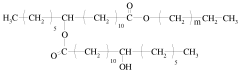
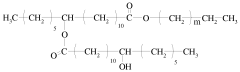
How Sodium Alginate Enhances Product Developments in Cosmetics?
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Alginate in Cosmetics: Background and Objectives
Sodium alginate, a versatile polysaccharide derived from brown seaweed, has emerged as a key ingredient in cosmetic formulations over the past few decades. Its unique properties have revolutionized product development in the cosmetics industry, offering innovative solutions to long-standing challenges in texture, stability, and efficacy.
The journey of sodium alginate in cosmetics began in the mid-20th century when researchers first recognized its potential as a thickening and stabilizing agent. Initially used primarily in food and pharmaceutical industries, its application in cosmetics gained momentum in the 1980s as formulators sought natural, biodegradable alternatives to synthetic ingredients.
As consumer demand for clean and green beauty products surged in the early 2000s, sodium alginate's popularity in cosmetics skyrocketed. Its natural origin, coupled with its multifunctional properties, aligned perfectly with the industry's shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly formulations. This trend has continued to accelerate, with sodium alginate now being a staple ingredient in a wide range of cosmetic products, from skincare to hair care.
The evolution of sodium alginate in cosmetics has been marked by continuous innovation and research. Early applications focused on its gelling and thickening properties, primarily in creams and lotions. However, as technology advanced, formulators discovered its potential in creating novel textures, enhancing product stability, and even in developing smart delivery systems for active ingredients.
Today, the objectives of sodium alginate use in cosmetics extend far beyond its initial applications. Researchers and product developers are exploring its potential in creating responsive and adaptable formulations that can adjust to environmental conditions or skin needs. There is also growing interest in leveraging sodium alginate's film-forming properties to develop long-lasting and water-resistant cosmetic products.
Furthermore, the cosmetics industry is increasingly focusing on the synergistic effects of sodium alginate with other ingredients. This includes its role in enhancing the efficacy of active ingredients and its potential in developing multi-functional cosmetic products that can address multiple skin or hair concerns simultaneously.
As we look to the future, the trajectory of sodium alginate in cosmetics points towards even more sophisticated applications. The industry aims to harness its properties for developing smart cosmetics, personalized formulations, and products that can adapt to individual skin types and environmental conditions. This aligns with the broader trend of precision cosmetics and the growing consumer demand for tailored beauty solutions.
The journey of sodium alginate in cosmetics began in the mid-20th century when researchers first recognized its potential as a thickening and stabilizing agent. Initially used primarily in food and pharmaceutical industries, its application in cosmetics gained momentum in the 1980s as formulators sought natural, biodegradable alternatives to synthetic ingredients.
As consumer demand for clean and green beauty products surged in the early 2000s, sodium alginate's popularity in cosmetics skyrocketed. Its natural origin, coupled with its multifunctional properties, aligned perfectly with the industry's shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly formulations. This trend has continued to accelerate, with sodium alginate now being a staple ingredient in a wide range of cosmetic products, from skincare to hair care.
The evolution of sodium alginate in cosmetics has been marked by continuous innovation and research. Early applications focused on its gelling and thickening properties, primarily in creams and lotions. However, as technology advanced, formulators discovered its potential in creating novel textures, enhancing product stability, and even in developing smart delivery systems for active ingredients.
Today, the objectives of sodium alginate use in cosmetics extend far beyond its initial applications. Researchers and product developers are exploring its potential in creating responsive and adaptable formulations that can adjust to environmental conditions or skin needs. There is also growing interest in leveraging sodium alginate's film-forming properties to develop long-lasting and water-resistant cosmetic products.
Furthermore, the cosmetics industry is increasingly focusing on the synergistic effects of sodium alginate with other ingredients. This includes its role in enhancing the efficacy of active ingredients and its potential in developing multi-functional cosmetic products that can address multiple skin or hair concerns simultaneously.
As we look to the future, the trajectory of sodium alginate in cosmetics points towards even more sophisticated applications. The industry aims to harness its properties for developing smart cosmetics, personalized formulations, and products that can adapt to individual skin types and environmental conditions. This aligns with the broader trend of precision cosmetics and the growing consumer demand for tailored beauty solutions.
Market Demand Analysis for Alginate-Based Cosmetics
The global cosmetics market has witnessed a significant shift towards natural and sustainable ingredients, with sodium alginate emerging as a key player in this trend. Market research indicates a growing demand for alginate-based cosmetics, driven by consumer preferences for eco-friendly, plant-derived products. The market size for alginate-based cosmetics is projected to expand rapidly, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding industry averages over the next five years.
Consumer awareness of the benefits of sodium alginate in skincare and haircare products has been steadily increasing. This natural polysaccharide, derived from brown seaweed, is valued for its moisturizing, thickening, and stabilizing properties. The rise in demand is particularly notable in facial masks, anti-aging creams, and hair styling products, where sodium alginate's ability to form gels and films is highly prized.
The Asia-Pacific region, especially countries like South Korea and Japan, leads the market demand for alginate-based cosmetics. These markets have a strong tradition of using seaweed-derived ingredients in beauty products and are at the forefront of innovative cosmetic formulations. North America and Europe are also experiencing substantial growth in this sector, driven by the clean beauty movement and increasing consumer interest in marine-based ingredients.
Environmental concerns and sustainability goals are major factors fueling the demand for sodium alginate in cosmetics. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, they are seeking alternatives to synthetic ingredients and microplastics. Sodium alginate, being biodegradable and sourced from renewable marine resources, aligns perfectly with these consumer values.
The versatility of sodium alginate is another key driver of its market demand. It can be used in a wide range of cosmetic products, from cleansers and toners to more complex formulations like sunscreens and color cosmetics. This versatility allows cosmetic manufacturers to innovate across multiple product categories, expanding their alginate-based offerings.
However, the market also faces challenges. The supply chain for sodium alginate can be sensitive to environmental factors affecting seaweed harvests. Additionally, there is growing competition from other natural hydrocolloids and the need for consistent quality in raw materials. Despite these challenges, the overall market trajectory remains positive, with technological advancements in extraction and purification processes expected to further boost the quality and availability of sodium alginate for cosmetic applications.
Consumer awareness of the benefits of sodium alginate in skincare and haircare products has been steadily increasing. This natural polysaccharide, derived from brown seaweed, is valued for its moisturizing, thickening, and stabilizing properties. The rise in demand is particularly notable in facial masks, anti-aging creams, and hair styling products, where sodium alginate's ability to form gels and films is highly prized.
The Asia-Pacific region, especially countries like South Korea and Japan, leads the market demand for alginate-based cosmetics. These markets have a strong tradition of using seaweed-derived ingredients in beauty products and are at the forefront of innovative cosmetic formulations. North America and Europe are also experiencing substantial growth in this sector, driven by the clean beauty movement and increasing consumer interest in marine-based ingredients.
Environmental concerns and sustainability goals are major factors fueling the demand for sodium alginate in cosmetics. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, they are seeking alternatives to synthetic ingredients and microplastics. Sodium alginate, being biodegradable and sourced from renewable marine resources, aligns perfectly with these consumer values.
The versatility of sodium alginate is another key driver of its market demand. It can be used in a wide range of cosmetic products, from cleansers and toners to more complex formulations like sunscreens and color cosmetics. This versatility allows cosmetic manufacturers to innovate across multiple product categories, expanding their alginate-based offerings.
However, the market also faces challenges. The supply chain for sodium alginate can be sensitive to environmental factors affecting seaweed harvests. Additionally, there is growing competition from other natural hydrocolloids and the need for consistent quality in raw materials. Despite these challenges, the overall market trajectory remains positive, with technological advancements in extraction and purification processes expected to further boost the quality and availability of sodium alginate for cosmetic applications.
Current State and Challenges in Sodium Alginate Application
Sodium alginate has gained significant traction in the cosmetics industry due to its versatile properties and natural origin. Currently, it is widely used as a thickening agent, emulsifier, and stabilizer in various cosmetic formulations. The application of sodium alginate in skincare products, particularly in face masks and creams, has shown promising results in improving skin hydration and elasticity.
However, the current state of sodium alginate application in cosmetics faces several challenges. One of the primary issues is the variability in quality and purity of commercially available sodium alginate. This inconsistency can lead to unpredictable performance in final products, affecting their stability and efficacy. Manufacturers often struggle to maintain consistent product quality across batches due to these variations.
Another significant challenge is the limited solubility of sodium alginate in certain formulations. While it dissolves well in water, its compatibility with oil-based ingredients can be problematic, restricting its use in some cosmetic applications. This limitation has prompted researchers to explore chemical modifications and blending techniques to enhance its versatility.
The cosmetics industry is also grappling with the challenge of incorporating sodium alginate into more sophisticated delivery systems. While it has shown potential in encapsulation and controlled release of active ingredients, optimizing these systems for various cosmetic formulations remains a complex task. Researchers are working on developing advanced techniques to improve the stability and efficacy of sodium alginate-based delivery systems in diverse cosmetic products.
Furthermore, the increasing demand for natural and sustainable ingredients in cosmetics has put pressure on the sodium alginate supply chain. Ensuring a consistent and sustainable source of high-quality sodium alginate, derived from seaweed, is becoming increasingly challenging. This has led to efforts in developing alternative production methods and exploring new algal sources to meet the growing demand.
Regulatory compliance presents another hurdle in the widespread adoption of sodium alginate in cosmetics. While generally recognized as safe, the regulatory landscape for its use in different cosmetic applications varies across regions. Manufacturers must navigate these regulatory differences to ensure compliance in global markets.
Lastly, there is an ongoing challenge in fully understanding and harnessing the potential of sodium alginate in advanced cosmetic applications. While its basic properties are well-known, research into its interactions with other cosmetic ingredients, its long-term effects on skin health, and its potential in innovative formulations is still evolving. This gap in knowledge presents both a challenge and an opportunity for further research and development in the cosmetics industry.
However, the current state of sodium alginate application in cosmetics faces several challenges. One of the primary issues is the variability in quality and purity of commercially available sodium alginate. This inconsistency can lead to unpredictable performance in final products, affecting their stability and efficacy. Manufacturers often struggle to maintain consistent product quality across batches due to these variations.
Another significant challenge is the limited solubility of sodium alginate in certain formulations. While it dissolves well in water, its compatibility with oil-based ingredients can be problematic, restricting its use in some cosmetic applications. This limitation has prompted researchers to explore chemical modifications and blending techniques to enhance its versatility.
The cosmetics industry is also grappling with the challenge of incorporating sodium alginate into more sophisticated delivery systems. While it has shown potential in encapsulation and controlled release of active ingredients, optimizing these systems for various cosmetic formulations remains a complex task. Researchers are working on developing advanced techniques to improve the stability and efficacy of sodium alginate-based delivery systems in diverse cosmetic products.
Furthermore, the increasing demand for natural and sustainable ingredients in cosmetics has put pressure on the sodium alginate supply chain. Ensuring a consistent and sustainable source of high-quality sodium alginate, derived from seaweed, is becoming increasingly challenging. This has led to efforts in developing alternative production methods and exploring new algal sources to meet the growing demand.
Regulatory compliance presents another hurdle in the widespread adoption of sodium alginate in cosmetics. While generally recognized as safe, the regulatory landscape for its use in different cosmetic applications varies across regions. Manufacturers must navigate these regulatory differences to ensure compliance in global markets.
Lastly, there is an ongoing challenge in fully understanding and harnessing the potential of sodium alginate in advanced cosmetic applications. While its basic properties are well-known, research into its interactions with other cosmetic ingredients, its long-term effects on skin health, and its potential in innovative formulations is still evolving. This gap in knowledge presents both a challenge and an opportunity for further research and development in the cosmetics industry.
Existing Sodium Alginate Formulations in Cosmetics
01 Improved drug delivery systems using sodium alginate
Sodium alginate is utilized in advanced drug delivery systems to enhance the controlled release and bioavailability of various pharmaceuticals. These formulations often involve the creation of hydrogels or microspheres that can encapsulate drugs and provide sustained release profiles. The use of sodium alginate in this context can improve drug efficacy and reduce side effects.- Improved drug delivery systems: Sodium alginate is used to enhance drug delivery systems, particularly for controlled release formulations. It can be combined with other polymers or materials to create matrices that provide sustained release of active ingredients. This approach improves bioavailability and reduces dosing frequency, enhancing the overall efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
- Enhanced wound healing applications: Sodium alginate is utilized in advanced wound dressings and healing products. Its ability to absorb exudates, maintain a moist environment, and promote tissue regeneration is enhanced through various formulations and combinations with other materials. These improvements result in faster healing times and reduced risk of infection in wound care applications.
- Improved food and beverage applications: In the food industry, sodium alginate products are enhanced to provide better texture, stability, and functional properties. Modifications in molecular weight, cross-linking, or combination with other hydrocolloids result in improved gelling, thickening, and emulsifying capabilities. These enhancements lead to better quality and longer shelf life in various food and beverage products.
- Advanced cosmetic formulations: Sodium alginate is used to enhance cosmetic products by improving their texture, stability, and skin-feel properties. Modified forms of sodium alginate or its combinations with other ingredients can lead to better moisturizing effects, improved film-forming capabilities, and enhanced delivery of active ingredients in skincare and haircare products.
- Environmental and industrial applications: Sodium alginate products are enhanced for various environmental and industrial applications. These include improved water treatment processes, enhanced oil recovery techniques, and advanced materials for 3D printing and tissue engineering. Modifications in the alginate structure or its combinations with other materials lead to better performance in these diverse applications.
02 Enhanced wound healing and tissue engineering applications
Sodium alginate-based materials are being developed for improved wound dressings and tissue engineering scaffolds. These materials can absorb wound exudates, maintain a moist environment, and promote tissue regeneration. Modifications to sodium alginate, such as crosslinking or blending with other polymers, can enhance its mechanical properties and biocompatibility for these applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Food and beverage industry applications
Innovations in sodium alginate use for the food and beverage industry focus on improving texture, stability, and shelf-life of products. This includes the development of novel emulsifiers, thickeners, and gelling agents based on sodium alginate. These enhancements can lead to better quality and longer-lasting food products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental applications and water treatment
Sodium alginate is being explored for various environmental applications, particularly in water treatment processes. This includes the development of adsorbents for heavy metal removal, flocculants for wastewater treatment, and materials for oil spill cleanup. The biodegradability and non-toxicity of sodium alginate make it an attractive option for eco-friendly solutions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Nanotechnology and composite materials
Sodium alginate is being incorporated into nanotechnology and composite material development. This includes the creation of nanofibers, nanoparticles, and hybrid materials that combine sodium alginate with other substances like graphene or metal oxides. These advanced materials can have applications in areas such as electronics, sensors, and biomedical engineering.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sodium Alginate Cosmetic Development
The sodium alginate market in cosmetics is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for natural and sustainable ingredients. The global market size is expanding, with major players like Beiersdorf AG, L'Oréal SA, and Colgate-Palmolive Co. investing in alginate-based product development. Technological advancements by companies such as FMC Corp. and Nagase ChemteX Corp. are enhancing the efficacy and versatility of sodium alginate in cosmetic formulations. Research institutions like Ocean University of China and Guangdong Ocean University are contributing to the scientific understanding of alginate properties, further accelerating innovation in this field. The technology is maturing rapidly, with a growing number of patents and product launches indicating increased commercial viability and market adoption.
Beiersdorf AG
Technical Solution: Beiersdorf AG has incorporated sodium alginate into various skincare formulations to enhance product performance. Their research has focused on utilizing sodium alginate's film-forming properties to create long-lasting, water-resistant sunscreens and moisturizers[13]. Beiersdorf has developed sodium alginate-based gel formulations that provide a cooling effect and improved skin hydration for after-sun products[14]. They have also explored the use of sodium alginate as a natural alternative to synthetic thickeners in cleansing products, offering improved texture and mildness[15]. Beiersdorf's innovations include sodium alginate complexes that help to stabilize emulsions and improve the delivery of oil-soluble active ingredients in skincare products[16].
Strengths: Strong brand recognition (e.g., NIVEA), extensive consumer research capabilities. Weaknesses: Highly competitive skincare market, potential challenges in natural ingredient sourcing and sustainability.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has integrated sodium alginate into its cosmetic and personal care product lines to enhance performance and sustainability. Their research has focused on developing sodium alginate-based formulations for hair styling products that provide strong hold while maintaining a natural feel[17]. Henkel has also explored the use of sodium alginate as a rheology modifier in liquid soaps and shower gels, improving texture and stability[18]. In skincare, Henkel has developed sodium alginate complexes that form a protective barrier on the skin, helping to reduce irritation and improve moisturization[19]. Their innovations include sodium alginate-based microencapsulation technologies for fragrance delivery in personal care products, providing long-lasting scent release[20].
Strengths: Diverse product portfolio, strong presence in both consumer and professional markets. Weaknesses: Intense competition in personal care sector, potential challenges in raw material cost fluctuations.
Innovative Sodium Alginate Applications in Skincare
Kit comprising an alginate and a complexing agent in the form of a water-insoluble salt
PatentWO2009080627A2
Innovation
- A kit comprising a first composition with an alginic acid-based compound and a water-insoluble complexing agent salt, and a second composition with an acid, both including film-forming polymers, which form a gas-releasing gel upon application, providing a volumizing effect and allowing easy removal with a chelating agent.
Kit comprising an alginate and a complexing agent in the form of a water-soluble salt
PatentWO2009080628A2
Innovation
- A kit comprising a first composition with an alginic acid-based compound and a gas-releasing water-soluble salt, and a second composition with an acid and a complexing agent, applied in alternating coats to create a volumizing effect on keratin materials, with the option to remove the film using a sequestrant.
Regulatory Framework for Alginate in Cosmetic Products
The regulatory framework for alginate in cosmetic products is a critical aspect of product development and market entry. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of sodium alginate in cosmetics under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. The FDA classifies sodium alginate as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food and cosmetic products, allowing its incorporation into various formulations.
In the European Union, the use of sodium alginate in cosmetics is regulated by the European Commission's Cosmetic Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009. This regulation ensures the safety of cosmetic products and their ingredients. Sodium alginate is listed in the EU's database of cosmetic ingredients (CosIng) with the reference number 1301, indicating its approval for use in cosmetic formulations.
The International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) recognizes sodium alginate under the name "Algin," facilitating its identification in product labeling across different markets. This standardization helps manufacturers comply with global labeling requirements and enables consumers to make informed choices.
Japan's regulatory body, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, includes sodium alginate in its list of approved cosmetic ingredients. The Japanese Standards for Cosmetic Ingredients (JSCI) provides guidelines for the use of alginate in cosmetic products, ensuring compliance with safety and quality standards.
In China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) regulates cosmetic ingredients. Sodium alginate is included in the Inventory of Existing Cosmetic Ingredients in China (IECIC), allowing its use in cosmetic formulations subject to specific concentration limits and application types.
Globally, the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel has evaluated the safety of algin and related alginate compounds for use in cosmetics. Their assessment concluded that these ingredients are safe in the present practices of use and concentration in cosmetic formulations.
Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) when incorporating sodium alginate into cosmetic products. This ensures the quality, safety, and efficacy of the final product. Additionally, many regulatory bodies require stability testing and preservative efficacy testing for cosmetic formulations containing sodium alginate to guarantee product integrity throughout its shelf life.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in cosmetic regulations, the sourcing of sodium alginate from seaweed is viewed favorably. Many regulatory frameworks are beginning to incorporate guidelines for sustainable sourcing and biodegradability of cosmetic ingredients, which may impact future regulations surrounding alginate use in cosmetics.
In the European Union, the use of sodium alginate in cosmetics is regulated by the European Commission's Cosmetic Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009. This regulation ensures the safety of cosmetic products and their ingredients. Sodium alginate is listed in the EU's database of cosmetic ingredients (CosIng) with the reference number 1301, indicating its approval for use in cosmetic formulations.
The International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) recognizes sodium alginate under the name "Algin," facilitating its identification in product labeling across different markets. This standardization helps manufacturers comply with global labeling requirements and enables consumers to make informed choices.
Japan's regulatory body, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, includes sodium alginate in its list of approved cosmetic ingredients. The Japanese Standards for Cosmetic Ingredients (JSCI) provides guidelines for the use of alginate in cosmetic products, ensuring compliance with safety and quality standards.
In China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) regulates cosmetic ingredients. Sodium alginate is included in the Inventory of Existing Cosmetic Ingredients in China (IECIC), allowing its use in cosmetic formulations subject to specific concentration limits and application types.
Globally, the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel has evaluated the safety of algin and related alginate compounds for use in cosmetics. Their assessment concluded that these ingredients are safe in the present practices of use and concentration in cosmetic formulations.
Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) when incorporating sodium alginate into cosmetic products. This ensures the quality, safety, and efficacy of the final product. Additionally, many regulatory bodies require stability testing and preservative efficacy testing for cosmetic formulations containing sodium alginate to guarantee product integrity throughout its shelf life.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in cosmetic regulations, the sourcing of sodium alginate from seaweed is viewed favorably. Many regulatory frameworks are beginning to incorporate guidelines for sustainable sourcing and biodegradability of cosmetic ingredients, which may impact future regulations surrounding alginate use in cosmetics.
Sustainability Aspects of Sodium Alginate in Cosmetics
Sodium alginate, derived from brown seaweed, has gained significant attention in the cosmetics industry due to its sustainable and eco-friendly properties. As consumers become increasingly conscious of environmental issues, the sustainability aspects of sodium alginate have become a crucial factor in product development and marketing strategies.
One of the primary sustainability advantages of sodium alginate is its renewable source. Brown seaweed, from which sodium alginate is extracted, grows rapidly and does not require land, freshwater, or fertilizers for cultivation. This makes it a highly sustainable alternative to synthetic ingredients, reducing the environmental impact of cosmetic production.
The harvesting process of seaweed for sodium alginate production is generally considered environmentally friendly. Many seaweed farms employ sustainable harvesting techniques that allow for natural regeneration, ensuring the long-term viability of seaweed populations. This approach aligns with the principles of circular economy and responsible resource management.
In terms of biodegradability, sodium alginate offers significant benefits. Unlike many synthetic polymers used in cosmetics, sodium alginate is naturally biodegradable and does not contribute to microplastic pollution in aquatic ecosystems. This characteristic is particularly important as the cosmetics industry faces increasing scrutiny over its environmental impact.
The production process of sodium alginate is relatively low-impact compared to many synthetic ingredients. It requires minimal chemical processing and energy input, further reducing its carbon footprint. Additionally, the extraction process generates minimal waste, as most of the seaweed biomass can be utilized for various purposes.
Sodium alginate's versatility in cosmetic formulations also contributes to its sustainability profile. Its ability to replace multiple synthetic ingredients in a single formulation can lead to simplified product compositions, potentially reducing the overall environmental impact of the final product.
Furthermore, the use of sodium alginate in cosmetics supports sustainable seaweed farming practices, which can have positive environmental effects. Seaweed farms can act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate climate change. They also provide habitats for marine life, contributing to biodiversity conservation.
As the cosmetics industry moves towards more sustainable practices, sodium alginate's eco-friendly properties position it as a key ingredient for future product developments. Its use aligns with the growing consumer demand for natural, sustainable, and environmentally responsible cosmetic products.
One of the primary sustainability advantages of sodium alginate is its renewable source. Brown seaweed, from which sodium alginate is extracted, grows rapidly and does not require land, freshwater, or fertilizers for cultivation. This makes it a highly sustainable alternative to synthetic ingredients, reducing the environmental impact of cosmetic production.
The harvesting process of seaweed for sodium alginate production is generally considered environmentally friendly. Many seaweed farms employ sustainable harvesting techniques that allow for natural regeneration, ensuring the long-term viability of seaweed populations. This approach aligns with the principles of circular economy and responsible resource management.
In terms of biodegradability, sodium alginate offers significant benefits. Unlike many synthetic polymers used in cosmetics, sodium alginate is naturally biodegradable and does not contribute to microplastic pollution in aquatic ecosystems. This characteristic is particularly important as the cosmetics industry faces increasing scrutiny over its environmental impact.
The production process of sodium alginate is relatively low-impact compared to many synthetic ingredients. It requires minimal chemical processing and energy input, further reducing its carbon footprint. Additionally, the extraction process generates minimal waste, as most of the seaweed biomass can be utilized for various purposes.
Sodium alginate's versatility in cosmetic formulations also contributes to its sustainability profile. Its ability to replace multiple synthetic ingredients in a single formulation can lead to simplified product compositions, potentially reducing the overall environmental impact of the final product.
Furthermore, the use of sodium alginate in cosmetics supports sustainable seaweed farming practices, which can have positive environmental effects. Seaweed farms can act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate climate change. They also provide habitats for marine life, contributing to biodiversity conservation.
As the cosmetics industry moves towards more sustainable practices, sodium alginate's eco-friendly properties position it as a key ingredient for future product developments. Its use aligns with the growing consumer demand for natural, sustainable, and environmentally responsible cosmetic products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!