Sodium Alginate as a Tool for Environmental Research Solutions
JUL 14, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Alginate Background and Research Objectives
Sodium alginate, a naturally occurring polysaccharide derived from brown seaweed, has gained significant attention in environmental research due to its unique properties and versatile applications. This biopolymer has a rich history dating back to its discovery in the 1880s, with its potential for industrial use recognized in the early 20th century. Over the years, sodium alginate has evolved from a food additive and textile industry component to a promising tool in environmental remediation and sustainable technology development.
The evolution of sodium alginate research has been driven by the growing need for eco-friendly solutions to address pressing environmental challenges. Its biodegradability, non-toxicity, and ability to form hydrogels have made it an attractive candidate for various environmental applications. The increasing focus on sustainable materials and green chemistry has further propelled the exploration of sodium alginate's potential in recent decades.
Current research objectives in the field of sodium alginate as an environmental tool are multifaceted and ambitious. One primary goal is to develop advanced water treatment technologies utilizing sodium alginate-based materials. This includes the creation of novel adsorbents and membranes for the removal of heavy metals, organic pollutants, and emerging contaminants from water sources. Researchers aim to enhance the efficiency, selectivity, and reusability of these materials to address the global challenge of water scarcity and pollution.
Another significant objective is the application of sodium alginate in soil remediation and agriculture. Studies are focused on developing sodium alginate-based carriers for controlled release of fertilizers and pesticides, reducing environmental impact while improving crop yields. Additionally, researchers are exploring its potential in soil stabilization and erosion control, particularly in areas affected by desertification or industrial activities.
The development of biodegradable packaging materials is another key research area. With the growing concern over plastic pollution, sodium alginate offers a promising alternative for creating eco-friendly packaging solutions. Researchers are working on improving the mechanical properties, barrier characteristics, and durability of alginate-based films and coatings to meet industry standards while maintaining biodegradability.
Furthermore, the use of sodium alginate in air purification systems is an emerging field of study. Scientists are investigating its potential in capturing airborne pollutants and particulate matter, aiming to develop efficient and sustainable air filtration technologies. This research direction aligns with the global efforts to combat air pollution and improve indoor air quality.
As environmental challenges continue to evolve, so do the research objectives for sodium alginate applications. The overarching goal is to harness the full potential of this versatile biopolymer to create innovative, sustainable, and cost-effective solutions for a wide range of environmental issues. By focusing on these objectives, researchers aim to position sodium alginate as a key player in the development of next-generation environmental technologies.
The evolution of sodium alginate research has been driven by the growing need for eco-friendly solutions to address pressing environmental challenges. Its biodegradability, non-toxicity, and ability to form hydrogels have made it an attractive candidate for various environmental applications. The increasing focus on sustainable materials and green chemistry has further propelled the exploration of sodium alginate's potential in recent decades.
Current research objectives in the field of sodium alginate as an environmental tool are multifaceted and ambitious. One primary goal is to develop advanced water treatment technologies utilizing sodium alginate-based materials. This includes the creation of novel adsorbents and membranes for the removal of heavy metals, organic pollutants, and emerging contaminants from water sources. Researchers aim to enhance the efficiency, selectivity, and reusability of these materials to address the global challenge of water scarcity and pollution.
Another significant objective is the application of sodium alginate in soil remediation and agriculture. Studies are focused on developing sodium alginate-based carriers for controlled release of fertilizers and pesticides, reducing environmental impact while improving crop yields. Additionally, researchers are exploring its potential in soil stabilization and erosion control, particularly in areas affected by desertification or industrial activities.
The development of biodegradable packaging materials is another key research area. With the growing concern over plastic pollution, sodium alginate offers a promising alternative for creating eco-friendly packaging solutions. Researchers are working on improving the mechanical properties, barrier characteristics, and durability of alginate-based films and coatings to meet industry standards while maintaining biodegradability.
Furthermore, the use of sodium alginate in air purification systems is an emerging field of study. Scientists are investigating its potential in capturing airborne pollutants and particulate matter, aiming to develop efficient and sustainable air filtration technologies. This research direction aligns with the global efforts to combat air pollution and improve indoor air quality.
As environmental challenges continue to evolve, so do the research objectives for sodium alginate applications. The overarching goal is to harness the full potential of this versatile biopolymer to create innovative, sustainable, and cost-effective solutions for a wide range of environmental issues. By focusing on these objectives, researchers aim to position sodium alginate as a key player in the development of next-generation environmental technologies.
Environmental Applications Market Analysis
The market for environmental applications of sodium alginate is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and the need for sustainable solutions. Sodium alginate, derived from brown seaweed, has gained attention for its versatility and eco-friendly properties in various environmental applications.
In the water treatment sector, sodium alginate has shown promising results as a flocculant and adsorbent for removing heavy metals, dyes, and other pollutants from wastewater. The global water treatment chemicals market, which includes flocculants, is projected to grow steadily in the coming years, providing a substantial opportunity for sodium alginate-based solutions.
The soil remediation market is another area where sodium alginate is gaining traction. Its ability to form hydrogels and encapsulate beneficial microorganisms makes it an effective tool for improving soil quality and promoting plant growth in contaminated or degraded soils. As urbanization and industrial activities continue to impact soil health, the demand for eco-friendly remediation solutions is expected to rise.
In the field of air pollution control, sodium alginate is being explored for its potential in capturing and sequestering carbon dioxide. With global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions intensifying, technologies that can effectively capture and store CO2 are becoming increasingly valuable. This presents a significant opportunity for sodium alginate-based materials in the growing carbon capture and storage market.
The packaging industry is also adopting sodium alginate for the development of biodegradable and compostable materials. As consumers and regulators push for more sustainable packaging solutions, the demand for alginate-based alternatives to traditional plastics is expected to grow substantially in the coming years.
Furthermore, sodium alginate is finding applications in environmental monitoring and sensing technologies. Its ability to form responsive hydrogels makes it suitable for developing sensors that can detect and measure various environmental pollutants. This aligns with the increasing focus on real-time environmental monitoring and the growing market for smart environmental technologies.
The agriculture sector represents another significant market for sodium alginate applications. Its use in controlled-release fertilizers and as a soil conditioner is gaining attention due to the increasing need for sustainable agricultural practices and improved crop yields. The global market for biostimulants and soil amendments, which includes alginate-based products, is expected to expand as farmers seek environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional agrochemicals.
Overall, the market for environmental applications of sodium alginate is diverse and expanding. As research continues to uncover new applications and improve existing ones, the demand for sodium alginate in environmental solutions is likely to grow across multiple sectors, driven by global sustainability goals and increasing environmental regulations.
In the water treatment sector, sodium alginate has shown promising results as a flocculant and adsorbent for removing heavy metals, dyes, and other pollutants from wastewater. The global water treatment chemicals market, which includes flocculants, is projected to grow steadily in the coming years, providing a substantial opportunity for sodium alginate-based solutions.
The soil remediation market is another area where sodium alginate is gaining traction. Its ability to form hydrogels and encapsulate beneficial microorganisms makes it an effective tool for improving soil quality and promoting plant growth in contaminated or degraded soils. As urbanization and industrial activities continue to impact soil health, the demand for eco-friendly remediation solutions is expected to rise.
In the field of air pollution control, sodium alginate is being explored for its potential in capturing and sequestering carbon dioxide. With global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions intensifying, technologies that can effectively capture and store CO2 are becoming increasingly valuable. This presents a significant opportunity for sodium alginate-based materials in the growing carbon capture and storage market.
The packaging industry is also adopting sodium alginate for the development of biodegradable and compostable materials. As consumers and regulators push for more sustainable packaging solutions, the demand for alginate-based alternatives to traditional plastics is expected to grow substantially in the coming years.
Furthermore, sodium alginate is finding applications in environmental monitoring and sensing technologies. Its ability to form responsive hydrogels makes it suitable for developing sensors that can detect and measure various environmental pollutants. This aligns with the increasing focus on real-time environmental monitoring and the growing market for smart environmental technologies.
The agriculture sector represents another significant market for sodium alginate applications. Its use in controlled-release fertilizers and as a soil conditioner is gaining attention due to the increasing need for sustainable agricultural practices and improved crop yields. The global market for biostimulants and soil amendments, which includes alginate-based products, is expected to expand as farmers seek environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional agrochemicals.
Overall, the market for environmental applications of sodium alginate is diverse and expanding. As research continues to uncover new applications and improve existing ones, the demand for sodium alginate in environmental solutions is likely to grow across multiple sectors, driven by global sustainability goals and increasing environmental regulations.
Current Challenges in Sodium Alginate Research
Despite the promising potential of sodium alginate in environmental research solutions, several challenges currently hinder its widespread application and effectiveness. One of the primary obstacles is the variability in the composition and properties of sodium alginate derived from different sources. This inconsistency can lead to unpredictable performance in environmental applications, making it difficult to standardize protocols and achieve reproducible results across different studies.
Another significant challenge lies in the stability of sodium alginate under various environmental conditions. While it exhibits excellent properties in certain settings, its performance can be compromised in extreme pH levels, high temperatures, or in the presence of certain ions. This limitation restricts its use in diverse environmental scenarios and necessitates the development of more robust formulations.
The biodegradability of sodium alginate, while generally considered an advantage, can also pose challenges in long-term environmental applications. Rapid degradation may limit its effectiveness in sustained-release systems or long-term remediation projects. Conversely, in some cases, the rate of biodegradation may be too slow, potentially leading to accumulation in the environment.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness remain significant hurdles in the widespread adoption of sodium alginate-based solutions. The production of high-quality sodium alginate on an industrial scale can be expensive, and the extraction process from natural sources may have environmental implications. Developing more efficient and sustainable production methods is crucial for its broader application in environmental research and remediation.
The interaction of sodium alginate with various pollutants and environmental matrices is not fully understood. While it shows promise in adsorbing certain contaminants, its selectivity and capacity for different types of pollutants need further investigation. Additionally, the potential for sodium alginate to release adsorbed contaminants under changing environmental conditions requires thorough examination to ensure the long-term safety and efficacy of remediation efforts.
Regulatory challenges and the lack of standardized testing protocols for sodium alginate-based environmental solutions also impede their widespread adoption. The absence of clear guidelines for assessing the safety and effectiveness of these materials in environmental applications creates uncertainty for researchers and potential end-users.
Lastly, the integration of sodium alginate with other materials or technologies to enhance its performance and overcome its limitations presents both opportunities and challenges. While composite materials show promise, optimizing these combinations and understanding their long-term environmental impacts require extensive research and development efforts.
Another significant challenge lies in the stability of sodium alginate under various environmental conditions. While it exhibits excellent properties in certain settings, its performance can be compromised in extreme pH levels, high temperatures, or in the presence of certain ions. This limitation restricts its use in diverse environmental scenarios and necessitates the development of more robust formulations.
The biodegradability of sodium alginate, while generally considered an advantage, can also pose challenges in long-term environmental applications. Rapid degradation may limit its effectiveness in sustained-release systems or long-term remediation projects. Conversely, in some cases, the rate of biodegradation may be too slow, potentially leading to accumulation in the environment.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness remain significant hurdles in the widespread adoption of sodium alginate-based solutions. The production of high-quality sodium alginate on an industrial scale can be expensive, and the extraction process from natural sources may have environmental implications. Developing more efficient and sustainable production methods is crucial for its broader application in environmental research and remediation.
The interaction of sodium alginate with various pollutants and environmental matrices is not fully understood. While it shows promise in adsorbing certain contaminants, its selectivity and capacity for different types of pollutants need further investigation. Additionally, the potential for sodium alginate to release adsorbed contaminants under changing environmental conditions requires thorough examination to ensure the long-term safety and efficacy of remediation efforts.
Regulatory challenges and the lack of standardized testing protocols for sodium alginate-based environmental solutions also impede their widespread adoption. The absence of clear guidelines for assessing the safety and effectiveness of these materials in environmental applications creates uncertainty for researchers and potential end-users.
Lastly, the integration of sodium alginate with other materials or technologies to enhance its performance and overcome its limitations presents both opportunities and challenges. While composite materials show promise, optimizing these combinations and understanding their long-term environmental impacts require extensive research and development efforts.
Existing Environmental Solutions Using Sodium Alginate
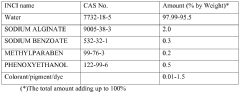
01 Use of sodium alginate in drug delivery systems
Sodium alginate is utilized in various drug delivery systems due to its biocompatibility and ability to form gels. It can be used to encapsulate drugs, control release rates, and improve drug stability. This versatile polymer is particularly useful in developing oral, topical, and injectable formulations.- Use of sodium alginate in drug delivery systems: Sodium alginate is utilized in various drug delivery systems due to its biocompatibility and ability to form gels. It can be used to encapsulate drugs, control release rates, and improve drug stability. This versatile polymer is particularly useful in developing oral, topical, and injectable formulations.
- Sodium alginate in wound healing applications: Sodium alginate is employed in wound dressings and healing products due to its moisture-retaining properties and ability to create a protective barrier. It can absorb wound exudates, maintain a moist environment conducive to healing, and facilitate the removal of dressings without damaging newly formed tissue.
- Sodium alginate as a thickening and stabilizing agent: In food and cosmetic industries, sodium alginate serves as an effective thickening and stabilizing agent. It can improve texture, viscosity, and emulsion stability in various products such as sauces, creams, and lotions. Its ability to form gels in the presence of calcium ions is particularly useful in creating structured food products.
- Sodium alginate in 3D bioprinting and tissue engineering: Sodium alginate is used as a bioink component in 3D bioprinting applications and tissue engineering. Its ability to form hydrogels that can encapsulate cells makes it suitable for creating scaffolds and structures that mimic natural tissues. This polymer can be used to print complex tissue-like structures with controlled porosity and mechanical properties.
- Sodium alginate in environmental applications: Sodium alginate finds applications in environmental remediation and water treatment processes. It can be used as an adsorbent for heavy metal removal from wastewater, as a flocculant in water purification, and in the development of biodegradable packaging materials. Its biodegradability and non-toxicity make it an eco-friendly choice for various environmental applications.
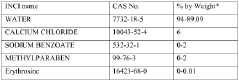
02 Sodium alginate in wound healing applications
Sodium alginate is employed in wound dressings and healing products due to its moisture-retention properties and ability to create a protective barrier. It can absorb wound exudates, maintain a moist environment conducive to healing, and facilitate the removal of dressings without damaging newly formed tissue.Expand Specific Solutions03 Sodium alginate as a thickening and stabilizing agent
In food and cosmetic industries, sodium alginate serves as an effective thickening and stabilizing agent. It can improve texture, viscosity, and emulsion stability in various products such as sauces, creams, and lotions. Its ability to form gels in the presence of calcium ions is particularly useful in creating unique textures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sodium alginate in 3D bioprinting and tissue engineering
Sodium alginate is utilized in 3D bioprinting and tissue engineering applications due to its biocompatibility and ability to form hydrogels. It can be used as a bioink to create scaffolds for cell growth and tissue regeneration. The polymer's properties allow for the creation of complex structures that mimic natural tissue environments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sodium alginate in environmental applications
Sodium alginate finds use in environmental applications such as water treatment and soil remediation. It can act as a flocculant to remove contaminants from water and as a soil conditioner to improve water retention and nutrient availability. Its biodegradability makes it an eco-friendly option for various environmental solutions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Alginate Research
The research on sodium alginate as an environmental solution tool is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for sodium alginate is expanding, driven by its versatile applications in environmental remediation, water treatment, and sustainable materials. The technology's maturity varies across different applications, with some areas more developed than others. Key players in this field include Solvay SA, a major chemical company with expertise in alginate production, and Alginor ASA, specializing in seaweed-based solutions. Academic institutions like the Ocean University of China and the National University of Singapore are contributing to research advancements, while companies such as Qingdao Bright Moon Seaweed Group Co., Ltd. are focusing on industrial-scale production and applications.
Alginor ASA
Technical Solution: Alginor ASA has developed a biorefinery process for the complete utilization of brown algae, focusing on sodium alginate extraction. Their proprietary AORTA™ technology enables the production of high-quality sodium alginate with controlled molecular weight and viscosity[1]. This process allows for the extraction of multiple valuable compounds from seaweed, including alginates, while minimizing waste. The company has also invested in sustainable harvesting practices to ensure a consistent supply of raw materials[2]. Their research extends to the application of sodium alginate in various environmental solutions, such as water treatment, soil remediation, and biodegradable packaging materials[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive biorefinery approach, sustainable harvesting practices, and diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Dependence on seaweed availability and potential environmental concerns related to large-scale harvesting.
Qingdao Bright Moon Seaweed Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Qingdao Bright Moon Seaweed Group Co., Ltd. has developed advanced extraction and purification techniques for sodium alginate production from various seaweed species. Their research focuses on optimizing the extraction process to enhance the yield and quality of sodium alginate[1]. The company has invested in developing environmentally friendly extraction methods that reduce chemical usage and energy consumption[2]. They have also explored the application of sodium alginate in wastewater treatment, particularly for heavy metal removal and oil spill cleanup[3]. Additionally, the company has conducted research on the use of sodium alginate in soil improvement and as a carrier for controlled-release fertilizers[4].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, diverse seaweed sources, and a wide range of environmental applications. Weaknesses: Potential competition from synthetic alternatives and dependence on seaweed cultivation areas.
Innovative Alginate Modifications for Environmental Use
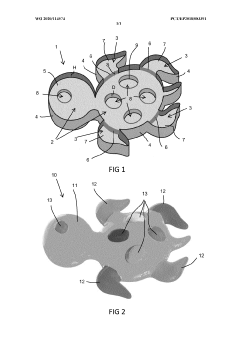
Method for casting a gel object
PatentWO2020114574A1
Innovation
- A method involving a casting mould with separate sub-volumes and two gel-forming compositions, one containing sodium alginate and the other calcium chloride, allowing for rapid gel formation and creation of multi-colored objects, along with a kit-of-parts including colorants and additives for a safe and food-grade gel experience.
Regulatory Framework for Alginate in Environmental Research
The regulatory framework for alginate in environmental research is a complex and evolving landscape that encompasses various national and international guidelines, standards, and policies. At the forefront of this framework are environmental protection agencies, such as the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Environment Agency (EEA), which play crucial roles in setting standards and monitoring the use of alginate in environmental applications.
In the United States, the EPA has established specific guidelines for the use of alginate in environmental remediation projects, particularly in the context of soil and water treatment. These guidelines outline the permissible concentrations of alginate in different environmental matrices and specify the approved methods for its application. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also contributes to the regulatory framework by overseeing the safety aspects of alginate when used in applications that may indirectly affect food or water sources.
On the international stage, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has developed guidelines for testing the environmental fate and behavior of substances, including alginate. These guidelines provide standardized methods for assessing the biodegradability, bioaccumulation potential, and ecotoxicity of alginate in various environmental compartments.
The European Union has implemented the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, which applies to alginate when used in environmental research and applications. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers of alginate are required to register the substance and provide detailed information on its properties, potential risks, and safe use practices.
In addition to these overarching regulations, many countries have their own specific requirements for the use of alginate in environmental research. For instance, Canada's Environmental Protection Act includes provisions for the assessment and management of substances used in environmental applications, which would encompass alginate-based solutions.
The regulatory framework also extends to the disposal and environmental release of alginate-containing materials. Waste management regulations in many jurisdictions classify alginate-based products used in environmental research as special waste, requiring specific handling and disposal procedures to minimize environmental impact.
As environmental research involving alginate continues to advance, regulatory bodies are actively working to update and refine their frameworks. This ongoing process aims to strike a balance between promoting innovative environmental solutions and ensuring the protection of ecosystems and human health. Researchers and organizations working with alginate must stay informed about these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maximize the potential of alginate as a tool for environmental research solutions.
In the United States, the EPA has established specific guidelines for the use of alginate in environmental remediation projects, particularly in the context of soil and water treatment. These guidelines outline the permissible concentrations of alginate in different environmental matrices and specify the approved methods for its application. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also contributes to the regulatory framework by overseeing the safety aspects of alginate when used in applications that may indirectly affect food or water sources.
On the international stage, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has developed guidelines for testing the environmental fate and behavior of substances, including alginate. These guidelines provide standardized methods for assessing the biodegradability, bioaccumulation potential, and ecotoxicity of alginate in various environmental compartments.
The European Union has implemented the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, which applies to alginate when used in environmental research and applications. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers of alginate are required to register the substance and provide detailed information on its properties, potential risks, and safe use practices.
In addition to these overarching regulations, many countries have their own specific requirements for the use of alginate in environmental research. For instance, Canada's Environmental Protection Act includes provisions for the assessment and management of substances used in environmental applications, which would encompass alginate-based solutions.
The regulatory framework also extends to the disposal and environmental release of alginate-containing materials. Waste management regulations in many jurisdictions classify alginate-based products used in environmental research as special waste, requiring specific handling and disposal procedures to minimize environmental impact.
As environmental research involving alginate continues to advance, regulatory bodies are actively working to update and refine their frameworks. This ongoing process aims to strike a balance between promoting innovative environmental solutions and ensuring the protection of ecosystems and human health. Researchers and organizations working with alginate must stay informed about these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maximize the potential of alginate as a tool for environmental research solutions.
Sustainability Impact of Sodium Alginate Solutions
The sustainability impact of sodium alginate solutions in environmental research is significant and multifaceted. Sodium alginate, derived from brown seaweed, offers a range of eco-friendly applications that contribute to sustainable practices across various industries. Its biodegradability and non-toxic nature make it an attractive alternative to synthetic materials, reducing environmental pollution and waste accumulation.
In water treatment, sodium alginate serves as an effective flocculant and adsorbent for removing heavy metals and other pollutants from wastewater. This application not only improves water quality but also reduces the need for harsh chemical treatments, minimizing the environmental footprint of water purification processes. The use of sodium alginate in this context aligns with circular economy principles, as it repurposes a natural resource for environmental remediation.
Soil remediation is another area where sodium alginate demonstrates substantial sustainability benefits. When used as a soil amendment, it enhances soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability. This leads to improved crop yields and reduced water consumption in agriculture, addressing food security concerns while conserving water resources. Additionally, sodium alginate's ability to immobilize contaminants in soil contributes to the restoration of polluted land, making it suitable for sustainable land management practices.
In the field of air quality improvement, sodium alginate-based materials show promise as efficient air filters. These filters can capture particulate matter and other airborne pollutants, contributing to cleaner air in both indoor and outdoor environments. The biodegradability of these filters also ensures that they do not contribute to long-term waste accumulation, unlike many synthetic filter materials.
The production of sodium alginate itself has a relatively low environmental impact compared to many synthetic materials. Seaweed cultivation for alginate extraction can be done sustainably, with minimal use of fertilizers or freshwater resources. Moreover, seaweed farming can contribute to carbon sequestration, potentially offsetting some of the carbon emissions associated with alginate production and processing.
In the context of sustainable packaging, sodium alginate-based materials offer biodegradable alternatives to conventional plastics. These materials can be used to create food packaging, coatings, and films that decompose naturally, reducing plastic pollution in landfills and oceans. This application aligns with global efforts to reduce single-use plastics and promote circular economy principles in packaging design.
The versatility of sodium alginate in environmental applications extends to its potential in developing sustainable energy solutions. Research into alginate-based materials for energy storage, such as in batteries or supercapacitors, could contribute to the advancement of renewable energy technologies, further enhancing its role in sustainable development.
In water treatment, sodium alginate serves as an effective flocculant and adsorbent for removing heavy metals and other pollutants from wastewater. This application not only improves water quality but also reduces the need for harsh chemical treatments, minimizing the environmental footprint of water purification processes. The use of sodium alginate in this context aligns with circular economy principles, as it repurposes a natural resource for environmental remediation.
Soil remediation is another area where sodium alginate demonstrates substantial sustainability benefits. When used as a soil amendment, it enhances soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability. This leads to improved crop yields and reduced water consumption in agriculture, addressing food security concerns while conserving water resources. Additionally, sodium alginate's ability to immobilize contaminants in soil contributes to the restoration of polluted land, making it suitable for sustainable land management practices.
In the field of air quality improvement, sodium alginate-based materials show promise as efficient air filters. These filters can capture particulate matter and other airborne pollutants, contributing to cleaner air in both indoor and outdoor environments. The biodegradability of these filters also ensures that they do not contribute to long-term waste accumulation, unlike many synthetic filter materials.
The production of sodium alginate itself has a relatively low environmental impact compared to many synthetic materials. Seaweed cultivation for alginate extraction can be done sustainably, with minimal use of fertilizers or freshwater resources. Moreover, seaweed farming can contribute to carbon sequestration, potentially offsetting some of the carbon emissions associated with alginate production and processing.
In the context of sustainable packaging, sodium alginate-based materials offer biodegradable alternatives to conventional plastics. These materials can be used to create food packaging, coatings, and films that decompose naturally, reducing plastic pollution in landfills and oceans. This application aligns with global efforts to reduce single-use plastics and promote circular economy principles in packaging design.
The versatility of sodium alginate in environmental applications extends to its potential in developing sustainable energy solutions. Research into alginate-based materials for energy storage, such as in batteries or supercapacitors, could contribute to the advancement of renewable energy technologies, further enhancing its role in sustainable development.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!