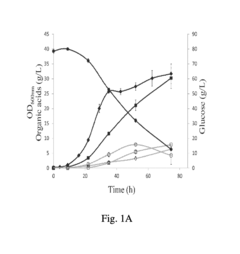
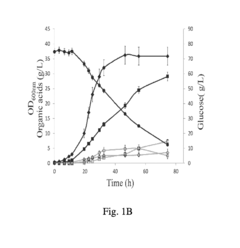
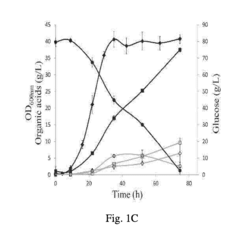
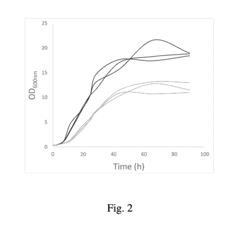
How to Develop Targeted Propionic Acid Technologies for Industries?
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Tech Evolution and Objectives
Propionic acid has been a subject of industrial interest for decades, with its applications spanning various sectors including food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. The evolution of propionic acid technologies has been driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and efficient production methods, as well as the need for targeted applications in specific industries.
The journey of propionic acid technology began in the early 20th century with traditional petrochemical-based production methods. These processes, while effective, were energy-intensive and relied heavily on non-renewable resources. As environmental concerns grew, the focus shifted towards developing more sustainable production techniques.
In the 1990s, biotechnological approaches gained traction, with researchers exploring microbial fermentation as an alternative production method. This marked a significant milestone in the evolution of propionic acid technologies, opening up new possibilities for eco-friendly and cost-effective production.
The early 2000s saw a surge in research aimed at optimizing fermentation processes and identifying novel microbial strains capable of producing propionic acid with higher yields and purity. This period also witnessed the emergence of metabolic engineering techniques, allowing scientists to modify microorganisms for enhanced propionic acid production.
As we entered the 2010s, the focus shifted towards developing targeted propionic acid technologies for specific industrial applications. This involved tailoring the production processes and product characteristics to meet the unique requirements of different sectors, such as food preservation, animal feed additives, and pharmaceuticals.
The current technological landscape is characterized by a dual approach: continuous improvement of existing production methods and exploration of novel, disruptive technologies. Advanced fermentation techniques, coupled with process intensification strategies, are being developed to increase productivity and reduce production costs.
Looking ahead, the objectives for propionic acid technologies are multifaceted. There is a strong emphasis on further enhancing the sustainability of production processes, with a focus on utilizing renewable feedstocks and minimizing environmental impact. Researchers are also working towards developing high-purity propionic acid formulations for specialized applications in the pharmaceutical and personal care industries.
Another key objective is the integration of propionic acid production with other industrial processes, creating synergies and improving overall resource efficiency. This includes exploring the potential of propionic acid as a platform chemical for the synthesis of various value-added products.
In conclusion, the evolution of propionic acid technologies reflects a journey from conventional petrochemical processes to advanced, sustainable, and targeted production methods. The future objectives are centered on innovation, sustainability, and customization to meet the diverse needs of various industries.
The journey of propionic acid technology began in the early 20th century with traditional petrochemical-based production methods. These processes, while effective, were energy-intensive and relied heavily on non-renewable resources. As environmental concerns grew, the focus shifted towards developing more sustainable production techniques.
In the 1990s, biotechnological approaches gained traction, with researchers exploring microbial fermentation as an alternative production method. This marked a significant milestone in the evolution of propionic acid technologies, opening up new possibilities for eco-friendly and cost-effective production.
The early 2000s saw a surge in research aimed at optimizing fermentation processes and identifying novel microbial strains capable of producing propionic acid with higher yields and purity. This period also witnessed the emergence of metabolic engineering techniques, allowing scientists to modify microorganisms for enhanced propionic acid production.
As we entered the 2010s, the focus shifted towards developing targeted propionic acid technologies for specific industrial applications. This involved tailoring the production processes and product characteristics to meet the unique requirements of different sectors, such as food preservation, animal feed additives, and pharmaceuticals.
The current technological landscape is characterized by a dual approach: continuous improvement of existing production methods and exploration of novel, disruptive technologies. Advanced fermentation techniques, coupled with process intensification strategies, are being developed to increase productivity and reduce production costs.
Looking ahead, the objectives for propionic acid technologies are multifaceted. There is a strong emphasis on further enhancing the sustainability of production processes, with a focus on utilizing renewable feedstocks and minimizing environmental impact. Researchers are also working towards developing high-purity propionic acid formulations for specialized applications in the pharmaceutical and personal care industries.
Another key objective is the integration of propionic acid production with other industrial processes, creating synergies and improving overall resource efficiency. This includes exploring the potential of propionic acid as a platform chemical for the synthesis of various value-added products.
In conclusion, the evolution of propionic acid technologies reflects a journey from conventional petrochemical processes to advanced, sustainable, and targeted production methods. The future objectives are centered on innovation, sustainability, and customization to meet the diverse needs of various industries.
Industrial Demand Analysis for Propionic Acid
The global demand for propionic acid has been steadily increasing, driven by its diverse applications across various industries. The food and feed industry represents the largest market segment for propionic acid, accounting for a significant portion of the total consumption. In this sector, propionic acid is primarily used as a preservative and mold inhibitor in animal feed, bakery products, and other food items.
The pharmaceutical industry is another key consumer of propionic acid, utilizing it in the production of various medications and as a precursor for vitamin E synthesis. The growing emphasis on healthcare and the expanding pharmaceutical sector in emerging economies are expected to further boost the demand for propionic acid in this segment.
In the agriculture sector, propionic acid finds application as a crop protection agent and in the production of herbicides. The increasing focus on sustainable agriculture practices and the need for improved crop yields are driving the demand for propionic acid-based products in this industry.
The chemical industry also contributes significantly to the demand for propionic acid, using it as an intermediate in the production of plastics, solvents, and other chemicals. The growth of the construction and automotive industries, particularly in developing regions, is expected to fuel the demand for propionic acid in this sector.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key growth driver for propionic acid demand, owing to rapid industrialization, increasing population, and changing dietary habits. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with established food and feed industries driving consistent demand.
The global propionic acid market is projected to experience steady growth in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to be in the mid-single digits. This growth is attributed to the expanding applications of propionic acid across various industries and the increasing awareness of its benefits in food preservation and animal nutrition.
However, the market faces challenges such as volatility in raw material prices and stringent regulations regarding the use of chemical preservatives in food products. These factors may impact the overall demand and market dynamics for propionic acid in certain regions.
To address these challenges and capitalize on the growing demand, industry players are focusing on developing targeted propionic acid technologies. These efforts include improving production efficiency, exploring new application areas, and developing eco-friendly formulations to meet evolving consumer preferences and regulatory requirements.
The pharmaceutical industry is another key consumer of propionic acid, utilizing it in the production of various medications and as a precursor for vitamin E synthesis. The growing emphasis on healthcare and the expanding pharmaceutical sector in emerging economies are expected to further boost the demand for propionic acid in this segment.
In the agriculture sector, propionic acid finds application as a crop protection agent and in the production of herbicides. The increasing focus on sustainable agriculture practices and the need for improved crop yields are driving the demand for propionic acid-based products in this industry.
The chemical industry also contributes significantly to the demand for propionic acid, using it as an intermediate in the production of plastics, solvents, and other chemicals. The growth of the construction and automotive industries, particularly in developing regions, is expected to fuel the demand for propionic acid in this sector.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key growth driver for propionic acid demand, owing to rapid industrialization, increasing population, and changing dietary habits. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with established food and feed industries driving consistent demand.
The global propionic acid market is projected to experience steady growth in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to be in the mid-single digits. This growth is attributed to the expanding applications of propionic acid across various industries and the increasing awareness of its benefits in food preservation and animal nutrition.
However, the market faces challenges such as volatility in raw material prices and stringent regulations regarding the use of chemical preservatives in food products. These factors may impact the overall demand and market dynamics for propionic acid in certain regions.
To address these challenges and capitalize on the growing demand, industry players are focusing on developing targeted propionic acid technologies. These efforts include improving production efficiency, exploring new application areas, and developing eco-friendly formulations to meet evolving consumer preferences and regulatory requirements.
Current Challenges in Propionic Acid Production
The production of propionic acid faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread industrial application. One of the primary issues is the low yield and productivity of current fermentation processes. Traditional methods often result in limited conversion rates, leading to inefficient resource utilization and increased production costs. This challenge is compounded by the formation of by-products during fermentation, which not only reduces the overall yield but also complicates downstream processing and purification steps.
Another major hurdle is the high energy consumption associated with propionic acid production. The separation and purification processes, particularly distillation, require substantial energy inputs, contributing to elevated operational expenses and environmental concerns. This energy-intensive nature of production poses a significant barrier to achieving cost-effective and sustainable manufacturing at industrial scales.
The sensitivity of propionic acid-producing microorganisms to environmental conditions presents an additional challenge. Factors such as pH, temperature, and substrate concentration can significantly impact microbial growth and acid production. Maintaining optimal conditions throughout the fermentation process is crucial but often difficult to achieve consistently in large-scale industrial settings.
Furthermore, the inhibitory effect of propionic acid on microbial growth creates a self-limiting factor in fermentation. As the acid accumulates, it can suppress further production by the microorganisms, leading to decreased efficiency and productivity over time. This phenomenon necessitates the development of more robust microbial strains or innovative fermentation strategies to overcome product inhibition.
The availability and cost of raw materials also pose challenges for propionic acid production. The reliance on specific substrates, such as glucose or glycerol, can lead to fluctuations in production costs based on market prices of these feedstocks. Additionally, the competition for these raw materials with other industries can affect supply chain stability and overall production economics.
Lastly, the environmental impact of propionic acid production remains a concern. Current processes may generate waste streams that require treatment, and the use of fossil fuel-derived substrates contributes to the carbon footprint of production. Addressing these environmental challenges is crucial for developing sustainable and eco-friendly propionic acid technologies that align with growing industrial demands for green chemistry solutions.
Another major hurdle is the high energy consumption associated with propionic acid production. The separation and purification processes, particularly distillation, require substantial energy inputs, contributing to elevated operational expenses and environmental concerns. This energy-intensive nature of production poses a significant barrier to achieving cost-effective and sustainable manufacturing at industrial scales.
The sensitivity of propionic acid-producing microorganisms to environmental conditions presents an additional challenge. Factors such as pH, temperature, and substrate concentration can significantly impact microbial growth and acid production. Maintaining optimal conditions throughout the fermentation process is crucial but often difficult to achieve consistently in large-scale industrial settings.
Furthermore, the inhibitory effect of propionic acid on microbial growth creates a self-limiting factor in fermentation. As the acid accumulates, it can suppress further production by the microorganisms, leading to decreased efficiency and productivity over time. This phenomenon necessitates the development of more robust microbial strains or innovative fermentation strategies to overcome product inhibition.
The availability and cost of raw materials also pose challenges for propionic acid production. The reliance on specific substrates, such as glucose or glycerol, can lead to fluctuations in production costs based on market prices of these feedstocks. Additionally, the competition for these raw materials with other industries can affect supply chain stability and overall production economics.
Lastly, the environmental impact of propionic acid production remains a concern. Current processes may generate waste streams that require treatment, and the use of fossil fuel-derived substrates contributes to the carbon footprint of production. Addressing these environmental challenges is crucial for developing sustainable and eco-friendly propionic acid technologies that align with growing industrial demands for green chemistry solutions.
Existing Propionic Acid Production Methods
01 Production methods of propionic acid
Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods for producing propionic acid are described, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis routes, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of propionic acid production for industrial applications.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective against molds and bacteria, extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in bakery items and dairy products.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations: Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in pharmaceutical formulations. They are used as excipients, pH adjusters, and in some cases, as active pharmaceutical ingredients for various therapeutic purposes.
- Propionic acid in agricultural applications: Propionic acid is utilized in agriculture for various purposes, including as a grain preservative, animal feed additive, and herbicide. It helps prevent mold growth in stored grains and improves feed efficiency in livestock.
- Environmental and safety considerations of propionic acid: Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of propionic acid production and use. This includes developing greener production methods, studying biodegradability, and assessing potential health effects of exposure.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid is widely used as a food preservative due to its antimicrobial properties. It is effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical industry
Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the synthesis of various drugs, as intermediates in drug manufacturing processes, and in some cases, as active pharmaceutical ingredients themselves.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling
The handling and storage of propionic acid require specific safety measures due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Proper containment, neutralization techniques, and waste management practices are essential for safe and environmentally responsible use of propionic acid in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions05 Propionic acid derivatives and their applications
Various derivatives of propionic acid, such as esters and salts, are synthesized and used in different industries. These derivatives often have unique properties and applications, including use as plasticizers, solvents, and intermediates in the production of other chemicals.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Propionic Acid Industry
The development of targeted propionic acid technologies for industries is in a growth phase, with increasing market demand and expanding applications across various sectors. The global market size for propionic acid is projected to reach several billion dollars by 2025, driven by its use in food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and chemical synthesis. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with key players like DSM IP Assets BV, Dow Global Technologies LLC, and BASF Corp. leading innovation. These companies are focusing on improving production efficiency, developing bio-based processes, and exploring novel applications. Universities such as The Ohio State University and Nanjing Tech University are contributing to fundamental research, while industry giants like PetroChina Co., Ltd. and Saudi Arabian Oil Co. are investing in large-scale production capabilities, indicating a maturing but still evolving technological landscape.
DSM IP Assets BV
Technical Solution: DSM has developed a bio-based route for propionic acid production using renewable resources. Their technology utilizes engineered microorganisms to ferment sugars into propionic acid. The process involves a two-step fermentation: first, glucose is converted to 3-hydroxypropionic acid, which is then further converted to propionic acid [1]. DSM's approach incorporates advanced metabolic engineering techniques to optimize the microbial strains for improved yield and productivity. The company has also implemented continuous fermentation processes to enhance efficiency and reduce production costs [2].
Strengths: Sustainable bio-based production, reduced reliance on fossil fuels, potential for cost-effectiveness at scale. Weaknesses: May face challenges in achieving high concentrations and purities compared to petrochemical routes.
Arkema France SA
Technical Solution: Arkema has developed an innovative process for producing bio-based acrylic acid, which can be further converted to propionic acid. Their technology uses glycerol, a by-product of biodiesel production, as a renewable feedstock. The process involves a multi-step catalytic conversion: glycerol is first dehydrated to acrolein, which is then oxidized to acrylic acid [3]. Arkema has optimized the catalyst systems for each step, achieving high selectivity and yield. The company has also implemented advanced separation and purification techniques to ensure product quality. Additionally, Arkema has explored the direct production of propionic acid from renewable resources using similar catalytic approaches [4].
Strengths: Utilizes abundant renewable feedstock, integrates with existing biodiesel industry, potential for high-purity products. Weaknesses: Multi-step process may increase complexity and costs, catalyst stability and longevity could be challenging.
Innovative Propionic Acid Synthesis Approaches
Methods for producing propionic acid
PatentWO2024226289A1
Innovation
- A method involving the dehydration of 3-hydroxypropionic acid to form acrylic acid using a first catalyst, followed by hydrogenation of acrylic acid to propionic acid using a second catalyst, with specific temperature and pressure conditions, and optionally using a polymerization inhibitor to prevent acrylic acid polymerization.
Improved propionibacterium strains for the production of propionic acid
PatentInactiveUS20190071697A1
Innovation
- Selecting and combining Propionibacterium strains with high potential for propionic acid production, such as P. acidipropionici ATCC 4875 and P. acidipropionici ATCC 55737, through genome shuffling to create novel strains with improved growth rates and reduced byproduct production, such as P. acidipropionici F3E8, which achieves enhanced propionic acid yields and growth rates.
Environmental Impact of Propionic Acid Manufacturing
The environmental impact of propionic acid manufacturing is a critical consideration in the development of targeted technologies for various industries. The production process of propionic acid traditionally involves petrochemical routes, which can have significant environmental implications. These include greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, and the generation of hazardous waste products.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the carbon footprint associated with propionic acid production. Conventional methods often rely on fossil fuel-based feedstocks, contributing to increased CO2 emissions. The energy-intensive nature of the manufacturing process further exacerbates this issue, as substantial amounts of heat and pressure are required for the chemical reactions to occur efficiently.
Water usage and potential contamination are also notable environmental factors. The production process typically requires large volumes of water for cooling and separation stages. Improper handling or disposal of wastewater can lead to the pollution of local water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially human health.
Air pollution is another significant environmental impact of propionic acid manufacturing. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants may be released during production, potentially contributing to smog formation and respiratory health issues in surrounding communities. Stringent emission control measures are necessary to mitigate these risks.
The use of catalysts in propionic acid synthesis presents both opportunities and challenges from an environmental perspective. While catalysts can improve reaction efficiency and reduce energy requirements, their production and disposal may involve toxic materials that require careful management to prevent environmental contamination.
As industries seek more sustainable production methods, there is a growing focus on developing greener alternatives for propionic acid manufacturing. Biotechnological approaches, such as fermentation using renewable biomass feedstocks, offer promising avenues for reducing the environmental footprint. These methods can potentially decrease reliance on fossil fuels and minimize waste generation.
Lifecycle assessment (LCA) studies are increasingly being employed to comprehensively evaluate the environmental impact of propionic acid production. These assessments consider all stages of the product lifecycle, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, providing valuable insights for process optimization and environmental management strategies.
Regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally friendly products are driving innovation in cleaner production technologies. Industries are exploring process intensification techniques, such as reactive distillation and membrane separation, to enhance efficiency and reduce resource consumption in propionic acid manufacturing.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the carbon footprint associated with propionic acid production. Conventional methods often rely on fossil fuel-based feedstocks, contributing to increased CO2 emissions. The energy-intensive nature of the manufacturing process further exacerbates this issue, as substantial amounts of heat and pressure are required for the chemical reactions to occur efficiently.
Water usage and potential contamination are also notable environmental factors. The production process typically requires large volumes of water for cooling and separation stages. Improper handling or disposal of wastewater can lead to the pollution of local water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially human health.
Air pollution is another significant environmental impact of propionic acid manufacturing. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants may be released during production, potentially contributing to smog formation and respiratory health issues in surrounding communities. Stringent emission control measures are necessary to mitigate these risks.
The use of catalysts in propionic acid synthesis presents both opportunities and challenges from an environmental perspective. While catalysts can improve reaction efficiency and reduce energy requirements, their production and disposal may involve toxic materials that require careful management to prevent environmental contamination.
As industries seek more sustainable production methods, there is a growing focus on developing greener alternatives for propionic acid manufacturing. Biotechnological approaches, such as fermentation using renewable biomass feedstocks, offer promising avenues for reducing the environmental footprint. These methods can potentially decrease reliance on fossil fuels and minimize waste generation.
Lifecycle assessment (LCA) studies are increasingly being employed to comprehensively evaluate the environmental impact of propionic acid production. These assessments consider all stages of the product lifecycle, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, providing valuable insights for process optimization and environmental management strategies.
Regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally friendly products are driving innovation in cleaner production technologies. Industries are exploring process intensification techniques, such as reactive distillation and membrane separation, to enhance efficiency and reduce resource consumption in propionic acid manufacturing.
Regulatory Framework for Propionic Acid Use
The regulatory framework for propionic acid use is a critical aspect of its industrial application, encompassing various guidelines and standards set by governmental and international bodies. These regulations primarily focus on ensuring the safe production, handling, storage, and use of propionic acid across different industries.
In the food industry, propionic acid is widely used as a preservative. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has classified it as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also approved its use as a food additive (E280) within specified limits. These regulations typically define the maximum permissible levels of propionic acid in various food products to ensure consumer safety.
For industrial applications, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States has established exposure limits for workers handling propionic acid. The permissible exposure limit (PEL) is set at 10 parts per million (ppm) for an 8-hour time-weighted average. Similar guidelines exist in other countries, such as the workplace exposure standards set by Safe Work Australia.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in the use of propionic acid. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates its release into the environment under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the registration and assessment of chemical substances, including propionic acid.
Transportation of propionic acid is subject to strict regulations due to its corrosive nature. The U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) classifies it as a Class 8 corrosive substance, requiring specific packaging, labeling, and handling procedures. Internationally, the transport of propionic acid is regulated by the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods.
As industries develop targeted propionic acid technologies, compliance with these regulatory frameworks is essential. This includes adhering to specific concentration limits in end products, implementing proper safety measures in production facilities, and ensuring appropriate waste management practices. Companies must also stay informed about regional variations in regulations, as standards may differ between countries or economic zones.
Furthermore, the development of new applications for propionic acid may necessitate additional regulatory scrutiny. For instance, its increasing use in pharmaceuticals or novel industrial processes may require new safety assessments and potentially lead to the establishment of additional regulatory guidelines. As such, ongoing dialogue between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies is crucial to ensure that the regulatory framework evolves in tandem with technological advancements in propionic acid applications.
In the food industry, propionic acid is widely used as a preservative. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has classified it as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also approved its use as a food additive (E280) within specified limits. These regulations typically define the maximum permissible levels of propionic acid in various food products to ensure consumer safety.
For industrial applications, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States has established exposure limits for workers handling propionic acid. The permissible exposure limit (PEL) is set at 10 parts per million (ppm) for an 8-hour time-weighted average. Similar guidelines exist in other countries, such as the workplace exposure standards set by Safe Work Australia.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in the use of propionic acid. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates its release into the environment under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the registration and assessment of chemical substances, including propionic acid.
Transportation of propionic acid is subject to strict regulations due to its corrosive nature. The U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) classifies it as a Class 8 corrosive substance, requiring specific packaging, labeling, and handling procedures. Internationally, the transport of propionic acid is regulated by the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods.
As industries develop targeted propionic acid technologies, compliance with these regulatory frameworks is essential. This includes adhering to specific concentration limits in end products, implementing proper safety measures in production facilities, and ensuring appropriate waste management practices. Companies must also stay informed about regional variations in regulations, as standards may differ between countries or economic zones.
Furthermore, the development of new applications for propionic acid may necessitate additional regulatory scrutiny. For instance, its increasing use in pharmaceuticals or novel industrial processes may require new safety assessments and potentially lead to the establishment of additional regulatory guidelines. As such, ongoing dialogue between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies is crucial to ensure that the regulatory framework evolves in tandem with technological advancements in propionic acid applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!