Optimizing Lithium Hydroxide Reactor Design For Efficiency
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Hydroxide Reactor Technology Evolution and Objectives
Lithium hydroxide production technology has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from small-scale laboratory methods to sophisticated industrial processes. The earliest commercial production began in the 1920s using simple batch reactors where lithium carbonate was reacted with calcium hydroxide. This rudimentary approach suffered from low yields, inconsistent product quality, and significant waste generation. The 1950s marked a pivotal shift with the introduction of continuous flow reactors, which improved throughput but still faced efficiency challenges.
The energy crisis of the 1970s catalyzed renewed interest in optimizing chemical processes, leading to the development of more energy-efficient reactor designs incorporating heat recovery systems. By the 1990s, computer-aided design tools enabled more sophisticated reactor modeling, allowing engineers to simulate and optimize reaction conditions before physical implementation. This period saw the introduction of fluidized bed reactors for lithium hydroxide production, offering better heat transfer characteristics and reaction uniformity.
The 21st century has witnessed exponential growth in lithium demand driven by battery technologies, pushing reactor technology toward higher efficiency and sustainability. Modern lithium hydroxide reactors increasingly incorporate advanced materials resistant to the highly caustic environment, precision control systems for optimal reaction parameters, and integrated purification processes to minimize downstream processing requirements.
Current technological objectives focus on several key areas. Energy efficiency remains paramount, with goals to reduce the thermal energy required per kilogram of product by at least 30% compared to conventional designs. Water conservation represents another critical objective, as traditional processes consume significant quantities of water for both reaction and purification stages. Innovative reactor designs aim to reduce water usage by implementing closed-loop systems and advanced separation technologies.
Process intensification constitutes a major technological goal, with efforts directed toward developing compact reactor designs that maintain or increase throughput while reducing physical footprint and capital expenditure. Simultaneously, there is growing emphasis on reaction selectivity to minimize unwanted side products that compromise purity and necessitate additional purification steps.
The overarching technological objective remains developing reactor systems capable of producing battery-grade lithium hydroxide (≥99.5% purity) with minimal energy input, reduced environmental impact, and lower production costs. This includes exploring novel catalytic approaches, alternative reaction pathways, and hybrid reactor configurations that combine the advantages of different reactor types to optimize overall performance across the production cycle.
The energy crisis of the 1970s catalyzed renewed interest in optimizing chemical processes, leading to the development of more energy-efficient reactor designs incorporating heat recovery systems. By the 1990s, computer-aided design tools enabled more sophisticated reactor modeling, allowing engineers to simulate and optimize reaction conditions before physical implementation. This period saw the introduction of fluidized bed reactors for lithium hydroxide production, offering better heat transfer characteristics and reaction uniformity.
The 21st century has witnessed exponential growth in lithium demand driven by battery technologies, pushing reactor technology toward higher efficiency and sustainability. Modern lithium hydroxide reactors increasingly incorporate advanced materials resistant to the highly caustic environment, precision control systems for optimal reaction parameters, and integrated purification processes to minimize downstream processing requirements.
Current technological objectives focus on several key areas. Energy efficiency remains paramount, with goals to reduce the thermal energy required per kilogram of product by at least 30% compared to conventional designs. Water conservation represents another critical objective, as traditional processes consume significant quantities of water for both reaction and purification stages. Innovative reactor designs aim to reduce water usage by implementing closed-loop systems and advanced separation technologies.
Process intensification constitutes a major technological goal, with efforts directed toward developing compact reactor designs that maintain or increase throughput while reducing physical footprint and capital expenditure. Simultaneously, there is growing emphasis on reaction selectivity to minimize unwanted side products that compromise purity and necessitate additional purification steps.
The overarching technological objective remains developing reactor systems capable of producing battery-grade lithium hydroxide (≥99.5% purity) with minimal energy input, reduced environmental impact, and lower production costs. This includes exploring novel catalytic approaches, alternative reaction pathways, and hybrid reactor configurations that combine the advantages of different reactor types to optimize overall performance across the production cycle.
Market Demand Analysis for Efficient Lithium Hydroxide Production
The global lithium hydroxide market is experiencing unprecedented growth, primarily driven by the rapid expansion of the electric vehicle (EV) industry. As of 2023, the market value has reached approximately $2.5 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.2% through 2030. This surge in demand is directly linked to lithium hydroxide's critical role in manufacturing high-nickel content cathode materials for EV batteries, which offer superior energy density and longer driving ranges compared to traditional lithium carbonate-based alternatives.
Battery manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing efficiency in lithium hydroxide production processes due to mounting cost pressures across the supply chain. The average production cost of battery-grade lithium hydroxide currently stands at $15,000-$18,000 per ton, with reactor design inefficiencies accounting for approximately 25% of production costs. Industry stakeholders are actively seeking solutions that can reduce energy consumption, which typically represents 30-35% of operational expenses in lithium hydroxide production facilities.
Regional market analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates demand, accounting for 65% of global consumption, with China leading manufacturing capacity. North America and Europe are rapidly expanding their domestic production capabilities to reduce dependency on Asian imports, with planned capacity increases of 200% and 150% respectively over the next five years. This regionalization trend is creating new market opportunities for advanced reactor technologies that can be deployed in these emerging production hubs.
The sustainability aspect of lithium hydroxide production has become increasingly important to end-users. Major automotive manufacturers have established targets to reduce the carbon footprint of their battery supply chains by 30-40% by 2030. Consequently, there is growing demand for reactor designs that minimize water usage, reduce waste generation, and lower overall environmental impact. Production processes that can demonstrate a 20% or greater reduction in carbon emissions are commanding premium pricing in the market.
Industry surveys indicate that manufacturers are willing to invest in reactor optimization technologies that offer payback periods of less than three years. The market particularly values solutions that can increase yield rates above the current industry average of 85-90%, reduce reaction time by at least 15%, and improve product purity to consistently achieve 99.5% or higher battery-grade specifications. These performance metrics have become standard requirements in procurement decisions for new production facilities.
The market landscape is further shaped by emerging applications beyond EVs, including grid-scale energy storage systems, which are projected to consume an additional 15% of global lithium hydroxide production by 2028. This diversification of end-use applications is creating demand for more flexible production systems that can adjust to varying purity requirements and production volumes.
Battery manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing efficiency in lithium hydroxide production processes due to mounting cost pressures across the supply chain. The average production cost of battery-grade lithium hydroxide currently stands at $15,000-$18,000 per ton, with reactor design inefficiencies accounting for approximately 25% of production costs. Industry stakeholders are actively seeking solutions that can reduce energy consumption, which typically represents 30-35% of operational expenses in lithium hydroxide production facilities.
Regional market analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates demand, accounting for 65% of global consumption, with China leading manufacturing capacity. North America and Europe are rapidly expanding their domestic production capabilities to reduce dependency on Asian imports, with planned capacity increases of 200% and 150% respectively over the next five years. This regionalization trend is creating new market opportunities for advanced reactor technologies that can be deployed in these emerging production hubs.
The sustainability aspect of lithium hydroxide production has become increasingly important to end-users. Major automotive manufacturers have established targets to reduce the carbon footprint of their battery supply chains by 30-40% by 2030. Consequently, there is growing demand for reactor designs that minimize water usage, reduce waste generation, and lower overall environmental impact. Production processes that can demonstrate a 20% or greater reduction in carbon emissions are commanding premium pricing in the market.
Industry surveys indicate that manufacturers are willing to invest in reactor optimization technologies that offer payback periods of less than three years. The market particularly values solutions that can increase yield rates above the current industry average of 85-90%, reduce reaction time by at least 15%, and improve product purity to consistently achieve 99.5% or higher battery-grade specifications. These performance metrics have become standard requirements in procurement decisions for new production facilities.
The market landscape is further shaped by emerging applications beyond EVs, including grid-scale energy storage systems, which are projected to consume an additional 15% of global lithium hydroxide production by 2028. This diversification of end-use applications is creating demand for more flexible production systems that can adjust to varying purity requirements and production volumes.
Current Reactor Design Challenges and Limitations
The current lithium hydroxide reactor design faces several significant challenges that limit production efficiency and scalability. Traditional batch reactors, which have been the industry standard for decades, suffer from inherent heat and mass transfer limitations. These limitations create temperature gradients within the reaction vessel, leading to inconsistent product quality and reduced conversion rates. The exothermic nature of the lithium hydroxide formation reaction further complicates thermal management, often requiring complex cooling systems that increase both capital and operational costs.
Scale-up difficulties represent another major hurdle in current reactor designs. As reactor volumes increase, the surface-to-volume ratio decreases, exacerbating heat transfer problems and creating "hot spots" that can degrade product quality or potentially compromise safety. Many existing reactors also struggle with mixing inefficiencies, particularly with the heterogeneous reaction systems typical in lithium hydroxide production, where solid-liquid interactions are critical to reaction kinetics.
Energy consumption remains excessively high in conventional reactor designs, with significant thermal losses and inefficient heat recovery systems. Most reactors operate in energy-intensive batch modes rather than more efficient continuous processes, resulting in substantial downtime between batches for cleaning, maintenance, and preparation. This batch-oriented approach also creates production bottlenecks and limits throughput capacity.
Material compatibility issues further complicate reactor design. The highly alkaline environment of lithium hydroxide production is corrosive to many conventional construction materials, necessitating expensive corrosion-resistant alloys or specialized coatings that add to capital costs and maintenance requirements. These materials often have suboptimal thermal conductivity properties, further hindering efficient heat transfer.
Process control and monitoring capabilities in existing reactors frequently lack the precision required for optimal lithium hydroxide production. Many systems rely on outdated instrumentation that provides insufficient real-time data on critical parameters such as temperature distribution, concentration gradients, and reaction progression. This limitation prevents implementation of advanced control strategies that could otherwise optimize yield and quality.
Waste generation and environmental impact constitute additional challenges. Current reactor designs typically produce significant waste streams requiring treatment before discharge, including unreacted materials and byproducts. Water consumption is often excessive, particularly in cooling systems and post-reaction processing. These environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important as regulatory requirements tighten globally.
Scale-up difficulties represent another major hurdle in current reactor designs. As reactor volumes increase, the surface-to-volume ratio decreases, exacerbating heat transfer problems and creating "hot spots" that can degrade product quality or potentially compromise safety. Many existing reactors also struggle with mixing inefficiencies, particularly with the heterogeneous reaction systems typical in lithium hydroxide production, where solid-liquid interactions are critical to reaction kinetics.
Energy consumption remains excessively high in conventional reactor designs, with significant thermal losses and inefficient heat recovery systems. Most reactors operate in energy-intensive batch modes rather than more efficient continuous processes, resulting in substantial downtime between batches for cleaning, maintenance, and preparation. This batch-oriented approach also creates production bottlenecks and limits throughput capacity.
Material compatibility issues further complicate reactor design. The highly alkaline environment of lithium hydroxide production is corrosive to many conventional construction materials, necessitating expensive corrosion-resistant alloys or specialized coatings that add to capital costs and maintenance requirements. These materials often have suboptimal thermal conductivity properties, further hindering efficient heat transfer.
Process control and monitoring capabilities in existing reactors frequently lack the precision required for optimal lithium hydroxide production. Many systems rely on outdated instrumentation that provides insufficient real-time data on critical parameters such as temperature distribution, concentration gradients, and reaction progression. This limitation prevents implementation of advanced control strategies that could otherwise optimize yield and quality.
Waste generation and environmental impact constitute additional challenges. Current reactor designs typically produce significant waste streams requiring treatment before discharge, including unreacted materials and byproducts. Water consumption is often excessive, particularly in cooling systems and post-reaction processing. These environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important as regulatory requirements tighten globally.
State-of-the-Art Reactor Optimization Approaches
01 Reactor design optimization for lithium hydroxide production
Optimizing reactor design is crucial for improving lithium hydroxide production efficiency. This includes considerations for reactor geometry, mixing mechanisms, and heat transfer systems. Advanced reactor designs incorporate features that enhance reaction kinetics, improve mass transfer, and ensure uniform temperature distribution. These optimizations lead to higher conversion rates and improved product quality while reducing energy consumption.- Reactor design optimization for lithium hydroxide production: Optimizing reactor design is crucial for improving lithium hydroxide production efficiency. This includes considerations for reactor geometry, mixing mechanisms, and heat transfer systems. Advanced reactor designs incorporate features that enhance reaction kinetics, improve mass transfer, and ensure uniform temperature distribution. These optimizations lead to higher conversion rates and better quality lithium hydroxide product.
- Process parameter control and monitoring systems: Effective control and monitoring of process parameters significantly impacts lithium hydroxide reactor efficiency. Key parameters include temperature, pressure, concentration, pH, and residence time. Advanced monitoring systems with real-time feedback mechanisms allow for precise control of reaction conditions, leading to optimized conversion rates and reduced energy consumption. Automated control systems help maintain optimal operating conditions throughout the production process.
- Feedstock preparation and purification techniques: The quality and preparation of lithium-containing feedstock significantly affects reactor efficiency. Various purification techniques are employed to remove impurities that could inhibit reactions or contaminate the final product. Methods include selective precipitation, ion exchange, solvent extraction, and membrane filtration. Proper feedstock preparation ensures higher reaction rates, improved product purity, and extended reactor component lifespan.
- Catalytic systems and reaction enhancement: Catalytic systems can significantly enhance lithium hydroxide production efficiency. Various catalysts and reaction promoters accelerate conversion rates while operating at lower temperatures and pressures. Some systems incorporate novel materials that selectively facilitate desired reactions while inhibiting side reactions. These enhancements result in higher yields, reduced energy requirements, and improved process economics.
- Continuous flow and integrated production systems: Continuous flow reactors and integrated production systems offer advantages over batch processing for lithium hydroxide production. These systems provide better control over reaction conditions, more efficient heat transfer, and reduced downtime. Integration of multiple process steps, including extraction, conversion, and purification, minimizes material handling and intermediate storage requirements. Such systems achieve higher throughput, consistent product quality, and improved overall process efficiency.
02 Process parameter control and monitoring systems
Effective control and monitoring of process parameters significantly impact lithium hydroxide reactor efficiency. Key parameters include temperature, pressure, concentration, pH, and residence time. Advanced monitoring systems with real-time feedback mechanisms allow for precise control of reaction conditions. Automated control systems can adjust parameters dynamically to maintain optimal reaction conditions, resulting in improved yield and consistent product quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Innovative catalysts and reaction enhancers
The use of specialized catalysts and reaction enhancers can significantly improve lithium hydroxide reactor efficiency. These materials accelerate reaction rates, lower activation energy requirements, and improve selectivity. Some innovations include novel heterogeneous catalysts, nano-structured materials, and surface-modified catalysts that provide increased active sites for reactions. These enhancements result in faster conversion rates and higher yields while potentially operating at lower temperatures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Continuous flow and multi-stage reactor systems
Continuous flow and multi-stage reactor systems offer significant advantages over batch processing for lithium hydroxide production. These systems provide better control over reaction conditions, more efficient heat transfer, and improved mixing. Multi-stage configurations allow for optimized conditions at each reaction phase, resulting in higher conversion rates and product purity. Continuous processing also reduces downtime between batches, increasing overall production capacity and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy efficiency and waste reduction techniques
Improving energy efficiency and reducing waste are critical aspects of lithium hydroxide reactor optimization. Techniques include heat recovery systems, energy-efficient mixing mechanisms, and process intensification methods. Waste reduction approaches focus on recycling process streams, recovering unreacted materials, and minimizing byproduct formation. These improvements not only enhance reactor efficiency but also reduce environmental impact and operating costs, making the overall process more sustainable.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Reactor Design
The lithium hydroxide reactor design optimization market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by the expanding electric vehicle battery sector. The market size is projected to reach significant scale as lithium hydroxide remains critical for high-performance cathode materials. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across players. Industry leaders like BASF, LG Chem, and Samsung SDI have established advanced reactor technologies, while newer entrants such as LG Energy Solution and Guangdong Bangpu are rapidly developing innovative approaches. Research institutions including RIST and IFP Energies Nouvelles are contributing breakthrough optimization techniques. The competitive landscape features both chemical conglomerates and specialized battery material producers collaborating on efficiency improvements to address growing sustainability concerns and production scalability challenges.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed an advanced continuous flow reactor system for lithium hydroxide production that significantly improves efficiency compared to traditional batch processes. Their technology employs a multi-stage precipitation approach with precise temperature and pH control throughout the reaction pathway. The system incorporates specialized mixing elements that ensure uniform distribution of reactants and optimize mass transfer rates. BASF's reactor design features integrated heat recovery systems that capture and reuse thermal energy from exothermic reactions, reducing overall energy consumption by approximately 30%. Additionally, their process utilizes proprietary catalysts that accelerate reaction kinetics while maintaining high product purity (>99.5% LiOH).
Strengths: Superior energy efficiency through heat recovery systems; high product purity; reduced reaction time compared to batch processes; scalable design suitable for industrial production. Weaknesses: Higher initial capital investment; requires specialized maintenance expertise; system complexity may present operational challenges in certain environments.
LG Chem Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Chem has pioneered a lithium hydroxide reactor design that employs a direct lithium extraction (DLE) approach combined with an optimized electrochemical conversion process. Their system utilizes selective ion exchange membranes to efficiently separate lithium ions from source materials before conversion to hydroxide. The reactor incorporates advanced electrode materials with high surface area and catalytic properties, enabling operation at lower temperatures (60-80°C versus conventional 90-100°C) while maintaining high conversion rates. LG Chem's design features a modular configuration that allows for flexible scaling and includes real-time monitoring systems with AI-driven process control algorithms that continuously adjust reaction parameters for maximum efficiency. The company reports yield improvements of approximately 15-20% compared to conventional methods.
Strengths: Lower energy requirements due to reduced operating temperatures; modular design allows for capacity adjustments; advanced process control systems maximize yield; reduced water consumption compared to traditional methods. Weaknesses: Higher complexity in control systems requires specialized technical expertise; membrane components may require periodic replacement; initial setup costs are relatively high.
Key Patents and Innovations in Reactor Efficiency Enhancement
High-efficiency method for producing lithium hydroxide from lithium carbonate through process improvement
PatentWO2024215014A1
Innovation
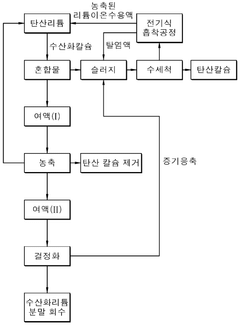
- A method involving the mixing of lithium carbonate with calcium hydroxide in a slurry, followed by filtration, concentration, and crystallization under controlled temperature and pressure conditions to enhance lithium hydroxide recovery and purity, utilizing a Membrane Captive Deionization process for ion recovery and recycling of wastewater and sludge.
Reactor for carrying out gas-liquid, liquid-liquid or gas-liquid-solid chemical reactions
PatentInactiveEP1140349A1
Innovation
- A reactor design featuring a downwardly directed jet nozzle with a concentric guide tube and integrated heat exchanger, allowing for directed internal loop flow and precise control of flow conditions, ensuring intensive phase mixing and isothermal operation through the use of a heat exchanger with heat exchange tubes welded between plates, parallel to the guide tube.
Sustainability Considerations in Lithium Hydroxide Production
Sustainability considerations in lithium hydroxide production have become increasingly critical as global demand for lithium compounds continues to surge with the expansion of electric vehicle markets and energy storage systems. The environmental footprint of lithium hydroxide manufacturing processes presents significant challenges that must be addressed through innovative reactor design approaches.
Water consumption represents one of the most pressing sustainability concerns in lithium hydroxide production. Conventional reactor designs typically require substantial water inputs, with some processes consuming up to 500,000 gallons per ton of lithium hydroxide produced. Optimized reactor designs incorporating closed-loop water recycling systems can reduce freshwater requirements by 60-70%, significantly decreasing the strain on local water resources, particularly in arid regions where many lithium operations are located.
Energy efficiency improvements in reactor design offer another pathway toward sustainability. Traditional lithium hydroxide reactors operate at high temperatures (often exceeding 250°C) and pressures, resulting in substantial energy consumption. Advanced reactor configurations featuring improved heat exchange systems, better insulation materials, and energy recovery mechanisms can reduce overall energy requirements by 30-45%, directly translating to lower carbon emissions and operational costs.
Chemical waste management represents a third critical sustainability dimension. Conventional lithium hydroxide production generates significant quantities of sodium sulfate and calcium carbonate byproducts, which often require disposal. Innovative reactor designs incorporating selective precipitation chambers and continuous filtration systems can improve byproduct quality, enabling their commercialization for applications in construction materials, paper manufacturing, and agricultural products.
Carbon emissions associated with lithium hydroxide production must also be addressed through reactor optimization. Current production methods generate approximately 5-15 tons of CO₂ equivalent per ton of lithium hydroxide. Reactor designs that incorporate renewable energy integration points, electrification of heating elements, and carbon capture capabilities can substantially reduce these emissions, aligning production with increasingly stringent carbon regulations and corporate sustainability commitments.
Land use impacts and biodiversity considerations further influence sustainable reactor design. Compact, modular reactor configurations that minimize physical footprint can reduce habitat disruption and land transformation. Additionally, reactor systems designed with end-of-life considerations, featuring easily separable components and recyclable catalysts and materials, support circular economy principles and reduce long-term environmental impacts.
Water consumption represents one of the most pressing sustainability concerns in lithium hydroxide production. Conventional reactor designs typically require substantial water inputs, with some processes consuming up to 500,000 gallons per ton of lithium hydroxide produced. Optimized reactor designs incorporating closed-loop water recycling systems can reduce freshwater requirements by 60-70%, significantly decreasing the strain on local water resources, particularly in arid regions where many lithium operations are located.
Energy efficiency improvements in reactor design offer another pathway toward sustainability. Traditional lithium hydroxide reactors operate at high temperatures (often exceeding 250°C) and pressures, resulting in substantial energy consumption. Advanced reactor configurations featuring improved heat exchange systems, better insulation materials, and energy recovery mechanisms can reduce overall energy requirements by 30-45%, directly translating to lower carbon emissions and operational costs.
Chemical waste management represents a third critical sustainability dimension. Conventional lithium hydroxide production generates significant quantities of sodium sulfate and calcium carbonate byproducts, which often require disposal. Innovative reactor designs incorporating selective precipitation chambers and continuous filtration systems can improve byproduct quality, enabling their commercialization for applications in construction materials, paper manufacturing, and agricultural products.
Carbon emissions associated with lithium hydroxide production must also be addressed through reactor optimization. Current production methods generate approximately 5-15 tons of CO₂ equivalent per ton of lithium hydroxide. Reactor designs that incorporate renewable energy integration points, electrification of heating elements, and carbon capture capabilities can substantially reduce these emissions, aligning production with increasingly stringent carbon regulations and corporate sustainability commitments.
Land use impacts and biodiversity considerations further influence sustainable reactor design. Compact, modular reactor configurations that minimize physical footprint can reduce habitat disruption and land transformation. Additionally, reactor systems designed with end-of-life considerations, featuring easily separable components and recyclable catalysts and materials, support circular economy principles and reduce long-term environmental impacts.
Economic Impact of Optimized Reactor Design
The optimization of lithium hydroxide reactor design presents significant economic implications across multiple dimensions of the lithium value chain. Enhanced reactor efficiency directly translates to reduced production costs, with optimized designs potentially decreasing energy consumption by 15-25% compared to conventional systems. This energy reduction represents substantial operational savings, particularly as energy costs constitute approximately 30-40% of total production expenses in lithium hydroxide manufacturing.
Capital expenditure benefits are equally compelling, as streamlined reactor designs with improved heat transfer capabilities and reduced material requirements can lower initial investment costs by 10-15%. The economic advantage extends to maintenance expenses, where optimized flow dynamics and reduced scaling issues minimize downtime and extend equipment lifespan, resulting in 20-30% lower maintenance costs over the reactor's operational life.
From a market perspective, more efficient reactors enable manufacturers to increase production capacity while maintaining quality standards, creating a competitive advantage in the rapidly growing lithium market. With global lithium hydroxide demand projected to grow at a CAGR of 18.3% through 2030, producers with optimized reactor technology can capture larger market share and command premium pricing for consistent, high-quality output.
The economic benefits extend beyond direct manufacturing costs to include environmental compliance savings. Optimized reactors typically generate fewer waste products and emissions, reducing treatment costs and potential regulatory penalties. In jurisdictions with carbon pricing mechanisms, the reduced carbon footprint from energy-efficient operations translates to quantifiable financial benefits, estimated at $5-15 per ton of lithium hydroxide produced.
Supply chain resilience represents another economic dimension, as more efficient reactors can operate with greater flexibility regarding feedstock quality variations. This adaptability reduces dependency on premium-grade raw materials, allowing manufacturers to source from a wider supplier base and potentially negotiate more favorable terms.
The cumulative economic impact of these efficiency improvements is substantial, with industry analyses suggesting that fully optimized lithium hydroxide reactor designs could reduce total production costs by 18-22%, significantly enhancing profit margins in an increasingly competitive market landscape. These economic benefits make reactor optimization a strategic priority for producers seeking sustainable competitive advantage in the expanding lithium chemicals sector.
Capital expenditure benefits are equally compelling, as streamlined reactor designs with improved heat transfer capabilities and reduced material requirements can lower initial investment costs by 10-15%. The economic advantage extends to maintenance expenses, where optimized flow dynamics and reduced scaling issues minimize downtime and extend equipment lifespan, resulting in 20-30% lower maintenance costs over the reactor's operational life.
From a market perspective, more efficient reactors enable manufacturers to increase production capacity while maintaining quality standards, creating a competitive advantage in the rapidly growing lithium market. With global lithium hydroxide demand projected to grow at a CAGR of 18.3% through 2030, producers with optimized reactor technology can capture larger market share and command premium pricing for consistent, high-quality output.
The economic benefits extend beyond direct manufacturing costs to include environmental compliance savings. Optimized reactors typically generate fewer waste products and emissions, reducing treatment costs and potential regulatory penalties. In jurisdictions with carbon pricing mechanisms, the reduced carbon footprint from energy-efficient operations translates to quantifiable financial benefits, estimated at $5-15 per ton of lithium hydroxide produced.
Supply chain resilience represents another economic dimension, as more efficient reactors can operate with greater flexibility regarding feedstock quality variations. This adaptability reduces dependency on premium-grade raw materials, allowing manufacturers to source from a wider supplier base and potentially negotiate more favorable terms.
The cumulative economic impact of these efficiency improvements is substantial, with industry analyses suggesting that fully optimized lithium hydroxide reactor designs could reduce total production costs by 18-22%, significantly enhancing profit margins in an increasingly competitive market landscape. These economic benefits make reactor optimization a strategic priority for producers seeking sustainable competitive advantage in the expanding lithium chemicals sector.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!