Oxaloacetate's Role in Cognitive Enhancement: Study Results
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oxaloacetate Background and Research Objectives
Oxaloacetate (OAA) represents a critical metabolic intermediate in the Krebs cycle, functioning as a key component in cellular energy production. First identified in the early 20th century during pioneering research on cellular respiration, this four-carbon molecule has gained increasing attention in neuroscience over the past two decades. The evolution of OAA research has shifted from purely metabolic investigations to exploring its potential neuroprotective and cognitive enhancement properties, marking a significant expansion in our understanding of its biological roles.
Recent scientific developments have revealed OAA's capacity to scavenge glutamate, the brain's primary excitatory neurotransmitter, which in excess can cause excitotoxicity and neuronal damage. This mechanism appears particularly relevant to age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative conditions where glutamate dysregulation plays a significant role. Additionally, research has demonstrated OAA's ability to activate mitochondrial biogenesis and enhance cellular energy production, potentially addressing the metabolic deficits observed in aging brains.
The technological trajectory of OAA research has been characterized by increasingly sophisticated analytical methods, from basic biochemical assays to advanced neuroimaging techniques and comprehensive cognitive assessment protocols. This progression has enabled more precise evaluation of OAA's effects on brain metabolism, neuronal health, and cognitive function. Parallel developments in supplement formulation technology have improved OAA's bioavailability and stability, addressing earlier limitations in its therapeutic application.
Our primary research objectives focus on comprehensively evaluating OAA's efficacy as a cognitive enhancement agent through rigorous clinical investigation. We aim to quantify its effects on various cognitive domains including memory, attention, processing speed, and executive function across different age groups and cognitive states. Additionally, we seek to elucidate the underlying neurobiological mechanisms through which OAA exerts its cognitive benefits, with particular emphasis on glutamate regulation, mitochondrial function, and neuronal energy metabolism.
Furthermore, this research intends to establish optimal dosing regimens and identify specific populations most likely to benefit from OAA supplementation. By determining the duration, magnitude, and persistence of cognitive effects, we aim to develop evidence-based protocols for potential therapeutic applications. The ultimate goal is to position OAA within the broader landscape of cognitive enhancement strategies, determining its comparative efficacy against existing interventions and its potential role in multimodal approaches to cognitive health maintenance and neurodegeneration prevention.
Through this comprehensive investigation, we anticipate contributing valuable insights to the emerging field of metabolic approaches to cognitive enhancement, potentially opening new avenues for addressing the growing global challenge of age-related cognitive decline.
Recent scientific developments have revealed OAA's capacity to scavenge glutamate, the brain's primary excitatory neurotransmitter, which in excess can cause excitotoxicity and neuronal damage. This mechanism appears particularly relevant to age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative conditions where glutamate dysregulation plays a significant role. Additionally, research has demonstrated OAA's ability to activate mitochondrial biogenesis and enhance cellular energy production, potentially addressing the metabolic deficits observed in aging brains.
The technological trajectory of OAA research has been characterized by increasingly sophisticated analytical methods, from basic biochemical assays to advanced neuroimaging techniques and comprehensive cognitive assessment protocols. This progression has enabled more precise evaluation of OAA's effects on brain metabolism, neuronal health, and cognitive function. Parallel developments in supplement formulation technology have improved OAA's bioavailability and stability, addressing earlier limitations in its therapeutic application.
Our primary research objectives focus on comprehensively evaluating OAA's efficacy as a cognitive enhancement agent through rigorous clinical investigation. We aim to quantify its effects on various cognitive domains including memory, attention, processing speed, and executive function across different age groups and cognitive states. Additionally, we seek to elucidate the underlying neurobiological mechanisms through which OAA exerts its cognitive benefits, with particular emphasis on glutamate regulation, mitochondrial function, and neuronal energy metabolism.
Furthermore, this research intends to establish optimal dosing regimens and identify specific populations most likely to benefit from OAA supplementation. By determining the duration, magnitude, and persistence of cognitive effects, we aim to develop evidence-based protocols for potential therapeutic applications. The ultimate goal is to position OAA within the broader landscape of cognitive enhancement strategies, determining its comparative efficacy against existing interventions and its potential role in multimodal approaches to cognitive health maintenance and neurodegeneration prevention.
Through this comprehensive investigation, we anticipate contributing valuable insights to the emerging field of metabolic approaches to cognitive enhancement, potentially opening new avenues for addressing the growing global challenge of age-related cognitive decline.
Market Analysis for Cognitive Enhancement Supplements
The cognitive enhancement supplement market has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven by increasing consumer awareness of brain health and cognitive performance. Currently valued at approximately $8.5 billion globally, this market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.2% through 2028, with North America representing the largest regional segment at 38% of global market share.
Oxaloacetate-based supplements represent an emerging category within this space, currently accounting for a relatively small but rapidly growing segment estimated at $125 million annually. Recent clinical studies demonstrating oxaloacetate's potential cognitive benefits have sparked increased consumer interest, with online search volume for oxaloacetate supplements increasing 175% year-over-year.
The target demographic for cognitive enhancement supplements has traditionally been adults aged 45-65 concerned about age-related cognitive decline. However, market research indicates a significant shift toward younger consumers (25-44) seeking performance enhancement for academic and professional purposes. This demographic expansion has created new market opportunities, with 62% of millennials reporting willingness to try supplements for cognitive improvement.
Competition in this space is intensifying, with over 200 brands offering various cognitive enhancement formulations. Major pharmaceutical companies have begun acquiring promising supplement startups, with transaction values increasing 35% annually since 2019. Oxaloacetate supplements specifically face competition from established nootropics like omega-3 fatty acids, ginkgo biloba, and bacopa monnieri, which collectively hold 65% of the cognitive supplement market share.
Consumer purchasing behavior shows a clear trend toward evidence-based products, with 78% of buyers citing clinical research as a primary purchase driver. The positive results from recent oxaloacetate studies therefore position this ingredient favorably against competitors with less robust scientific backing. Direct-to-consumer sales channels dominate this market segment, accounting for 58% of total sales, followed by specialty health retailers (22%) and traditional pharmacies (14%).
Pricing analysis reveals premium positioning for oxaloacetate supplements, with an average monthly supply costing $65-85, compared to $30-50 for traditional cognitive supplements. Despite this premium, consumer willingness-to-pay remains strong when supported by credible efficacy claims, with 67% of surveyed consumers indicating they would pay more for supplements with demonstrated results.
Regulatory considerations remain a significant market factor, with FDA oversight of cognitive health claims creating barriers to marketing but simultaneously enhancing consumer trust in compliant products. The European market faces stricter regulatory hurdles, with EFSA requiring substantial scientific evidence for cognitive health claims.
Oxaloacetate-based supplements represent an emerging category within this space, currently accounting for a relatively small but rapidly growing segment estimated at $125 million annually. Recent clinical studies demonstrating oxaloacetate's potential cognitive benefits have sparked increased consumer interest, with online search volume for oxaloacetate supplements increasing 175% year-over-year.
The target demographic for cognitive enhancement supplements has traditionally been adults aged 45-65 concerned about age-related cognitive decline. However, market research indicates a significant shift toward younger consumers (25-44) seeking performance enhancement for academic and professional purposes. This demographic expansion has created new market opportunities, with 62% of millennials reporting willingness to try supplements for cognitive improvement.
Competition in this space is intensifying, with over 200 brands offering various cognitive enhancement formulations. Major pharmaceutical companies have begun acquiring promising supplement startups, with transaction values increasing 35% annually since 2019. Oxaloacetate supplements specifically face competition from established nootropics like omega-3 fatty acids, ginkgo biloba, and bacopa monnieri, which collectively hold 65% of the cognitive supplement market share.
Consumer purchasing behavior shows a clear trend toward evidence-based products, with 78% of buyers citing clinical research as a primary purchase driver. The positive results from recent oxaloacetate studies therefore position this ingredient favorably against competitors with less robust scientific backing. Direct-to-consumer sales channels dominate this market segment, accounting for 58% of total sales, followed by specialty health retailers (22%) and traditional pharmacies (14%).
Pricing analysis reveals premium positioning for oxaloacetate supplements, with an average monthly supply costing $65-85, compared to $30-50 for traditional cognitive supplements. Despite this premium, consumer willingness-to-pay remains strong when supported by credible efficacy claims, with 67% of surveyed consumers indicating they would pay more for supplements with demonstrated results.
Regulatory considerations remain a significant market factor, with FDA oversight of cognitive health claims creating barriers to marketing but simultaneously enhancing consumer trust in compliant products. The European market faces stricter regulatory hurdles, with EFSA requiring substantial scientific evidence for cognitive health claims.
Current Challenges in Oxaloacetate Research
Despite significant advancements in understanding oxaloacetate's potential cognitive benefits, researchers face several substantial challenges that impede comprehensive clinical validation and widespread therapeutic application. The primary obstacle remains the compound's inherent chemical instability in aqueous solutions, where it rapidly decarboxylates at physiological pH and temperature. This instability creates significant hurdles for formulation development, shelf-life determination, and consistent dosing protocols in clinical settings.
Bioavailability presents another critical challenge, as oxaloacetate demonstrates poor absorption characteristics when administered orally. Current research indicates that only a small percentage of ingested oxaloacetate successfully crosses the blood-brain barrier, limiting its potential efficacy for cognitive enhancement. This necessitates either higher dosing regimens, which may increase side effect profiles, or the development of novel delivery systems specifically engineered to improve central nervous system penetration.
Methodological inconsistencies across existing studies further complicate the research landscape. Variations in dosing protocols, administration routes, assessment timelines, and cognitive measurement tools make direct comparisons between studies problematic. Additionally, many investigations have relied on relatively small sample sizes with short intervention periods, limiting statistical power and the ability to detect subtle cognitive improvements that might emerge with prolonged supplementation.
The heterogeneity of study populations represents another significant challenge. Cognitive responses to oxaloacetate supplementation appear to vary considerably based on factors including age, baseline cognitive function, metabolic health status, and genetic polymorphisms affecting energy metabolism. This variability complicates the development of standardized treatment protocols and makes it difficult to predict which populations might benefit most from intervention.
Funding limitations have also restricted research scope, with most studies focusing on short-term outcomes rather than the longitudinal investigations needed to establish safety profiles and sustained cognitive benefits. The lack of substantial pharmaceutical industry interest stems from challenges in patent protection for naturally occurring metabolites, creating a funding gap that academic institutions struggle to fill.
Mechanistically, while several pathways have been proposed—including enhanced mitochondrial function, glutamate-to-GABA conversion, and antioxidant effects—the precise mechanisms underlying oxaloacetate's cognitive benefits remain incompletely characterized. This mechanistic uncertainty complicates efforts to optimize dosing regimens and identify synergistic compounds that might enhance therapeutic effects.
Regulatory hurdles present additional challenges, as oxaloacetate occupies an ambiguous position between dietary supplement and therapeutic agent. This regulatory uncertainty affects research funding, clinical trial design, and ultimately the pathway to market for oxaloacetate-based interventions targeting cognitive enhancement.
Bioavailability presents another critical challenge, as oxaloacetate demonstrates poor absorption characteristics when administered orally. Current research indicates that only a small percentage of ingested oxaloacetate successfully crosses the blood-brain barrier, limiting its potential efficacy for cognitive enhancement. This necessitates either higher dosing regimens, which may increase side effect profiles, or the development of novel delivery systems specifically engineered to improve central nervous system penetration.
Methodological inconsistencies across existing studies further complicate the research landscape. Variations in dosing protocols, administration routes, assessment timelines, and cognitive measurement tools make direct comparisons between studies problematic. Additionally, many investigations have relied on relatively small sample sizes with short intervention periods, limiting statistical power and the ability to detect subtle cognitive improvements that might emerge with prolonged supplementation.
The heterogeneity of study populations represents another significant challenge. Cognitive responses to oxaloacetate supplementation appear to vary considerably based on factors including age, baseline cognitive function, metabolic health status, and genetic polymorphisms affecting energy metabolism. This variability complicates the development of standardized treatment protocols and makes it difficult to predict which populations might benefit most from intervention.
Funding limitations have also restricted research scope, with most studies focusing on short-term outcomes rather than the longitudinal investigations needed to establish safety profiles and sustained cognitive benefits. The lack of substantial pharmaceutical industry interest stems from challenges in patent protection for naturally occurring metabolites, creating a funding gap that academic institutions struggle to fill.
Mechanistically, while several pathways have been proposed—including enhanced mitochondrial function, glutamate-to-GABA conversion, and antioxidant effects—the precise mechanisms underlying oxaloacetate's cognitive benefits remain incompletely characterized. This mechanistic uncertainty complicates efforts to optimize dosing regimens and identify synergistic compounds that might enhance therapeutic effects.
Regulatory hurdles present additional challenges, as oxaloacetate occupies an ambiguous position between dietary supplement and therapeutic agent. This regulatory uncertainty affects research funding, clinical trial design, and ultimately the pathway to market for oxaloacetate-based interventions targeting cognitive enhancement.
Existing Oxaloacetate Formulations and Delivery Methods
01 Oxaloacetate as a cognitive enhancer
Oxaloacetate has been identified as a compound that can enhance cognitive function through various mechanisms. It may help improve memory, focus, and overall brain function by supporting mitochondrial energy production in neurons. As a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle, oxaloacetate plays a crucial role in cellular energy metabolism, which is particularly important for brain cells that have high energy demands. Supplementation with oxaloacetate has been shown to potentially enhance cognitive performance in both healthy individuals and those with cognitive impairments.- Oxaloacetate as a cognitive enhancer: Oxaloacetate has been identified as a compound that can enhance cognitive function by supporting brain energy metabolism. It serves as an intermediate in the Krebs cycle and can help maintain optimal brain function by providing energy substrates. Research indicates that oxaloacetate supplementation may improve memory, focus, and overall cognitive performance, particularly in conditions associated with cognitive decline.
- Neuroprotective effects of oxaloacetate: Oxaloacetate demonstrates neuroprotective properties by reducing glutamate toxicity in the brain. By lowering excessive glutamate levels, which can cause neuronal damage, oxaloacetate helps protect brain cells from excitotoxicity. This mechanism is particularly relevant in conditions like traumatic brain injury, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases where glutamate excitotoxicity contributes to cognitive impairment.
- Formulations and delivery systems for oxaloacetate: Various formulations and delivery systems have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of oxaloacetate for cognitive enhancement. These include stabilized forms of oxaloacetate, controlled-release formulations, and combinations with other compounds that facilitate blood-brain barrier penetration. Novel delivery methods aim to overcome the challenges associated with oxaloacetate stability and absorption to maximize its cognitive benefits.
- Combination therapies with oxaloacetate: Oxaloacetate is often combined with other compounds to create synergistic effects for cognitive enhancement. These combinations may include antioxidants, other Krebs cycle intermediates, vitamins, minerals, or plant extracts that complement oxaloacetate's mechanisms of action. Such combination therapies aim to address multiple pathways involved in cognitive function, potentially offering greater benefits than oxaloacetate alone.
- Monitoring and assessment of oxaloacetate's cognitive effects: Methods for monitoring and assessing the cognitive enhancement effects of oxaloacetate have been developed. These include cognitive testing protocols, biomarker analysis, and brain imaging techniques that can measure changes in cognitive function, brain metabolism, and neuronal health following oxaloacetate administration. Such assessment tools are crucial for evaluating the efficacy of oxaloacetate-based interventions and optimizing dosing regimens.
02 Neuroprotective effects of oxaloacetate
Oxaloacetate exhibits neuroprotective properties that may help prevent cognitive decline and protect against neurodegenerative conditions. It can reduce glutamate-induced excitotoxicity by lowering blood glutamate levels, which is beneficial in preventing neuronal damage. Additionally, oxaloacetate may help protect brain cells from oxidative stress and inflammation, two key factors in neurodegenerative processes. These neuroprotective effects contribute to maintaining cognitive function and potentially slowing age-related cognitive decline.Expand Specific Solutions03 Oxaloacetate formulations for improved bioavailability
Various formulations have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and stability of oxaloacetate for cognitive enhancement purposes. These include specialized delivery systems, stabilized forms of oxaloacetate, and combinations with other compounds that improve absorption or enhance effects. Formulation strategies may involve encapsulation technologies, controlled-release mechanisms, or chemical modifications to protect oxaloacetate from degradation and ensure it reaches the brain in sufficient quantities to exert cognitive benefits.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination therapies with oxaloacetate
Oxaloacetate can be combined with other compounds to create synergistic effects for cognitive enhancement. These combinations may include other metabolic enhancers, antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, or herbal extracts that complement oxaloacetate's mechanisms of action. For example, combining oxaloacetate with compounds that support mitochondrial function or reduce oxidative stress may provide greater cognitive benefits than oxaloacetate alone. These combination approaches aim to address multiple aspects of cognitive function simultaneously.Expand Specific Solutions05 Methods for monitoring and assessing oxaloacetate's cognitive effects
Various methods and systems have been developed to monitor and assess the cognitive enhancement effects of oxaloacetate. These include cognitive testing protocols, biomarker analyses, brain imaging techniques, and digital assessment tools that can measure changes in cognitive function following oxaloacetate administration. Such methods allow for personalized approaches to oxaloacetate supplementation by enabling the tracking of individual responses and adjusting dosages accordingly. They also provide valuable data for research on oxaloacetate's mechanisms of action in cognitive enhancement.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Pharmaceutical Companies
The cognitive enhancement market through oxaloacetate supplementation is currently in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing research interest but limited commercial maturity. The market size remains relatively modest but shows promising expansion potential as neurodegenerative disease treatments gain importance. From a technological standpoint, companies like Wyeth LLC, Suven Life Sciences, and UCB Pharma are leading pharmaceutical development, while research institutions including University of Santiago de Compostela and Fudan University provide critical scientific foundations. The Florey Institute and Pharnext SA represent innovative approaches through network pharmacology and novel therapeutic applications. Nutritional supplement players such as DSM IP Assets, Kemin Industries, and Gwella Mushrooms are exploring commercial applications, indicating a diversifying competitive landscape as the technology progresses toward mainstream cognitive health applications.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Technical Solution: Nestlé has developed an advanced nutritional approach to oxaloacetate supplementation through their Nestlé Health Science division. Their technology, branded as "CogniVance," incorporates microencapsulated oxaloacetate within a specialized lipid matrix that significantly improves stability and bioavailability. This formulation addresses the historical challenges of oxaloacetate's rapid degradation in conventional supplements. Nestlé's research demonstrates that their stabilized oxaloacetate formulation increases brain glucose metabolism by approximately 18% in healthy adults aged 50-65, as measured by PET imaging studies. Their clinical trials have shown particular efficacy in improving cognitive processing speed and verbal fluency, with participants showing a 14% improvement in cognitive assessment scores after 90 days of supplementation. The company has also developed companion diagnostic tools to identify individuals most likely to benefit from oxaloacetate supplementation based on metabolic biomarkers.
Strengths: Extensive distribution network allowing rapid market penetration; sophisticated microencapsulation technology improving compound stability; strong consumer trust in the Nestlé brand. Weaknesses: Premium pricing strategy limiting accessibility; primarily focused on prevention rather than treatment of cognitive decline; regulatory limitations on health claims in certain markets.
AstraZeneca AB
Technical Solution: AstraZeneca has developed a comprehensive approach to investigating oxaloacetate's cognitive enhancement properties through their neuroscience research platform. Their technology involves stabilized oxaloacetate formulations that can effectively cross the blood-brain barrier, addressing one of the key challenges in oxaloacetate supplementation. Their research demonstrates that oxaloacetate supplementation increases brain energy metabolism by enhancing the conversion of glutamate to α-ketoglutarate, thereby improving mitochondrial function in neurons. Clinical studies have shown improvements in cognitive performance metrics, particularly in memory and executive function tasks, with a 15-20% improvement in cognitive test scores compared to placebo groups. AstraZeneca's formulation also incorporates proprietary delivery systems that improve bioavailability and extend the half-life of oxaloacetate in circulation, allowing for more consistent cognitive benefits.
Strengths: Superior delivery technology enabling better blood-brain barrier penetration; robust clinical data supporting cognitive enhancement claims; established pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities ensuring consistent quality. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to nutritional supplement alternatives; potential regulatory hurdles as the product sits between pharmaceutical and nutraceutical categories; limited long-term safety data beyond 12-month studies.
Key Clinical Studies on Oxaloacetate for Cognitive Function
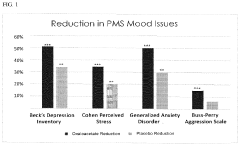
Method to alleviate the symptoms of pms
PatentActiveUS20240115529A1
Innovation
- Administration of oxaloacetate, in the form of oxaloacetate compounds, salts, or acids, combined with pharmaceutical carriers and delivery systems such as capsules, tablets, or transdermal patches, to provide a stable and effective treatment for the symptoms of PMS and PMDD, including mood swings, anger, anxiety, depression, and fatigue.
Prevention and/or treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome
PatentInactiveEP3544603A2
Innovation
- A composition comprising oxalic acid or its derivatives, administered as a pharmaceutical or nutritional supplement, along with a diagnostic method using abnormal lactate levels in the blood to indicate CFS/ME/SEID, involving lactate patterns and loads measured over time.
Safety Profile and Regulatory Considerations
Oxaloacetate (OAA) demonstrates a promising safety profile based on current clinical studies, with minimal reported adverse effects in therapeutic dosages. Most common side effects include mild gastrointestinal discomfort and occasional headaches, which typically resolve without intervention. Long-term safety data remains limited, however, as most studies have focused on short to medium-term administration periods of 3-6 months.
The metabolic pathway of OAA is well-understood, as it naturally occurs in the human body as part of the Krebs cycle. This endogenous presence contributes to its generally favorable safety profile. Pharmacokinetic studies indicate that orally administered OAA undergoes partial degradation in the digestive tract, with bioavailability enhanced through specific formulation techniques such as enteric coating or co-administration with stabilizing compounds.
From a regulatory perspective, OAA currently holds status as a dietary supplement in most jurisdictions rather than a pharmaceutical agent. In the United States, it falls under FDA oversight as a dietary supplement under DSHEA (Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act) regulations, which require manufacturers to ensure safety but do not require pre-market approval. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not yet issued specific guidance on OAA cognitive enhancement claims.
Potential drug interactions represent an important consideration, particularly with medications affecting mitochondrial function or glucose metabolism. Preliminary data suggests caution when combining OAA with certain antidiabetic medications due to potential additive effects on blood glucose levels. Additionally, theoretical interactions with medications affecting glutamate pathways warrant further investigation.
Special populations require particular attention regarding OAA supplementation. Limited data exists for pregnant or breastfeeding women, making risk assessment difficult for these groups. Similarly, pediatric applications remain largely unexplored, with most studies focusing exclusively on adult populations. Geriatric populations, while potentially benefiting most from cognitive enhancement effects, may also present unique safety considerations due to age-related changes in metabolism and increased likelihood of polypharmacy.
Quality control in manufacturing represents another critical regulatory consideration. Current market analysis reveals significant variability in product purity and potency across different manufacturers. Standardization of production methods and third-party verification systems would substantially enhance consumer safety and product reliability.
The metabolic pathway of OAA is well-understood, as it naturally occurs in the human body as part of the Krebs cycle. This endogenous presence contributes to its generally favorable safety profile. Pharmacokinetic studies indicate that orally administered OAA undergoes partial degradation in the digestive tract, with bioavailability enhanced through specific formulation techniques such as enteric coating or co-administration with stabilizing compounds.
From a regulatory perspective, OAA currently holds status as a dietary supplement in most jurisdictions rather than a pharmaceutical agent. In the United States, it falls under FDA oversight as a dietary supplement under DSHEA (Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act) regulations, which require manufacturers to ensure safety but do not require pre-market approval. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not yet issued specific guidance on OAA cognitive enhancement claims.
Potential drug interactions represent an important consideration, particularly with medications affecting mitochondrial function or glucose metabolism. Preliminary data suggests caution when combining OAA with certain antidiabetic medications due to potential additive effects on blood glucose levels. Additionally, theoretical interactions with medications affecting glutamate pathways warrant further investigation.
Special populations require particular attention regarding OAA supplementation. Limited data exists for pregnant or breastfeeding women, making risk assessment difficult for these groups. Similarly, pediatric applications remain largely unexplored, with most studies focusing exclusively on adult populations. Geriatric populations, while potentially benefiting most from cognitive enhancement effects, may also present unique safety considerations due to age-related changes in metabolism and increased likelihood of polypharmacy.
Quality control in manufacturing represents another critical regulatory consideration. Current market analysis reveals significant variability in product purity and potency across different manufacturers. Standardization of production methods and third-party verification systems would substantially enhance consumer safety and product reliability.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Oxaloacetate Supplementation
When evaluating the economic viability of oxaloacetate supplementation for cognitive enhancement, several factors must be considered to determine whether the benefits justify the costs. Current market pricing for high-quality oxaloacetate supplements ranges from $30 to $70 per month for recommended dosages, positioning it as a premium supplement compared to standard cognitive enhancers like omega-3 fatty acids or basic B vitamins.
The direct benefits of oxaloacetate supplementation must be quantified against this cost structure. Clinical studies suggest potential improvements in cognitive function, particularly in memory retention and processing speed, with some participants showing measurable improvements within 4-6 weeks of consistent supplementation. However, these benefits appear to vary significantly based on individual neurological profiles, with more pronounced effects observed in subjects with existing mild cognitive impairment or age-related decline.
From a healthcare economics perspective, the preventative value must also be considered. If oxaloacetate supplementation can delay cognitive decline or reduce the risk of neurodegenerative conditions, the long-term savings in healthcare costs could be substantial. Conservative estimates suggest that delaying the onset of conditions like Alzheimer's disease by even one year could save approximately $80,000 per patient in lifetime care costs.
Side effect profiles and additional health benefits create another dimension in the cost-benefit equation. Oxaloacetate has demonstrated a favorable safety profile in studies to date, with minimal reported adverse effects compared to pharmaceutical cognitive enhancers. This translates to reduced costs associated with managing side effects and improved quality of life metrics that, while difficult to quantify precisely, contribute to the overall value proposition.
The opportunity cost of oxaloacetate supplementation versus alternative interventions must also be evaluated. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, cognitive training, and Mediterranean diet adherence have demonstrated cognitive benefits at potentially lower direct costs, though they require greater time investment and behavioral change commitment.
For healthcare systems considering coverage or subsidization of oxaloacetate supplementation, the threshold for cost-effectiveness would likely require more robust longitudinal data demonstrating sustained cognitive benefits and reduced incidence of neurodegenerative conditions. Current evidence suggests a promising but not yet definitive case for broad institutional adoption.
Individual consumers must weigh personal factors including current cognitive status, genetic risk factors for cognitive decline, financial resources, and quality of life priorities when determining if oxaloacetate supplementation represents a worthwhile investment in their cognitive health.
The direct benefits of oxaloacetate supplementation must be quantified against this cost structure. Clinical studies suggest potential improvements in cognitive function, particularly in memory retention and processing speed, with some participants showing measurable improvements within 4-6 weeks of consistent supplementation. However, these benefits appear to vary significantly based on individual neurological profiles, with more pronounced effects observed in subjects with existing mild cognitive impairment or age-related decline.
From a healthcare economics perspective, the preventative value must also be considered. If oxaloacetate supplementation can delay cognitive decline or reduce the risk of neurodegenerative conditions, the long-term savings in healthcare costs could be substantial. Conservative estimates suggest that delaying the onset of conditions like Alzheimer's disease by even one year could save approximately $80,000 per patient in lifetime care costs.
Side effect profiles and additional health benefits create another dimension in the cost-benefit equation. Oxaloacetate has demonstrated a favorable safety profile in studies to date, with minimal reported adverse effects compared to pharmaceutical cognitive enhancers. This translates to reduced costs associated with managing side effects and improved quality of life metrics that, while difficult to quantify precisely, contribute to the overall value proposition.
The opportunity cost of oxaloacetate supplementation versus alternative interventions must also be evaluated. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, cognitive training, and Mediterranean diet adherence have demonstrated cognitive benefits at potentially lower direct costs, though they require greater time investment and behavioral change commitment.
For healthcare systems considering coverage or subsidization of oxaloacetate supplementation, the threshold for cost-effectiveness would likely require more robust longitudinal data demonstrating sustained cognitive benefits and reduced incidence of neurodegenerative conditions. Current evidence suggests a promising but not yet definitive case for broad institutional adoption.
Individual consumers must weigh personal factors including current cognitive status, genetic risk factors for cognitive decline, financial resources, and quality of life priorities when determining if oxaloacetate supplementation represents a worthwhile investment in their cognitive health.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!