Optimize Lithium Hydroxide Manufacturing: Energy Minimization
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Hydroxide Manufacturing Evolution and Objectives
Lithium hydroxide manufacturing has undergone significant evolution since its initial industrial production in the mid-20th century. Originally, the dominant method involved the reaction of lithium carbonate with calcium hydroxide, a process characterized by high energy consumption and considerable waste generation. The 1970s saw the introduction of the electrolysis method, which offered improved purity but still required substantial electrical input.
The industry experienced a transformative shift in the 1990s with the development of the lithium carbonate-sodium hydroxide conversion process, which reduced energy requirements by approximately 15% compared to earlier methods. This period marked the beginning of energy efficiency considerations in lithium hydroxide production, though environmental concerns remained secondary to production capacity and product quality.
The 2000s witnessed accelerated technological advancement driven by the emerging electric vehicle (EV) market. The growing demand for high-purity lithium hydroxide for cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries necessitated more efficient and scalable manufacturing processes. This market pressure catalyzed research into energy optimization across the production chain, from raw material extraction to final product refinement.
Recent technological developments have focused on direct lithium extraction (DLE) methods from brines and integration of renewable energy sources into manufacturing processes. These innovations aim to address the dual challenges of increasing production capacity while simultaneously reducing the carbon footprint associated with lithium hydroxide manufacturing.
The primary objective in optimizing lithium hydroxide manufacturing for energy minimization is to develop processes that maintain or enhance product quality while significantly reducing energy consumption across the entire production lifecycle. This includes minimizing thermal energy requirements during evaporation and crystallization stages, optimizing electrical consumption in electrolysis and pumping operations, and reducing energy-intensive transportation between processing stages.
Secondary objectives include decreasing water consumption, minimizing chemical reagent usage, and reducing waste generation, all of which indirectly contribute to energy efficiency through reduced resource processing requirements. The industry also aims to develop modular and scalable production systems that can efficiently adapt to varying production demands without sacrificing energy performance.
The ultimate goal is to establish manufacturing processes that can produce battery-grade lithium hydroxide with an energy intensity reduction of 30-40% compared to current industry standards, while maintaining competitive production costs and meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This ambitious target requires a multidisciplinary approach combining chemical engineering innovations, process optimization, and integration of advanced energy management systems.
The industry experienced a transformative shift in the 1990s with the development of the lithium carbonate-sodium hydroxide conversion process, which reduced energy requirements by approximately 15% compared to earlier methods. This period marked the beginning of energy efficiency considerations in lithium hydroxide production, though environmental concerns remained secondary to production capacity and product quality.
The 2000s witnessed accelerated technological advancement driven by the emerging electric vehicle (EV) market. The growing demand for high-purity lithium hydroxide for cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries necessitated more efficient and scalable manufacturing processes. This market pressure catalyzed research into energy optimization across the production chain, from raw material extraction to final product refinement.
Recent technological developments have focused on direct lithium extraction (DLE) methods from brines and integration of renewable energy sources into manufacturing processes. These innovations aim to address the dual challenges of increasing production capacity while simultaneously reducing the carbon footprint associated with lithium hydroxide manufacturing.
The primary objective in optimizing lithium hydroxide manufacturing for energy minimization is to develop processes that maintain or enhance product quality while significantly reducing energy consumption across the entire production lifecycle. This includes minimizing thermal energy requirements during evaporation and crystallization stages, optimizing electrical consumption in electrolysis and pumping operations, and reducing energy-intensive transportation between processing stages.
Secondary objectives include decreasing water consumption, minimizing chemical reagent usage, and reducing waste generation, all of which indirectly contribute to energy efficiency through reduced resource processing requirements. The industry also aims to develop modular and scalable production systems that can efficiently adapt to varying production demands without sacrificing energy performance.
The ultimate goal is to establish manufacturing processes that can produce battery-grade lithium hydroxide with an energy intensity reduction of 30-40% compared to current industry standards, while maintaining competitive production costs and meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This ambitious target requires a multidisciplinary approach combining chemical engineering innovations, process optimization, and integration of advanced energy management systems.
Market Demand Analysis for Energy-Efficient Lithium Hydroxide
The global market for lithium hydroxide has experienced unprecedented growth in recent years, primarily driven by the rapid expansion of the electric vehicle (EV) industry. As of 2023, the market size for lithium hydroxide reached approximately $3.2 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.5% through 2030. This robust growth trajectory underscores the critical importance of energy-efficient manufacturing processes in meeting escalating demand while maintaining economic viability.
Energy costs represent a significant portion of lithium hydroxide production expenses, accounting for 30-35% of total manufacturing costs. This economic reality has created strong market pressure for energy-optimized production methods. A recent industry survey revealed that 78% of lithium producers identified energy efficiency as their top priority for process improvement, highlighting the market's clear demand signal for innovation in this area.
The battery sector remains the dominant consumer of lithium hydroxide, absorbing approximately 65% of global production. Within this segment, manufacturers of high-nickel cathode materials for EV batteries specifically require high-purity lithium hydroxide, creating a premium market segment with stringent specifications but higher profit margins. These manufacturers have consistently expressed willingness to pay 5-8% price premiums for materials produced through environmentally sustainable and energy-efficient processes.
Regional market analysis indicates that Asia-Pacific currently dominates demand, accounting for 58% of global consumption, followed by Europe (24%) and North America (15%). However, all regions are implementing increasingly stringent environmental regulations that directly impact production economics. The European Union's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, for instance, will impose additional costs on high-energy-intensity imports starting in 2026, creating a clear market advantage for energy-efficient production methods.
Consumer-facing industries, particularly automotive manufacturers, are facing mounting pressure to demonstrate sustainable supply chains. This has translated into formal sustainability requirements being incorporated into 62% of new lithium hydroxide supply contracts signed in 2022-2023, compared to just 18% in 2018-2019. This trend represents a fundamental shift in market dynamics that directly rewards energy efficiency innovations.
The market is also witnessing increased interest from non-traditional sectors, including grid-scale energy storage systems and advanced ceramics, which collectively represent an emerging demand segment growing at 18% annually. These applications often have different purity requirements but share sensitivity to embedded energy costs, further broadening the market appeal of energy-optimized production technologies.
Energy costs represent a significant portion of lithium hydroxide production expenses, accounting for 30-35% of total manufacturing costs. This economic reality has created strong market pressure for energy-optimized production methods. A recent industry survey revealed that 78% of lithium producers identified energy efficiency as their top priority for process improvement, highlighting the market's clear demand signal for innovation in this area.
The battery sector remains the dominant consumer of lithium hydroxide, absorbing approximately 65% of global production. Within this segment, manufacturers of high-nickel cathode materials for EV batteries specifically require high-purity lithium hydroxide, creating a premium market segment with stringent specifications but higher profit margins. These manufacturers have consistently expressed willingness to pay 5-8% price premiums for materials produced through environmentally sustainable and energy-efficient processes.
Regional market analysis indicates that Asia-Pacific currently dominates demand, accounting for 58% of global consumption, followed by Europe (24%) and North America (15%). However, all regions are implementing increasingly stringent environmental regulations that directly impact production economics. The European Union's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, for instance, will impose additional costs on high-energy-intensity imports starting in 2026, creating a clear market advantage for energy-efficient production methods.
Consumer-facing industries, particularly automotive manufacturers, are facing mounting pressure to demonstrate sustainable supply chains. This has translated into formal sustainability requirements being incorporated into 62% of new lithium hydroxide supply contracts signed in 2022-2023, compared to just 18% in 2018-2019. This trend represents a fundamental shift in market dynamics that directly rewards energy efficiency innovations.
The market is also witnessing increased interest from non-traditional sectors, including grid-scale energy storage systems and advanced ceramics, which collectively represent an emerging demand segment growing at 18% annually. These applications often have different purity requirements but share sensitivity to embedded energy costs, further broadening the market appeal of energy-optimized production technologies.
Current Technologies and Energy Challenges in LiOH Production
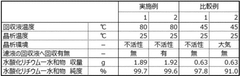
Lithium hydroxide (LiOH) production currently employs several established technologies, each with distinct energy profiles and efficiency challenges. The dominant commercial method involves the reaction of lithium carbonate with calcium hydroxide, a process that requires significant thermal energy for calcination and subsequent purification steps. This route typically consumes 5-7 GJ of energy per ton of LiOH produced, with approximately 60% attributed to heating requirements and 25% to mechanical operations such as grinding and mixing.
Alternative production pathways include the electrolysis of lithium chloride solutions and direct extraction from brines. The electrolytic method, while offering higher purity products, demands substantial electrical energy inputs of 7-9 GJ per ton, making it less favorable in regions with high electricity costs. Direct extraction technologies, though promising for their potential to reduce processing steps, remain energy-intensive during the concentration and purification phases.
Energy consumption in LiOH manufacturing is distributed across multiple process stages. Initial mineral processing and beneficiation account for 15-20% of total energy requirements, while chemical conversion represents 40-45%. Purification and crystallization processes consume another 25-30%, with drying and packaging operations requiring the remaining 10-15%. This distribution highlights the need for a holistic approach to energy optimization across the entire production chain.
The industry faces several critical energy-related challenges. Temperature management during exothermic reactions represents a significant technical hurdle, as inefficient heat recovery systems currently waste up to 30% of thermal energy. Water management also poses challenges, with evaporation and drying processes accounting for approximately 35% of the thermal energy budget in conventional operations.
Equipment efficiency presents another substantial opportunity for improvement. Current industrial reactors operate at 65-75% of theoretical efficiency, while separation and filtration systems typically achieve only 60-70% energy efficiency. Modernization of this equipment could potentially reduce overall energy consumption by 15-25%.
Regulatory pressures and market demands are increasingly driving the need for energy optimization. Carbon taxation and emissions regulations in key manufacturing regions have increased operational costs by 8-12% in recent years. Meanwhile, battery manufacturers are demanding lower carbon footprint materials, creating market incentives for energy-efficient production methods that can reduce embedded carbon by 20-30% compared to conventional processes.
The geographical distribution of production facilities relative to raw material sources further compounds energy challenges, with transportation accounting for an additional 0.8-1.2 GJ per ton in embodied energy costs for the final product.
Alternative production pathways include the electrolysis of lithium chloride solutions and direct extraction from brines. The electrolytic method, while offering higher purity products, demands substantial electrical energy inputs of 7-9 GJ per ton, making it less favorable in regions with high electricity costs. Direct extraction technologies, though promising for their potential to reduce processing steps, remain energy-intensive during the concentration and purification phases.
Energy consumption in LiOH manufacturing is distributed across multiple process stages. Initial mineral processing and beneficiation account for 15-20% of total energy requirements, while chemical conversion represents 40-45%. Purification and crystallization processes consume another 25-30%, with drying and packaging operations requiring the remaining 10-15%. This distribution highlights the need for a holistic approach to energy optimization across the entire production chain.
The industry faces several critical energy-related challenges. Temperature management during exothermic reactions represents a significant technical hurdle, as inefficient heat recovery systems currently waste up to 30% of thermal energy. Water management also poses challenges, with evaporation and drying processes accounting for approximately 35% of the thermal energy budget in conventional operations.
Equipment efficiency presents another substantial opportunity for improvement. Current industrial reactors operate at 65-75% of theoretical efficiency, while separation and filtration systems typically achieve only 60-70% energy efficiency. Modernization of this equipment could potentially reduce overall energy consumption by 15-25%.
Regulatory pressures and market demands are increasingly driving the need for energy optimization. Carbon taxation and emissions regulations in key manufacturing regions have increased operational costs by 8-12% in recent years. Meanwhile, battery manufacturers are demanding lower carbon footprint materials, creating market incentives for energy-efficient production methods that can reduce embedded carbon by 20-30% compared to conventional processes.
The geographical distribution of production facilities relative to raw material sources further compounds energy challenges, with transportation accounting for an additional 0.8-1.2 GJ per ton in embodied energy costs for the final product.
Current Energy Optimization Solutions in LiOH Manufacturing
01 Energy-efficient lithium hydroxide production methods
Various energy-efficient methods have been developed for manufacturing lithium hydroxide. These methods focus on reducing the overall energy consumption during the production process through optimized reaction conditions, improved heat recovery systems, and innovative process designs. Energy efficiency is achieved by minimizing heat loss, utilizing renewable energy sources, and implementing advanced control systems that optimize energy usage throughout the manufacturing process.- Energy-efficient lithium hydroxide production methods: Various energy-efficient methods have been developed for manufacturing lithium hydroxide. These methods focus on reducing energy consumption during the production process through optimized reaction conditions, improved heat management, and innovative process designs. These approaches aim to minimize the overall energy footprint while maintaining high-quality lithium hydroxide production, which is crucial for sustainable manufacturing practices in the battery materials industry.
- Direct lithium extraction and conversion processes: Direct extraction methods for obtaining lithium from various sources and converting it to lithium hydroxide have been developed to reduce energy requirements. These processes often bypass traditional evaporation steps and utilize selective adsorption, ion exchange, or electrochemical techniques to extract lithium directly from brines, clays, or other sources. The direct conversion to lithium hydroxide minimizes intermediate steps, resulting in significant energy savings compared to conventional methods.
- Renewable energy integration in lithium hydroxide production: Integration of renewable energy sources in lithium hydroxide manufacturing processes has been developed to reduce carbon footprint and energy costs. These methods incorporate solar, wind, geothermal, or other renewable energy sources to power energy-intensive steps in the production process. Some approaches also utilize waste heat recovery systems to improve overall energy efficiency, making the manufacturing process more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
- Low-temperature lithium hydroxide synthesis techniques: Low-temperature synthesis methods for lithium hydroxide production have been developed to reduce energy consumption. These techniques operate at significantly lower temperatures than traditional processes, which typically require high heat inputs. By utilizing catalysts, specialized reactants, or novel reaction pathways, these methods achieve the conversion to lithium hydroxide while consuming less thermal energy, resulting in more energy-efficient production processes.
- Recycling and circular economy approaches for lithium hydroxide production: Recycling methods for recovering lithium from spent batteries and other lithium-containing waste streams have been developed to reduce the energy required for primary lithium hydroxide production. These processes focus on efficient extraction of lithium compounds from waste materials and their conversion to battery-grade lithium hydroxide. By implementing circular economy principles, these methods significantly reduce the overall energy footprint compared to traditional mining and processing of lithium from primary sources.
02 Direct extraction processes for lithium hydroxide production
Direct extraction processes have been developed to produce lithium hydroxide with lower energy requirements. These processes involve extracting lithium directly from brine or mineral sources using selective sorbents or membranes, bypassing energy-intensive concentration steps. The direct extraction approach reduces the need for large evaporation ponds and extensive thermal processing, resulting in significant energy savings compared to traditional methods.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrolysis-based lithium hydroxide production
Electrolysis-based methods for producing lithium hydroxide offer energy advantages over conventional processes. These methods utilize electrochemical cells to convert lithium salts directly into lithium hydroxide, avoiding multiple chemical conversion steps. By optimizing electrode materials, cell design, and operating parameters, these electrolysis processes can achieve higher energy efficiency while maintaining product quality and production rates.Expand Specific Solutions04 Waste heat recovery in lithium hydroxide manufacturing
Waste heat recovery systems have been integrated into lithium hydroxide manufacturing processes to improve overall energy efficiency. These systems capture and reuse thermal energy that would otherwise be lost during various stages of production, such as crystallization, drying, and calcination. The recovered heat can be redirected to preheat process streams, generate steam, or support other thermal requirements within the facility, significantly reducing the total energy consumption.Expand Specific Solutions05 Renewable energy integration in lithium hydroxide production
Manufacturing processes for lithium hydroxide have been redesigned to incorporate renewable energy sources, reducing dependence on fossil fuels. These innovations include solar thermal systems for process heating, wind or solar electricity for electrolysis steps, and biomass energy for thermal operations. By integrating renewable energy, manufacturers can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of lithium hydroxide production while potentially lowering long-term energy costs.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Lithium Hydroxide Production
The lithium hydroxide manufacturing optimization market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by the electric vehicle battery sector. The market is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies like BASF SE and emerging specialists such as Lilac Solutions focusing on energy-efficient extraction technologies. Technical maturity varies significantly across players, with companies like Tianqi Lithium and General Lithium leading in commercial-scale production, while POSCO Holdings and LG Energy Solution are advancing innovative process technologies. Research institutions including RIST and Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes are contributing to energy minimization breakthroughs. The competitive landscape features both traditional chemical manufacturers and battery industry players seeking vertical integration to secure supply chains and reduce production costs.
General Lithium Corp.
Technical Solution: General Lithium has pioneered a direct lithium extraction and conversion process that significantly reduces energy consumption in lithium hydroxide production. Their technology employs a selective adsorption method that eliminates the energy-intensive evaporation steps traditionally required in lithium processing. The process operates at near-ambient temperatures (30-40°C) for the extraction phase, dramatically reducing thermal energy needs compared to conventional methods that require temperatures exceeding 80°C. General Lithium's system incorporates proprietary adsorbent materials with high lithium selectivity and rapid kinetics, enabling efficient extraction with minimal energy input. The conversion stage utilizes an electrochemical process that directly converts lithium chloride to lithium hydroxide, bypassing the energy-intensive calcination and reaction steps of the traditional Solvay process. This direct conversion approach reduces overall energy consumption by approximately 40-50% compared to conventional methods. Additionally, the company has implemented a modular design that allows for precise energy management and scaling according to production needs.
Strengths: The direct extraction and conversion process eliminates multiple energy-intensive steps, providing substantial energy savings. The modular design enables flexible implementation and gradual capacity expansion with optimized energy efficiency. Weaknesses: The specialized adsorbent materials require periodic regeneration, adding an energy requirement not present in traditional methods. The process may be more sensitive to impurities in the feed solution, potentially requiring additional purification steps that consume energy.
Tianqi Lithium Corp.
Technical Solution: Tianqi Lithium has developed an advanced energy-efficient lithium hydroxide manufacturing process that integrates multiple innovations to minimize energy consumption. Their approach utilizes a low-temperature conversion method that operates at approximately 20-30% lower temperatures than conventional processes, significantly reducing thermal energy requirements. The company employs a proprietary heat recovery system that captures and recycles thermal energy from various process stages, achieving energy recovery rates of up to 65%. Additionally, Tianqi has implemented advanced electrolysis technology with specialized electrode materials that reduce electricity consumption by approximately 15-20% compared to industry standards. Their process also incorporates a closed-loop water system that minimizes water usage and treatment energy by recycling process water with over 85% efficiency. The company has further optimized their manufacturing through digitalization and AI-controlled process parameters that continuously adjust operating conditions to maintain optimal energy efficiency.
Strengths: Tianqi's integrated approach provides comprehensive energy savings across multiple process stages rather than focusing on a single aspect. Their established market position enables rapid scaling and implementation of innovations. Weaknesses: The advanced heat recovery systems require significant upfront capital investment, potentially limiting adoption in smaller operations. The process optimization is highly dependent on specific raw material quality, requiring additional energy for preprocessing when using lower-grade feedstock.
Critical Patents and Innovations in Energy-Efficient Production
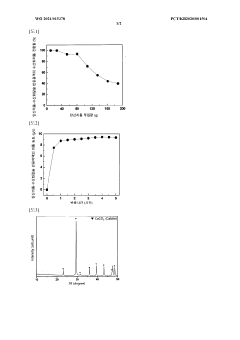
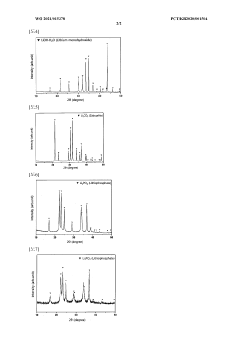
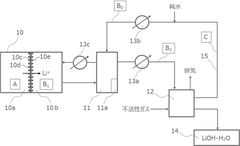
Method for producing lithium hydroxide
PatentWO2021015378A1
Innovation
- A method involving the reaction of lithium carbonate and calcium hydroxide at room temperature to produce a lithium hydroxide solution, followed by concentration and filtration to separate solid lithium hydroxide, with subsequent recovery of lithium from filtrates using carbonate or phosphate materials to minimize energy consumption and lithium loss.
Method for producing lithium hydroxide
PatentWO2022097715A1
Innovation
- A method involving the use of a Li selectively permeable membrane to recover Li ions from lithium secondary battery extracts, followed by temperature adjustment and crystallization to produce high-purity lithium hydroxide, allowing for energy-efficient production without the need for specific stock solutions and reducing energy consumption.
Environmental Impact Assessment and Sustainability Metrics
The environmental impact of lithium hydroxide manufacturing processes extends far beyond energy consumption, encompassing water usage, greenhouse gas emissions, waste generation, and land disturbance. Traditional manufacturing methods typically produce 5-7 tons of CO2 equivalent per ton of lithium hydroxide, primarily from fossil fuel-powered heating and chemical reactions. Water consumption is equally concerning, with conventional processes requiring 50-70 cubic meters of water per ton of product, often in water-stressed regions where lithium resources are abundant.
Energy optimization strategies offer significant environmental benefits. Implementing heat recovery systems can reduce carbon emissions by 15-25%, while renewable energy integration can decrease the carbon footprint by up to 40% compared to fossil fuel-dependent operations. Advanced membrane technologies for lithium extraction demonstrate potential water savings of 30-50% over traditional evaporation methods.
Sustainability metrics must be standardized across the industry to enable meaningful comparisons and progress tracking. Key performance indicators should include energy intensity (GJ/ton of product), water consumption ratio, carbon intensity (tCO2e/ton), waste generation rate, and chemical usage efficiency. Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies specific to lithium hydroxide production are essential for comprehensive environmental impact evaluation, considering raw material extraction through end-of-life management.
Regulatory compliance represents another critical dimension, with increasingly stringent environmental standards in major markets. The EU Battery Directive and similar regulations in North America and Asia are establishing mandatory carbon footprint declarations and maximum thresholds for environmental impact. Companies implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes gain competitive advantages through regulatory readiness and sustainability certification.
Biodiversity impact assessment is emerging as an important consideration, particularly for operations near sensitive ecosystems. Energy-optimized processes typically require smaller physical footprints and reduced resource extraction, thereby minimizing habitat disruption. Leading manufacturers are adopting biodiversity net gain approaches, implementing restoration projects to offset unavoidable impacts.
Social sustainability metrics are increasingly integrated with environmental assessments, recognizing that energy-efficient operations often correlate with improved community relations and reduced health impacts on surrounding populations. Comprehensive sustainability frameworks now incorporate both quantitative environmental metrics and qualitative social indicators to provide a holistic view of manufacturing impacts.
Energy optimization strategies offer significant environmental benefits. Implementing heat recovery systems can reduce carbon emissions by 15-25%, while renewable energy integration can decrease the carbon footprint by up to 40% compared to fossil fuel-dependent operations. Advanced membrane technologies for lithium extraction demonstrate potential water savings of 30-50% over traditional evaporation methods.
Sustainability metrics must be standardized across the industry to enable meaningful comparisons and progress tracking. Key performance indicators should include energy intensity (GJ/ton of product), water consumption ratio, carbon intensity (tCO2e/ton), waste generation rate, and chemical usage efficiency. Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies specific to lithium hydroxide production are essential for comprehensive environmental impact evaluation, considering raw material extraction through end-of-life management.
Regulatory compliance represents another critical dimension, with increasingly stringent environmental standards in major markets. The EU Battery Directive and similar regulations in North America and Asia are establishing mandatory carbon footprint declarations and maximum thresholds for environmental impact. Companies implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes gain competitive advantages through regulatory readiness and sustainability certification.
Biodiversity impact assessment is emerging as an important consideration, particularly for operations near sensitive ecosystems. Energy-optimized processes typically require smaller physical footprints and reduced resource extraction, thereby minimizing habitat disruption. Leading manufacturers are adopting biodiversity net gain approaches, implementing restoration projects to offset unavoidable impacts.
Social sustainability metrics are increasingly integrated with environmental assessments, recognizing that energy-efficient operations often correlate with improved community relations and reduced health impacts on surrounding populations. Comprehensive sustainability frameworks now incorporate both quantitative environmental metrics and qualitative social indicators to provide a holistic view of manufacturing impacts.
Regulatory Framework for Lithium Processing Industries
The regulatory landscape for lithium processing industries has evolved significantly in response to growing environmental concerns and the strategic importance of lithium in the global energy transition. Regulatory frameworks governing lithium hydroxide manufacturing vary considerably across regions but generally focus on environmental protection, resource conservation, and energy efficiency standards.
In North America, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established specific guidelines for chemical manufacturing processes, including lithium hydroxide production. These regulations mandate regular environmental impact assessments and compliance with the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act. Additionally, the Department of Energy's Advanced Manufacturing Office provides incentives for energy-efficient manufacturing processes, offering tax benefits for companies that implement energy minimization technologies.
The European Union implements more stringent regulations through its Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) and the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS). Lithium processing facilities must adhere to Best Available Techniques (BAT) reference documents, which specifically address energy efficiency in chemical manufacturing. The EU's Circular Economy Action Plan further encourages manufacturers to adopt closed-loop systems that minimize waste and energy consumption throughout the production lifecycle.
In Australia, a major lithium producer, the regulatory framework includes the National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting (NGER) scheme, which requires lithium processors to report energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. The Australian government also offers the Emissions Reduction Fund to incentivize energy efficiency improvements in industrial processes, including lithium hydroxide manufacturing.
China, as the world's largest lithium processor, has implemented its Energy Conservation Law and the Industrial Green Development Plan, which set mandatory energy efficiency targets for chemical manufacturing industries. These regulations are complemented by financial incentives for companies that exceed energy efficiency benchmarks and penalties for those failing to meet minimum standards.
International standards such as ISO 50001 for Energy Management Systems provide a globally recognized framework for lithium processors to systematically improve energy performance. Adherence to these standards is increasingly becoming a competitive necessity as downstream customers, particularly in the electric vehicle sector, demand environmentally responsible supply chains.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a move toward more comprehensive lifecycle assessments for lithium products, with greater emphasis on embodied energy and carbon footprints. Several jurisdictions are developing specific regulations for critical mineral processing that include energy intensity benchmarks and mandatory reporting of energy consumption per unit of production.
In North America, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established specific guidelines for chemical manufacturing processes, including lithium hydroxide production. These regulations mandate regular environmental impact assessments and compliance with the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act. Additionally, the Department of Energy's Advanced Manufacturing Office provides incentives for energy-efficient manufacturing processes, offering tax benefits for companies that implement energy minimization technologies.
The European Union implements more stringent regulations through its Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) and the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS). Lithium processing facilities must adhere to Best Available Techniques (BAT) reference documents, which specifically address energy efficiency in chemical manufacturing. The EU's Circular Economy Action Plan further encourages manufacturers to adopt closed-loop systems that minimize waste and energy consumption throughout the production lifecycle.
In Australia, a major lithium producer, the regulatory framework includes the National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting (NGER) scheme, which requires lithium processors to report energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. The Australian government also offers the Emissions Reduction Fund to incentivize energy efficiency improvements in industrial processes, including lithium hydroxide manufacturing.
China, as the world's largest lithium processor, has implemented its Energy Conservation Law and the Industrial Green Development Plan, which set mandatory energy efficiency targets for chemical manufacturing industries. These regulations are complemented by financial incentives for companies that exceed energy efficiency benchmarks and penalties for those failing to meet minimum standards.
International standards such as ISO 50001 for Energy Management Systems provide a globally recognized framework for lithium processors to systematically improve energy performance. Adherence to these standards is increasingly becoming a competitive necessity as downstream customers, particularly in the electric vehicle sector, demand environmentally responsible supply chains.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a move toward more comprehensive lifecycle assessments for lithium products, with greater emphasis on embodied energy and carbon footprints. Several jurisdictions are developing specific regulations for critical mineral processing that include energy intensity benchmarks and mandatory reporting of energy consumption per unit of production.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!