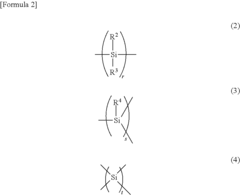Integrating Polysilane in Industrial Design Innovations
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Background and Integration Goals
Polysilane, a class of inorganic polymers with a silicon backbone, has emerged as a promising material in various industrial applications. The development of polysilane can be traced back to the 1920s when the first synthesis of these compounds was reported. However, it wasn't until the 1980s that significant advancements in polysilane research led to a deeper understanding of their unique properties and potential applications.
The evolution of polysilane technology has been driven by the growing demand for advanced materials with tailored properties in industries such as electronics, optics, and energy. As researchers explored the structure-property relationships of polysilanes, they discovered their exceptional electronic and optical characteristics, including high photosensitivity, conductivity, and luminescence.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards integrating polysilanes into industrial design innovations. This integration aims to leverage the material's unique properties to enhance the performance and functionality of various products and systems. The primary goals of polysilane integration in industrial design include improving energy efficiency, enhancing durability, and enabling novel functionalities in electronic and optical devices.
One of the key objectives is to exploit the photosensitive nature of polysilanes to develop advanced photoresists for semiconductor manufacturing. This application has the potential to revolutionize the production of high-resolution microelectronic components, enabling the creation of smaller and more efficient devices.
Another important goal is to harness the conductive properties of polysilanes for the development of flexible and transparent electrodes. This could lead to significant advancements in the field of flexible electronics, including wearable devices and foldable displays.
The integration of polysilanes in industrial design also aims to capitalize on their luminescent properties for the creation of novel lighting solutions and display technologies. This could result in more energy-efficient and longer-lasting lighting systems, as well as improved color rendering in displays.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the potential of polysilanes in energy storage and conversion applications. The goal is to develop high-performance materials for solar cells, batteries, and fuel cells, leveraging the unique electronic properties of polysilanes to enhance energy efficiency and storage capacity.
As the field of polysilane research continues to evolve, the integration goals are expanding to include sustainability and environmental considerations. There is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly synthesis methods and exploring the biodegradability of polysilane-based materials, aligning with the global push towards more sustainable industrial practices.
The evolution of polysilane technology has been driven by the growing demand for advanced materials with tailored properties in industries such as electronics, optics, and energy. As researchers explored the structure-property relationships of polysilanes, they discovered their exceptional electronic and optical characteristics, including high photosensitivity, conductivity, and luminescence.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards integrating polysilanes into industrial design innovations. This integration aims to leverage the material's unique properties to enhance the performance and functionality of various products and systems. The primary goals of polysilane integration in industrial design include improving energy efficiency, enhancing durability, and enabling novel functionalities in electronic and optical devices.
One of the key objectives is to exploit the photosensitive nature of polysilanes to develop advanced photoresists for semiconductor manufacturing. This application has the potential to revolutionize the production of high-resolution microelectronic components, enabling the creation of smaller and more efficient devices.
Another important goal is to harness the conductive properties of polysilanes for the development of flexible and transparent electrodes. This could lead to significant advancements in the field of flexible electronics, including wearable devices and foldable displays.
The integration of polysilanes in industrial design also aims to capitalize on their luminescent properties for the creation of novel lighting solutions and display technologies. This could result in more energy-efficient and longer-lasting lighting systems, as well as improved color rendering in displays.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the potential of polysilanes in energy storage and conversion applications. The goal is to develop high-performance materials for solar cells, batteries, and fuel cells, leveraging the unique electronic properties of polysilanes to enhance energy efficiency and storage capacity.
As the field of polysilane research continues to evolve, the integration goals are expanding to include sustainability and environmental considerations. There is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly synthesis methods and exploring the biodegradability of polysilane-based materials, aligning with the global push towards more sustainable industrial practices.
Industrial Design Market Demand Analysis
The integration of polysilane in industrial design innovations has sparked significant market interest due to its unique properties and potential applications. The industrial design sector has shown a growing demand for advanced materials that can enhance product performance, aesthetics, and sustainability. Polysilane, with its silicon-based backbone structure, offers a promising avenue for addressing these market needs.
Market analysis indicates that the global industrial design market is experiencing steady growth, driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and the need for sustainable solutions. The incorporation of polysilane in this sector aligns well with these trends, particularly in areas where lightweight, durable, and multifunctional materials are required.
One of the key market demands that polysilane can address is the need for improved electronic and optoelectronic components. As the consumer electronics industry continues to evolve, there is a growing requirement for materials that can enhance the performance of displays, sensors, and other electronic devices. Polysilane's unique electronic properties make it an attractive option for developing next-generation electronic materials.
In the automotive and aerospace industries, there is a strong demand for lightweight materials that can improve fuel efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Polysilane-based composites have shown potential in this area, offering a combination of strength, low density, and thermal stability. This aligns with the market trend towards more sustainable and eco-friendly transportation solutions.
The construction and architecture sectors are also showing interest in innovative materials for both structural and aesthetic purposes. Polysilane's ability to be processed into various forms, including films and coatings, opens up possibilities for creating novel architectural elements and smart building materials. This addresses the market demand for materials that can enhance energy efficiency, durability, and design flexibility in construction projects.
Furthermore, the healthcare and medical device industry is exploring new materials for advanced medical applications. Polysilane's biocompatibility and potential for functionalization make it an interesting candidate for developing innovative medical devices, implants, and drug delivery systems. This aligns with the growing market demand for personalized and high-performance medical solutions.
The packaging industry, driven by sustainability concerns and regulations, is seeking alternatives to traditional plastics. Polysilane-based materials could potentially offer biodegradable or easily recyclable packaging solutions, addressing the market demand for environmentally friendly packaging options.
Overall, the market demand for polysilane in industrial design innovations is multifaceted, spanning various sectors and applications. As industries continue to seek advanced materials that can offer improved performance, sustainability, and novel functionalities, polysilane presents a promising avenue for innovation and market growth in the industrial design landscape.
Market analysis indicates that the global industrial design market is experiencing steady growth, driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and the need for sustainable solutions. The incorporation of polysilane in this sector aligns well with these trends, particularly in areas where lightweight, durable, and multifunctional materials are required.
One of the key market demands that polysilane can address is the need for improved electronic and optoelectronic components. As the consumer electronics industry continues to evolve, there is a growing requirement for materials that can enhance the performance of displays, sensors, and other electronic devices. Polysilane's unique electronic properties make it an attractive option for developing next-generation electronic materials.
In the automotive and aerospace industries, there is a strong demand for lightweight materials that can improve fuel efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Polysilane-based composites have shown potential in this area, offering a combination of strength, low density, and thermal stability. This aligns with the market trend towards more sustainable and eco-friendly transportation solutions.
The construction and architecture sectors are also showing interest in innovative materials for both structural and aesthetic purposes. Polysilane's ability to be processed into various forms, including films and coatings, opens up possibilities for creating novel architectural elements and smart building materials. This addresses the market demand for materials that can enhance energy efficiency, durability, and design flexibility in construction projects.
Furthermore, the healthcare and medical device industry is exploring new materials for advanced medical applications. Polysilane's biocompatibility and potential for functionalization make it an interesting candidate for developing innovative medical devices, implants, and drug delivery systems. This aligns with the growing market demand for personalized and high-performance medical solutions.
The packaging industry, driven by sustainability concerns and regulations, is seeking alternatives to traditional plastics. Polysilane-based materials could potentially offer biodegradable or easily recyclable packaging solutions, addressing the market demand for environmentally friendly packaging options.
Overall, the market demand for polysilane in industrial design innovations is multifaceted, spanning various sectors and applications. As industries continue to seek advanced materials that can offer improved performance, sustainability, and novel functionalities, polysilane presents a promising avenue for innovation and market growth in the industrial design landscape.
Polysilane Technology Status and Challenges
Polysilane technology has made significant strides in recent years, yet it still faces several challenges in its integration into industrial design innovations. The current status of polysilane technology is characterized by a growing interest in its unique properties, particularly its photosensitivity and semiconductor capabilities. Research institutions and industry leaders across the globe are actively exploring its potential applications in various fields, including optoelectronics, photolithography, and advanced materials.
One of the primary challenges in polysilane technology is the optimization of its synthesis process. While several methods have been developed, including Wurtz coupling and electrochemical synthesis, achieving consistent molecular weight distribution and structural uniformity remains a significant hurdle. This inconsistency can lead to variations in the material's properties, affecting its performance in industrial applications.
Another major challenge lies in enhancing the stability of polysilanes. These materials are known to be sensitive to UV light and oxygen, which can cause degradation and limit their long-term usability. Researchers are actively working on developing more stable polysilane derivatives and protective coatings to mitigate this issue, but a universally effective solution has yet to be found.
The scalability of polysilane production presents another significant challenge. Current synthesis methods are often limited to laboratory-scale production, making it difficult to meet the potential industrial demand. Developing cost-effective and efficient large-scale production techniques is crucial for the widespread adoption of polysilane in industrial design innovations.
In terms of geographical distribution, polysilane research and development are primarily concentrated in advanced economies, with Japan, the United States, and several European countries leading the way. However, emerging economies, particularly China, are showing increased interest and investment in this technology, potentially shifting the global landscape of polysilane innovation.
The integration of polysilanes into existing manufacturing processes and product designs poses additional challenges. Many industries are hesitant to adopt new materials without extensive testing and validation, which can be time-consuming and costly. Overcoming this barrier requires not only technological advancements but also effective demonstration of polysilane's benefits in real-world applications.
Despite these challenges, the potential of polysilane in industrial design innovations remains promising. Ongoing research is focused on addressing these issues, with particular emphasis on improving synthesis methods, enhancing material stability, and exploring novel applications. As these challenges are gradually overcome, polysilane technology is expected to play an increasingly important role in various industrial sectors, potentially revolutionizing areas such as flexible electronics, advanced coatings, and next-generation photovoltaics.
One of the primary challenges in polysilane technology is the optimization of its synthesis process. While several methods have been developed, including Wurtz coupling and electrochemical synthesis, achieving consistent molecular weight distribution and structural uniformity remains a significant hurdle. This inconsistency can lead to variations in the material's properties, affecting its performance in industrial applications.
Another major challenge lies in enhancing the stability of polysilanes. These materials are known to be sensitive to UV light and oxygen, which can cause degradation and limit their long-term usability. Researchers are actively working on developing more stable polysilane derivatives and protective coatings to mitigate this issue, but a universally effective solution has yet to be found.
The scalability of polysilane production presents another significant challenge. Current synthesis methods are often limited to laboratory-scale production, making it difficult to meet the potential industrial demand. Developing cost-effective and efficient large-scale production techniques is crucial for the widespread adoption of polysilane in industrial design innovations.
In terms of geographical distribution, polysilane research and development are primarily concentrated in advanced economies, with Japan, the United States, and several European countries leading the way. However, emerging economies, particularly China, are showing increased interest and investment in this technology, potentially shifting the global landscape of polysilane innovation.
The integration of polysilanes into existing manufacturing processes and product designs poses additional challenges. Many industries are hesitant to adopt new materials without extensive testing and validation, which can be time-consuming and costly. Overcoming this barrier requires not only technological advancements but also effective demonstration of polysilane's benefits in real-world applications.
Despite these challenges, the potential of polysilane in industrial design innovations remains promising. Ongoing research is focused on addressing these issues, with particular emphasis on improving synthesis methods, enhancing material stability, and exploring novel applications. As these challenges are gradually overcome, polysilane technology is expected to play an increasingly important role in various industrial sectors, potentially revolutionizing areas such as flexible electronics, advanced coatings, and next-generation photovoltaics.
Current Polysilane Integration Solutions
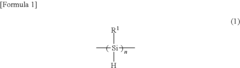
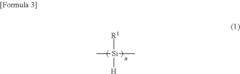
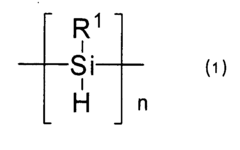
01 Synthesis and properties of polysilanes
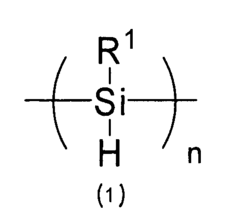
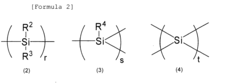
Polysilanes are silicon-based polymers with unique electronic and optical properties. They can be synthesized through various methods, including Wurtz coupling of dichlorosilanes. These materials exhibit high thermal stability, photosensitivity, and conductivity, making them suitable for various applications in electronics and photonics.- Synthesis and properties of polysilanes: Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These silicon-based polymers have applications in electronics, optics, and materials science due to their electronic and optical characteristics. The synthesis methods and resulting properties can be tailored for specific applications.
- Polysilane-based coatings and films: Polysilanes are used to create coatings and films with specific properties. These coatings can be applied to various substrates and may offer benefits such as improved durability, optical properties, or electrical conductivity. The composition and application methods of these coatings are optimized for different uses.
- Polysilanes in photoresist and lithography applications: Polysilanes play a role in photoresist formulations and lithography processes. Their photosensitive properties make them suitable for use in semiconductor manufacturing and other microfabrication techniques. The development of polysilane-based photoresists aims to improve resolution and performance in lithographic processes.
- Functionalization and modification of polysilanes: Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or create new materials. This includes the addition of various functional groups, copolymerization with other monomers, or post-polymerization modifications. These processes allow for the creation of tailored materials with specific characteristics for diverse applications.
- Polysilanes in electronic and optoelectronic devices: Polysilanes are utilized in the development of electronic and optoelectronic devices. Their unique electronic properties make them suitable for applications such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photovoltaic cells, and other semiconductor devices. Research focuses on optimizing polysilane structures for improved device performance.
02 Applications of polysilanes in coatings and films
Polysilanes can be used to create thin films and coatings with specific properties. These materials can be applied to various substrates to enhance their surface characteristics, such as improved adhesion, wear resistance, or optical properties. The films can be formed through methods like spin-coating or vapor deposition.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polysilanes in photoresist and lithography applications
Polysilanes have found use in photoresist formulations for lithography processes. Their photosensitivity and ability to undergo photochemical reactions make them suitable for creating patterns in microelectronics manufacturing. These materials can be used in both positive and negative photoresists, offering high resolution and good etching resistance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Functionalization and modification of polysilanes
Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. This can involve the incorporation of various organic groups or other elements into the polymer backbone or as side chains. Such modifications can alter the material's electronic, optical, or mechanical properties, expanding their potential applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilanes in semiconductor and electronic applications
Polysilanes have potential applications in semiconductor and electronic devices due to their unique electronic properties. They can be used as precursors for silicon-based materials, as charge transport layers in organic electronics, or as active components in sensors and photovoltaic devices. Their conductivity and photosensitivity make them attractive for various electronic applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Polysilane Industry
The integration of polysilane in industrial design innovations is in an emerging phase, with a growing market driven by advancements in materials science and increasing demand for high-performance polymers. The global market for polysilane-based products is expanding, though still relatively small compared to established polymer markets. Technologically, polysilane integration is progressing rapidly, with companies like JSR Corp., Momentive Performance Materials, and Dow Silicones Corp. leading research and development efforts. These firms are exploring applications in electronics, coatings, and advanced materials. While the technology shows promise, it is still in the early stages of commercial adoption, with ongoing efforts to improve processability, stability, and cost-effectiveness for widespread industrial use.
JSR Corp.
Technical Solution: JSR Corp. has developed innovative polysilane-based materials for industrial design applications. Their approach involves synthesizing novel polysilane structures with tailored optical and electronic properties. JSR's polysilanes feature high transparency, excellent thermal stability, and tunable refractive indices[1]. The company has successfully integrated these materials into advanced coatings, films, and composite materials for various industries including electronics, automotive, and construction[2]. JSR's polysilane technology enables the creation of scratch-resistant, self-healing surfaces and high-performance optical components[3].
Strengths: Customizable material properties, versatile applications across industries. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs, limited long-term performance data in some applications.
Momentive Performance Materials, Inc.
Technical Solution: Momentive has developed a range of polysilane-based materials for industrial design innovations. Their approach focuses on creating hybrid organic-inorganic polysilane compounds that combine the benefits of both material classes. Momentive's polysilanes exhibit enhanced thermal stability, improved mechanical properties, and unique optical characteristics[4]. The company has successfully applied these materials in advanced coatings, adhesives, and electronic components. Momentive's polysilane technology enables the development of high-performance, durable materials for extreme environments and specialized industrial applications[5].
Strengths: Excellent material performance in harsh conditions, wide range of potential applications. Weaknesses: Complex synthesis processes, may require specialized handling and processing.
Innovative Polysilane Applications
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Polysilane and resin composition containing polysilane
PatentInactiveEP1958979A1
Innovation
- Introducing a Si-H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Environmental Impact of Polysilane Use
The integration of polysilane in industrial design innovations brings forth significant environmental considerations that warrant careful examination. Polysilane, a silicon-based polymer, exhibits unique properties that make it attractive for various applications, yet its environmental impact must be thoroughly assessed.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with polysilane use is its production process. The synthesis of polysilane typically involves energy-intensive methods and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. This raises questions about the carbon footprint and overall sustainability of polysilane manufacturing. However, recent advancements in green chemistry have led to the development of more environmentally friendly synthesis routes, which may mitigate some of these concerns.
The durability and longevity of polysilane-based products contribute positively to their environmental profile. Products incorporating polysilane often demonstrate enhanced resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and chemical degradation. This increased lifespan can lead to reduced waste generation and resource consumption over time, as fewer replacements are needed.
End-of-life considerations for polysilane-containing products present both challenges and opportunities. While silicon-based polymers are generally not biodegradable, they can be recycled or repurposed in certain applications. The development of efficient recycling processes for polysilane materials is an area of ongoing research, with potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of these materials.
The use of polysilane in photovoltaic applications showcases its potential for positive environmental impact. Polysilane-based solar cells offer improved efficiency and durability compared to traditional silicon solar cells, potentially leading to increased adoption of renewable energy technologies. This application aligns with global efforts to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
Water and soil contamination risks associated with polysilane use are generally low, as the material is relatively inert and non-toxic. However, the potential release of nanoparticles during the wear and tear of polysilane-containing products is an area that requires further investigation to ensure long-term environmental safety.
In the context of industrial design, the incorporation of polysilane can lead to the creation of more energy-efficient products. For instance, its use in lightweight materials for transportation can result in reduced fuel consumption and emissions. Similarly, its application in thermal insulation can improve energy efficiency in buildings, contributing to overall environmental sustainability.
As the adoption of polysilane in industrial design continues to grow, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand its environmental implications. This holistic approach will enable designers and engineers to make informed decisions that balance the material's innovative potential with ecological responsibility.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with polysilane use is its production process. The synthesis of polysilane typically involves energy-intensive methods and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. This raises questions about the carbon footprint and overall sustainability of polysilane manufacturing. However, recent advancements in green chemistry have led to the development of more environmentally friendly synthesis routes, which may mitigate some of these concerns.
The durability and longevity of polysilane-based products contribute positively to their environmental profile. Products incorporating polysilane often demonstrate enhanced resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and chemical degradation. This increased lifespan can lead to reduced waste generation and resource consumption over time, as fewer replacements are needed.
End-of-life considerations for polysilane-containing products present both challenges and opportunities. While silicon-based polymers are generally not biodegradable, they can be recycled or repurposed in certain applications. The development of efficient recycling processes for polysilane materials is an area of ongoing research, with potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of these materials.
The use of polysilane in photovoltaic applications showcases its potential for positive environmental impact. Polysilane-based solar cells offer improved efficiency and durability compared to traditional silicon solar cells, potentially leading to increased adoption of renewable energy technologies. This application aligns with global efforts to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
Water and soil contamination risks associated with polysilane use are generally low, as the material is relatively inert and non-toxic. However, the potential release of nanoparticles during the wear and tear of polysilane-containing products is an area that requires further investigation to ensure long-term environmental safety.
In the context of industrial design, the incorporation of polysilane can lead to the creation of more energy-efficient products. For instance, its use in lightweight materials for transportation can result in reduced fuel consumption and emissions. Similarly, its application in thermal insulation can improve energy efficiency in buildings, contributing to overall environmental sustainability.
As the adoption of polysilane in industrial design continues to grow, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand its environmental implications. This holistic approach will enable designers and engineers to make informed decisions that balance the material's innovative potential with ecological responsibility.
Polysilane Safety Regulations
The integration of polysilane in industrial design innovations necessitates a comprehensive understanding of safety regulations to ensure responsible and sustainable implementation. Polysilane, a class of silicon-based polymers, presents unique challenges in terms of handling, processing, and disposal, requiring stringent safety measures throughout its lifecycle.
Regulatory bodies, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), have established guidelines for the safe use of polysilane in industrial settings. These regulations primarily focus on worker protection, environmental impact mitigation, and proper waste management.
In terms of worker safety, OSHA mandates the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling polysilane materials. This includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and respiratory protection to prevent inhalation of potentially harmful vapors. Additionally, proper ventilation systems must be installed in areas where polysilane is processed or stored to minimize exposure risks.
Environmental regulations surrounding polysilane usage address potential soil and water contamination. The EPA requires industrial facilities to implement spill prevention and containment measures, as well as proper disposal protocols for polysilane waste. This often involves specialized treatment processes to neutralize or stabilize the material before disposal in designated hazardous waste facilities.
Fire safety is another critical aspect of polysilane regulations, as certain forms of the material can be highly flammable. Industrial facilities must adhere to strict fire prevention and suppression protocols, including the installation of appropriate fire detection and extinguishing systems, as well as the implementation of emergency response plans.
Transportation of polysilane materials is subject to Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations, which dictate proper packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements. These measures ensure the safe transport of polysilane across various modes of transportation, minimizing the risk of accidents or spills during transit.
As research into polysilane applications continues to expand, regulatory frameworks are evolving to keep pace with new developments. Emerging regulations are focusing on the potential long-term environmental impacts of polysilane use, including its biodegradability and potential for bioaccumulation in ecosystems.
Compliance with these safety regulations is not only a legal requirement but also a crucial factor in the successful integration of polysilane in industrial design innovations. Companies must invest in comprehensive training programs for employees involved in polysilane handling and processing, ensuring a thorough understanding of safety protocols and emergency procedures.
Regulatory bodies, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), have established guidelines for the safe use of polysilane in industrial settings. These regulations primarily focus on worker protection, environmental impact mitigation, and proper waste management.
In terms of worker safety, OSHA mandates the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling polysilane materials. This includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and respiratory protection to prevent inhalation of potentially harmful vapors. Additionally, proper ventilation systems must be installed in areas where polysilane is processed or stored to minimize exposure risks.
Environmental regulations surrounding polysilane usage address potential soil and water contamination. The EPA requires industrial facilities to implement spill prevention and containment measures, as well as proper disposal protocols for polysilane waste. This often involves specialized treatment processes to neutralize or stabilize the material before disposal in designated hazardous waste facilities.
Fire safety is another critical aspect of polysilane regulations, as certain forms of the material can be highly flammable. Industrial facilities must adhere to strict fire prevention and suppression protocols, including the installation of appropriate fire detection and extinguishing systems, as well as the implementation of emergency response plans.
Transportation of polysilane materials is subject to Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations, which dictate proper packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements. These measures ensure the safe transport of polysilane across various modes of transportation, minimizing the risk of accidents or spills during transit.
As research into polysilane applications continues to expand, regulatory frameworks are evolving to keep pace with new developments. Emerging regulations are focusing on the potential long-term environmental impacts of polysilane use, including its biodegradability and potential for bioaccumulation in ecosystems.
Compliance with these safety regulations is not only a legal requirement but also a crucial factor in the successful integration of polysilane in industrial design innovations. Companies must invest in comprehensive training programs for employees involved in polysilane handling and processing, ensuring a thorough understanding of safety protocols and emergency procedures.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!