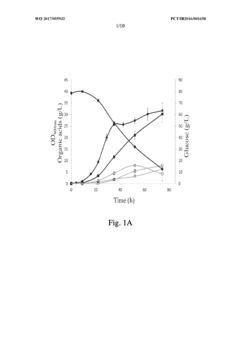
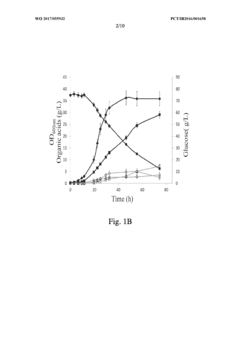
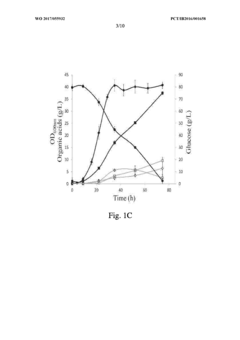
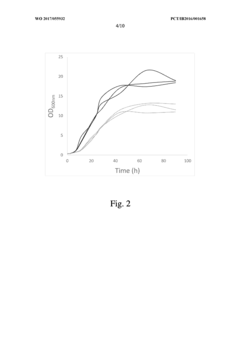
Addressing Industry Needs with Propionic Acid Advances
JUL 3, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Evolution
Propionic acid has undergone significant evolution since its discovery in the mid-19th century. Initially recognized as a byproduct of bacterial fermentation, it was primarily studied for its role in dairy products and ruminant digestion. The early 20th century saw the development of synthetic production methods, marking a crucial turning point in its industrial application.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the petrochemical industry's growth led to increased propionic acid production through the hydrocarboxylation of ethylene. This process, along with the oxidation of propionaldehyde, became the dominant manufacturing methods, enabling large-scale production to meet growing industrial demands.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a surge in research on propionic acid's antimicrobial properties. This period saw its widespread adoption in food preservation, particularly in bakery products and animal feed. Concurrently, the chemical industry began exploring its potential as a precursor for various compounds, including cellulose acetate propionate and herbicides.
The late 20th century brought about a renewed interest in biotechnological production methods. Researchers focused on optimizing fermentation processes using Propionibacterium strains, aiming to develop more sustainable and cost-effective production techniques. This shift aligned with growing environmental concerns and the push for greener chemical processes.
The early 21st century has been characterized by a focus on enhancing propionic acid's purity and developing novel applications. Advanced purification techniques have enabled the production of high-grade propionic acid suitable for pharmaceutical and personal care products. Additionally, its role in biodegradable plastics and as a building block for other chemicals has gained prominence.
Recent years have seen a convergence of traditional chemical engineering and biotechnology in propionic acid production. Hybrid processes combining fermentation with chemical catalysis are being explored to maximize yield and efficiency. Furthermore, genetic engineering of microorganisms for improved propionic acid production is an active area of research, promising potential breakthroughs in biosynthesis.
The evolution of propionic acid technology has been driven by the interplay of market demands, environmental considerations, and scientific advancements. From its humble beginnings as a fermentation byproduct to its current status as a versatile industrial chemical, propionic acid's journey reflects the broader trends in chemical engineering and biotechnology. As industry needs continue to evolve, further innovations in propionic acid production and application are anticipated, potentially revolutionizing its role in various sectors.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the petrochemical industry's growth led to increased propionic acid production through the hydrocarboxylation of ethylene. This process, along with the oxidation of propionaldehyde, became the dominant manufacturing methods, enabling large-scale production to meet growing industrial demands.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a surge in research on propionic acid's antimicrobial properties. This period saw its widespread adoption in food preservation, particularly in bakery products and animal feed. Concurrently, the chemical industry began exploring its potential as a precursor for various compounds, including cellulose acetate propionate and herbicides.
The late 20th century brought about a renewed interest in biotechnological production methods. Researchers focused on optimizing fermentation processes using Propionibacterium strains, aiming to develop more sustainable and cost-effective production techniques. This shift aligned with growing environmental concerns and the push for greener chemical processes.
The early 21st century has been characterized by a focus on enhancing propionic acid's purity and developing novel applications. Advanced purification techniques have enabled the production of high-grade propionic acid suitable for pharmaceutical and personal care products. Additionally, its role in biodegradable plastics and as a building block for other chemicals has gained prominence.
Recent years have seen a convergence of traditional chemical engineering and biotechnology in propionic acid production. Hybrid processes combining fermentation with chemical catalysis are being explored to maximize yield and efficiency. Furthermore, genetic engineering of microorganisms for improved propionic acid production is an active area of research, promising potential breakthroughs in biosynthesis.
The evolution of propionic acid technology has been driven by the interplay of market demands, environmental considerations, and scientific advancements. From its humble beginnings as a fermentation byproduct to its current status as a versatile industrial chemical, propionic acid's journey reflects the broader trends in chemical engineering and biotechnology. As industry needs continue to evolve, further innovations in propionic acid production and application are anticipated, potentially revolutionizing its role in various sectors.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for propionic acid has been steadily increasing due to its versatile applications across various industries. In the food and beverage sector, propionic acid serves as a crucial preservative, extending the shelf life of baked goods, dairy products, and processed foods. This application has seen significant growth, driven by the rising consumer demand for convenience foods and the need for longer-lasting products in global supply chains.
The animal feed industry represents another major market for propionic acid. As livestock production continues to expand worldwide, the demand for effective feed preservatives has surged. Propionic acid's ability to inhibit mold growth and prevent feed spoilage has made it an essential component in animal nutrition, particularly in regions with challenging climatic conditions.
In the pharmaceutical and personal care industries, propionic acid finds applications as an intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs and cosmetic products. The growing emphasis on personal hygiene and healthcare has further boosted the demand for propionic acid in these sectors.
The chemical industry utilizes propionic acid as a precursor for the production of cellulose acetate propionate, a material used in various applications such as eyeglass frames, tool handles, and automotive parts. The expanding automotive and consumer goods industries have contributed to the increased demand for this derivative.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest consumers of propionic acid, owing to their well-established food processing and animal feed industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing industrialization, changing dietary habits, and the expansion of livestock farming.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5-6% for the global propionic acid market over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the expanding food and beverage industry, particularly in developing economies, and the increasing adoption of propionic acid in animal feed applications.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards bio-based propionic acid production methods, driven by sustainability concerns and the push for greener alternatives. This trend is expected to create new opportunities for market players and potentially reshape the competitive landscape in the coming years.
The animal feed industry represents another major market for propionic acid. As livestock production continues to expand worldwide, the demand for effective feed preservatives has surged. Propionic acid's ability to inhibit mold growth and prevent feed spoilage has made it an essential component in animal nutrition, particularly in regions with challenging climatic conditions.
In the pharmaceutical and personal care industries, propionic acid finds applications as an intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs and cosmetic products. The growing emphasis on personal hygiene and healthcare has further boosted the demand for propionic acid in these sectors.
The chemical industry utilizes propionic acid as a precursor for the production of cellulose acetate propionate, a material used in various applications such as eyeglass frames, tool handles, and automotive parts. The expanding automotive and consumer goods industries have contributed to the increased demand for this derivative.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest consumers of propionic acid, owing to their well-established food processing and animal feed industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing industrialization, changing dietary habits, and the expansion of livestock farming.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5-6% for the global propionic acid market over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the expanding food and beverage industry, particularly in developing economies, and the increasing adoption of propionic acid in animal feed applications.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards bio-based propionic acid production methods, driven by sustainability concerns and the push for greener alternatives. This trend is expected to create new opportunities for market players and potentially reshape the competitive landscape in the coming years.
Technical Challenges
Propionic acid production and application face several technical challenges that require innovative solutions to meet growing industry demands. One of the primary obstacles is the high production cost associated with traditional fermentation methods. The current processes often suffer from low yields and productivity, making it difficult to achieve economically viable large-scale production.
Another significant challenge lies in the purification and separation of propionic acid from fermentation broths. The presence of impurities and by-products necessitates complex downstream processing, which adds to the overall production costs and reduces efficiency. Developing more effective separation techniques is crucial for improving the quality and purity of the final product.
The sustainability of propionic acid production is also a pressing concern. Many current production methods rely on non-renewable petrochemical feedstocks, which are not environmentally friendly and subject to price volatility. There is a growing need to develop bio-based production routes that utilize renewable resources and reduce the carbon footprint of the manufacturing process.
Microbial strain improvement presents another technical hurdle. Enhancing the productivity and tolerance of microorganisms used in fermentation is essential for increasing yields and reducing production costs. This involves genetic engineering and metabolic pathway optimization to create more robust and efficient strains capable of withstanding harsh fermentation conditions.
Process intensification is a critical area that requires attention. Developing continuous fermentation processes and integrating upstream and downstream operations could significantly improve productivity and reduce energy consumption. However, implementing such advanced systems presents technical challenges in terms of process control and scalability.
The stability and shelf life of propionic acid products pose additional challenges, particularly in food preservation applications. Developing formulations that maintain efficacy over extended periods while meeting regulatory requirements for food safety is an ongoing technical challenge that requires innovative solutions.
Lastly, the versatility of propionic acid applications demands the development of tailored products for specific industries. Creating specialized derivatives and formulations that meet the unique requirements of diverse sectors such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products requires extensive research and development efforts.
Addressing these technical challenges will be crucial for advancing propionic acid technology and meeting the evolving needs of various industries. Overcoming these obstacles will pave the way for more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective production methods, ultimately expanding the market potential of propionic acid and its derivatives.
Another significant challenge lies in the purification and separation of propionic acid from fermentation broths. The presence of impurities and by-products necessitates complex downstream processing, which adds to the overall production costs and reduces efficiency. Developing more effective separation techniques is crucial for improving the quality and purity of the final product.
The sustainability of propionic acid production is also a pressing concern. Many current production methods rely on non-renewable petrochemical feedstocks, which are not environmentally friendly and subject to price volatility. There is a growing need to develop bio-based production routes that utilize renewable resources and reduce the carbon footprint of the manufacturing process.
Microbial strain improvement presents another technical hurdle. Enhancing the productivity and tolerance of microorganisms used in fermentation is essential for increasing yields and reducing production costs. This involves genetic engineering and metabolic pathway optimization to create more robust and efficient strains capable of withstanding harsh fermentation conditions.
Process intensification is a critical area that requires attention. Developing continuous fermentation processes and integrating upstream and downstream operations could significantly improve productivity and reduce energy consumption. However, implementing such advanced systems presents technical challenges in terms of process control and scalability.
The stability and shelf life of propionic acid products pose additional challenges, particularly in food preservation applications. Developing formulations that maintain efficacy over extended periods while meeting regulatory requirements for food safety is an ongoing technical challenge that requires innovative solutions.
Lastly, the versatility of propionic acid applications demands the development of tailored products for specific industries. Creating specialized derivatives and formulations that meet the unique requirements of diverse sectors such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products requires extensive research and development efforts.
Addressing these technical challenges will be crucial for advancing propionic acid technology and meeting the evolving needs of various industries. Overcoming these obstacles will pave the way for more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective production methods, ultimately expanding the market potential of propionic acid and its derivatives.
Current Solutions
01 Production methods of propionic acid
Various methods for producing propionic acid are described, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis routes, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of propionic acid production for industrial applications.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective in inhibiting the growth of mold and certain bacteria, thereby extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly baked goods and dairy products.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations: Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the formulation of various medications, including topical treatments for skin conditions and as intermediates in the synthesis of certain drugs.
- Industrial applications of propionic acid: Propionic acid has diverse industrial applications beyond food and pharmaceuticals. It is used in the production of plastics, herbicides, and as a chemical intermediate in various manufacturing processes. Its properties make it valuable in industries such as agriculture, polymers, and chemical synthesis.
- Purification and processing of propionic acid: Various methods and technologies are employed for the purification and processing of propionic acid. These include distillation techniques, crystallization processes, and the use of specific additives or solvents to improve the purity and quality of the final product for different industrial applications.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective against molds and bacteria, extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in bakery and dairy industries.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations
Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in pharmaceutical formulations as excipients, pH adjusters, or active ingredients. They are used in various drug delivery systems and topical preparations for their beneficial properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Propionic acid in agricultural applications
Propionic acid is utilized in agriculture for various purposes, including as a grain preservative, silage additive, and herbicide. It helps prevent mold growth in stored grains and improves the quality of animal feed.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations of propionic acid
Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of propionic acid production and use. This includes developing greener production methods, studying biodegradation, and assessing potential health effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The propionic acid market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The global market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate expected to be in the high single digits. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with major players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., PetroChina Co., Ltd., and Dow Global Technologies LLC leading innovation efforts. These companies are focusing on developing more efficient production processes and exploring new applications. Emerging players such as Novomer, Inc. and 6K Inc. are introducing novel technologies that could potentially disrupt the market. The industry is also seeing increased interest in sustainable production methods, with companies like Braskem SA and Fluid Energy Group Ltd. exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petrochemical processes.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced catalytic processes for propionic acid production. Their approach involves the carbonylation of ethylene using carbon monoxide and a homogeneous catalyst system. This method achieves high selectivity and yield, with reported conversion rates of over 95% [1]. Sinopec has also implemented a novel purification technique that reduces energy consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional distillation methods [3]. Additionally, they have explored the use of bio-based feedstocks, such as biomass-derived ethanol, to produce green propionic acid, aligning with sustainability goals [5].
Strengths: High conversion rates, energy-efficient purification, and exploration of sustainable feedstocks. Weaknesses: Dependence on ethylene availability and potential catalyst cost issues.
Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Nippon Shokubai has pioneered a unique approach to propionic acid production using their proprietary oxidation technology. Their process utilizes a mixed metal oxide catalyst to directly oxidize propionaldehyde, achieving yields of up to 98% [2]. This method offers advantages in terms of raw material flexibility, as propionaldehyde can be derived from various sources. The company has also developed a continuous flow reactor system that enhances process efficiency and reduces reaction time by approximately 40% compared to batch processes [4]. Furthermore, Nippon Shokubai has implemented advanced process control systems that optimize reaction conditions in real-time, leading to improved product quality and consistency [6].
Strengths: High yield, raw material flexibility, and advanced process control. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in catalyst stability and regeneration.
Innovative Technologies
Improved propionibacterium strains for the production of propionic acid
PatentWO2017055932A2
Innovation
- Genome shuffling between selected Propionibacterium strains, such as P. acidipropionici ATCC 4875 and P. acidipropionici ATCC 55737, to generate novel strains with enhanced growth rates and propionic acid production, utilizing genetic material exchange to create strains with improved metabolic pathways and regulatory mechanisms.
Biotechnological production of propanol and/or propionic acid
PatentInactiveUS20200231994A1
Innovation
- A biotechnological method involving the use of ethanol and acetate in the presence of carbon dioxide, utilizing propionogen microorganisms like Clostridium neopropionicum to selectively produce propanol and propionic acid, with exogenously added acetate maintaining a concentration of at least 1 g/L to reduce by-product formation and enhance yield.
Environmental Impact
Propionic acid production and utilization have significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The manufacturing process of propionic acid traditionally relies on petrochemical feedstocks, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. However, recent advances in biotechnological production methods offer more sustainable alternatives. Fermentation-based processes using renewable biomass as feedstock can substantially reduce the carbon footprint of propionic acid production.
The environmental impact of propionic acid extends beyond its production to its applications. As a widely used food preservative, it helps reduce food waste by extending shelf life, thereby indirectly contributing to the conservation of resources and reduction of methane emissions from landfills. In agriculture, propionic acid's use as a grain preservative minimizes post-harvest losses, enhancing food security while reducing the need for additional cultivation and associated environmental pressures.
In the animal feed industry, propionic acid serves as an effective mold inhibitor, improving feed quality and animal health. This application indirectly contributes to more efficient livestock production, potentially reducing the overall environmental footprint of animal agriculture. However, it is crucial to consider the potential ecological effects of increased propionic acid use in agricultural settings, particularly its impact on soil microbiota and aquatic ecosystems if improperly managed.
The chemical industry's use of propionic acid in the production of cellulose acetate propionate (CAP) and other polymers presents both challenges and opportunities from an environmental perspective. While these materials offer improved properties and durability, their end-of-life management requires careful consideration to prevent environmental accumulation. Advances in biodegradable propionic acid-based polymers could provide more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional plastics.
As industries increasingly adopt propionic acid and its derivatives, it becomes imperative to implement comprehensive life cycle assessments. These assessments should evaluate the environmental impacts from raw material extraction through production, use, and disposal. Such analyses can guide the development of more sustainable production methods and applications, ensuring that advancements in propionic acid technology align with global environmental goals and circular economy principles.
The environmental impact of propionic acid extends beyond its production to its applications. As a widely used food preservative, it helps reduce food waste by extending shelf life, thereby indirectly contributing to the conservation of resources and reduction of methane emissions from landfills. In agriculture, propionic acid's use as a grain preservative minimizes post-harvest losses, enhancing food security while reducing the need for additional cultivation and associated environmental pressures.
In the animal feed industry, propionic acid serves as an effective mold inhibitor, improving feed quality and animal health. This application indirectly contributes to more efficient livestock production, potentially reducing the overall environmental footprint of animal agriculture. However, it is crucial to consider the potential ecological effects of increased propionic acid use in agricultural settings, particularly its impact on soil microbiota and aquatic ecosystems if improperly managed.
The chemical industry's use of propionic acid in the production of cellulose acetate propionate (CAP) and other polymers presents both challenges and opportunities from an environmental perspective. While these materials offer improved properties and durability, their end-of-life management requires careful consideration to prevent environmental accumulation. Advances in biodegradable propionic acid-based polymers could provide more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional plastics.
As industries increasingly adopt propionic acid and its derivatives, it becomes imperative to implement comprehensive life cycle assessments. These assessments should evaluate the environmental impacts from raw material extraction through production, use, and disposal. Such analyses can guide the development of more sustainable production methods and applications, ensuring that advancements in propionic acid technology align with global environmental goals and circular economy principles.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding propionic acid plays a crucial role in shaping its production, distribution, and application across various industries. As a widely used preservative and chemical intermediate, propionic acid is subject to a complex web of regulations that aim to ensure its safe use and environmental sustainability.
In the food industry, propionic acid is regulated as a food additive in many countries. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved its use as a preservative in certain food products, with specific limitations on concentration levels. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has established guidelines for its use in food preservation, setting acceptable daily intake levels and maximum residue limits.
Environmental regulations also significantly impact the propionic acid industry. The production process and waste management are subject to strict environmental protection laws in many jurisdictions. Manufacturers must adhere to emissions standards and implement proper disposal methods for byproducts. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees these aspects under the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act.
Occupational safety regulations are another critical component of the regulatory framework. Organizations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States have established exposure limits and safety protocols for workers handling propionic acid. These regulations mandate proper personal protective equipment, ventilation systems, and emergency response procedures in production facilities.
Transportation of propionic acid is governed by international and national regulations for hazardous materials. The United Nations' Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods classifies propionic acid and provides guidelines for its safe transportation. Individual countries have implemented these recommendations into their national laws, such as the U.S. Department of Transportation's Hazardous Materials Regulations.
As the applications of propionic acid expand, regulatory bodies are continuously updating their frameworks to address new concerns and technological advancements. For instance, the growing use of propionic acid in sustainable agriculture has prompted regulatory agencies to reassess its environmental impact and establish guidelines for its use as a soil amendment or crop protection agent.
The global nature of the propionic acid market necessitates harmonization of regulations across different regions. International organizations like the Codex Alimentarius Commission work towards establishing global standards for food additives, including propionic acid. However, discrepancies in regulations between countries can create challenges for manufacturers and exporters, highlighting the need for ongoing efforts to align regulatory frameworks internationally.
In the food industry, propionic acid is regulated as a food additive in many countries. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved its use as a preservative in certain food products, with specific limitations on concentration levels. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has established guidelines for its use in food preservation, setting acceptable daily intake levels and maximum residue limits.
Environmental regulations also significantly impact the propionic acid industry. The production process and waste management are subject to strict environmental protection laws in many jurisdictions. Manufacturers must adhere to emissions standards and implement proper disposal methods for byproducts. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees these aspects under the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act.
Occupational safety regulations are another critical component of the regulatory framework. Organizations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States have established exposure limits and safety protocols for workers handling propionic acid. These regulations mandate proper personal protective equipment, ventilation systems, and emergency response procedures in production facilities.
Transportation of propionic acid is governed by international and national regulations for hazardous materials. The United Nations' Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods classifies propionic acid and provides guidelines for its safe transportation. Individual countries have implemented these recommendations into their national laws, such as the U.S. Department of Transportation's Hazardous Materials Regulations.
As the applications of propionic acid expand, regulatory bodies are continuously updating their frameworks to address new concerns and technological advancements. For instance, the growing use of propionic acid in sustainable agriculture has prompted regulatory agencies to reassess its environmental impact and establish guidelines for its use as a soil amendment or crop protection agent.
The global nature of the propionic acid market necessitates harmonization of regulations across different regions. International organizations like the Codex Alimentarius Commission work towards establishing global standards for food additives, including propionic acid. However, discrepancies in regulations between countries can create challenges for manufacturers and exporters, highlighting the need for ongoing efforts to align regulatory frameworks internationally.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!