartphone manufacturers have increasingly adopted foldable display technology incorporating UTG, with annual shipments of foldable smartphones reaching 7.1 million units in 2021 and expected to surpass 30 million by 2025.
Beyond smartphones, significant market demand for UTG is emerging in wearable devices, particularly smartwatches and fitness trackers, which require thin, lightweight, and durable display solutions. The automotive industry also presents substantial growth opportunities, with curved dashboard displays and entertainment systems increasingly incorporating flexible display technology.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the UTG market, accounting for over 70% of global production capacity, with South Korea and China leading manufacturing capabilities. North America and Europe represent significant consumption markets, driven by high consumer adoption rates of premium electronic devices.
Consumer preference surveys indicate that durability remains the primary concern for potential buyers of foldable devices, with 78% of respondents citing concerns about screen damage at the fold. This highlights the critical importance of UTG quality in market acceptance and adoption rates of flexible display technologies.
Supply chain analysis reveals potential bottlenecks in UTG production, with limited suppliers capable of meeting the stringent quality requirements for commercial applications. This supply constraint has created a seller's market, with UTG commanding premium pricing that impacts end-product costs and potentially limits mass-market adoption.
Industry forecasts suggest that technological advancements in UTG manufacturing processes could reduce production costs by approximately 40% over the next three years, potentially accelerating market penetration across multiple device categories. Additionally, emerging applications in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) headsets represent new growth vectors for UTG technology, with these segments expected to grow at 45% annually through 2026.
Consumer electronics represents the largest application segment for UTG-based flexible displays, with smartphones accounting for approximately 65% of the total market share. Major smartphone manufacturers have increasingly adopted foldable display technology incorporating UTG, with annual shipments of foldable smartphones reaching 7.1 million units in 2021 and expected to surpass 30 million by 2025.
Beyond smartphones, significant market demand for UTG is emerging in wearable devices, particularly smartwatches and fitness trackers, which require thin, lightweight, and durable display solutions. The automotive industry also presents substantial growth opportunities, with curved dashboard displays and entertainment systems increasingly incorporating flexible display technology.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the UTG market, accounting for over 70% of global production capacity, with South Korea and China leading manufacturing capabilities. North America and Europe represent significant consumption markets, driven by high consumer adoption rates of premium electronic devices.
Consumer preference surveys indicate that durability remains the primary concern for potential buyers of foldable devices, with 78% of respondents citing concerns about screen damage at the fold. This highlights the critical importance of UTG quality in market acceptance and adoption rates of flexible display technologies.
Supply chain analysis reveals potential bottlenecks in UTG production, with limited suppliers capable of meeting the stringent quality requirements for commercial applications. This supply constraint has created a seller's market, with UTG commanding premium pricing that impacts end-product costs and potentially limits mass-market adoption.
Industry forecasts suggest that technological advancements in UTG manufacturing processes could reduce production costs by approximately 40% over the next three years, potentially accelerating market penetration across multiple device categories. Additionally, emerging applications in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) headsets represent new growth vectors for UTG technology, with these segments expected to grow at 45% annually through 2026.
UTG Technical Challenges and Global Development Status
Ultra-thin glass (UTG) technology faces significant technical challenges despite its promising applications in flexible displays. The primary obstacle remains achieving consistent ultra-thin glass production with thicknesses below 100 micrometers while maintaining adequate flexibility and durability. Current manufacturing processes struggle with yield rates, as thinner glass becomes exponentially more susceptible to defects and breakage during production.
Surface quality control represents another major challenge, as microscopic flaws can lead to catastrophic failure when the glass is bent. The industry continues to grapple with achieving atomically smooth surfaces at scale, with current defect rates significantly higher than those acceptable for mass production of premium flexible devices.
Mechanical reliability under repeated folding cycles presents ongoing difficulties. While UTG offers superior scratch resistance compared to polymer alternatives, it still exhibits micro-crack formation after extended folding cycles, typically showing performance degradation after 100,000-200,000 folds—below the ideal threshold for long-term consumer device usage.
Globally, South Korea leads UTG development and implementation, with Samsung and LG Display pioneering commercial applications in foldable smartphones. Their technological advantage stems from vertical integration with glass suppliers and substantial R&D investments dating back to 2015. Japan maintains strong positions in specialized glass formulation technology, with AGC and NEG focusing on chemical strengthening processes specifically optimized for ultra-thin applications.
German precision engineering firms dominate the equipment sector for UTG processing, with companies like Schott developing proprietary down-draw techniques that have achieved glass thicknesses approaching 30 micrometers in laboratory settings. Chinese manufacturers are rapidly closing the technology gap through strategic acquisitions and government-backed research initiatives, particularly in the areas of mass production techniques and cost optimization.
The United States contributes primarily through materials science innovations, with Corning's specialized glass compositions showing promising results in balancing flexibility with durability. However, full commercialization remains limited by scaling challenges.
Recent technological breakthroughs include hybrid glass-polymer composite structures that maintain the surface properties of glass while leveraging polymer flexibility, though these approaches introduce new integration challenges at manufacturing interfaces. The development of specialized ion-exchange processes for ultra-thin substrates has shown promise in laboratory settings but requires further refinement for industrial implementation.
Surface quality control represents another major challenge, as microscopic flaws can lead to catastrophic failure when the glass is bent. The industry continues to grapple with achieving atomically smooth surfaces at scale, with current defect rates significantly higher than those acceptable for mass production of premium flexible devices.
Mechanical reliability under repeated folding cycles presents ongoing difficulties. While UTG offers superior scratch resistance compared to polymer alternatives, it still exhibits micro-crack formation after extended folding cycles, typically showing performance degradation after 100,000-200,000 folds—below the ideal threshold for long-term consumer device usage.
Globally, South Korea leads UTG development and implementation, with Samsung and LG Display pioneering commercial applications in foldable smartphones. Their technological advantage stems from vertical integration with glass suppliers and substantial R&D investments dating back to 2015. Japan maintains strong positions in specialized glass formulation technology, with AGC and NEG focusing on chemical strengthening processes specifically optimized for ultra-thin applications.
German precision engineering firms dominate the equipment sector for UTG processing, with companies like Schott developing proprietary down-draw techniques that have achieved glass thicknesses approaching 30 micrometers in laboratory settings. Chinese manufacturers are rapidly closing the technology gap through strategic acquisitions and government-backed research initiatives, particularly in the areas of mass production techniques and cost optimization.
The United States contributes primarily through materials science innovations, with Corning's specialized glass compositions showing promising results in balancing flexibility with durability. However, full commercialization remains limited by scaling challenges.
Recent technological breakthroughs include hybrid glass-polymer composite structures that maintain the surface properties of glass while leveraging polymer flexibility, though these approaches introduce new integration challenges at manufacturing interfaces. The development of specialized ion-exchange processes for ultra-thin substrates has shown promise in laboratory settings but requires further refinement for industrial implementation.
Current UTG Manufacturing Solutions
01 Manufacturing methods for Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG)
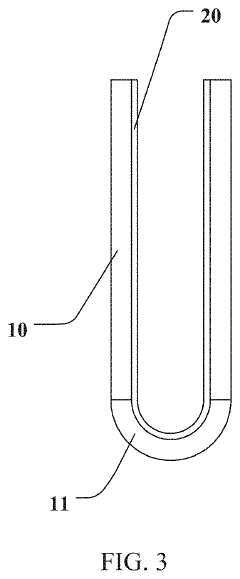
Various manufacturing techniques are employed to produce Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG) with precise thickness control and optimal properties. These methods include specialized drawing processes, chemical etching, and polishing techniques that can achieve glass thicknesses below 100 micrometers while maintaining structural integrity. Advanced processing parameters and temperature control during manufacturing ensure the glass meets the required specifications for flexibility and durability.- Manufacturing methods for Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG): Various manufacturing methods are employed to produce Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG) with desired properties. These methods include specialized drawing processes, chemical etching, and polishing techniques that allow for the production of glass sheets with thicknesses in the micrometer range while maintaining structural integrity. Advanced processing techniques help control the thickness uniformity and surface quality, which are critical for applications in flexible displays and electronic devices.
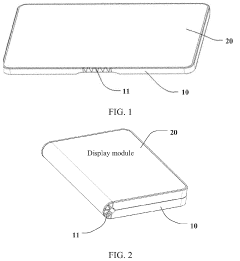
- UTG applications in flexible display technology: Ultra-Thin Glass serves as a key component in flexible display technology, providing superior optical clarity and scratch resistance compared to polymer alternatives. When incorporated into foldable smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, UTG enables display panels to bend repeatedly without damage while maintaining excellent visual quality. The glass is typically combined with additional protective layers to enhance durability while preserving flexibility.
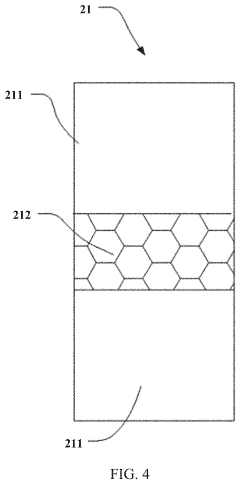
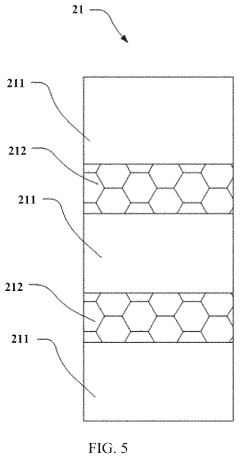
- UTG protective coating and reinforcement technologies: To enhance the durability of Ultra-Thin Glass, various protective coating and reinforcement technologies have been developed. These include hard coating layers, polymer laminates, and specialized surface treatments that improve scratch resistance and impact strength without compromising flexibility. Some approaches involve applying composite materials or nano-coatings to the glass surface, creating a hybrid material with enhanced mechanical properties while maintaining optical transparency.
- UTG integration with touch sensors and display modules: Integration methods for combining Ultra-Thin Glass with touch sensors and display modules have been developed to create complete display assemblies. These techniques include specialized bonding processes, alignment methods, and connection technologies that maintain the flexibility of the overall structure. The integration process must account for the different mechanical properties of glass, touch sensors, and display components to ensure reliable performance during bending and folding operations.
- UTG handling and processing equipment: Specialized equipment and handling systems have been developed for the processing, transportation, and assembly of Ultra-Thin Glass. These systems include vacuum handling tools, precision cutting equipment, and automated assembly lines designed to minimize stress and prevent damage to the delicate glass sheets. Advanced inspection systems are also employed to detect microscopic defects that could lead to failure points when the glass is subjected to bending forces in flexible devices.
02 UTG applications in flexible display technology
Ultra-Thin Glass serves as a critical component in flexible display technologies, particularly for foldable smartphones and other bendable electronic devices. The glass provides superior optical clarity and scratch resistance compared to polymer alternatives while enabling the necessary flexibility for folding mechanisms. UTG-based displays offer improved touch sensitivity, color reproduction, and overall visual quality while maintaining the ability to withstand repeated folding cycles.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protective coating systems for UTG
To enhance the durability and performance of Ultra-Thin Glass, various protective coating systems have been developed. These include hard coatings to improve scratch resistance, anti-fingerprint layers, and specialized films that maintain the glass flexibility while providing additional protection. Multi-layer coating approaches can combine different functional materials to achieve optimal balance between protection and flexibility, extending the lifespan of UTG-based products.Expand Specific Solutions04 UTG lamination and integration techniques
Specialized lamination and integration techniques are essential for incorporating Ultra-Thin Glass into electronic devices. These methods include precision adhesive application, vacuum lamination processes, and temperature-controlled bonding that maintain the integrity of the glass while securing it to other device components. Advanced integration approaches address challenges related to stress distribution during bending and ensure reliable connections between the glass and electronic components.Expand Specific Solutions05 UTG reinforcement and structural enhancement
Various methods have been developed to reinforce Ultra-Thin Glass and enhance its structural properties without compromising flexibility. These include ion exchange strengthening, composite structures with polymer layers, and specialized edge treatment techniques. Reinforcement approaches can significantly improve the impact resistance and overall durability of UTG while maintaining its ultra-thin profile and optical properties, making it more suitable for commercial applications in consumer electronics.Expand Specific Solutions
Key UTG Suppliers and Competitive Landscape
The ultra-thin glass (UTG) market for flexible displays is currently in a growth phase, with increasing adoption in foldable smartphones and wearable devices. The market is projected to expand significantly as flexible display technology matures, with an estimated global market size exceeding $3 billion by 2025. Technologically, UTG manufacturing remains challenging, requiring specialized expertise in glass thinning and strengthening processes. Leading players include Corning, SCHOTT AG, and Samsung Display, who have established strong intellectual property positions, while Chinese manufacturers like BOE Technology, Triumph Science & Technology, and Dongxu Technology are rapidly advancing their capabilities. Western companies maintain technological leadership, but Asian manufacturers, particularly from China and South Korea, are closing the gap through aggressive R&D investments and strategic partnerships across the supply chain.
Corning, Inc.
Technical Solution: Corning has developed Willow Glass, an ultra-thin flexible glass substrate with thickness ranging from 50 to 100 microns, specifically engineered for flexible displays. Their manufacturing process utilizes fusion draw technology which creates pristine surfaces without requiring post-production polishing. This results in glass with exceptional dimensional stability, superior surface quality, and high optical transparency (>99% transmission). Corning's UTG incorporates ion-exchange strengthening technology that creates compressive stress layers on the glass surface, significantly improving mechanical durability while maintaining flexibility. Their proprietary formulation includes aluminum silicate composition that enhances resistance to repeated bending cycles (tested to withstand over 200,000 fold cycles at 3mm radius). Additionally, Corning has developed specialized handling and processing techniques for ultra-thin glass, including temporary carrier systems that allow conventional display manufacturing equipment to process these delicate substrates efficiently.
Strengths: Superior optical clarity and transmission compared to polymer alternatives; exceptional thermal stability allowing higher processing temperatures; better barrier properties against oxygen and moisture; superior scratch resistance. Weaknesses: Higher initial production costs compared to plastic substrates; requires specialized handling equipment; more brittle than polymer alternatives despite strengthening treatments; limited to larger bend radius compared to some polymer solutions.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung Electronics has developed an integrated UTG (Ultra-Thin Glass) solution for their flexible display products that builds upon Samsung Display's core technology while adding device-specific optimizations. Their approach incorporates a multi-layer protection system with the UTG core sandwiched between specialized polymer layers that enhance impact resistance while maintaining optical clarity. Samsung Electronics has implemented a proprietary bonding process that uses optically clear adhesives specifically formulated to maintain flexibility through repeated folding cycles while minimizing delamination risks. Their UTG implementation includes a specialized hinge mechanism designed to distribute stress evenly across the glass surface during folding, maintaining a consistent bend radius that minimizes localized stress points. Samsung has developed an advanced touch sensor integration process specifically optimized for UTG, using patterned metal nanowires that maintain conductivity through repeated bending cycles. Additionally, their manufacturing process incorporates real-time stress testing at multiple production stages to ensure consistent quality and durability. Samsung Electronics' UTG solution features a specialized edge sealing technology that prevents moisture ingress and edge damage, addressing key failure points in flexible display implementations.
Strengths: Comprehensive end-to-end solution from materials to final device integration; proven commercial implementation across multiple product generations; advanced multi-layer protection system enhancing durability; optimized mechanical design to distribute folding stress. Weaknesses: Higher cost structure compared to plastic alternatives; proprietary technology limiting supply chain flexibility; requires complex manufacturing processes; potential for damage with excessive force despite protective measures.
Critical UTG Patents and Technical Literature
Flexible Display Cover, Flexible Display Module, And Flexible Display Apparatus
PatentActiveUS20220118744A1
Innovation
- A flexible display cover comprising a glass layer with a hardened layer and a flexible protective layer, where the glass layer is chemically strengthened and coated with a hardened material to enhance scratch and impact resistance, and an anti-shatter layer is optionally included to prevent glass fragmentation.
Ultra-thin glass cover plate processing technology
PatentActiveCN113582553A
Innovation
- Chemical etching is used to passivate the edges of ultra-thin glass, combined with laser cutting and surface etching optimization, and hydrofluoric acid/nitric acid/sulfuric acid solution is used for immersion etching to repair chipping defects and improve the bending performance and impact resistance of the glass. Strength, while using ultrasonic vibrators and foam tubes to reduce the production of fixture marks.
Supply Chain Risk Assessment for UTG Procurement
The procurement of Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG) for flexible displays represents a significant supply chain challenge due to the specialized nature of this material and its critical role in next-generation display technologies. A comprehensive risk assessment framework is essential to ensure stable supply and mitigate potential disruptions in the UTG procurement process.
Geographic concentration presents a primary risk factor, with UTG production currently dominated by a limited number of suppliers in South Korea, Japan, and Germany. This concentration creates vulnerability to regional disruptions such as natural disasters, political instability, or localized economic downturns. The 2011 Tohoku earthquake in Japan demonstrated how geographic concentration can severely impact specialized materials supply chains, with some electronics manufacturers experiencing months of disruption.
Technical complexity in UTG manufacturing introduces additional risk dimensions. The production process requires specialized equipment, precise temperature control, and clean room environments. Any technical failures or quality control issues at supplier facilities can result in significant production delays and quality inconsistencies. The yield rates for UTG remain relatively low compared to standard glass, amplifying supply uncertainty.
Market dynamics further complicate the UTG supply landscape. As flexible display adoption accelerates across smartphones, wearables, and automotive applications, demand volatility creates challenges in capacity planning. The limited supplier base often results in allocation scenarios during high-demand periods, potentially leading to price fluctuations and extended lead times. Historical data indicates UTG price premiums of 30-40% during supply constraints.
Regulatory and compliance factors must also be considered in risk assessment. UTG manufacturing involves various chemicals and processes subject to environmental regulations that vary by region. Changes in regulatory frameworks can impact production capabilities, compliance costs, and ultimately material availability. Additionally, intellectual property considerations may restrict supplier selection based on licensing agreements and patent landscapes.
Financial stability of UTG suppliers represents another critical risk dimension. The capital-intensive nature of UTG production facilities means that supplier financial health directly impacts long-term supply reliability. Regular financial assessment of key suppliers, including debt ratios, profitability trends, and capital expenditure plans, should be incorporated into the risk evaluation process.
Transportation logistics for UTG present unique challenges due to the fragile nature of the material. Specialized packaging, handling procedures, and transportation methods are required to minimize breakage and contamination risks. The extended global supply chains typical in the display industry amplify these logistical vulnerabilities, particularly when considering intercontinental shipping requirements.
Geographic concentration presents a primary risk factor, with UTG production currently dominated by a limited number of suppliers in South Korea, Japan, and Germany. This concentration creates vulnerability to regional disruptions such as natural disasters, political instability, or localized economic downturns. The 2011 Tohoku earthquake in Japan demonstrated how geographic concentration can severely impact specialized materials supply chains, with some electronics manufacturers experiencing months of disruption.
Technical complexity in UTG manufacturing introduces additional risk dimensions. The production process requires specialized equipment, precise temperature control, and clean room environments. Any technical failures or quality control issues at supplier facilities can result in significant production delays and quality inconsistencies. The yield rates for UTG remain relatively low compared to standard glass, amplifying supply uncertainty.
Market dynamics further complicate the UTG supply landscape. As flexible display adoption accelerates across smartphones, wearables, and automotive applications, demand volatility creates challenges in capacity planning. The limited supplier base often results in allocation scenarios during high-demand periods, potentially leading to price fluctuations and extended lead times. Historical data indicates UTG price premiums of 30-40% during supply constraints.
Regulatory and compliance factors must also be considered in risk assessment. UTG manufacturing involves various chemicals and processes subject to environmental regulations that vary by region. Changes in regulatory frameworks can impact production capabilities, compliance costs, and ultimately material availability. Additionally, intellectual property considerations may restrict supplier selection based on licensing agreements and patent landscapes.
Financial stability of UTG suppliers represents another critical risk dimension. The capital-intensive nature of UTG production facilities means that supplier financial health directly impacts long-term supply reliability. Regular financial assessment of key suppliers, including debt ratios, profitability trends, and capital expenditure plans, should be incorporated into the risk evaluation process.
Transportation logistics for UTG present unique challenges due to the fragile nature of the material. Specialized packaging, handling procedures, and transportation methods are required to minimize breakage and contamination risks. The extended global supply chains typical in the display industry amplify these logistical vulnerabilities, particularly when considering intercontinental shipping requirements.
Quality Control Standards for UTG in Flexible Displays
Quality control standards for Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG) in flexible displays represent a critical framework for ensuring consistent product performance and reliability in this rapidly evolving technology sector. These standards must address the unique properties of UTG, which typically ranges from 30 to 100 micrometers in thickness, significantly thinner than conventional display glass.
The primary quality parameters for UTG include dimensional precision, with thickness uniformity tolerances typically maintained within ±5 micrometers across the entire glass sheet. Surface quality standards demand exceptionally low defect rates, with specifications typically allowing no visible scratches, inclusions, or bubbles larger than 10 micrometers under standard inspection conditions.
Optical performance metrics form another crucial aspect of UTG quality control, requiring transmittance rates exceeding 90% across the visible spectrum. Haze values must remain below 0.5%, and yellowness index variations should not exceed ±0.3 units between production batches to ensure color consistency in the final display products.
Mechanical property verification includes standardized testing for flexibility endurance, with UTG expected to withstand at least 200,000 bending cycles at a radius of 5mm without developing micro-cracks or optical degradation. Tensile strength requirements typically specify minimum values of 800 MPa, while surface hardness standards often mandate a minimum of 6H on the pencil hardness scale.
Chemical durability testing protocols require UTG to demonstrate resistance to common environmental contaminants, including acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. Standard immersion tests typically specify no visible degradation after 24-hour exposure to specified chemical agents, with optical property changes limited to less than 1%.
Process control standards for UTG manufacturing emphasize statistical process control (SPC) methodologies, with suppliers expected to maintain Cpk values of at least 1.33 for critical parameters. Real-time monitoring systems must track key variables including temperature profiles, drawing speeds, and environmental conditions throughout the production process.
Certification requirements typically include compliance with international standards such as IEC 62679 for flexible display components, along with material safety documentation and full traceability records for each production batch. Suppliers must maintain detailed documentation of all quality control procedures, test results, and process parameters for a minimum of five years after production.
The primary quality parameters for UTG include dimensional precision, with thickness uniformity tolerances typically maintained within ±5 micrometers across the entire glass sheet. Surface quality standards demand exceptionally low defect rates, with specifications typically allowing no visible scratches, inclusions, or bubbles larger than 10 micrometers under standard inspection conditions.
Optical performance metrics form another crucial aspect of UTG quality control, requiring transmittance rates exceeding 90% across the visible spectrum. Haze values must remain below 0.5%, and yellowness index variations should not exceed ±0.3 units between production batches to ensure color consistency in the final display products.
Mechanical property verification includes standardized testing for flexibility endurance, with UTG expected to withstand at least 200,000 bending cycles at a radius of 5mm without developing micro-cracks or optical degradation. Tensile strength requirements typically specify minimum values of 800 MPa, while surface hardness standards often mandate a minimum of 6H on the pencil hardness scale.
Chemical durability testing protocols require UTG to demonstrate resistance to common environmental contaminants, including acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. Standard immersion tests typically specify no visible degradation after 24-hour exposure to specified chemical agents, with optical property changes limited to less than 1%.
Process control standards for UTG manufacturing emphasize statistical process control (SPC) methodologies, with suppliers expected to maintain Cpk values of at least 1.33 for critical parameters. Real-time monitoring systems must track key variables including temperature profiles, drawing speeds, and environmental conditions throughout the production process.
Certification requirements typically include compliance with international standards such as IEC 62679 for flexible display components, along with material safety documentation and full traceability records for each production batch. Suppliers must maintain detailed documentation of all quality control procedures, test results, and process parameters for a minimum of five years after production.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!