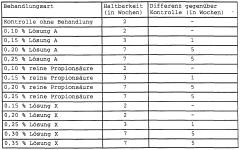
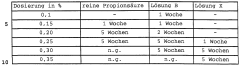
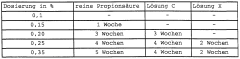
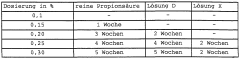
Propionic Acid: Emerging Solutions for Food Preservation
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Evolution and Objectives
Propionic acid has a rich history in food preservation, dating back to its discovery in the mid-19th century. Initially identified as a byproduct of bacterial fermentation, its potential as a preservative was not immediately recognized. The evolution of propionic acid as a food preservative began in earnest in the early 20th century, as researchers and food scientists started to explore its antimicrobial properties.
The journey of propionic acid in food preservation has been marked by several key milestones. In the 1930s, its effectiveness against mold growth in baked goods was first documented, leading to its widespread adoption in the baking industry. This discovery paved the way for further research into its broader applications in food preservation.
Throughout the mid-20th century, propionic acid's role expanded beyond bakery products. Its ability to inhibit the growth of various microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi, made it an attractive option for preserving a wide range of food products. This period saw significant advancements in understanding the mechanism of action of propionic acid, which in turn led to more efficient and targeted applications.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed a surge in research focused on optimizing the use of propionic acid in food preservation. This included studies on its synergistic effects with other preservatives, its impact on food quality and nutritional value, and the development of novel delivery systems to enhance its efficacy.
Current technological trends in propionic acid research are centered around several key objectives. One primary goal is to enhance the antimicrobial efficacy of propionic acid while minimizing its impact on food flavor and texture. This involves developing new formulations and delivery methods that allow for lower concentrations of the acid to be used without compromising its preservative effects.
Another significant objective is to expand the application of propionic acid to new food categories. While it has been traditionally used in baked goods and dairy products, researchers are exploring its potential in preserving fresh produce, meat products, and ready-to-eat meals. This expansion requires overcoming challenges related to pH sensitivity and compatibility with different food matrices.
Sustainability and eco-friendliness have also become crucial objectives in the evolution of propionic acid technology. There is a growing focus on developing bio-based production methods for propionic acid, moving away from petrochemical-based processes. This aligns with the broader trend towards green chemistry and sustainable food production practices.
The journey of propionic acid in food preservation has been marked by several key milestones. In the 1930s, its effectiveness against mold growth in baked goods was first documented, leading to its widespread adoption in the baking industry. This discovery paved the way for further research into its broader applications in food preservation.
Throughout the mid-20th century, propionic acid's role expanded beyond bakery products. Its ability to inhibit the growth of various microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi, made it an attractive option for preserving a wide range of food products. This period saw significant advancements in understanding the mechanism of action of propionic acid, which in turn led to more efficient and targeted applications.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed a surge in research focused on optimizing the use of propionic acid in food preservation. This included studies on its synergistic effects with other preservatives, its impact on food quality and nutritional value, and the development of novel delivery systems to enhance its efficacy.
Current technological trends in propionic acid research are centered around several key objectives. One primary goal is to enhance the antimicrobial efficacy of propionic acid while minimizing its impact on food flavor and texture. This involves developing new formulations and delivery methods that allow for lower concentrations of the acid to be used without compromising its preservative effects.
Another significant objective is to expand the application of propionic acid to new food categories. While it has been traditionally used in baked goods and dairy products, researchers are exploring its potential in preserving fresh produce, meat products, and ready-to-eat meals. This expansion requires overcoming challenges related to pH sensitivity and compatibility with different food matrices.
Sustainability and eco-friendliness have also become crucial objectives in the evolution of propionic acid technology. There is a growing focus on developing bio-based production methods for propionic acid, moving away from petrochemical-based processes. This aligns with the broader trend towards green chemistry and sustainable food production practices.
Food Preservation Market Analysis
The food preservation market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for extended shelf life and food safety. As of 2021, the global food preservatives market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8% through 2026. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising awareness of food waste reduction and the need for efficient preservation methods in the food and beverage industry.
Propionic acid, as an emerging solution for food preservation, is gaining traction in this expanding market. Its effectiveness in inhibiting mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly bakery items, has positioned it as a promising alternative to traditional preservatives. The market for propionic acid in food preservation applications is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% from 2021 to 2026, outpacing the overall food preservatives market.
The demand for propionic acid in food preservation is driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing consumer preference for clean label products with natural or naturally derived preservatives. Propionic acid, being a naturally occurring substance, aligns well with this trend. Secondly, stringent food safety regulations across various regions are pushing food manufacturers to adopt more effective preservation methods, further boosting the demand for propionic acid.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the propionic acid market for food preservation, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, changing dietary habits, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India.
In terms of application segments, bakery products represent the largest market for propionic acid as a preservative, followed by dairy and processed meat products. The bakery segment alone accounts for approximately 40% of the total propionic acid usage in food preservation. This is primarily due to the effectiveness of propionic acid in preventing mold growth in bread and other baked goods, thereby extending their shelf life significantly.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the propionic acid market faces challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and competition from other preservatives. However, ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of propionic acid-based preservation solutions are expected to address these challenges and further drive market growth in the coming years.
Propionic acid, as an emerging solution for food preservation, is gaining traction in this expanding market. Its effectiveness in inhibiting mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly bakery items, has positioned it as a promising alternative to traditional preservatives. The market for propionic acid in food preservation applications is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% from 2021 to 2026, outpacing the overall food preservatives market.
The demand for propionic acid in food preservation is driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing consumer preference for clean label products with natural or naturally derived preservatives. Propionic acid, being a naturally occurring substance, aligns well with this trend. Secondly, stringent food safety regulations across various regions are pushing food manufacturers to adopt more effective preservation methods, further boosting the demand for propionic acid.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the propionic acid market for food preservation, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, changing dietary habits, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India.
In terms of application segments, bakery products represent the largest market for propionic acid as a preservative, followed by dairy and processed meat products. The bakery segment alone accounts for approximately 40% of the total propionic acid usage in food preservation. This is primarily due to the effectiveness of propionic acid in preventing mold growth in bread and other baked goods, thereby extending their shelf life significantly.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the propionic acid market faces challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and competition from other preservatives. However, ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of propionic acid-based preservation solutions are expected to address these challenges and further drive market growth in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Propionic Acid Usage
Despite the widespread use of propionic acid as a food preservative, several challenges persist in its application, limiting its effectiveness and broader adoption in the food industry. One of the primary concerns is the high concentration required for effective antimicrobial action, which can negatively impact the sensory properties of food products. The characteristic pungent odor and sharp taste of propionic acid can alter the flavor profile of treated foods, potentially leading to consumer rejection.
Another significant challenge is the limited spectrum of antimicrobial activity exhibited by propionic acid. While it is highly effective against molds and some bacteria, its efficacy against a broader range of microorganisms, particularly certain pathogenic bacteria, is less pronounced. This limitation necessitates the use of additional preservatives in many applications, complicating formulations and potentially increasing costs.
The pH-dependent activity of propionic acid presents another hurdle in its usage. The compound is most effective in its undissociated form, which predominates at lower pH levels. However, many food products have a pH above the pKa of propionic acid, reducing its antimicrobial efficacy. This pH sensitivity restricts its application in a wide range of food products, particularly those with neutral or slightly alkaline pH.
Stability issues also pose challenges in propionic acid usage. The compound can be volatile and may gradually evaporate from food products during storage, potentially compromising long-term preservation efficacy. This volatility is particularly problematic in products with extended shelf lives or those subjected to temperature fluctuations during storage and distribution.
Furthermore, there are growing concerns about the potential health effects of synthetic preservatives, including propionic acid, among consumers. This has led to increased demand for natural alternatives, putting pressure on food manufacturers to reduce or eliminate synthetic preservatives. The challenge lies in finding natural substitutes that can match the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of propionic acid.
Regulatory constraints and varying global standards for propionic acid usage in food preservation add another layer of complexity. Different countries have different maximum permissible levels and approved applications for propionic acid, complicating international trade and product formulation for global markets. Manufacturers must navigate these regulatory differences, which can increase costs and limit market access.
Lastly, the production of propionic acid itself faces sustainability challenges. Traditional production methods rely on petrochemical feedstocks, raising environmental concerns. The industry is under pressure to develop more sustainable production processes, but achieving cost-effective, large-scale bio-based production remains a significant challenge.
Another significant challenge is the limited spectrum of antimicrobial activity exhibited by propionic acid. While it is highly effective against molds and some bacteria, its efficacy against a broader range of microorganisms, particularly certain pathogenic bacteria, is less pronounced. This limitation necessitates the use of additional preservatives in many applications, complicating formulations and potentially increasing costs.
The pH-dependent activity of propionic acid presents another hurdle in its usage. The compound is most effective in its undissociated form, which predominates at lower pH levels. However, many food products have a pH above the pKa of propionic acid, reducing its antimicrobial efficacy. This pH sensitivity restricts its application in a wide range of food products, particularly those with neutral or slightly alkaline pH.
Stability issues also pose challenges in propionic acid usage. The compound can be volatile and may gradually evaporate from food products during storage, potentially compromising long-term preservation efficacy. This volatility is particularly problematic in products with extended shelf lives or those subjected to temperature fluctuations during storage and distribution.
Furthermore, there are growing concerns about the potential health effects of synthetic preservatives, including propionic acid, among consumers. This has led to increased demand for natural alternatives, putting pressure on food manufacturers to reduce or eliminate synthetic preservatives. The challenge lies in finding natural substitutes that can match the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of propionic acid.
Regulatory constraints and varying global standards for propionic acid usage in food preservation add another layer of complexity. Different countries have different maximum permissible levels and approved applications for propionic acid, complicating international trade and product formulation for global markets. Manufacturers must navigate these regulatory differences, which can increase costs and limit market access.
Lastly, the production of propionic acid itself faces sustainability challenges. Traditional production methods rely on petrochemical feedstocks, raising environmental concerns. The industry is under pressure to develop more sustainable production processes, but achieving cost-effective, large-scale bio-based production remains a significant challenge.
Existing Propionic Acid Solutions
01 Production methods of propionic acid
Various methods for producing propionic acid are described, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis routes, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of propionic acid production for industrial applications.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid is widely used as a food preservative due to its antimicrobial properties. It is effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical industry: Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the synthesis of various drugs, as intermediates in drug manufacturing processes, and in some cases, as active pharmaceutical ingredients themselves.
- Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling: The handling and storage of propionic acid require specific safety measures due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Proper containment, neutralization techniques, and waste management strategies are essential for safe and environmentally responsible use of propionic acid in industrial settings.
- Purification and quality control of propionic acid: Various methods are employed for the purification and quality control of propionic acid to meet industry standards. These may include distillation techniques, chromatographic methods, and spectroscopic analyses to ensure the purity and consistency of the final product for different applications.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in bakery items and dairy products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations
Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in pharmaceutical formulations. They are used as excipients, pH adjusters, and in some cases, as active pharmaceutical ingredients for various therapeutic purposes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Propionic acid in polymer and chemical synthesis
Propionic acid serves as a precursor or intermediate in the synthesis of various polymers and chemicals. It is used in the production of cellulose plastics, perfumes, and other industrial chemicals, contributing to the development of new materials and products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling
The handling, storage, and disposal of propionic acid require specific safety measures due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Innovations in this area focus on developing safer handling methods, reducing emissions, and improving workplace safety in industries using propionic acid.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Food Preservative Industry
The propionic acid market for food preservation is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for natural preservatives and extended shelf-life products. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating continued growth due to rising food safety concerns and clean label trends. Technologically, propionic acid solutions are advancing, with companies like BASF, Corbion (Purac Biochem), and Kemin Industries leading innovation. These firms are developing enhanced formulations and application methods to improve efficacy and broaden usage across various food categories. While the technology is mature, ongoing research focuses on optimizing production processes, exploring new sources, and enhancing antimicrobial properties to meet evolving industry needs.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a novel approach to propionic acid production using renewable resources. Their process involves fermenting glycerol, a byproduct of biodiesel production, using proprietary bacterial strains. This method achieves a yield of up to 0.8 g propionic acid per g glycerol [1]. The company has also engineered a controlled-release system for propionic acid, encapsulating it in biodegradable polymers. This technology allows for sustained antimicrobial activity in food products, extending shelf life by up to 40% in some applications [3]. Additionally, BASF has explored synergistic combinations of propionic acid with other preservatives, enhancing its efficacy at lower concentrations.
Strengths: Sustainable production method, innovative controlled-release technology, and synergistic formulations. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs compared to traditional methods, and limited scalability of the fermentation process.
Purac Biochem BV
Technical Solution: Purac Biochem has developed a proprietary fermentation process for producing high-purity propionic acid from renewable resources. Their technology utilizes genetically modified Propionibacterium strains that can achieve conversion rates of up to 95% from glucose feedstock [2]. The company has also introduced a novel purification method that reduces energy consumption by 30% compared to traditional distillation processes [4]. Purac's propionic acid products are marketed under the brand name PURASAL®, which includes specialized formulations for various food preservation applications. They have recently launched a line of propionic acid-based preservatives that are certified for use in organic food products, addressing the growing demand for natural preservatives.
Strengths: High-purity product, energy-efficient production, and specialized formulations for organic foods. Weaknesses: Reliance on specific bacterial strains may limit production flexibility, and potential regulatory challenges for genetically modified organisms.
Innovative Propionic Acid Applications
Propionic acid, ammonia, propanediol and water solutions and the use thereof
PatentInactiveEP1222862A2
Innovation
- A solution comprising 78.0 to 93.0% propionic acid, 0.5 to 5.0% ammonia, 1.0 to 6.0% propanediol, and up to 10.0% water, with optional additional C1-C8 carboxylic acids and surfactants, which reduces water content and enhances biocidal and biostatic effects while minimizing corrosiveness and odor.
Propionic acid, ammonia, propanediol and water solutions and the use thereof
PatentWO1998042205A1
Innovation
- A solution comprising 78.0 - 93.0% propionic acid, 0.5 - 5.0% ammonia, 1.0 - 6.0% propanediol, and 0.1 - 10.0% water, with optional auxiliaries like surfactants and other carboxylic acids, which reduces water content and enhances biocidal and biostatic effects while minimizing corrosive and odor issues.
Regulatory Framework for Food Additives
The regulatory framework for food additives plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of propionic acid as a food preservative. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of food additives, including propionic acid. The FDA has classified propionic acid as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food products, subject to specific limitations and conditions.
Under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, propionic acid is approved for use as a preservative in various food categories. The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, Part 184, Subpart B, Section 184.1081 outlines the specific requirements for propionic acid use in food. This regulation stipulates the maximum levels of propionic acid that can be added to different food types, ensuring that its use remains within safe limits.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety of food additives. Propionic acid is listed as E280 in the EU's food additive regulations. The EFSA has established an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) for propionic acid and its salts, which guides manufacturers on the appropriate usage levels in food products.
The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) provides international standards for food additives, including propionic acid. JECFA has evaluated the safety of propionic acid and established specifications for its use in food preservation. These guidelines are often adopted or referenced by countries developing their own regulatory frameworks for food additives.
Many countries have their own regulatory bodies that oversee the use of food additives. For example, in Canada, Health Canada regulates food additives through the Food and Drug Regulations. In Australia and New Zealand, Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) is responsible for setting standards for food additives, including propionic acid.
Regulatory frameworks also address labeling requirements for foods containing propionic acid. In many jurisdictions, manufacturers must declare the presence of propionic acid on food labels, either by its common name or by its E-number (E280). This transparency allows consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase and consume.
As new research emerges on the safety and efficacy of propionic acid, regulatory bodies continually review and update their guidelines. This ongoing process ensures that the use of propionic acid in food preservation remains aligned with the latest scientific evidence and continues to prioritize consumer safety.
Under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, propionic acid is approved for use as a preservative in various food categories. The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, Part 184, Subpart B, Section 184.1081 outlines the specific requirements for propionic acid use in food. This regulation stipulates the maximum levels of propionic acid that can be added to different food types, ensuring that its use remains within safe limits.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety of food additives. Propionic acid is listed as E280 in the EU's food additive regulations. The EFSA has established an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) for propionic acid and its salts, which guides manufacturers on the appropriate usage levels in food products.
The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) provides international standards for food additives, including propionic acid. JECFA has evaluated the safety of propionic acid and established specifications for its use in food preservation. These guidelines are often adopted or referenced by countries developing their own regulatory frameworks for food additives.
Many countries have their own regulatory bodies that oversee the use of food additives. For example, in Canada, Health Canada regulates food additives through the Food and Drug Regulations. In Australia and New Zealand, Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) is responsible for setting standards for food additives, including propionic acid.
Regulatory frameworks also address labeling requirements for foods containing propionic acid. In many jurisdictions, manufacturers must declare the presence of propionic acid on food labels, either by its common name or by its E-number (E280). This transparency allows consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase and consume.
As new research emerges on the safety and efficacy of propionic acid, regulatory bodies continually review and update their guidelines. This ongoing process ensures that the use of propionic acid in food preservation remains aligned with the latest scientific evidence and continues to prioritize consumer safety.
Environmental Impact of Propionic Acid
Propionic acid, while effective in food preservation, has potential environmental impacts that warrant careful consideration. The production and use of propionic acid can contribute to various environmental concerns, including air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource depletion.
In terms of air pollution, the manufacturing process of propionic acid may release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. These emissions can contribute to smog formation and negatively impact local air quality. Additionally, the transportation and storage of propionic acid may result in fugitive emissions, further exacerbating air pollution issues.
Water pollution is another significant concern associated with propionic acid production and use. Industrial wastewater from manufacturing facilities may contain traces of propionic acid and other chemical byproducts. If not properly treated, these contaminants can enter water bodies, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and affecting water quality for human consumption.
The production of propionic acid also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily through energy consumption in manufacturing processes. The carbon footprint of propionic acid production varies depending on the energy sources used and the efficiency of production methods. As climate change concerns intensify, there is growing pressure to reduce the carbon intensity of chemical production processes, including those for propionic acid.
Resource depletion is an additional environmental consideration. Propionic acid is typically derived from petrochemical sources, which are non-renewable. The extraction and processing of these raw materials can lead to habitat destruction, biodiversity loss, and the depletion of finite resources.
However, it is important to note that the use of propionic acid in food preservation can indirectly contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing food waste. By extending the shelf life of food products, propionic acid helps minimize the amount of food that spoils before consumption, thereby reducing the environmental impact associated with food production, transportation, and disposal.
To mitigate the environmental impacts of propionic acid, several approaches are being explored. These include developing more sustainable production methods, such as bio-based propionic acid derived from renewable resources. Additionally, improving manufacturing efficiency, implementing closed-loop systems for water and chemical recycling, and adopting cleaner energy sources can help reduce the environmental footprint of propionic acid production.
As the food industry continues to prioritize sustainability, there is a growing emphasis on developing environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional preservatives. This trend may drive innovation in propionic acid production and application, leading to more sustainable practices throughout its lifecycle.
In terms of air pollution, the manufacturing process of propionic acid may release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. These emissions can contribute to smog formation and negatively impact local air quality. Additionally, the transportation and storage of propionic acid may result in fugitive emissions, further exacerbating air pollution issues.
Water pollution is another significant concern associated with propionic acid production and use. Industrial wastewater from manufacturing facilities may contain traces of propionic acid and other chemical byproducts. If not properly treated, these contaminants can enter water bodies, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and affecting water quality for human consumption.
The production of propionic acid also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily through energy consumption in manufacturing processes. The carbon footprint of propionic acid production varies depending on the energy sources used and the efficiency of production methods. As climate change concerns intensify, there is growing pressure to reduce the carbon intensity of chemical production processes, including those for propionic acid.
Resource depletion is an additional environmental consideration. Propionic acid is typically derived from petrochemical sources, which are non-renewable. The extraction and processing of these raw materials can lead to habitat destruction, biodiversity loss, and the depletion of finite resources.
However, it is important to note that the use of propionic acid in food preservation can indirectly contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing food waste. By extending the shelf life of food products, propionic acid helps minimize the amount of food that spoils before consumption, thereby reducing the environmental impact associated with food production, transportation, and disposal.
To mitigate the environmental impacts of propionic acid, several approaches are being explored. These include developing more sustainable production methods, such as bio-based propionic acid derived from renewable resources. Additionally, improving manufacturing efficiency, implementing closed-loop systems for water and chemical recycling, and adopting cleaner energy sources can help reduce the environmental footprint of propionic acid production.
As the food industry continues to prioritize sustainability, there is a growing emphasis on developing environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional preservatives. This trend may drive innovation in propionic acid production and application, leading to more sustainable practices throughout its lifecycle.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!