Investigating Opaque Polypropylene Sheet Applications
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Opaque PP Sheet Tech Background and Objectives
Opaque polypropylene (PP) sheets have emerged as a versatile and increasingly popular material in various industries over the past few decades. The development of opaque PP sheets can be traced back to the 1950s when polypropylene was first synthesized. Since then, continuous advancements in polymer science and manufacturing techniques have led to significant improvements in the properties and applications of opaque PP sheets.
The evolution of opaque PP sheet technology has been driven by the growing demand for lightweight, durable, and cost-effective materials in sectors such as packaging, automotive, construction, and consumer goods. Key milestones in this journey include the development of advanced additives to enhance opacity, improved extrusion processes for better sheet uniformity, and the introduction of multi-layer structures for enhanced performance characteristics.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing opaque PP sheets with enhanced sustainability profiles. This includes efforts to increase the use of recycled content, improve recyclability, and reduce overall environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. The industry is also exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-based polypropylene, aligning with global trends towards more sustainable materials.
The primary technical objectives in the field of opaque PP sheets revolve around several key areas. Firstly, there is a push to further improve the mechanical properties of the sheets, including impact resistance, flexural strength, and dimensional stability. This is particularly important for applications in automotive interiors and durable consumer goods.
Secondly, there is a growing emphasis on enhancing the surface quality and aesthetics of opaque PP sheets. This includes developing new textures, improving color consistency, and achieving a high-quality finish that can compete with more expensive materials in premium applications.
Another critical objective is to expand the temperature range in which opaque PP sheets can effectively operate. This involves improving heat resistance for high-temperature applications and enhancing low-temperature impact strength for cold climate uses.
Furthermore, there is ongoing research into improving the barrier properties of opaque PP sheets, particularly for packaging applications. This includes developing multi-layer structures that can provide enhanced protection against moisture, oxygen, and other environmental factors.
Lastly, a significant focus is placed on sustainability and circularity. The industry aims to increase the recyclability of opaque PP sheets, develop effective recycling processes, and incorporate a higher percentage of recycled content without compromising performance. This aligns with broader industry goals of reducing plastic waste and moving towards a more circular economy.
The evolution of opaque PP sheet technology has been driven by the growing demand for lightweight, durable, and cost-effective materials in sectors such as packaging, automotive, construction, and consumer goods. Key milestones in this journey include the development of advanced additives to enhance opacity, improved extrusion processes for better sheet uniformity, and the introduction of multi-layer structures for enhanced performance characteristics.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing opaque PP sheets with enhanced sustainability profiles. This includes efforts to increase the use of recycled content, improve recyclability, and reduce overall environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. The industry is also exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-based polypropylene, aligning with global trends towards more sustainable materials.
The primary technical objectives in the field of opaque PP sheets revolve around several key areas. Firstly, there is a push to further improve the mechanical properties of the sheets, including impact resistance, flexural strength, and dimensional stability. This is particularly important for applications in automotive interiors and durable consumer goods.
Secondly, there is a growing emphasis on enhancing the surface quality and aesthetics of opaque PP sheets. This includes developing new textures, improving color consistency, and achieving a high-quality finish that can compete with more expensive materials in premium applications.
Another critical objective is to expand the temperature range in which opaque PP sheets can effectively operate. This involves improving heat resistance for high-temperature applications and enhancing low-temperature impact strength for cold climate uses.
Furthermore, there is ongoing research into improving the barrier properties of opaque PP sheets, particularly for packaging applications. This includes developing multi-layer structures that can provide enhanced protection against moisture, oxygen, and other environmental factors.
Lastly, a significant focus is placed on sustainability and circularity. The industry aims to increase the recyclability of opaque PP sheets, develop effective recycling processes, and incorporate a higher percentage of recycled content without compromising performance. This aligns with broader industry goals of reducing plastic waste and moving towards a more circular economy.
Market Demand Analysis for Opaque PP Sheets
The market demand for opaque polypropylene (PP) sheets has been steadily growing across various industries due to their unique properties and versatile applications. These sheets offer excellent chemical resistance, high impact strength, and good thermal insulation, making them ideal for a wide range of uses.
In the packaging industry, opaque PP sheets have gained significant traction, particularly in the food and beverage sector. The demand is driven by the sheets' ability to protect products from light exposure, which helps extend shelf life and maintain product quality. Additionally, the food-safe properties of PP make it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to comply with stringent safety regulations.
The automotive industry has also shown increased interest in opaque PP sheets. These materials are being used for interior components, such as door panels and dashboard elements, due to their lightweight nature and ability to be easily molded into complex shapes. As the automotive sector continues to focus on weight reduction and fuel efficiency, the demand for opaque PP sheets is expected to rise further.
In the construction and building materials market, opaque PP sheets are finding applications in temporary protective coverings, signage, and even as alternatives to traditional materials in certain architectural elements. The durability and weather resistance of these sheets make them suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, contributing to their growing popularity in this sector.
The healthcare and medical device industry is another significant driver of demand for opaque PP sheets. The material's resistance to chemicals and ease of sterilization make it ideal for medical packaging, laboratory equipment, and disposable medical devices. As healthcare needs continue to expand globally, this sector is expected to contribute substantially to the overall market growth.
Consumer goods manufacturers are increasingly incorporating opaque PP sheets into their product designs. From household appliances to consumer electronics, these sheets are being used for casings, panels, and protective elements. The ability to color and texture the sheets allows for customization and branding opportunities, further enhancing their appeal in this market segment.
The agriculture sector has also recognized the benefits of opaque PP sheets, particularly in greenhouse construction and crop protection. The sheets' ability to block harmful UV rays while allowing diffused light transmission creates optimal growing conditions for plants, driving demand in this niche but growing market segment.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the opaque PP sheet market to be in the mid-single digits over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the material's cost-effectiveness, recyclability, and the ongoing development of new applications across various industries. As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in material selection, the recyclable nature of PP is expected to further boost its market demand.
In the packaging industry, opaque PP sheets have gained significant traction, particularly in the food and beverage sector. The demand is driven by the sheets' ability to protect products from light exposure, which helps extend shelf life and maintain product quality. Additionally, the food-safe properties of PP make it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to comply with stringent safety regulations.
The automotive industry has also shown increased interest in opaque PP sheets. These materials are being used for interior components, such as door panels and dashboard elements, due to their lightweight nature and ability to be easily molded into complex shapes. As the automotive sector continues to focus on weight reduction and fuel efficiency, the demand for opaque PP sheets is expected to rise further.
In the construction and building materials market, opaque PP sheets are finding applications in temporary protective coverings, signage, and even as alternatives to traditional materials in certain architectural elements. The durability and weather resistance of these sheets make them suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, contributing to their growing popularity in this sector.
The healthcare and medical device industry is another significant driver of demand for opaque PP sheets. The material's resistance to chemicals and ease of sterilization make it ideal for medical packaging, laboratory equipment, and disposable medical devices. As healthcare needs continue to expand globally, this sector is expected to contribute substantially to the overall market growth.
Consumer goods manufacturers are increasingly incorporating opaque PP sheets into their product designs. From household appliances to consumer electronics, these sheets are being used for casings, panels, and protective elements. The ability to color and texture the sheets allows for customization and branding opportunities, further enhancing their appeal in this market segment.
The agriculture sector has also recognized the benefits of opaque PP sheets, particularly in greenhouse construction and crop protection. The sheets' ability to block harmful UV rays while allowing diffused light transmission creates optimal growing conditions for plants, driving demand in this niche but growing market segment.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the opaque PP sheet market to be in the mid-single digits over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the material's cost-effectiveness, recyclability, and the ongoing development of new applications across various industries. As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in material selection, the recyclable nature of PP is expected to further boost its market demand.
Current State and Challenges in Opaque PP Production
The production of opaque polypropylene (PP) sheets has seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industries. Currently, the manufacturing process primarily involves the incorporation of mineral fillers or pigments into the PP matrix to achieve opacity. Common fillers include calcium carbonate, talc, and titanium dioxide, each offering unique properties to the final product.
One of the main challenges in opaque PP production is achieving a balance between opacity and mechanical properties. As the filler content increases to enhance opacity, it often leads to a decrease in the material's strength and flexibility. Manufacturers are constantly working to optimize formulations that maintain high opacity without compromising the sheet's structural integrity.
Another significant hurdle is the uniform dispersion of fillers throughout the PP matrix. Inadequate dispersion can result in inconsistent opacity, surface defects, and weak points in the sheet. Advanced mixing technologies and compatibilizers are being employed to address this issue, but further improvements are needed to achieve perfect homogeneity.
The energy-intensive nature of opaque PP sheet production presents both economic and environmental challenges. The process requires high temperatures for melting and extruding the polymer, as well as additional energy for cooling and shaping the sheets. Efforts are underway to develop more energy-efficient production methods and equipment to reduce both costs and carbon footprint.
Color consistency across production batches remains a persistent challenge, particularly for custom colors. Slight variations in raw materials or processing conditions can lead to noticeable color differences, which is unacceptable for many high-end applications. Sophisticated color management systems and in-line monitoring technologies are being implemented to address this issue.
Recycling opaque PP sheets poses another significant challenge. The presence of fillers and additives complicates the recycling process, often resulting in downcycled products. There is a growing focus on developing easily recyclable opaque PP formulations and improving recycling technologies to support circular economy initiatives.
Lastly, meeting increasingly stringent regulatory requirements, particularly for food contact applications, presents ongoing challenges. Manufacturers must continually adapt their formulations and processes to comply with evolving standards while maintaining product performance and cost-effectiveness.
One of the main challenges in opaque PP production is achieving a balance between opacity and mechanical properties. As the filler content increases to enhance opacity, it often leads to a decrease in the material's strength and flexibility. Manufacturers are constantly working to optimize formulations that maintain high opacity without compromising the sheet's structural integrity.
Another significant hurdle is the uniform dispersion of fillers throughout the PP matrix. Inadequate dispersion can result in inconsistent opacity, surface defects, and weak points in the sheet. Advanced mixing technologies and compatibilizers are being employed to address this issue, but further improvements are needed to achieve perfect homogeneity.
The energy-intensive nature of opaque PP sheet production presents both economic and environmental challenges. The process requires high temperatures for melting and extruding the polymer, as well as additional energy for cooling and shaping the sheets. Efforts are underway to develop more energy-efficient production methods and equipment to reduce both costs and carbon footprint.
Color consistency across production batches remains a persistent challenge, particularly for custom colors. Slight variations in raw materials or processing conditions can lead to noticeable color differences, which is unacceptable for many high-end applications. Sophisticated color management systems and in-line monitoring technologies are being implemented to address this issue.
Recycling opaque PP sheets poses another significant challenge. The presence of fillers and additives complicates the recycling process, often resulting in downcycled products. There is a growing focus on developing easily recyclable opaque PP formulations and improving recycling technologies to support circular economy initiatives.
Lastly, meeting increasingly stringent regulatory requirements, particularly for food contact applications, presents ongoing challenges. Manufacturers must continually adapt their formulations and processes to comply with evolving standards while maintaining product performance and cost-effectiveness.
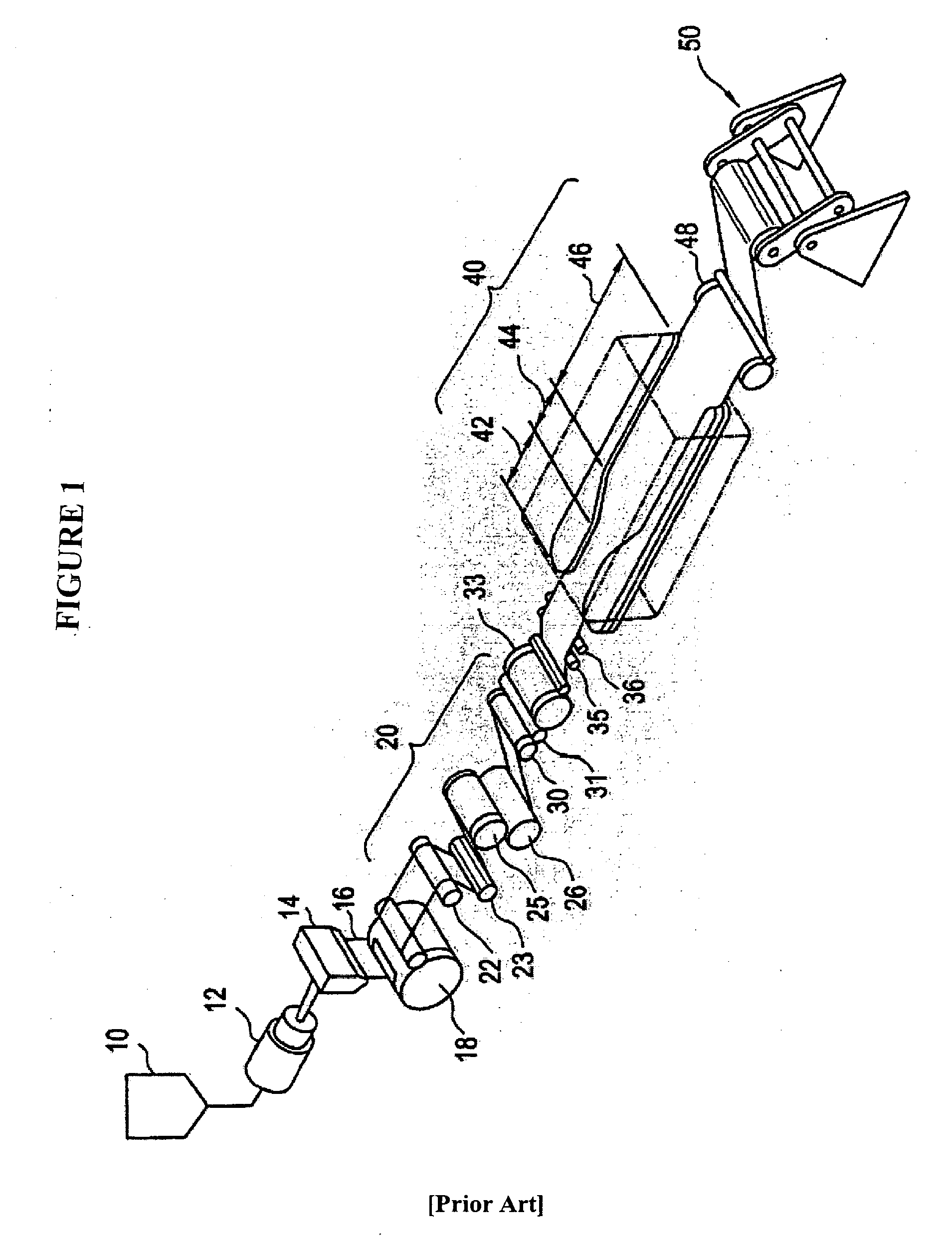
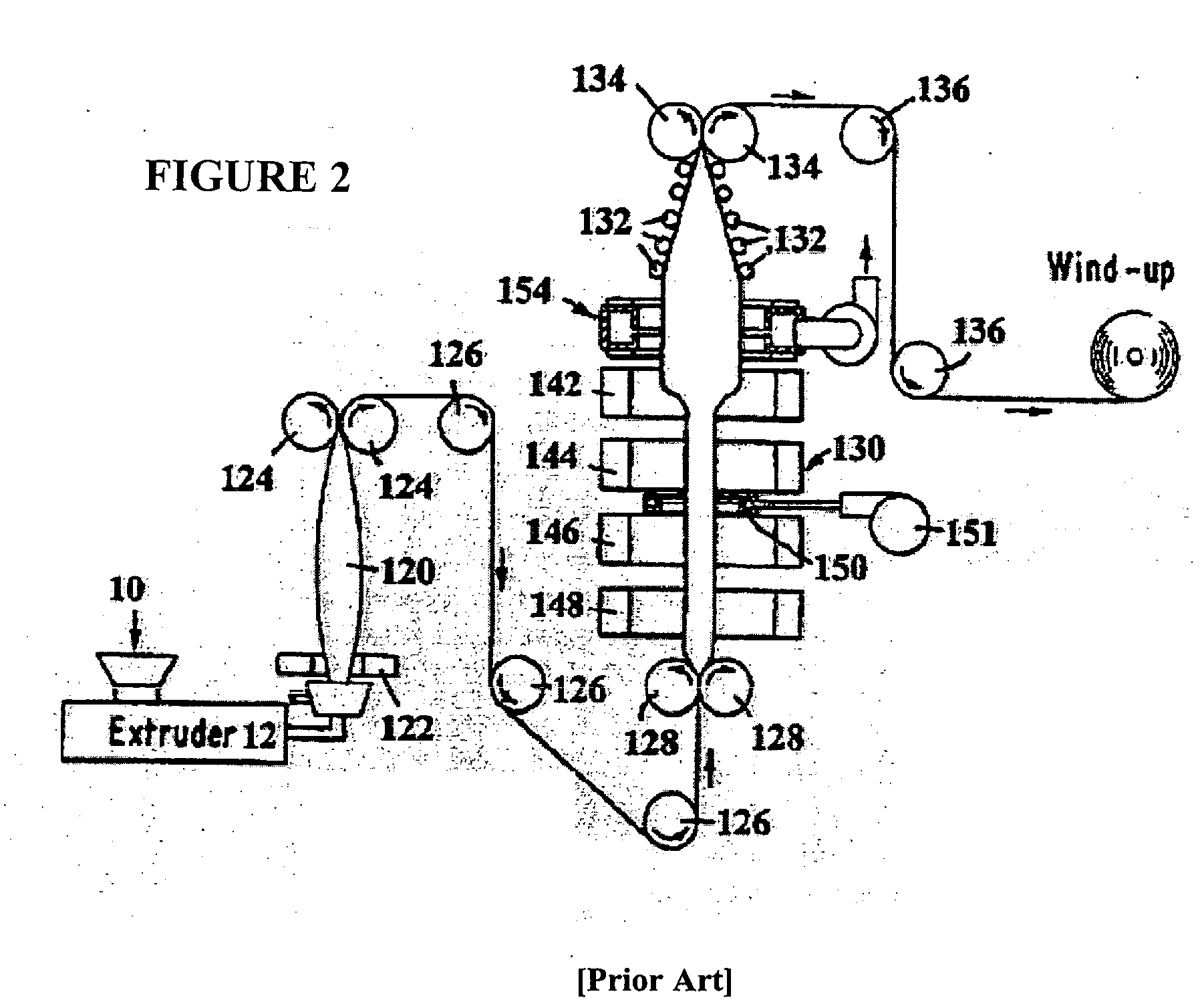
Existing Opaque PP Sheet Production Methods
01 Composition and additives for opaque polypropylene sheets
Opaque polypropylene sheets can be produced by incorporating various additives into the polypropylene matrix. These additives may include opacifying agents, fillers, and other materials that enhance opacity and other desired properties. The specific composition and combination of additives can be tailored to achieve the desired level of opacity and performance characteristics.- Composition and additives for opaque polypropylene sheets: Opaque polypropylene sheets can be formulated with various additives to enhance opacity and other properties. These may include inorganic fillers, pigments, and other polymeric materials. The specific combination of additives can be tailored to achieve desired levels of opacity, mechanical strength, and processability.
- Manufacturing processes for opaque polypropylene sheets: Various manufacturing processes can be employed to produce opaque polypropylene sheets. These may include extrusion, calendering, or other sheet-forming techniques. The specific process parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and cooling rates, can be optimized to achieve the desired sheet properties and opacity levels.
- Surface treatment of opaque polypropylene sheets: Surface treatments can be applied to opaque polypropylene sheets to enhance their properties or appearance. These treatments may include corona discharge, flame treatment, or the application of coatings. Such treatments can improve printability, adhesion, or other surface characteristics of the sheets.
- Multilayer structures incorporating opaque polypropylene sheets: Opaque polypropylene sheets can be incorporated into multilayer structures to create composite materials with enhanced properties. These structures may combine the opacity of the polypropylene layer with other materials to achieve specific performance characteristics, such as improved barrier properties or mechanical strength.
- Applications of opaque polypropylene sheets: Opaque polypropylene sheets find applications in various industries due to their unique properties. They can be used in packaging, automotive components, consumer goods, and construction materials. The opacity and other characteristics of these sheets make them suitable for applications where light blocking or aesthetic appearance is important.
02 Manufacturing processes for opaque polypropylene sheets
Various manufacturing processes can be employed to produce opaque polypropylene sheets. These may include extrusion, calendering, or other sheet-forming techniques. The specific process parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and cooling rates, can be optimized to achieve the desired opacity and physical properties of the final product.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface treatments for opaque polypropylene sheets
Surface treatments can be applied to opaque polypropylene sheets to enhance their properties or appearance. These treatments may include corona discharge, flame treatment, or the application of coatings. Such treatments can improve printability, adhesion, or other surface characteristics while maintaining the sheet's opacity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of opaque polypropylene sheets
Opaque polypropylene sheets find applications in various industries due to their unique properties. They can be used in packaging, signage, automotive components, and consumer goods. The opacity of these sheets makes them suitable for applications where light transmission needs to be blocked or reduced.Expand Specific Solutions05 Multilayer structures incorporating opaque polypropylene sheets
Opaque polypropylene sheets can be incorporated into multilayer structures to create products with enhanced properties. These structures may combine the opacity of polypropylene with other materials to achieve specific performance characteristics, such as improved barrier properties or mechanical strength.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Opaque PP Sheet Industry
The opaque polypropylene sheet market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in packaging, automotive, and consumer goods industries. The global market size is estimated to be in the billions of dollars, with steady annual growth projected. Technologically, the field is moderately mature but continues to evolve, with companies like Idemitsu Unitech, Total Petrochemicals, and Mitsui Chemicals leading innovation. These firms, along with others like Kingfa Sci. & Tech. and SABIC, are investing in R&D to improve product properties such as durability, heat resistance, and sustainability. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large petrochemical corporations and specialized materials companies, with increasing focus on eco-friendly solutions and advanced applications.
Mitsui Chemicals, Inc.
Technical Solution: Mitsui Chemicals has developed advanced opaque polypropylene (OPP) sheets with enhanced properties. Their technology focuses on improving the opacity and mechanical strength of PP sheets through a proprietary multi-layer extrusion process[1]. This process allows for the incorporation of specialized additives and fillers that enhance light-scattering properties, resulting in improved opacity without compromising the sheet's flexibility[2]. The company has also implemented a surface treatment technology that enhances printability and adhesion properties of the OPP sheets, making them suitable for various packaging and labeling applications[3].
Strengths: Superior opacity and printability, versatile applications in packaging. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs due to specialized processes and additives.
Braskem America, Inc.
Technical Solution: Braskem has focused on developing opaque polypropylene sheets with enhanced environmental credentials. Their approach involves using bio-based polypropylene derived from sugarcane ethanol as a base material for OPP sheet production[11]. The company has developed a proprietary additive package that enhances the opacity of these bio-based sheets without compromising their recyclability[12]. Braskem's technology also includes a controlled cooling process during sheet extrusion, which optimizes the crystalline structure of PP for improved mechanical properties and opacity[13]. Additionally, they have implemented a surface treatment technology that enhances the sheets' printability and bonding characteristics[14].
Strengths: Eco-friendly production using bio-based materials, good balance of opacity and recyclability. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in achieving ultra-high opacity levels compared to conventional mineral-filled OPP sheets.
Core Innovations in Opaque PP Sheet Technology
Beta-nucleation concentrates for film applications
PatentInactiveUS20060177632A1
Innovation
- A beta nucleant masterbatch with a higher concentration of nucleating agents is used, allowing for easier incorporation into non-nucleated polypropylene resin, enabling the production of extruded sheets with high beta crystallinity and reducing transition times by blending the masterbatch with the resin before extrusion.
Transparent polypropylene formulations that become opaque upon exposure to sufficient heat
PatentInactiveAU2003209306A1
Innovation
- A clarified polypropylene formulation incorporating a non-polypropylene polymeric additive with a refractive index similar to polypropylene at room temperature and a melting temperature between 60°C to 100°C, which changes to an amorphous state at elevated temperatures, causing the article to become opaque and return to transparent upon cooling, allowing for reversible temperature indication.
Environmental Impact of Opaque PP Sheets
The environmental impact of opaque polypropylene (PP) sheets is a critical consideration in their application and lifecycle management. These sheets, while offering numerous benefits in various industries, also pose potential environmental challenges that require careful assessment and mitigation strategies.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with opaque PP sheets is their production process. The manufacturing of these sheets involves the use of petrochemical resources, which contributes to the depletion of non-renewable fossil fuels. Additionally, the production process generates greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide, which contributes to global warming and climate change. The energy-intensive nature of PP sheet production also raises questions about its overall carbon footprint.
Waste management is another significant environmental issue related to opaque PP sheets. While polypropylene is recyclable, the opacity and potential additives in these sheets can complicate the recycling process. Many recycling facilities may not be equipped to handle these specialized materials effectively, leading to a higher likelihood of PP sheets ending up in landfills or incinerators. This contributes to the growing problem of plastic waste accumulation in the environment.
The durability of opaque PP sheets, while advantageous for many applications, can also be problematic from an environmental perspective. These sheets can persist in the environment for extended periods, potentially causing harm to wildlife and ecosystems if not properly disposed of or managed. Marine pollution is a particular concern, as plastic debris in oceans can have devastating effects on marine life.
However, it's important to note that opaque PP sheets also offer some environmental benefits. Their lightweight nature can lead to reduced transportation emissions compared to heavier alternative materials. Additionally, their durability and resistance to degradation mean they can be used for long-term applications, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements and associated resource consumption.
Efforts are being made to improve the environmental profile of opaque PP sheets. These include the development of bio-based polypropylene, which reduces reliance on fossil fuels, and the incorporation of recycled content into new PP sheets. Advances in recycling technologies are also being pursued to better handle these materials at the end of their lifecycle.
In conclusion, while opaque PP sheets present certain environmental challenges, ongoing research and development in sustainable production methods, improved recycling technologies, and responsible use and disposal practices are crucial in mitigating their environmental impact. Balancing the functional benefits of these materials with environmental considerations remains a key focus for manufacturers and users alike.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with opaque PP sheets is their production process. The manufacturing of these sheets involves the use of petrochemical resources, which contributes to the depletion of non-renewable fossil fuels. Additionally, the production process generates greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide, which contributes to global warming and climate change. The energy-intensive nature of PP sheet production also raises questions about its overall carbon footprint.
Waste management is another significant environmental issue related to opaque PP sheets. While polypropylene is recyclable, the opacity and potential additives in these sheets can complicate the recycling process. Many recycling facilities may not be equipped to handle these specialized materials effectively, leading to a higher likelihood of PP sheets ending up in landfills or incinerators. This contributes to the growing problem of plastic waste accumulation in the environment.
The durability of opaque PP sheets, while advantageous for many applications, can also be problematic from an environmental perspective. These sheets can persist in the environment for extended periods, potentially causing harm to wildlife and ecosystems if not properly disposed of or managed. Marine pollution is a particular concern, as plastic debris in oceans can have devastating effects on marine life.
However, it's important to note that opaque PP sheets also offer some environmental benefits. Their lightweight nature can lead to reduced transportation emissions compared to heavier alternative materials. Additionally, their durability and resistance to degradation mean they can be used for long-term applications, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements and associated resource consumption.
Efforts are being made to improve the environmental profile of opaque PP sheets. These include the development of bio-based polypropylene, which reduces reliance on fossil fuels, and the incorporation of recycled content into new PP sheets. Advances in recycling technologies are also being pursued to better handle these materials at the end of their lifecycle.
In conclusion, while opaque PP sheets present certain environmental challenges, ongoing research and development in sustainable production methods, improved recycling technologies, and responsible use and disposal practices are crucial in mitigating their environmental impact. Balancing the functional benefits of these materials with environmental considerations remains a key focus for manufacturers and users alike.
Regulatory Framework for Opaque PP Applications
The regulatory framework for opaque polypropylene (PP) applications is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the development, production, and use of these materials across various industries. At the forefront of regulatory considerations are safety and environmental concerns, which have led to the establishment of stringent guidelines and standards.
In the food packaging sector, opaque PP sheets must comply with regulations set by agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). These bodies have established specific migration limits for chemical substances that may transfer from the packaging material to food. Manufacturers must ensure that their opaque PP products meet these requirements through rigorous testing and documentation.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in shaping the opaque PP industry. Many countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. This has led to increased focus on the recyclability of opaque PP sheets and the development of more sustainable production processes.
The automotive industry, another significant user of opaque PP sheets, faces regulations related to vehicle safety and emissions. Opaque PP components must meet flammability standards and contribute to overall vehicle weight reduction to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Regulations such as the European Union's End-of-Life Vehicles Directive also mandate the recyclability of automotive components, including those made from opaque PP.
In the construction sector, building codes and fire safety regulations dictate the use of opaque PP sheets in various applications. These materials must meet specific flame retardancy and smoke emission standards to be approved for use in buildings. Additionally, energy efficiency regulations are driving the development of opaque PP sheets with enhanced insulation properties.
The medical device industry is subject to particularly stringent regulations when using opaque PP sheets. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) require extensive documentation and testing to ensure the biocompatibility and sterility of medical-grade opaque PP products. Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is also mandatory for manufacturers in this sector.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important global concern, new regulations are emerging that focus on the circular economy and waste reduction. These regulations are likely to drive innovation in opaque PP sheet design, encouraging the development of products that are easier to recycle or biodegrade. Manufacturers are also being pushed to increase their use of recycled content in opaque PP sheets, which presents both challenges and opportunities for the industry.
In the food packaging sector, opaque PP sheets must comply with regulations set by agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). These bodies have established specific migration limits for chemical substances that may transfer from the packaging material to food. Manufacturers must ensure that their opaque PP products meet these requirements through rigorous testing and documentation.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in shaping the opaque PP industry. Many countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. This has led to increased focus on the recyclability of opaque PP sheets and the development of more sustainable production processes.
The automotive industry, another significant user of opaque PP sheets, faces regulations related to vehicle safety and emissions. Opaque PP components must meet flammability standards and contribute to overall vehicle weight reduction to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Regulations such as the European Union's End-of-Life Vehicles Directive also mandate the recyclability of automotive components, including those made from opaque PP.
In the construction sector, building codes and fire safety regulations dictate the use of opaque PP sheets in various applications. These materials must meet specific flame retardancy and smoke emission standards to be approved for use in buildings. Additionally, energy efficiency regulations are driving the development of opaque PP sheets with enhanced insulation properties.
The medical device industry is subject to particularly stringent regulations when using opaque PP sheets. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) require extensive documentation and testing to ensure the biocompatibility and sterility of medical-grade opaque PP products. Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is also mandatory for manufacturers in this sector.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important global concern, new regulations are emerging that focus on the circular economy and waste reduction. These regulations are likely to drive innovation in opaque PP sheet design, encouraging the development of products that are easier to recycle or biodegrade. Manufacturers are also being pushed to increase their use of recycled content in opaque PP sheets, which presents both challenges and opportunities for the industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!