The Role of Neopentane in Advanced Material Production
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Neopentane in Materials: Background and Objectives
Neopentane, a branched alkane with the molecular formula C5H12, has emerged as a crucial component in advanced material production. This compound's unique structural properties and chemical characteristics have positioned it at the forefront of materials science innovation. The evolution of neopentane's role in material synthesis can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers first recognized its potential as a blowing agent in polymer foam production.
Over the decades, the applications of neopentane have expanded significantly, driven by the growing demand for high-performance materials across various industries. The compound's low boiling point, high vapor pressure, and chemical stability have made it an ideal candidate for use in aerosol propellants, refrigerants, and as a precursor in the synthesis of specialty chemicals. These properties have also led to its incorporation in the development of advanced insulation materials and lightweight composites.
The technological trajectory of neopentane in materials science has been marked by continuous refinement and diversification of its applications. From its initial use in foam production, researchers have explored its potential in creating novel polymer structures, enhancing the properties of existing materials, and developing new manufacturing processes. The compound's ability to form stable, low-density structures has been particularly valuable in the aerospace and automotive industries, where weight reduction and thermal management are critical concerns.
Recent advancements in nanotechnology and materials engineering have opened up new avenues for neopentane utilization. Its role in the synthesis of nanostructured materials, such as aerogels and advanced polymer composites, has garnered significant attention from the scientific community. These developments have paved the way for materials with unprecedented combinations of strength, lightness, and thermal insulation properties.
The primary objective of current research and development efforts involving neopentane is to fully exploit its unique characteristics in the creation of next-generation materials. This includes optimizing its use in existing applications, such as improving the efficiency and environmental sustainability of foam production processes, as well as exploring entirely new areas of application. Researchers are particularly focused on leveraging neopentane's properties to address pressing global challenges, including energy efficiency, sustainable transportation, and advanced construction materials.
As we look to the future, the role of neopentane in advanced material production is expected to continue evolving. The compound's potential in emerging fields such as flexible electronics, smart materials, and biocompatible polymers presents exciting opportunities for innovation. By understanding and harnessing the fundamental properties of neopentane, scientists and engineers aim to push the boundaries of material design and performance, ultimately contributing to technological advancements across a wide spectrum of industries.
Over the decades, the applications of neopentane have expanded significantly, driven by the growing demand for high-performance materials across various industries. The compound's low boiling point, high vapor pressure, and chemical stability have made it an ideal candidate for use in aerosol propellants, refrigerants, and as a precursor in the synthesis of specialty chemicals. These properties have also led to its incorporation in the development of advanced insulation materials and lightweight composites.
The technological trajectory of neopentane in materials science has been marked by continuous refinement and diversification of its applications. From its initial use in foam production, researchers have explored its potential in creating novel polymer structures, enhancing the properties of existing materials, and developing new manufacturing processes. The compound's ability to form stable, low-density structures has been particularly valuable in the aerospace and automotive industries, where weight reduction and thermal management are critical concerns.
Recent advancements in nanotechnology and materials engineering have opened up new avenues for neopentane utilization. Its role in the synthesis of nanostructured materials, such as aerogels and advanced polymer composites, has garnered significant attention from the scientific community. These developments have paved the way for materials with unprecedented combinations of strength, lightness, and thermal insulation properties.
The primary objective of current research and development efforts involving neopentane is to fully exploit its unique characteristics in the creation of next-generation materials. This includes optimizing its use in existing applications, such as improving the efficiency and environmental sustainability of foam production processes, as well as exploring entirely new areas of application. Researchers are particularly focused on leveraging neopentane's properties to address pressing global challenges, including energy efficiency, sustainable transportation, and advanced construction materials.
As we look to the future, the role of neopentane in advanced material production is expected to continue evolving. The compound's potential in emerging fields such as flexible electronics, smart materials, and biocompatible polymers presents exciting opportunities for innovation. By understanding and harnessing the fundamental properties of neopentane, scientists and engineers aim to push the boundaries of material design and performance, ultimately contributing to technological advancements across a wide spectrum of industries.
Market Analysis for Neopentane-Based Materials
The market for neopentane-based materials has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for advanced materials in various industries. Neopentane, a branched alkane with the chemical formula C5H12, plays a crucial role in the production of high-performance polymers, foams, and specialty chemicals.
In the polymer industry, neopentane-based materials are gaining traction due to their exceptional properties, including low density, high thermal insulation, and excellent chemical resistance. These characteristics make them ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and construction sectors. The aerospace industry, in particular, has shown a strong interest in neopentane-based materials for their lightweight and thermal insulation properties, which contribute to improved fuel efficiency and overall performance of aircraft.
The construction sector represents another significant market for neopentane-based materials. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings has led to increased adoption of neopentane-based insulation materials. These materials offer superior thermal insulation properties compared to traditional alternatives, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower carbon footprints for buildings.
In the automotive industry, neopentane-based materials are finding applications in lightweight components and insulation systems. As vehicle manufacturers strive to meet stringent fuel efficiency and emission standards, the demand for lightweight materials with excellent thermal properties continues to rise. This trend is expected to drive further growth in the neopentane-based materials market.
The electronics industry is also emerging as a promising market for neopentane-based materials. These materials are being used in the production of high-performance circuit boards and electronic components, where their low dielectric constant and thermal stability properties are highly valued.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the neopentane-based materials market, owing to their well-established aerospace, automotive, and construction industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing construction activities, and growing automotive production in countries like China and India.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as volatile raw material prices and stringent environmental regulations regarding the use of certain chemicals in material production may impact the growth of the neopentane-based materials market. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these challenges and develop more sustainable production processes.
In conclusion, the market for neopentane-based materials shows promising growth potential across various industries. The unique properties of these materials, combined with increasing demand for high-performance and energy-efficient solutions, are expected to drive continued market expansion in the foreseeable future.
In the polymer industry, neopentane-based materials are gaining traction due to their exceptional properties, including low density, high thermal insulation, and excellent chemical resistance. These characteristics make them ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and construction sectors. The aerospace industry, in particular, has shown a strong interest in neopentane-based materials for their lightweight and thermal insulation properties, which contribute to improved fuel efficiency and overall performance of aircraft.
The construction sector represents another significant market for neopentane-based materials. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings has led to increased adoption of neopentane-based insulation materials. These materials offer superior thermal insulation properties compared to traditional alternatives, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower carbon footprints for buildings.
In the automotive industry, neopentane-based materials are finding applications in lightweight components and insulation systems. As vehicle manufacturers strive to meet stringent fuel efficiency and emission standards, the demand for lightweight materials with excellent thermal properties continues to rise. This trend is expected to drive further growth in the neopentane-based materials market.
The electronics industry is also emerging as a promising market for neopentane-based materials. These materials are being used in the production of high-performance circuit boards and electronic components, where their low dielectric constant and thermal stability properties are highly valued.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the neopentane-based materials market, owing to their well-established aerospace, automotive, and construction industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing construction activities, and growing automotive production in countries like China and India.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as volatile raw material prices and stringent environmental regulations regarding the use of certain chemicals in material production may impact the growth of the neopentane-based materials market. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these challenges and develop more sustainable production processes.
In conclusion, the market for neopentane-based materials shows promising growth potential across various industries. The unique properties of these materials, combined with increasing demand for high-performance and energy-efficient solutions, are expected to drive continued market expansion in the foreseeable future.
Current Challenges in Neopentane Utilization
Despite the potential of neopentane in advanced material production, several challenges currently hinder its widespread utilization. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost associated with neopentane production and purification. The complex synthesis process and stringent purity requirements for industrial applications contribute to elevated production expenses, limiting its economic viability in certain sectors.
Another significant challenge lies in the handling and storage of neopentane. As a highly volatile compound, neopentane requires specialized containment systems and safety protocols to prevent leaks and minimize environmental impact. This necessitates additional infrastructure investments and operational precautions, further increasing the overall cost of neopentane utilization.
The limited availability of neopentane poses a substantial hurdle for large-scale industrial applications. Current production capacities may not meet the growing demand in advanced material manufacturing, potentially creating supply chain bottlenecks and hindering the expansion of neopentane-based technologies.
Environmental concerns also present challenges in neopentane utilization. As a hydrocarbon compound, neopentane contributes to greenhouse gas emissions when released into the atmosphere. Stricter environmental regulations and sustainability goals in various industries necessitate the development of more efficient capture and recycling systems for neopentane, adding complexity to its industrial use.
The lack of comprehensive research on neopentane's long-term effects on various materials and processes poses another challenge. While its unique properties offer advantages in certain applications, the potential long-term impacts on material stability, performance, and degradation are not fully understood, requiring extensive studies and testing.
Compatibility issues with existing manufacturing processes and equipment present additional obstacles. Integrating neopentane into established production lines may require significant modifications or investments in new machinery, potentially deterring some manufacturers from adopting neopentane-based technologies.
Lastly, the development of alternative materials and processes that could potentially replace neopentane in certain applications poses a competitive challenge. Ongoing research into more sustainable or cost-effective substitutes may impact the long-term viability of neopentane in advanced material production, necessitating continuous innovation and optimization of neopentane-based technologies to maintain their relevance in the industry.
Another significant challenge lies in the handling and storage of neopentane. As a highly volatile compound, neopentane requires specialized containment systems and safety protocols to prevent leaks and minimize environmental impact. This necessitates additional infrastructure investments and operational precautions, further increasing the overall cost of neopentane utilization.
The limited availability of neopentane poses a substantial hurdle for large-scale industrial applications. Current production capacities may not meet the growing demand in advanced material manufacturing, potentially creating supply chain bottlenecks and hindering the expansion of neopentane-based technologies.
Environmental concerns also present challenges in neopentane utilization. As a hydrocarbon compound, neopentane contributes to greenhouse gas emissions when released into the atmosphere. Stricter environmental regulations and sustainability goals in various industries necessitate the development of more efficient capture and recycling systems for neopentane, adding complexity to its industrial use.
The lack of comprehensive research on neopentane's long-term effects on various materials and processes poses another challenge. While its unique properties offer advantages in certain applications, the potential long-term impacts on material stability, performance, and degradation are not fully understood, requiring extensive studies and testing.
Compatibility issues with existing manufacturing processes and equipment present additional obstacles. Integrating neopentane into established production lines may require significant modifications or investments in new machinery, potentially deterring some manufacturers from adopting neopentane-based technologies.
Lastly, the development of alternative materials and processes that could potentially replace neopentane in certain applications poses a competitive challenge. Ongoing research into more sustainable or cost-effective substitutes may impact the long-term viability of neopentane in advanced material production, necessitating continuous innovation and optimization of neopentane-based technologies to maintain their relevance in the industry.
Existing Neopentane-Based Material Solutions
01 Production and purification of neopentane
Various methods for producing and purifying neopentane are described. These include processes for separating neopentane from other hydrocarbons, such as using distillation or membrane separation techniques. The purification methods aim to obtain high-purity neopentane for industrial applications.- Production and purification of neopentane: Methods for producing and purifying neopentane, including various separation and distillation techniques to obtain high-purity neopentane from mixtures containing other hydrocarbons. These processes often involve multiple distillation steps, the use of specific catalysts, and precise temperature and pressure control.
- Applications of neopentane in chemical processes: Neopentane is used as a raw material or intermediate in various chemical processes, including the production of specialty chemicals, polymers, and fuel additives. Its unique structure and properties make it valuable in certain industrial applications where its stability and low reactivity are advantageous.
- Neopentane as a refrigerant or propellant: The use of neopentane as a refrigerant or propellant in various applications, including aerosol products and cooling systems. Its low boiling point and favorable thermodynamic properties make it suitable for these purposes, often as part of a blend with other compounds.
- Synthesis and modification of neopentane derivatives: Methods for synthesizing and modifying neopentane derivatives, such as neopentyl compounds, through various chemical reactions. These processes often involve the use of specific catalysts, reaction conditions, and purification techniques to obtain the desired products with high yield and purity.
- Neopentane in polymer and material science: The use of neopentane or its derivatives in polymer and material science applications, including as a blowing agent for foam production, a component in specialty plastics, or a modifier for improving material properties such as thermal stability or chemical resistance.
02 Use of neopentane in chemical reactions
Neopentane is utilized as a reactant or intermediate in various chemical processes. It can be used in the synthesis of other organic compounds, particularly in the production of specialty chemicals and pharmaceuticals. The unique structure of neopentane makes it valuable in certain chemical transformations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Neopentane as a refrigerant or propellant
The application of neopentane as a refrigerant or propellant is explored. Its properties, such as low boiling point and low global warming potential, make it suitable for use in cooling systems and aerosol products. Research focuses on optimizing its performance and safety in these applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Neopentane in polymer production
Neopentane is used in the production of certain polymers and plastics. It can serve as a blowing agent in the manufacture of foam materials or as a component in polymer formulations. The incorporation of neopentane can impart specific properties to the resulting materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations of neopentane
Research on the environmental impact and safety aspects of neopentane is conducted. This includes studies on its atmospheric behavior, potential as a greenhouse gas, and safety measures for handling and storage. Efforts are made to develop environmentally friendly applications and ensure safe usage of neopentane in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitors
The development of neopentane in advanced material production is in its early stages, with the market still emerging. The global market size is relatively small but growing, driven by increasing demand for high-performance materials in various industries. The technology is moderately mature, with ongoing research to expand applications. Key players like ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Wanhua Chemical Group, and JNC Corp. are investing in R&D to improve production processes and develop new neopentane-based materials. Smaller specialized firms and research institutions are also contributing to innovation in this field. As the technology advances, competition is expected to intensify, potentially leading to more cost-effective and diverse applications of neopentane in advanced materials.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed advanced processes for neopentane production and utilization in material synthesis. Their approach involves catalytic dehydrogenation of neopentane to produce isoprene, a key monomer in synthetic rubber production[1]. The company has also pioneered the use of neopentane as a blowing agent in the manufacture of expanded polystyrene (EPS) and extruded polystyrene (XPS) foams, offering improved insulation properties and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional blowing agents[2]. Additionally, ExxonMobil has explored the potential of neopentane as a working fluid in organic Rankine cycle (ORC) systems for waste heat recovery in industrial processes[3].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, established production infrastructure, and a diverse range of applications. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns associated with hydrocarbon-based processes and products.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has developed innovative applications of neopentane in the production of high-performance polyurethane materials. Their approach involves using neopentane as a physical blowing agent in the manufacture of rigid polyurethane foams, resulting in improved thermal insulation properties and reduced environmental impact[4]. The company has also explored the use of neopentane-based formulations in the production of microcellular polyurethane elastomers, offering enhanced durability and lightweight characteristics for automotive and industrial applications[5]. Furthermore, Wanhua has investigated the potential of neopentane as a solvent in the synthesis of specialty polyurethane dispersions, enabling the development of water-based coatings with improved performance and reduced VOC emissions[6].
Strengths: Strong focus on sustainable and high-performance materials, diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges associated with the use of hydrocarbon blowing agents in certain markets.
Innovative Neopentane Technologies Analysis
Production of Neopentane
PatentActiveUS20190177248A1
Innovation
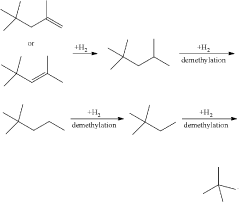
- A process involving the dimerization of isobutylene to form diisobutylene, followed by demethylation using a catalyst in the presence of hydrogen, which utilizes readily available isobutylene from refinery raffinate streams to produce neopentane with high yield and selectivity.
Processes to Make Neopentane Using Shell and Tube Reactors
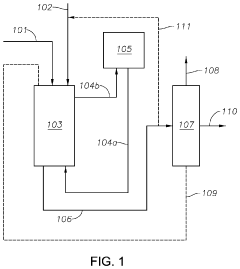
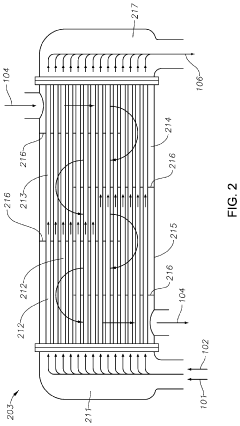
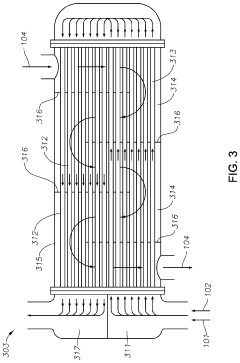
PatentActiveUS20190367429A1
Innovation
- The process involves demethylating C6-C8 alkanes in a shell and tube reactor to produce neopentane, utilizing a catalyst and controlling temperature to achieve high conversion and purity, with a shell and tube reactor design that includes a heat-exchange system to manage the exothermic nature of the reaction.
Environmental Impact of Neopentane Use
The use of neopentane in advanced material production raises significant environmental concerns that warrant careful consideration. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), neopentane can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone when released into the atmosphere. This can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems in affected populations, particularly in urban areas with high industrial activity.
Furthermore, neopentane has a global warming potential (GWP) that is higher than carbon dioxide, making it a potent greenhouse gas. Its release during manufacturing processes or through accidental leaks can contribute to climate change, albeit on a smaller scale compared to more prevalent greenhouse gases. This necessitates stringent emission control measures in facilities utilizing neopentane.
Water pollution is another potential environmental impact of neopentane use. Improper handling or disposal can result in contamination of water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. While neopentane has low water solubility, its presence in water can still have detrimental effects on marine life and water quality.
The production of neopentane itself also carries environmental implications. As a petroleum-derived compound, its manufacture contributes to the depletion of non-renewable resources and the associated environmental impacts of fossil fuel extraction and processing. This includes habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions from the petrochemical industry.
In terms of waste management, neopentane and materials containing it require special handling and disposal procedures. Improper disposal can lead to soil contamination and the release of harmful vapors. Recycling and safe disposal of neopentane-containing products present challenges that need to be addressed to minimize environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, industries using neopentane in advanced material production must implement robust emission control systems, leak detection protocols, and proper waste management practices. Additionally, research into more environmentally friendly alternatives or processes that reduce neopentane usage could help minimize its ecological footprint.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of VOCs like neopentane. Compliance with evolving environmental regulations and standards is crucial for industries utilizing this compound. This may include limits on emissions, requirements for best available technologies, and mandatory reporting of usage and releases.
Furthermore, neopentane has a global warming potential (GWP) that is higher than carbon dioxide, making it a potent greenhouse gas. Its release during manufacturing processes or through accidental leaks can contribute to climate change, albeit on a smaller scale compared to more prevalent greenhouse gases. This necessitates stringent emission control measures in facilities utilizing neopentane.
Water pollution is another potential environmental impact of neopentane use. Improper handling or disposal can result in contamination of water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. While neopentane has low water solubility, its presence in water can still have detrimental effects on marine life and water quality.
The production of neopentane itself also carries environmental implications. As a petroleum-derived compound, its manufacture contributes to the depletion of non-renewable resources and the associated environmental impacts of fossil fuel extraction and processing. This includes habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions from the petrochemical industry.
In terms of waste management, neopentane and materials containing it require special handling and disposal procedures. Improper disposal can lead to soil contamination and the release of harmful vapors. Recycling and safe disposal of neopentane-containing products present challenges that need to be addressed to minimize environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, industries using neopentane in advanced material production must implement robust emission control systems, leak detection protocols, and proper waste management practices. Additionally, research into more environmentally friendly alternatives or processes that reduce neopentane usage could help minimize its ecological footprint.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of VOCs like neopentane. Compliance with evolving environmental regulations and standards is crucial for industries utilizing this compound. This may include limits on emissions, requirements for best available technologies, and mandatory reporting of usage and releases.
Safety Regulations for Neopentane Handling
The handling of neopentane in advanced material production requires strict adherence to safety regulations due to its highly flammable nature and potential health hazards. Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have established comprehensive guidelines for the safe use, storage, and transportation of neopentane.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory when working with neopentane. This includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and flame-resistant clothing. Respiratory protection may also be necessary in certain situations, particularly when there is a risk of vapor inhalation. Regular training on proper PPE use and maintenance is essential for all personnel involved in neopentane handling.
Storage facilities for neopentane must meet specific requirements to prevent leaks and minimize fire risks. These include the use of explosion-proof electrical equipment, adequate ventilation systems, and specialized containment measures. Storage tanks should be equipped with pressure relief valves and be located in well-ventilated areas away from sources of ignition. Regular inspections and maintenance of storage facilities are crucial to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Transportation of neopentane is subject to strict regulations under the Department of Transportation (DOT) guidelines. Proper labeling, packaging, and documentation are required for all shipments. Vehicles used for transportation must be specially equipped to handle flammable materials and drivers must receive specialized training in hazardous material transport.
Emergency response protocols are a critical component of neopentane safety regulations. Facilities must have detailed emergency plans in place, including procedures for spill containment, fire suppression, and evacuation. Regular drills and simulations should be conducted to ensure all personnel are familiar with emergency procedures.
Monitoring and control systems play a vital role in maintaining safety during neopentane handling. This includes the use of gas detection systems, temperature and pressure monitors, and automated shut-off valves. Implementing a robust system of checks and balances, such as the use of permits for high-risk activities, helps to prevent accidents and ensure compliance with safety protocols.
Waste management and disposal of neopentane-containing materials must also adhere to strict environmental regulations. Proper disposal methods, including recycling where possible, should be employed to minimize environmental impact and comply with local and federal guidelines.
Regular safety audits and compliance checks are essential to maintain a high level of safety in neopentane handling. These audits should cover all aspects of neopentane use, from storage and handling procedures to emergency preparedness and employee training programs. Continuous improvement of safety measures based on audit findings and industry best practices is crucial for maintaining a safe working environment.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory when working with neopentane. This includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and flame-resistant clothing. Respiratory protection may also be necessary in certain situations, particularly when there is a risk of vapor inhalation. Regular training on proper PPE use and maintenance is essential for all personnel involved in neopentane handling.
Storage facilities for neopentane must meet specific requirements to prevent leaks and minimize fire risks. These include the use of explosion-proof electrical equipment, adequate ventilation systems, and specialized containment measures. Storage tanks should be equipped with pressure relief valves and be located in well-ventilated areas away from sources of ignition. Regular inspections and maintenance of storage facilities are crucial to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Transportation of neopentane is subject to strict regulations under the Department of Transportation (DOT) guidelines. Proper labeling, packaging, and documentation are required for all shipments. Vehicles used for transportation must be specially equipped to handle flammable materials and drivers must receive specialized training in hazardous material transport.
Emergency response protocols are a critical component of neopentane safety regulations. Facilities must have detailed emergency plans in place, including procedures for spill containment, fire suppression, and evacuation. Regular drills and simulations should be conducted to ensure all personnel are familiar with emergency procedures.
Monitoring and control systems play a vital role in maintaining safety during neopentane handling. This includes the use of gas detection systems, temperature and pressure monitors, and automated shut-off valves. Implementing a robust system of checks and balances, such as the use of permits for high-risk activities, helps to prevent accidents and ensure compliance with safety protocols.
Waste management and disposal of neopentane-containing materials must also adhere to strict environmental regulations. Proper disposal methods, including recycling where possible, should be employed to minimize environmental impact and comply with local and federal guidelines.
Regular safety audits and compliance checks are essential to maintain a high level of safety in neopentane handling. These audits should cover all aspects of neopentane use, from storage and handling procedures to emergency preparedness and employee training programs. Continuous improvement of safety measures based on audit findings and industry best practices is crucial for maintaining a safe working environment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!