How Sodium Alginate Supports Scalable Food Manufacturing Methods?
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Alginate in Food Manufacturing: Background and Objectives
Sodium alginate, a versatile polysaccharide derived from brown algae, has emerged as a crucial ingredient in modern food manufacturing processes. Its unique properties have revolutionized the way food products are developed, produced, and scaled for mass consumption. The journey of sodium alginate in the food industry began in the mid-20th century when its potential as a thickening and gelling agent was first recognized.
Over the years, the applications of sodium alginate in food manufacturing have expanded significantly, driven by the increasing demand for innovative food products and the need for more efficient production methods. The evolution of this technology has been marked by continuous research and development, leading to a deeper understanding of its molecular structure and functional properties.
The primary objective of utilizing sodium alginate in food manufacturing is to enhance product quality, improve texture, and increase production efficiency. Its ability to form stable gels, emulsions, and films has made it an indispensable ingredient in a wide range of food products, from dairy and bakery items to meat and seafood products.
One of the key drivers behind the adoption of sodium alginate in food manufacturing is its role in supporting scalable production methods. As the global food industry faces increasing pressure to meet the demands of a growing population, manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to optimize their processes and increase output without compromising quality. Sodium alginate has proven to be a valuable tool in achieving these goals.
The technology surrounding sodium alginate has evolved to address various challenges in food manufacturing, such as maintaining product consistency across large-scale production runs, extending shelf life, and improving the sensory attributes of processed foods. Its versatility has allowed food scientists and engineers to develop innovative solutions for complex manufacturing problems, leading to the creation of novel food products and more efficient production techniques.
As we explore the current state and future potential of sodium alginate in food manufacturing, it is essential to consider the broader context of food technology trends. The increasing focus on clean label ingredients, sustainable production practices, and functional foods has further emphasized the importance of natural additives like sodium alginate. Its plant-based origin and multifunctional properties align well with these industry trends, positioning it as a key ingredient for future food innovations.
The ongoing research in this field aims to unlock new applications and improve existing ones, with a particular focus on enhancing the scalability of food manufacturing processes. This includes exploring new sources of alginate, optimizing extraction methods, and developing advanced formulations that can address specific challenges in large-scale food production.
Over the years, the applications of sodium alginate in food manufacturing have expanded significantly, driven by the increasing demand for innovative food products and the need for more efficient production methods. The evolution of this technology has been marked by continuous research and development, leading to a deeper understanding of its molecular structure and functional properties.
The primary objective of utilizing sodium alginate in food manufacturing is to enhance product quality, improve texture, and increase production efficiency. Its ability to form stable gels, emulsions, and films has made it an indispensable ingredient in a wide range of food products, from dairy and bakery items to meat and seafood products.
One of the key drivers behind the adoption of sodium alginate in food manufacturing is its role in supporting scalable production methods. As the global food industry faces increasing pressure to meet the demands of a growing population, manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to optimize their processes and increase output without compromising quality. Sodium alginate has proven to be a valuable tool in achieving these goals.
The technology surrounding sodium alginate has evolved to address various challenges in food manufacturing, such as maintaining product consistency across large-scale production runs, extending shelf life, and improving the sensory attributes of processed foods. Its versatility has allowed food scientists and engineers to develop innovative solutions for complex manufacturing problems, leading to the creation of novel food products and more efficient production techniques.
As we explore the current state and future potential of sodium alginate in food manufacturing, it is essential to consider the broader context of food technology trends. The increasing focus on clean label ingredients, sustainable production practices, and functional foods has further emphasized the importance of natural additives like sodium alginate. Its plant-based origin and multifunctional properties align well with these industry trends, positioning it as a key ingredient for future food innovations.
The ongoing research in this field aims to unlock new applications and improve existing ones, with a particular focus on enhancing the scalability of food manufacturing processes. This includes exploring new sources of alginate, optimizing extraction methods, and developing advanced formulations that can address specific challenges in large-scale food production.
Market Demand Analysis for Sodium Alginate in Food Industry
The global market for sodium alginate in the food industry has been experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for convenience foods, functional ingredients, and clean label products. As a versatile ingredient derived from brown seaweed, sodium alginate plays a crucial role in supporting scalable food manufacturing methods, particularly in texture modification, stabilization, and encapsulation processes.
The food and beverage sector represents the largest application segment for sodium alginate, accounting for a substantial portion of the overall market share. This demand is primarily fueled by the rising consumer preference for processed and packaged foods, especially in developing economies where urbanization and changing lifestyles are driving the need for convenient food options.
In recent years, there has been a notable surge in the adoption of sodium alginate in the dairy industry, particularly in the production of low-fat and reduced-calorie products. Its ability to improve texture and mouthfeel without compromising taste has made it an invaluable ingredient for manufacturers looking to meet the growing consumer demand for healthier food options.
The bakery and confectionery sectors have also shown increased interest in sodium alginate due to its excellent gelling and stabilizing properties. It is widely used in the production of jams, jellies, and fruit fillings, where it helps maintain product consistency and extend shelf life. Additionally, the meat and poultry industry has been incorporating sodium alginate in restructured meat products to enhance texture and reduce cooking losses.
The clean label trend has further boosted the demand for sodium alginate as a natural ingredient. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with recognizable, natural ingredients, and sodium alginate, being derived from seaweed, aligns well with this preference. This has led to its increased use in organic and natural food products, expanding its market potential.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a key growth region for sodium alginate in the food industry. The rapid expansion of the processed food sector in countries like China and India, coupled with increasing disposable incomes and changing dietary habits, is driving the demand. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on innovative applications and clean label products.
The market demand for sodium alginate is also being influenced by its functional properties that support sustainable and efficient food manufacturing processes. Its ability to reduce food waste by extending shelf life and improving product stability aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in the food industry. Furthermore, its role in developing novel food products, such as plant-based alternatives and 3D printed foods, is opening up new avenues for market growth.
The food and beverage sector represents the largest application segment for sodium alginate, accounting for a substantial portion of the overall market share. This demand is primarily fueled by the rising consumer preference for processed and packaged foods, especially in developing economies where urbanization and changing lifestyles are driving the need for convenient food options.
In recent years, there has been a notable surge in the adoption of sodium alginate in the dairy industry, particularly in the production of low-fat and reduced-calorie products. Its ability to improve texture and mouthfeel without compromising taste has made it an invaluable ingredient for manufacturers looking to meet the growing consumer demand for healthier food options.
The bakery and confectionery sectors have also shown increased interest in sodium alginate due to its excellent gelling and stabilizing properties. It is widely used in the production of jams, jellies, and fruit fillings, where it helps maintain product consistency and extend shelf life. Additionally, the meat and poultry industry has been incorporating sodium alginate in restructured meat products to enhance texture and reduce cooking losses.
The clean label trend has further boosted the demand for sodium alginate as a natural ingredient. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with recognizable, natural ingredients, and sodium alginate, being derived from seaweed, aligns well with this preference. This has led to its increased use in organic and natural food products, expanding its market potential.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a key growth region for sodium alginate in the food industry. The rapid expansion of the processed food sector in countries like China and India, coupled with increasing disposable incomes and changing dietary habits, is driving the demand. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on innovative applications and clean label products.
The market demand for sodium alginate is also being influenced by its functional properties that support sustainable and efficient food manufacturing processes. Its ability to reduce food waste by extending shelf life and improving product stability aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in the food industry. Furthermore, its role in developing novel food products, such as plant-based alternatives and 3D printed foods, is opening up new avenues for market growth.
Current State and Challenges in Sodium Alginate Applications
Sodium alginate has gained significant traction in the food manufacturing industry due to its versatile properties and applications. Currently, it is widely used as a thickening agent, stabilizer, and emulsifier in various food products. The global market for sodium alginate in food applications is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for convenience foods and the rising popularity of plant-based alternatives.
One of the primary challenges in sodium alginate applications is maintaining consistent quality across large-scale production. The extraction process from brown seaweed can lead to variations in the molecular weight and composition of the alginate, affecting its functional properties. Manufacturers are investing in advanced purification and standardization techniques to address this issue and ensure uniform product performance.
Another significant challenge is the limited supply of raw materials. The harvesting of brown seaweed, the primary source of sodium alginate, is subject to environmental factors and seasonal variations. This can lead to supply chain disruptions and price fluctuations, impacting the scalability of food manufacturing processes that rely on sodium alginate.
The food industry is also grappling with the challenge of clean label trends. While sodium alginate is a natural ingredient, some consumers perceive it as an artificial additive. Manufacturers are working on improving communication strategies to educate consumers about the natural origin and safety of sodium alginate.
In terms of technological advancements, researchers are exploring new methods to enhance the functionality of sodium alginate. This includes developing modified alginates with improved stability and gelation properties, which could expand its applications in food manufacturing. Additionally, efforts are being made to optimize the extraction and processing techniques to increase yield and reduce production costs.
The regulatory landscape presents both opportunities and challenges for sodium alginate applications. While it is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA, there are ongoing discussions about its use in certain food categories and potential labeling requirements. Manufacturers need to stay abreast of evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maintain consumer trust.
Sustainability is emerging as a critical consideration in sodium alginate production. The industry is investing in sustainable harvesting practices and exploring alternative sources of alginates to reduce environmental impact. This includes research into cultivated seaweed farms and the potential use of microalgae as a more controlled and sustainable source of alginates.
One of the primary challenges in sodium alginate applications is maintaining consistent quality across large-scale production. The extraction process from brown seaweed can lead to variations in the molecular weight and composition of the alginate, affecting its functional properties. Manufacturers are investing in advanced purification and standardization techniques to address this issue and ensure uniform product performance.
Another significant challenge is the limited supply of raw materials. The harvesting of brown seaweed, the primary source of sodium alginate, is subject to environmental factors and seasonal variations. This can lead to supply chain disruptions and price fluctuations, impacting the scalability of food manufacturing processes that rely on sodium alginate.
The food industry is also grappling with the challenge of clean label trends. While sodium alginate is a natural ingredient, some consumers perceive it as an artificial additive. Manufacturers are working on improving communication strategies to educate consumers about the natural origin and safety of sodium alginate.
In terms of technological advancements, researchers are exploring new methods to enhance the functionality of sodium alginate. This includes developing modified alginates with improved stability and gelation properties, which could expand its applications in food manufacturing. Additionally, efforts are being made to optimize the extraction and processing techniques to increase yield and reduce production costs.
The regulatory landscape presents both opportunities and challenges for sodium alginate applications. While it is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA, there are ongoing discussions about its use in certain food categories and potential labeling requirements. Manufacturers need to stay abreast of evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maintain consumer trust.
Sustainability is emerging as a critical consideration in sodium alginate production. The industry is investing in sustainable harvesting practices and exploring alternative sources of alginates to reduce environmental impact. This includes research into cultivated seaweed farms and the potential use of microalgae as a more controlled and sustainable source of alginates.
Existing Sodium Alginate-based Food Manufacturing Solutions
01 Production methods for sodium alginate
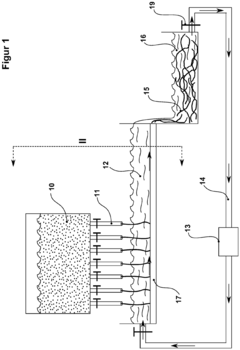
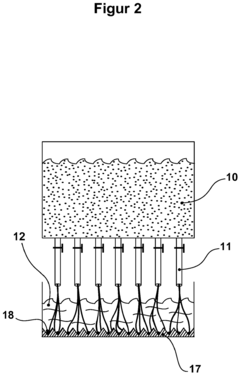
Various methods for producing sodium alginate on a scalable level are described. These include extraction from seaweed, fermentation processes, and chemical modifications of alginic acid. The production methods focus on improving yield, purity, and consistency of the final product while considering cost-effectiveness and environmental impact.- Production methods for sodium alginate: Various methods for producing sodium alginate on a scalable level are described. These include extraction from seaweed, fermentation processes, and chemical modifications of alginic acid. The production methods focus on improving yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness for industrial-scale manufacturing.
- Applications in pharmaceutical and biomedical industries: Sodium alginate's scalability is explored in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Its use in drug delivery systems, wound dressings, and tissue engineering scaffolds is discussed. The focus is on developing large-scale production methods that maintain the material's biocompatibility and functional properties.
- Food industry applications and scalability: The scalability of sodium alginate production for food industry applications is addressed. This includes its use as a thickening agent, stabilizer, and emulsifier in various food products. Methods for large-scale production that comply with food safety regulations and maintain consistent quality are discussed.
- Environmental and industrial applications: Sodium alginate's scalability for environmental and industrial applications is explored. This includes its use in water treatment, textile printing, and paper manufacturing. The focus is on developing cost-effective, large-scale production methods that meet the demands of these industries while maintaining environmental sustainability.
- Modification and enhancement techniques: Various techniques for modifying and enhancing sodium alginate to improve its scalability and functionality are discussed. These include chemical modifications, blending with other polymers, and nanotechnology approaches. The aim is to develop methods that can be scaled up for industrial production while enhancing the material's properties for specific applications.
02 Applications in pharmaceutical and biomedical industries
Sodium alginate's scalability is explored in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Its use in drug delivery systems, wound dressings, and tissue engineering scaffolds is discussed. The focus is on developing large-scale production methods that maintain the material's biocompatibility and functional properties for these high-value applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Food and beverage industry applications
The scalability of sodium alginate production for food and beverage applications is addressed. This includes its use as a thickening agent, stabilizer, and emulsifier in various products. Methods for large-scale production that meet food-grade standards and regulatory requirements are discussed.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial and environmental applications
Sodium alginate's scalability for industrial and environmental applications is explored. This includes its use in wastewater treatment, textile printing, and paper manufacturing. The focus is on developing cost-effective production methods that can meet the high-volume demands of these industries while maintaining product quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Modification and functionalization techniques
Various techniques for modifying and functionalizing sodium alginate to enhance its properties and expand its applications are discussed. These include chemical modifications, blending with other polymers, and incorporation of nanoparticles. The scalability of these processes for industrial production is addressed.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sodium Alginate Production and Food Manufacturing
The sodium alginate market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in food manufacturing for its versatile properties as a thickener, stabilizer, and emulsifier. The global market size is projected to expand significantly, fueled by the rising adoption of convenience foods and clean-label ingredients. Technologically, sodium alginate production is relatively mature, with established players like Freddy Hirsch Group AG and Corbion Biotech, Inc. leading the way. However, ongoing research by institutions such as Tianjin University and Shandong University is pushing the boundaries of its applications and production methods. Companies like Qingdao Bright Moon Seaweed Group Co., Ltd. are also contributing to advancements in seaweed-based products, further enhancing the scalability and efficiency of sodium alginate production for food manufacturing.
Corbion Biotech, Inc.
Technical Solution: Corbion Biotech has developed advanced sodium alginate-based solutions for scalable food manufacturing. Their technology focuses on improving texture, stability, and shelf-life of various food products. They have engineered a proprietary alginate extraction process that yields high-quality, consistent sodium alginate suitable for large-scale food production. Their method involves controlled fermentation of brown seaweed, followed by a purification process that removes impurities while preserving the functional properties of alginate[1]. This results in a food-grade sodium alginate that can be easily incorporated into various food systems, providing excellent gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties[2]. Corbion's sodium alginate supports scalable manufacturing by offering improved process efficiency, reduced production time, and enhanced product consistency across large batches[3].
Strengths: High-quality, consistent product suitable for large-scale production; Improved process efficiency and product consistency. Weaknesses: Potential higher cost compared to traditional extraction methods; Reliance on seaweed availability and quality.
Qingdao Bright Moon Seaweed Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Qingdao Bright Moon Seaweed Group has pioneered innovative sodium alginate production techniques tailored for scalable food manufacturing. Their approach involves a sustainable seaweed cultivation program, ensuring a steady supply of high-quality raw materials. The company employs a multi-stage extraction process that optimizes yield and purity of sodium alginate[1]. Their proprietary technology includes a rapid gelation system that allows for precise control of alginate properties, enabling customization for various food applications[2]. This system facilitates the production of sodium alginate with specific viscosity and gel strength profiles, crucial for large-scale food manufacturing. Additionally, they have developed a spray-drying technique that produces highly soluble sodium alginate powder, which significantly improves dispersion and hydration in food systems, reducing processing time in industrial settings[3].
Strengths: Sustainable raw material sourcing; Customizable alginate properties for different applications; Improved solubility for efficient industrial use. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs; Limited to seaweed-based alginate sources.
Core Innovations in Sodium Alginate Food Technology
Low-calorie food composition containing alginate and its production method
PatentActiveEP3348150A1
Innovation
- A low-calorie food composition using alginate, vegetable or fruit extracts, and mineral additives, with optional fish or meat extracts, that can be shaped into various forms without flour or eggs, allowing for immediate consumption and enhanced nutritional value.
Composition comprising at least one alginate for use in treatment and/or prevention of overweight
PatentActiveUS20160015736A1
Innovation
- A reconstitutable composition combining low viscosity and high viscosity alginates, along with a suspending agent, to create a clear, palatable, and easily mixable aqueous diet product that forms a strong gel in the stomach, reducing caloric intake and promoting satiety.
Regulatory Framework for Sodium Alginate in Food Industry
The regulatory framework for sodium alginate in the food industry is complex and multifaceted, reflecting its widespread use and importance in food manufacturing. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies sodium alginate as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), allowing its use in various food applications. The FDA has established specific guidelines for its use, including maximum allowable levels in different food categories.
In the European Union, sodium alginate is regulated under the E-number system as E401. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has conducted extensive safety assessments and established Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) levels for sodium alginate. These regulations ensure that the use of sodium alginate in food products remains within safe limits for consumer health.
Globally, the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) has evaluated sodium alginate and provided recommendations for its safe use in food. These international standards often serve as a reference point for countries developing their own regulatory frameworks.
Many countries have adopted specific regulations for sodium alginate use in food manufacturing. For instance, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has established guidelines for its use in various food categories. Similarly, Australia and New Zealand have incorporated sodium alginate regulations into their Food Standards Code.
The regulatory framework also addresses labeling requirements for products containing sodium alginate. In most jurisdictions, manufacturers must clearly indicate its presence on product labels, often under the category of thickeners or stabilizers.
As the food industry continues to innovate, regulatory bodies are constantly reviewing and updating their guidelines. Recent trends show an increased focus on the sourcing and sustainability of sodium alginate, with some regulations beginning to address the environmental impact of its production.
Compliance with these regulations is crucial for food manufacturers using sodium alginate in scalable production methods. Companies must stay informed about the specific requirements in each market they operate in, as regulations can vary significantly between countries and regions. This regulatory landscape not only ensures product safety but also influences manufacturing processes and product formulations across the global food industry.
In the European Union, sodium alginate is regulated under the E-number system as E401. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has conducted extensive safety assessments and established Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) levels for sodium alginate. These regulations ensure that the use of sodium alginate in food products remains within safe limits for consumer health.
Globally, the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) has evaluated sodium alginate and provided recommendations for its safe use in food. These international standards often serve as a reference point for countries developing their own regulatory frameworks.
Many countries have adopted specific regulations for sodium alginate use in food manufacturing. For instance, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has established guidelines for its use in various food categories. Similarly, Australia and New Zealand have incorporated sodium alginate regulations into their Food Standards Code.
The regulatory framework also addresses labeling requirements for products containing sodium alginate. In most jurisdictions, manufacturers must clearly indicate its presence on product labels, often under the category of thickeners or stabilizers.
As the food industry continues to innovate, regulatory bodies are constantly reviewing and updating their guidelines. Recent trends show an increased focus on the sourcing and sustainability of sodium alginate, with some regulations beginning to address the environmental impact of its production.
Compliance with these regulations is crucial for food manufacturers using sodium alginate in scalable production methods. Companies must stay informed about the specific requirements in each market they operate in, as regulations can vary significantly between countries and regions. This regulatory landscape not only ensures product safety but also influences manufacturing processes and product formulations across the global food industry.
Sustainability Aspects of Sodium Alginate in Food Production
Sodium alginate, derived from brown seaweed, has emerged as a sustainable ingredient in food manufacturing, offering numerous environmental benefits. Its production process requires minimal energy and chemical inputs, making it an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic additives. The harvesting of seaweed for alginate extraction also contributes to carbon sequestration, as seaweed farms act as natural carbon sinks.
In terms of resource efficiency, sodium alginate's versatility allows for its use in multiple applications within food production. This multi-functionality reduces the need for various single-purpose additives, thereby streamlining manufacturing processes and minimizing waste. Additionally, alginate's ability to form gels and stabilize emulsions can extend the shelf life of food products, potentially reducing food waste throughout the supply chain.
The biodegradability of sodium alginate further enhances its sustainability profile. Unlike many synthetic food additives, alginate naturally decomposes without leaving harmful residues in the environment. This characteristic aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible food products and packaging materials.
From a circular economy perspective, the production of sodium alginate creates opportunities for utilizing byproducts from other industries. For instance, waste streams from seafood processing can be repurposed for alginate extraction, promoting a more sustainable and integrated approach to resource management in the food sector.
In the context of scalable food manufacturing, sodium alginate's sustainability aspects become even more pronounced. Its ability to improve product consistency and stability at industrial scales means that food producers can maintain quality while reducing energy consumption and minimizing the use of less sustainable ingredients. This scalability factor is crucial for addressing the environmental challenges associated with large-scale food production.
Moreover, the use of sodium alginate in food manufacturing aligns with global efforts to reduce dependence on animal-derived ingredients. As a plant-based additive, it supports the development of vegan and vegetarian food products, contributing to more sustainable dietary patterns and potentially reducing the environmental footprint of food production.
Looking ahead, ongoing research into seaweed cultivation techniques and alginate extraction methods promises to further enhance the sustainability of sodium alginate. Innovations in these areas could lead to even more efficient production processes, reduced environmental impact, and expanded applications in sustainable food manufacturing.
In terms of resource efficiency, sodium alginate's versatility allows for its use in multiple applications within food production. This multi-functionality reduces the need for various single-purpose additives, thereby streamlining manufacturing processes and minimizing waste. Additionally, alginate's ability to form gels and stabilize emulsions can extend the shelf life of food products, potentially reducing food waste throughout the supply chain.
The biodegradability of sodium alginate further enhances its sustainability profile. Unlike many synthetic food additives, alginate naturally decomposes without leaving harmful residues in the environment. This characteristic aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible food products and packaging materials.
From a circular economy perspective, the production of sodium alginate creates opportunities for utilizing byproducts from other industries. For instance, waste streams from seafood processing can be repurposed for alginate extraction, promoting a more sustainable and integrated approach to resource management in the food sector.
In the context of scalable food manufacturing, sodium alginate's sustainability aspects become even more pronounced. Its ability to improve product consistency and stability at industrial scales means that food producers can maintain quality while reducing energy consumption and minimizing the use of less sustainable ingredients. This scalability factor is crucial for addressing the environmental challenges associated with large-scale food production.
Moreover, the use of sodium alginate in food manufacturing aligns with global efforts to reduce dependence on animal-derived ingredients. As a plant-based additive, it supports the development of vegan and vegetarian food products, contributing to more sustainable dietary patterns and potentially reducing the environmental footprint of food production.
Looking ahead, ongoing research into seaweed cultivation techniques and alginate extraction methods promises to further enhance the sustainability of sodium alginate. Innovations in these areas could lead to even more efficient production processes, reduced environmental impact, and expanded applications in sustainable food manufacturing.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!