Propionic Acid's Contribution to Future Climate Solutions
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Overview and Climate Goals
Propionic acid, a short-chain fatty acid, has emerged as a promising contributor to future climate solutions. This organic compound, naturally produced by certain bacteria and found in various food products, has gained attention for its potential to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable practices across multiple industries.
The development of propionic acid as a climate solution is rooted in its versatile chemical properties and wide-ranging applications. Historically used as a food preservative and animal feed additive, recent research has uncovered its potential in reducing methane emissions from livestock, enhancing carbon sequestration in soils, and serving as a renewable feedstock for biodegradable plastics.
As global efforts to combat climate change intensify, propionic acid aligns with several key environmental goals. Its ability to inhibit methanogenic bacteria in ruminant animals addresses the significant challenge of reducing methane emissions from the agricultural sector. Moreover, when used as a soil amendment, propionic acid can improve carbon retention, contributing to the broader objective of enhancing natural carbon sinks.
In the realm of sustainable materials, propionic acid serves as a building block for biodegradable polymers, offering an alternative to petroleum-based plastics. This application supports the transition towards a circular economy and reduces reliance on fossil fuel-derived products. Additionally, the production of propionic acid through fermentation processes using renewable resources aligns with the goals of developing bio-based economies and reducing carbon footprints in industrial production.
The technology surrounding propionic acid is evolving rapidly, with ongoing research focused on optimizing its production, enhancing its efficacy in various applications, and exploring new potential uses in climate mitigation strategies. Current technological goals include improving the efficiency of fermentation processes, developing novel formulations for agricultural applications, and expanding its use in sustainable material production.
As the global community strives to achieve net-zero emissions and implement sustainable practices across all sectors, propionic acid represents a multifaceted solution with the potential to contribute significantly to these efforts. Its development and application in climate solutions exemplify the innovative approaches necessary to address the complex challenges posed by climate change, bridging the gap between traditional industrial processes and sustainable, environmentally conscious practices.
The development of propionic acid as a climate solution is rooted in its versatile chemical properties and wide-ranging applications. Historically used as a food preservative and animal feed additive, recent research has uncovered its potential in reducing methane emissions from livestock, enhancing carbon sequestration in soils, and serving as a renewable feedstock for biodegradable plastics.
As global efforts to combat climate change intensify, propionic acid aligns with several key environmental goals. Its ability to inhibit methanogenic bacteria in ruminant animals addresses the significant challenge of reducing methane emissions from the agricultural sector. Moreover, when used as a soil amendment, propionic acid can improve carbon retention, contributing to the broader objective of enhancing natural carbon sinks.
In the realm of sustainable materials, propionic acid serves as a building block for biodegradable polymers, offering an alternative to petroleum-based plastics. This application supports the transition towards a circular economy and reduces reliance on fossil fuel-derived products. Additionally, the production of propionic acid through fermentation processes using renewable resources aligns with the goals of developing bio-based economies and reducing carbon footprints in industrial production.
The technology surrounding propionic acid is evolving rapidly, with ongoing research focused on optimizing its production, enhancing its efficacy in various applications, and exploring new potential uses in climate mitigation strategies. Current technological goals include improving the efficiency of fermentation processes, developing novel formulations for agricultural applications, and expanding its use in sustainable material production.
As the global community strives to achieve net-zero emissions and implement sustainable practices across all sectors, propionic acid represents a multifaceted solution with the potential to contribute significantly to these efforts. Its development and application in climate solutions exemplify the innovative approaches necessary to address the complex challenges posed by climate change, bridging the gap between traditional industrial processes and sustainable, environmentally conscious practices.
Market Analysis for Climate-Friendly Solutions
The market for climate-friendly solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing global awareness of climate change and the urgent need for sustainable practices. Propionic acid, a versatile organic compound, has emerged as a potential contributor to future climate solutions, particularly in the agricultural and industrial sectors.
In the agricultural market, propionic acid has gained traction as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional chemical preservatives. Its ability to inhibit mold growth in animal feed and silage has led to increased adoption among farmers seeking sustainable methods to reduce food waste and improve livestock health. This trend aligns with the growing demand for organic and environmentally responsible farming practices, creating a substantial market opportunity for propionic acid-based solutions.
The industrial sector presents another promising market for propionic acid in climate-friendly applications. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint, propionic acid has found use in the production of biodegradable plastics and environmentally friendly solvents. These applications cater to the increasing consumer demand for sustainable products and packaging, driving market growth in sectors such as food packaging, cosmetics, and consumer goods.
The global push for renewable energy sources has also opened new avenues for propionic acid in the biofuel industry. Its potential as a precursor for biofuel production aligns with the growing market for alternative energy solutions, particularly in regions with stringent emissions regulations and ambitious climate targets.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the propionic acid market, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing adoption of sustainable practices in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with established regulatory frameworks supporting the transition to greener technologies.
The market potential for propionic acid in climate-friendly solutions is further bolstered by supportive government policies and incentives aimed at promoting sustainable practices. Many countries have implemented carbon pricing mechanisms and environmental regulations that favor the adoption of eco-friendly alternatives, creating a favorable market environment for propionic acid-based products.
However, challenges remain in terms of cost competitiveness and scalability. While the demand for sustainable solutions is growing, price sensitivity in certain markets may slow adoption rates. Overcoming these barriers through technological advancements and economies of scale will be crucial for maximizing the market potential of propionic acid in climate solutions.
In the agricultural market, propionic acid has gained traction as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional chemical preservatives. Its ability to inhibit mold growth in animal feed and silage has led to increased adoption among farmers seeking sustainable methods to reduce food waste and improve livestock health. This trend aligns with the growing demand for organic and environmentally responsible farming practices, creating a substantial market opportunity for propionic acid-based solutions.
The industrial sector presents another promising market for propionic acid in climate-friendly applications. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint, propionic acid has found use in the production of biodegradable plastics and environmentally friendly solvents. These applications cater to the increasing consumer demand for sustainable products and packaging, driving market growth in sectors such as food packaging, cosmetics, and consumer goods.
The global push for renewable energy sources has also opened new avenues for propionic acid in the biofuel industry. Its potential as a precursor for biofuel production aligns with the growing market for alternative energy solutions, particularly in regions with stringent emissions regulations and ambitious climate targets.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the propionic acid market, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing adoption of sustainable practices in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with established regulatory frameworks supporting the transition to greener technologies.
The market potential for propionic acid in climate-friendly solutions is further bolstered by supportive government policies and incentives aimed at promoting sustainable practices. Many countries have implemented carbon pricing mechanisms and environmental regulations that favor the adoption of eco-friendly alternatives, creating a favorable market environment for propionic acid-based products.
However, challenges remain in terms of cost competitiveness and scalability. While the demand for sustainable solutions is growing, price sensitivity in certain markets may slow adoption rates. Overcoming these barriers through technological advancements and economies of scale will be crucial for maximizing the market potential of propionic acid in climate solutions.
Current Challenges in Propionic Acid Production
The production of propionic acid faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption as a climate solution. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost of production, which makes it less competitive compared to conventional fossil-based alternatives. The current production methods, primarily petrochemical processes and fermentation, are energy-intensive and require substantial capital investments, limiting scalability and market penetration.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to propionic acid production. Traditional petrochemical routes rely on fossil fuel feedstocks, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation. While bio-based production methods offer a more sustainable alternative, they often struggle with lower yields and efficiency compared to their petrochemical counterparts.
Feedstock availability and price volatility present another hurdle. Bio-based production methods depend on agricultural raw materials, which are subject to seasonal fluctuations, weather conditions, and competition with food crops. This can lead to supply chain instabilities and unpredictable production costs, making it difficult for manufacturers to maintain consistent output and pricing.
Technical limitations in fermentation processes also impede progress. Microbial strains used for propionic acid production often have low tolerance to the acid, resulting in reduced productivity and yield. Additionally, the separation and purification of propionic acid from fermentation broths remain complex and costly, further impacting overall production efficiency.
Regulatory hurdles and lack of standardization across different regions create barriers to market entry and expansion. Varying environmental regulations, product safety standards, and approval processes can slow down the adoption of propionic acid-based solutions in different industries and geographical areas.
Market acceptance and consumer awareness present additional challenges. Many potential end-users are unfamiliar with propionic acid's benefits as a climate solution, leading to hesitation in adopting new technologies or products incorporating this compound. Overcoming this requires extensive education and marketing efforts to demonstrate the environmental and economic advantages of propionic acid-based alternatives.
Lastly, the lack of a robust circular economy infrastructure for propionic acid and its derivatives hinders its potential as a sustainable solution. Developing efficient recycling and upcycling processes for propionic acid-based products is crucial to maximize its environmental benefits and create a closed-loop system that aligns with circular economy principles.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to propionic acid production. Traditional petrochemical routes rely on fossil fuel feedstocks, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation. While bio-based production methods offer a more sustainable alternative, they often struggle with lower yields and efficiency compared to their petrochemical counterparts.
Feedstock availability and price volatility present another hurdle. Bio-based production methods depend on agricultural raw materials, which are subject to seasonal fluctuations, weather conditions, and competition with food crops. This can lead to supply chain instabilities and unpredictable production costs, making it difficult for manufacturers to maintain consistent output and pricing.
Technical limitations in fermentation processes also impede progress. Microbial strains used for propionic acid production often have low tolerance to the acid, resulting in reduced productivity and yield. Additionally, the separation and purification of propionic acid from fermentation broths remain complex and costly, further impacting overall production efficiency.
Regulatory hurdles and lack of standardization across different regions create barriers to market entry and expansion. Varying environmental regulations, product safety standards, and approval processes can slow down the adoption of propionic acid-based solutions in different industries and geographical areas.
Market acceptance and consumer awareness present additional challenges. Many potential end-users are unfamiliar with propionic acid's benefits as a climate solution, leading to hesitation in adopting new technologies or products incorporating this compound. Overcoming this requires extensive education and marketing efforts to demonstrate the environmental and economic advantages of propionic acid-based alternatives.
Lastly, the lack of a robust circular economy infrastructure for propionic acid and its derivatives hinders its potential as a sustainable solution. Developing efficient recycling and upcycling processes for propionic acid-based products is crucial to maximize its environmental benefits and create a closed-loop system that aligns with circular economy principles.
Existing Climate Applications of Propionic Acid
01 Production methods of propionic acid
Various methods for producing propionic acid are described, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis routes, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of propionic acid production for industrial applications.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis routes, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of the final product.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in bakery items and dairy products.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical industry: Propionic acid finds applications in the pharmaceutical industry as a precursor for drug synthesis, as well as in the formulation of certain medications. It is used in the production of various pharmaceutical compounds and as an excipient in drug formulations.
- Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling: Proper handling, storage, and disposal of propionic acid are crucial due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Safety measures and regulations are implemented to minimize risks associated with its use in industrial and laboratory settings.
- Derivatives and related compounds of propionic acid: Various derivatives and related compounds of propionic acid are synthesized and utilized in different industries. These include esters, salts, and other modified forms of propionic acid, which often exhibit unique properties and applications.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective against molds and bacteria, extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in bakery goods and dairy products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations
Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in pharmaceutical formulations. They are used as excipients, pH adjusters, and in some cases, as active pharmaceutical ingredients for various therapeutic purposes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Propionic acid in agricultural applications
Propionic acid is utilized in agriculture for various purposes, including as a feed preservative, herbicide, and plant growth regulator. It helps in preventing mold growth in animal feed and can improve crop yields when used appropriately.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling
The handling, storage, and disposal of propionic acid require specific safety measures due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Proper containment, neutralization techniques, and waste management practices are essential for safe industrial use of propionic acid.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitors
The market for propionic acid's contribution to future climate solutions is in an early growth stage, with increasing interest driven by sustainability concerns. The global market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years as industries seek eco-friendly alternatives. While the technology is still developing, several key players are advancing research and applications. Companies like BASF, Dow Chemical, and LG Chem are leveraging their chemical expertise to explore propionic acid's potential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Academic institutions such as Jiangnan University and The University of Queensland are contributing to fundamental research, while specialized firms like Green Eco Labs are focusing on innovative applications. The involvement of major petrochemical companies like Sinopec indicates growing industry recognition of propionic acid's role in climate solutions.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) is developing innovative processes for propionic acid production as part of its climate solutions strategy. The company is focusing on bio-based production methods, utilizing renewable feedstocks to reduce carbon emissions. Sinopec's approach involves fermenting biomass-derived sugars using engineered microorganisms to produce propionic acid [1]. This process is coupled with advanced separation and purification techniques to ensure high product quality. Additionally, Sinopec is exploring catalytic routes for propionic acid synthesis from ethylene and carbon monoxide, which could potentially utilize captured CO2 as a feedstock [3]. The company is also investing in process intensification and energy integration to minimize the overall carbon footprint of propionic acid production.
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, extensive R&D resources, and integrated supply chain. Weaknesses: Potential high initial investment costs for bio-based processes and dependency on biomass availability.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. is at the forefront of developing sustainable propionic acid production methods to contribute to climate solutions. The company has invested in a proprietary bio-based production platform that utilizes renewable raw materials and engineered microorganisms [2]. This process significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional petrochemical routes. BASF is also exploring the integration of carbon capture and utilization (CCU) technologies in its propionic acid production, aiming to use captured CO2 as a feedstock [4]. Furthermore, the company is developing novel catalysts for the direct conversion of ethanol to propionic acid, which could leverage bioethanol as a renewable precursor. BASF's approach also includes the optimization of downstream processing to minimize energy consumption and waste generation in propionic acid purification.
Strengths: Strong research capabilities, global market presence, and expertise in process optimization. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up new technologies and competition from established petrochemical routes.
Innovative Propionic Acid Research for Climate
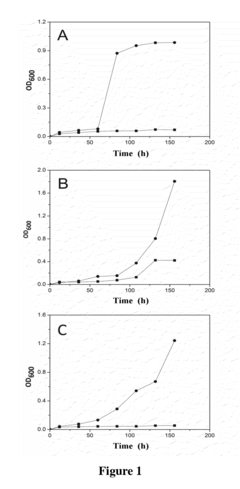
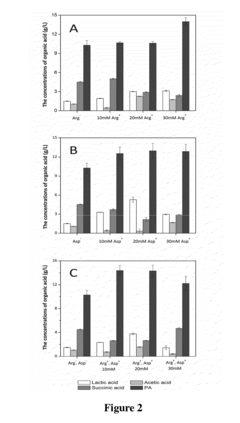
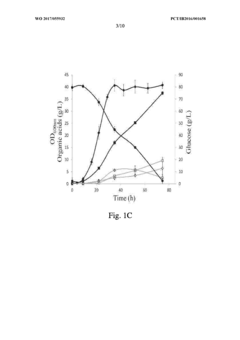
Method for Improving Acid tolerance of Propionibacterium acdipropionici
PatentInactiveUS20140178952A1
Innovation
- Adding arginine and/or aspartic acid to the culture medium during the cultivation of Propionibacterium acdipropionici to enhance acid tolerance and propionic acid productivity.
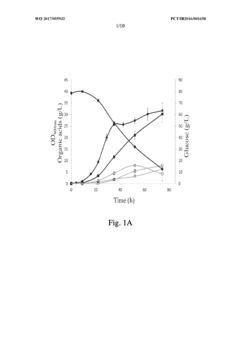
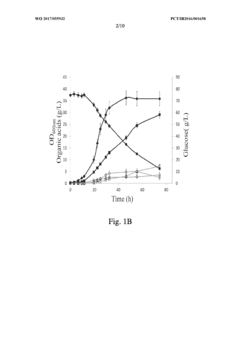
Improved propionibacterium strains for the production of propionic acid
PatentWO2017055932A2
Innovation
- Genome shuffling between selected Propionibacterium strains, such as P. acidipropionici ATCC 4875 and P. acidipropionici ATCC 55737, to generate novel strains with enhanced growth rates and propionic acid production, utilizing genetic material exchange to create strains with improved metabolic pathways and regulatory mechanisms.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Propionic acid's potential contribution to future climate solutions necessitates a comprehensive environmental impact assessment. This evaluation is crucial for understanding the full scope of its effects on ecosystems, biodiversity, and overall environmental health.
The production and utilization of propionic acid as a climate solution may lead to both positive and negative environmental impacts. On the positive side, its application in reducing methane emissions from livestock could significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions from the agricultural sector. This reduction in methane, a potent greenhouse gas, could contribute to mitigating global warming and its associated environmental consequences.
However, the large-scale production of propionic acid may have its own environmental footprint. The manufacturing process typically involves petrochemical feedstocks, which could lead to increased carbon dioxide emissions and potential air and water pollution if not properly managed. Additionally, the disposal of by-products and waste from production facilities needs careful consideration to prevent soil and water contamination.
The use of propionic acid in animal feed may also have indirect environmental impacts. While it reduces methane emissions, it's essential to assess any potential changes in nutrient cycling within agricultural systems and the subsequent effects on soil health and local ecosystems. Furthermore, the increased use of propionic acid could lead to changes in land use patterns, potentially affecting biodiversity and habitat conservation efforts.
Water usage and quality are other critical factors to consider. The production of propionic acid requires significant water inputs, and proper wastewater treatment is essential to prevent water pollution. Moreover, if propionic acid or its derivatives enter water systems, it could impact aquatic ecosystems and potentially affect drinking water sources.
Long-term ecological studies are necessary to fully understand the impact of propionic acid on various ecosystems. This includes assessing its effects on soil microorganisms, plant growth, and the overall balance of ecosystems where it's applied or produced. Such studies should also consider potential bioaccumulation in food chains and any unforeseen consequences on wildlife populations.
The environmental impact assessment should also consider the life cycle analysis of propionic acid, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal or recycling. This holistic approach will provide a more accurate picture of its overall environmental footprint and help in comparing it with alternative climate solutions.
The production and utilization of propionic acid as a climate solution may lead to both positive and negative environmental impacts. On the positive side, its application in reducing methane emissions from livestock could significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions from the agricultural sector. This reduction in methane, a potent greenhouse gas, could contribute to mitigating global warming and its associated environmental consequences.
However, the large-scale production of propionic acid may have its own environmental footprint. The manufacturing process typically involves petrochemical feedstocks, which could lead to increased carbon dioxide emissions and potential air and water pollution if not properly managed. Additionally, the disposal of by-products and waste from production facilities needs careful consideration to prevent soil and water contamination.
The use of propionic acid in animal feed may also have indirect environmental impacts. While it reduces methane emissions, it's essential to assess any potential changes in nutrient cycling within agricultural systems and the subsequent effects on soil health and local ecosystems. Furthermore, the increased use of propionic acid could lead to changes in land use patterns, potentially affecting biodiversity and habitat conservation efforts.
Water usage and quality are other critical factors to consider. The production of propionic acid requires significant water inputs, and proper wastewater treatment is essential to prevent water pollution. Moreover, if propionic acid or its derivatives enter water systems, it could impact aquatic ecosystems and potentially affect drinking water sources.
Long-term ecological studies are necessary to fully understand the impact of propionic acid on various ecosystems. This includes assessing its effects on soil microorganisms, plant growth, and the overall balance of ecosystems where it's applied or produced. Such studies should also consider potential bioaccumulation in food chains and any unforeseen consequences on wildlife populations.
The environmental impact assessment should also consider the life cycle analysis of propionic acid, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal or recycling. This holistic approach will provide a more accurate picture of its overall environmental footprint and help in comparing it with alternative climate solutions.
Regulatory Framework for Climate Solutions
The regulatory framework for climate solutions plays a crucial role in shaping the adoption and implementation of technologies like propionic acid in addressing climate change. As governments worldwide recognize the urgency of climate action, they are developing and refining policies to encourage sustainable practices and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
In the context of propionic acid's potential contribution to climate solutions, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on promoting circular economy principles and sustainable agriculture practices. The European Union, for instance, has introduced the Farm to Fork Strategy, which aims to make food systems fair, healthy, and environmentally friendly. This strategy indirectly supports the use of propionic acid as a sustainable feed preservative, aligning with the goal of reducing food waste and improving resource efficiency in agriculture.
Many countries are also implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, to incentivize the adoption of low-carbon technologies. These policies could potentially benefit the use of propionic acid in climate solutions by making carbon-intensive alternatives less economically viable. For example, if propionic acid production methods prove to have a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional feed preservation techniques, they may become more attractive under carbon pricing schemes.
Regulatory frameworks are also evolving to support research and development in climate-friendly technologies. Governments are offering grants, tax incentives, and other forms of support for companies and research institutions working on innovative climate solutions. This could accelerate the development of new applications for propionic acid in areas such as biofuel production or carbon capture and utilization.
However, the regulatory landscape for climate solutions is not without challenges. The lack of global harmonization in climate policies can create barriers to the widespread adoption of technologies like propionic acid. Different standards and regulations across regions may complicate the scaling up of production and distribution. Additionally, the regulatory approval process for new applications of propionic acid in climate solutions may be lengthy and complex, potentially slowing down innovation and market entry.
To address these challenges, international cooperation and standardization efforts are underway. Organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) are developing global standards for climate action and sustainable development, which could help create a more unified regulatory environment for climate solutions, including those involving propionic acid.
In the context of propionic acid's potential contribution to climate solutions, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on promoting circular economy principles and sustainable agriculture practices. The European Union, for instance, has introduced the Farm to Fork Strategy, which aims to make food systems fair, healthy, and environmentally friendly. This strategy indirectly supports the use of propionic acid as a sustainable feed preservative, aligning with the goal of reducing food waste and improving resource efficiency in agriculture.
Many countries are also implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, to incentivize the adoption of low-carbon technologies. These policies could potentially benefit the use of propionic acid in climate solutions by making carbon-intensive alternatives less economically viable. For example, if propionic acid production methods prove to have a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional feed preservation techniques, they may become more attractive under carbon pricing schemes.
Regulatory frameworks are also evolving to support research and development in climate-friendly technologies. Governments are offering grants, tax incentives, and other forms of support for companies and research institutions working on innovative climate solutions. This could accelerate the development of new applications for propionic acid in areas such as biofuel production or carbon capture and utilization.
However, the regulatory landscape for climate solutions is not without challenges. The lack of global harmonization in climate policies can create barriers to the widespread adoption of technologies like propionic acid. Different standards and regulations across regions may complicate the scaling up of production and distribution. Additionally, the regulatory approval process for new applications of propionic acid in climate solutions may be lengthy and complex, potentially slowing down innovation and market entry.
To address these challenges, international cooperation and standardization efforts are underway. Organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) are developing global standards for climate action and sustainable development, which could help create a more unified regulatory environment for climate solutions, including those involving propionic acid.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!