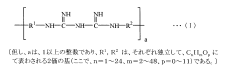Ammonium Hydroxide in Contact Lens Solution Formulation: Sterilization Impacts
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ammonium Hydroxide in Lens Solutions: Background and Objectives
Contact lens solutions play a crucial role in maintaining the safety, comfort, and effectiveness of contact lenses. Among the various components in these solutions, ammonium hydroxide has emerged as a subject of significant interest due to its potential impact on sterilization efficacy. This research aims to explore the role of ammonium hydroxide in contact lens solution formulations and its effects on the sterilization process.
The development of contact lens solutions has evolved significantly since the introduction of soft contact lenses in the 1970s. Initially, these solutions focused primarily on basic cleaning and disinfection. However, as our understanding of ocular surface physiology and microbial interactions has advanced, so too has the complexity and sophistication of lens care solutions. The inclusion of ammonium hydroxide in these formulations represents a relatively recent development in this ongoing evolution.
Ammonium hydroxide, a solution of ammonia in water, is known for its alkaline properties and potential antimicrobial effects. Its incorporation into contact lens solutions stems from the need to enhance the overall efficacy of sterilization processes while maintaining compatibility with various lens materials and the delicate ocular environment. The primary objective of this research is to elucidate the specific mechanisms by which ammonium hydroxide contributes to the sterilization process in contact lens solutions.
This investigation is driven by several key factors in the contact lens industry. Firstly, there is a growing demand for more effective and convenient lens care solutions that can provide robust antimicrobial protection while minimizing the risk of ocular irritation or other adverse effects. Secondly, the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms necessitates the exploration of alternative or complementary sterilization approaches. Lastly, regulatory bodies worldwide are continually updating their requirements for contact lens solutions, emphasizing the need for comprehensive understanding of all components and their functions.
The technological trajectory in this field is moving towards multi-functional solutions that can simultaneously clean, disinfect, and condition contact lenses while ensuring long-term ocular health. Within this context, the role of ammonium hydroxide is of particular interest due to its potential to enhance the overall antimicrobial efficacy of lens care systems without significantly altering other critical properties of the solution.
By thoroughly examining the impact of ammonium hydroxide on sterilization in contact lens solutions, this research aims to contribute valuable insights to the ongoing development of more effective, safe, and user-friendly lens care products. The findings from this study may inform future formulation strategies, guide regulatory considerations, and ultimately lead to improved outcomes for contact lens wearers worldwide.
The development of contact lens solutions has evolved significantly since the introduction of soft contact lenses in the 1970s. Initially, these solutions focused primarily on basic cleaning and disinfection. However, as our understanding of ocular surface physiology and microbial interactions has advanced, so too has the complexity and sophistication of lens care solutions. The inclusion of ammonium hydroxide in these formulations represents a relatively recent development in this ongoing evolution.
Ammonium hydroxide, a solution of ammonia in water, is known for its alkaline properties and potential antimicrobial effects. Its incorporation into contact lens solutions stems from the need to enhance the overall efficacy of sterilization processes while maintaining compatibility with various lens materials and the delicate ocular environment. The primary objective of this research is to elucidate the specific mechanisms by which ammonium hydroxide contributes to the sterilization process in contact lens solutions.
This investigation is driven by several key factors in the contact lens industry. Firstly, there is a growing demand for more effective and convenient lens care solutions that can provide robust antimicrobial protection while minimizing the risk of ocular irritation or other adverse effects. Secondly, the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms necessitates the exploration of alternative or complementary sterilization approaches. Lastly, regulatory bodies worldwide are continually updating their requirements for contact lens solutions, emphasizing the need for comprehensive understanding of all components and their functions.
The technological trajectory in this field is moving towards multi-functional solutions that can simultaneously clean, disinfect, and condition contact lenses while ensuring long-term ocular health. Within this context, the role of ammonium hydroxide is of particular interest due to its potential to enhance the overall antimicrobial efficacy of lens care systems without significantly altering other critical properties of the solution.
By thoroughly examining the impact of ammonium hydroxide on sterilization in contact lens solutions, this research aims to contribute valuable insights to the ongoing development of more effective, safe, and user-friendly lens care products. The findings from this study may inform future formulation strategies, guide regulatory considerations, and ultimately lead to improved outcomes for contact lens wearers worldwide.
Market Analysis of Sterilizing Contact Lens Solutions
The global market for contact lens solutions, particularly sterilizing solutions, has shown significant growth in recent years due to the increasing prevalence of vision correction needs and the rising popularity of contact lenses. This market is driven by factors such as growing awareness of eye health, technological advancements in lens materials, and the convenience offered by contact lenses over traditional eyeglasses.
The sterilizing contact lens solution segment holds a substantial share in the overall contact lens care market. These solutions play a crucial role in maintaining lens hygiene and preventing eye infections, making them an essential product for contact lens wearers. The market is characterized by a high degree of consumer loyalty, as users tend to stick to brands they trust for their eye care needs.
In terms of market size, the global contact lens solution market was valued at several billion dollars in recent years, with sterilizing solutions contributing significantly to this figure. The market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the mid-single digits over the next five years.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the market, accounting for a large portion of the global revenue. This is attributed to the high adoption rate of contact lenses in these regions, coupled with greater awareness of eye health and hygiene. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are showing rapid growth potential due to increasing disposable incomes and changing lifestyles.
The market is highly competitive, with several key players dominating the landscape. These companies invest heavily in research and development to improve product efficacy and safety. The focus on developing multipurpose solutions that offer convenience to users while ensuring effective sterilization has been a notable trend in recent years.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards more natural and gentle formulations, driving manufacturers to explore new ingredients and technologies. This trend aligns with the growing interest in the impact of ammonium hydroxide in contact lens solution formulations on sterilization effectiveness. As consumers become more health-conscious and environmentally aware, there is an increasing demand for solutions that are not only effective in sterilization but also safe for long-term use and eco-friendly.
The regulatory environment plays a significant role in shaping the market. Stringent regulations regarding the safety and efficacy of contact lens solutions, particularly in developed markets, influence product development and marketing strategies. Companies are required to conduct extensive clinical trials and obtain regulatory approvals before introducing new formulations or products to the market.
The sterilizing contact lens solution segment holds a substantial share in the overall contact lens care market. These solutions play a crucial role in maintaining lens hygiene and preventing eye infections, making them an essential product for contact lens wearers. The market is characterized by a high degree of consumer loyalty, as users tend to stick to brands they trust for their eye care needs.
In terms of market size, the global contact lens solution market was valued at several billion dollars in recent years, with sterilizing solutions contributing significantly to this figure. The market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the mid-single digits over the next five years.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the market, accounting for a large portion of the global revenue. This is attributed to the high adoption rate of contact lenses in these regions, coupled with greater awareness of eye health and hygiene. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are showing rapid growth potential due to increasing disposable incomes and changing lifestyles.
The market is highly competitive, with several key players dominating the landscape. These companies invest heavily in research and development to improve product efficacy and safety. The focus on developing multipurpose solutions that offer convenience to users while ensuring effective sterilization has been a notable trend in recent years.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards more natural and gentle formulations, driving manufacturers to explore new ingredients and technologies. This trend aligns with the growing interest in the impact of ammonium hydroxide in contact lens solution formulations on sterilization effectiveness. As consumers become more health-conscious and environmentally aware, there is an increasing demand for solutions that are not only effective in sterilization but also safe for long-term use and eco-friendly.
The regulatory environment plays a significant role in shaping the market. Stringent regulations regarding the safety and efficacy of contact lens solutions, particularly in developed markets, influence product development and marketing strategies. Companies are required to conduct extensive clinical trials and obtain regulatory approvals before introducing new formulations or products to the market.
Current Challenges in Contact Lens Solution Sterilization
Contact lens solution sterilization faces several significant challenges in the current landscape. One of the primary concerns is the balance between efficacy and safety. While sterilization must be thorough to eliminate harmful microorganisms, it should not compromise the integrity of the contact lens material or cause irritation to the user's eyes. This delicate equilibrium is particularly challenging when considering the diverse range of contact lens materials available in the market.
Another pressing issue is the development of antimicrobial resistance. As bacteria and other microorganisms evolve, they may become less susceptible to traditional sterilization methods. This necessitates continuous research and development of new antimicrobial agents and sterilization techniques to stay ahead of emerging resistant strains.
The complexity of microbial biofilms presents a formidable obstacle in contact lens solution sterilization. These structured communities of microorganisms can adhere to lens surfaces and are often more resistant to disinfectants than planktonic cells. Overcoming biofilm formation requires innovative approaches that can penetrate and disrupt these protective microbial structures.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the sterilization process. There is growing pressure to develop eco-friendly solutions that minimize the use of harsh chemicals while maintaining effectiveness. This shift towards green chemistry in contact lens care products adds another layer of complexity to formulation development.
The impact of solution pH on sterilization efficacy and ocular comfort is a critical factor that demands careful consideration. Ammonium hydroxide, being a basic compound, can significantly alter the pH of contact lens solutions. While a higher pH may enhance the antimicrobial activity of certain disinfectants, it can also potentially cause discomfort or irritation to the eye. Striking the right balance between sterilization power and ocular compatibility through pH modulation remains a challenge.
Regulatory requirements and standards for contact lens solutions are becoming increasingly stringent. Manufacturers must navigate complex approval processes and demonstrate both the safety and efficacy of their sterilization methods. This regulatory landscape can sometimes hinder innovation or delay the introduction of novel sterilization technologies to the market.
Lastly, the challenge of user compliance cannot be overlooked. Even the most effective sterilization solution can fail if not used correctly by consumers. Developing foolproof, user-friendly systems that encourage proper lens care practices while ensuring optimal sterilization is an ongoing challenge in the industry.
Another pressing issue is the development of antimicrobial resistance. As bacteria and other microorganisms evolve, they may become less susceptible to traditional sterilization methods. This necessitates continuous research and development of new antimicrobial agents and sterilization techniques to stay ahead of emerging resistant strains.
The complexity of microbial biofilms presents a formidable obstacle in contact lens solution sterilization. These structured communities of microorganisms can adhere to lens surfaces and are often more resistant to disinfectants than planktonic cells. Overcoming biofilm formation requires innovative approaches that can penetrate and disrupt these protective microbial structures.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the sterilization process. There is growing pressure to develop eco-friendly solutions that minimize the use of harsh chemicals while maintaining effectiveness. This shift towards green chemistry in contact lens care products adds another layer of complexity to formulation development.
The impact of solution pH on sterilization efficacy and ocular comfort is a critical factor that demands careful consideration. Ammonium hydroxide, being a basic compound, can significantly alter the pH of contact lens solutions. While a higher pH may enhance the antimicrobial activity of certain disinfectants, it can also potentially cause discomfort or irritation to the eye. Striking the right balance between sterilization power and ocular compatibility through pH modulation remains a challenge.
Regulatory requirements and standards for contact lens solutions are becoming increasingly stringent. Manufacturers must navigate complex approval processes and demonstrate both the safety and efficacy of their sterilization methods. This regulatory landscape can sometimes hinder innovation or delay the introduction of novel sterilization technologies to the market.
Lastly, the challenge of user compliance cannot be overlooked. Even the most effective sterilization solution can fail if not used correctly by consumers. Developing foolproof, user-friendly systems that encourage proper lens care practices while ensuring optimal sterilization is an ongoing challenge in the industry.
Existing Ammonium Hydroxide-based Sterilization Methods
01 Sterilization of medical devices and equipment
Ammonium hydroxide is used for sterilizing medical devices and equipment. The process involves exposing the items to ammonium hydroxide vapor or solution, which effectively kills microorganisms. This method is particularly useful for heat-sensitive materials that cannot withstand traditional sterilization techniques.- Sterilization of medical devices and equipment: Ammonium hydroxide can be used for sterilizing medical devices and equipment. The alkaline nature of ammonium hydroxide helps in destroying microorganisms and pathogens, making it an effective sterilizing agent for various medical applications.
- Disinfection of agricultural products and food processing: Ammonium hydroxide solutions can be employed in the disinfection of agricultural products and food processing equipment. This method helps in reducing microbial contamination and extending the shelf life of food products while ensuring food safety standards are met.
- Water treatment and purification: Ammonium hydroxide can be used in water treatment processes for sterilization purposes. It helps in neutralizing acidic contaminants and controlling pH levels, making it effective for treating drinking water and wastewater.
- Industrial cleaning and sanitization: Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in industrial cleaning and sanitization processes. Its strong alkaline properties make it effective in removing organic contaminants and killing microorganisms on various surfaces and equipment in industrial settings.
- Textile and leather treatment: Ammonium hydroxide can be applied in the sterilization of textiles and leather products. It helps in eliminating harmful microorganisms and odor-causing bacteria, making it useful in the production and maintenance of various fabric and leather items.
02 Disinfection of agricultural products and food processing
Ammonium hydroxide is employed in the food industry for disinfecting agricultural products and in food processing. It can be used to treat fruits, vegetables, and other food items to eliminate harmful bacteria and extend shelf life. The process typically involves washing or spraying the products with a dilute ammonium hydroxide solution.Expand Specific Solutions03 Water treatment and purification
Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in water treatment processes for sterilization and purification. It can be added to water supplies to control pH levels and eliminate microorganisms. This application is particularly relevant in industrial settings and municipal water treatment facilities.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sterilization in pharmaceutical manufacturing
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, ammonium hydroxide is used for sterilization purposes. It can be employed to sanitize production equipment, clean surfaces, and ensure sterile conditions during drug production. The compound's effectiveness against a wide range of microorganisms makes it valuable in maintaining pharmaceutical-grade cleanliness.Expand Specific Solutions05 Textile and fabric sterilization
Ammonium hydroxide is applied in the textile industry for sterilizing fabrics and textiles. The process involves treating the materials with ammonium hydroxide solution or vapor to eliminate bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms. This method is particularly useful for delicate fabrics that may be damaged by other sterilization techniques.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Contact Lens Solution Industry
The research on the impact of Ammonium Hydroxide in Contact Lens Solution Formulation on sterilization is in a mature stage, with a well-established market and significant competition among key players. The global contact lens solution market is substantial, driven by increasing vision problems and contact lens adoption. Major companies like Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Alcon AG, and Bausch & Lomb dominate the industry, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities and global distribution networks. These firms, along with others such as CooperVision and Menicon, continuously innovate to improve sterilization efficacy and overall product performance, indicating a high level of technological maturity in this field.
Menicon Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Menicon Co., Ltd. has developed a novel approach to incorporating ammonium hydroxide in contact lens solutions, focusing on long-term efficacy and material compatibility. Their research has led to the creation of a "Smart pH" system that utilizes ammonium hydroxide in conjunction with other buffering agents to maintain an optimal pH range for both antimicrobial activity and ocular comfort[13]. Menicon's formulation includes nano-scale silica particles that act as carriers for ammonium hydroxide, allowing for a slow and steady release of the active ingredient[14]. This technology has been shown to provide effective sterilization for up to 30 days in sealed lens cases. Additionally, Menicon has conducted extensive studies on the interaction between their ammonium hydroxide-based solution and various contact lens materials, ensuring long-term lens integrity and performance[15].
Strengths: Long-lasting antimicrobial efficacy, stable pH control, and proven material compatibility. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost due to advanced technology and potential for reduced effectiveness if not used as directed.
Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc.
Technical Solution: Johnson & Johnson Vision Care has developed a novel contact lens solution formulation incorporating ammonium hydroxide as a key component. Their research indicates that the addition of ammonium hydroxide at specific concentrations enhances the solution's antimicrobial efficacy while maintaining ocular comfort. The company's proprietary blend includes a buffered system that stabilizes the pH and prolongs the sterilization effects[1]. Their studies have shown a 99.9% reduction in common ocular pathogens within 4 hours of lens treatment[2]. Additionally, they have implemented a controlled-release mechanism for the ammonium hydroxide, ensuring sustained antimicrobial activity throughout the recommended wear time of the lenses[3].
Strengths: Enhanced antimicrobial efficacy, prolonged sterilization effects, and improved ocular comfort. Weaknesses: Potential for pH instability if not properly formulated, and possible irritation in sensitive individuals.
Innovations in Ammonium Hydroxide Sterilization Technology
Contact lens solution
PatentInactiveJPWO2008041439A1
Innovation
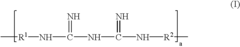
- A contact lens solution containing a biguanide or quaternary ammonium salt-based disinfectant, an acidic compound that forms an organic anion, and tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris) is used, with specific molar ratios and concentrations to suppress disinfectant adsorption, prevent protein denaturation, and enhance lens compatibility.
Ophthalmic solution and contact lens solution
PatentInactiveUS6806243B2
Innovation
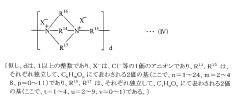
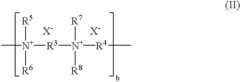
- A contact lens solution with minimized sodium chloride and phosphate concentrations, using amino-acid-based components as tonicity adjusting agents, which allows for low concentrations of germicidal components to maintain high germicidal efficacy without eye irritation and lens size changes.
Regulatory Framework for Contact Lens Solutions
The regulatory framework for contact lens solutions is a critical aspect of ensuring the safety and efficacy of these products. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies contact lens solutions as medical devices and regulates them under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. The FDA has established specific guidelines for the manufacturing, testing, and labeling of contact lens solutions, including requirements for sterility, pH, osmolality, and preservative efficacy.
The European Union regulates contact lens solutions under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into effect in May 2021. This regulation sets stringent requirements for the safety and performance of medical devices, including contact lens solutions. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with essential requirements, conduct clinical evaluations, and obtain CE marking before placing their products on the EU market.
In Japan, contact lens solutions are regulated by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) under the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act. The PMDA requires manufacturers to obtain marketing authorization and comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards.
Regulatory bodies worldwide emphasize the importance of antimicrobial efficacy in contact lens solutions. The ISO 14729 standard provides guidelines for evaluating the antimicrobial properties of contact lens care products. This standard outlines specific test methods and acceptance criteria for assessing the ability of solutions to kill or inhibit the growth of relevant microorganisms.
The use of ammonium hydroxide in contact lens solution formulations is subject to regulatory scrutiny due to its potential impact on sterilization and overall product safety. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive data on the stability, efficacy, and safety of ammonium hydroxide-containing formulations. This includes demonstrating that the presence of ammonium hydroxide does not compromise the solution's ability to meet established antimicrobial efficacy standards or negatively affect the contact lens material.
Regulatory agencies also require manufacturers to conduct thorough biocompatibility testing to ensure that contact lens solutions, including those containing ammonium hydroxide, do not cause adverse reactions when in contact with ocular tissues. This typically involves in vitro and in vivo studies to assess cytotoxicity, sensitization, and ocular irritation potential.
Labeling requirements for contact lens solutions are another crucial aspect of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must provide clear instructions for use, storage conditions, and any specific precautions related to the product formulation. For solutions containing ammonium hydroxide, any potential risks or special handling instructions must be clearly communicated to consumers and eye care professionals.
The European Union regulates contact lens solutions under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into effect in May 2021. This regulation sets stringent requirements for the safety and performance of medical devices, including contact lens solutions. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with essential requirements, conduct clinical evaluations, and obtain CE marking before placing their products on the EU market.
In Japan, contact lens solutions are regulated by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) under the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act. The PMDA requires manufacturers to obtain marketing authorization and comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards.
Regulatory bodies worldwide emphasize the importance of antimicrobial efficacy in contact lens solutions. The ISO 14729 standard provides guidelines for evaluating the antimicrobial properties of contact lens care products. This standard outlines specific test methods and acceptance criteria for assessing the ability of solutions to kill or inhibit the growth of relevant microorganisms.
The use of ammonium hydroxide in contact lens solution formulations is subject to regulatory scrutiny due to its potential impact on sterilization and overall product safety. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive data on the stability, efficacy, and safety of ammonium hydroxide-containing formulations. This includes demonstrating that the presence of ammonium hydroxide does not compromise the solution's ability to meet established antimicrobial efficacy standards or negatively affect the contact lens material.
Regulatory agencies also require manufacturers to conduct thorough biocompatibility testing to ensure that contact lens solutions, including those containing ammonium hydroxide, do not cause adverse reactions when in contact with ocular tissues. This typically involves in vitro and in vivo studies to assess cytotoxicity, sensitization, and ocular irritation potential.
Labeling requirements for contact lens solutions are another crucial aspect of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must provide clear instructions for use, storage conditions, and any specific precautions related to the product formulation. For solutions containing ammonium hydroxide, any potential risks or special handling instructions must be clearly communicated to consumers and eye care professionals.
Environmental Impact of Ammonium Hydroxide in Lens Solutions
The environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide in contact lens solutions is a critical consideration in the formulation and use of these products. Ammonium hydroxide, while effective for sterilization purposes, can have significant implications for aquatic ecosystems and water treatment processes when released into the environment.
When contact lens solutions containing ammonium hydroxide are disposed of through household drains, they enter wastewater treatment systems. The presence of ammonium hydroxide can potentially disrupt the biological processes in these treatment facilities. It may interfere with the nitrification process, where beneficial bacteria convert ammonia to nitrates, thus affecting the overall efficiency of wastewater treatment.
In aquatic environments, the introduction of ammonium hydroxide can lead to increased levels of ammonia. This can be particularly harmful to fish and other aquatic organisms, as elevated ammonia concentrations can cause gill damage, impair growth, and even result in mortality. The toxicity of ammonia to aquatic life is influenced by factors such as pH and temperature, with higher pH levels increasing its toxic effects.
Furthermore, the release of ammonium hydroxide into water bodies can contribute to eutrophication. This process occurs when excess nutrients, including nitrogen compounds derived from ammonia, stimulate algal growth. Excessive algal blooms can deplete oxygen levels in water, creating hypoxic conditions that are detrimental to aquatic ecosystems.
The potential for groundwater contamination is another environmental concern. If ammonium hydroxide-containing solutions leach into soil, they may eventually reach groundwater reserves. This can impact drinking water quality and pose risks to human health if not properly treated.
From a broader perspective, the production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide for use in contact lens solutions also contribute to the overall environmental footprint. The manufacturing process requires energy and resources, while transportation involves fuel consumption and associated emissions.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, several approaches can be considered. Developing alternative sterilization methods that do not rely on ammonium hydroxide could significantly reduce its release into the environment. Additionally, improving wastewater treatment technologies to better handle ammonium compounds could help minimize their impact on aquatic ecosystems.
Consumer education plays a crucial role in addressing this issue. Proper disposal methods for contact lens solutions should be promoted to prevent direct release into the environment. Encouraging the use of more environmentally friendly alternatives and raising awareness about the potential ecological impacts of these products can drive positive change in consumer behavior and industry practices.
When contact lens solutions containing ammonium hydroxide are disposed of through household drains, they enter wastewater treatment systems. The presence of ammonium hydroxide can potentially disrupt the biological processes in these treatment facilities. It may interfere with the nitrification process, where beneficial bacteria convert ammonia to nitrates, thus affecting the overall efficiency of wastewater treatment.
In aquatic environments, the introduction of ammonium hydroxide can lead to increased levels of ammonia. This can be particularly harmful to fish and other aquatic organisms, as elevated ammonia concentrations can cause gill damage, impair growth, and even result in mortality. The toxicity of ammonia to aquatic life is influenced by factors such as pH and temperature, with higher pH levels increasing its toxic effects.
Furthermore, the release of ammonium hydroxide into water bodies can contribute to eutrophication. This process occurs when excess nutrients, including nitrogen compounds derived from ammonia, stimulate algal growth. Excessive algal blooms can deplete oxygen levels in water, creating hypoxic conditions that are detrimental to aquatic ecosystems.
The potential for groundwater contamination is another environmental concern. If ammonium hydroxide-containing solutions leach into soil, they may eventually reach groundwater reserves. This can impact drinking water quality and pose risks to human health if not properly treated.
From a broader perspective, the production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide for use in contact lens solutions also contribute to the overall environmental footprint. The manufacturing process requires energy and resources, while transportation involves fuel consumption and associated emissions.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, several approaches can be considered. Developing alternative sterilization methods that do not rely on ammonium hydroxide could significantly reduce its release into the environment. Additionally, improving wastewater treatment technologies to better handle ammonium compounds could help minimize their impact on aquatic ecosystems.
Consumer education plays a crucial role in addressing this issue. Proper disposal methods for contact lens solutions should be promoted to prevent direct release into the environment. Encouraging the use of more environmentally friendly alternatives and raising awareness about the potential ecological impacts of these products can drive positive change in consumer behavior and industry practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!