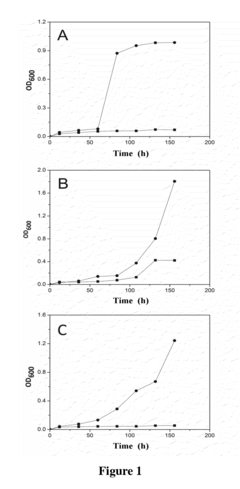
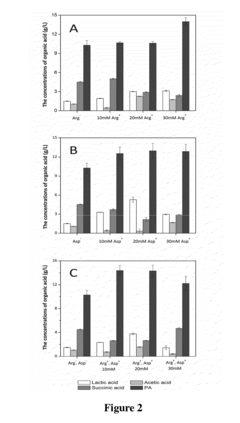
Best Practices for Propionic Acid Use in Preservation Techniques
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Preservation Background
Propionic acid has been utilized as a preservative in various industries for decades, with its application in food preservation dating back to the early 20th century. This organic compound, naturally occurring in some foods and produced by bacteria in the human gut, gained prominence as an effective antimicrobial agent due to its ability to inhibit the growth of molds and certain bacteria.
The evolution of propionic acid as a preservative is closely tied to the development of food science and the increasing demand for extended shelf life in food products. Initially used primarily in baked goods, its application has expanded to encompass a wide range of food items, including dairy products, animal feed, and processed meats. The growing awareness of food safety and the need for natural preservatives have further propelled the use of propionic acid in recent years.
In the realm of preservation techniques, propionic acid has emerged as a versatile solution, addressing multiple challenges in food storage and safety. Its effectiveness lies in its ability to lower pH levels, creating an environment inhospitable to many microorganisms. This property has made it particularly valuable in combating common food spoilage issues, such as mold growth in bread and bacterial proliferation in dairy products.
The technical goals associated with propionic acid preservation have evolved over time. Early objectives focused primarily on extending shelf life, but modern applications aim to achieve a delicate balance between preservation efficacy and maintaining the organoleptic properties of food products. Current research and development efforts are directed towards optimizing the use of propionic acid in combination with other preservatives, exploring synergistic effects that could enhance its antimicrobial action while minimizing potential impacts on taste and texture.
As the food industry continues to seek innovative preservation methods, propionic acid remains a subject of ongoing study. Researchers are investigating its potential in new applications, such as active packaging systems and as a component in edible coatings for fruits and vegetables. These emerging areas of research reflect the broader trend towards sustainable and multifunctional preservation techniques that align with consumer preferences for clean label products.
The trajectory of propionic acid in preservation techniques underscores the dynamic nature of food technology and the continuous pursuit of improved methods for ensuring food safety and quality. As regulatory frameworks evolve and consumer expectations shift, the role of propionic acid in preservation is likely to adapt, driving further innovation in its application and formulation.
The evolution of propionic acid as a preservative is closely tied to the development of food science and the increasing demand for extended shelf life in food products. Initially used primarily in baked goods, its application has expanded to encompass a wide range of food items, including dairy products, animal feed, and processed meats. The growing awareness of food safety and the need for natural preservatives have further propelled the use of propionic acid in recent years.
In the realm of preservation techniques, propionic acid has emerged as a versatile solution, addressing multiple challenges in food storage and safety. Its effectiveness lies in its ability to lower pH levels, creating an environment inhospitable to many microorganisms. This property has made it particularly valuable in combating common food spoilage issues, such as mold growth in bread and bacterial proliferation in dairy products.
The technical goals associated with propionic acid preservation have evolved over time. Early objectives focused primarily on extending shelf life, but modern applications aim to achieve a delicate balance between preservation efficacy and maintaining the organoleptic properties of food products. Current research and development efforts are directed towards optimizing the use of propionic acid in combination with other preservatives, exploring synergistic effects that could enhance its antimicrobial action while minimizing potential impacts on taste and texture.
As the food industry continues to seek innovative preservation methods, propionic acid remains a subject of ongoing study. Researchers are investigating its potential in new applications, such as active packaging systems and as a component in edible coatings for fruits and vegetables. These emerging areas of research reflect the broader trend towards sustainable and multifunctional preservation techniques that align with consumer preferences for clean label products.
The trajectory of propionic acid in preservation techniques underscores the dynamic nature of food technology and the continuous pursuit of improved methods for ensuring food safety and quality. As regulatory frameworks evolve and consumer expectations shift, the role of propionic acid in preservation is likely to adapt, driving further innovation in its application and formulation.
Market Analysis for Propionic Acid Preservatives
The global market for propionic acid preservatives has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for food preservation solutions and rising awareness about food safety. The market size was valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $1.8 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of around 6.5% during the forecast period.
The food and beverage industry remains the largest consumer of propionic acid preservatives, accounting for over 60% of the market share. This is primarily due to the effectiveness of propionic acid in preventing mold growth in baked goods, processed foods, and dairy products. The animal feed sector is also a significant contributor to market growth, with propionic acid being widely used as a preservative in animal feed to prevent spoilage and extend shelf life.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for propionic acid preservatives, collectively accounting for over 50% of the global market share. This dominance can be attributed to stringent food safety regulations, high consumer awareness, and the presence of major food processing industries in these regions. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, changing dietary habits, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by the presence of several key players, including BASF SE, Dow Inc., Eastman Chemical Company, and Perstorp Holding AB. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
One of the key trends shaping the market is the growing demand for natural and clean-label preservatives. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with minimal artificial additives, prompting manufacturers to explore natural alternatives to synthetic preservatives. This has led to the development of propionic acid derivatives from natural sources, such as fermentation processes using propionibacteria.
Another significant factor influencing the market is the increasing adoption of propionic acid preservatives in the pharmaceutical industry. The antimicrobial properties of propionic acid make it a valuable ingredient in various pharmaceutical formulations, particularly in topical medications and oral care products.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the propionic acid preservatives market. While the demand for packaged and processed foods with extended shelf life has increased, disruptions in the supply chain and temporary closures of food processing facilities have posed challenges to market growth. However, the long-term outlook remains positive, as the pandemic has heightened awareness about food safety and the importance of effective preservation techniques.
The food and beverage industry remains the largest consumer of propionic acid preservatives, accounting for over 60% of the market share. This is primarily due to the effectiveness of propionic acid in preventing mold growth in baked goods, processed foods, and dairy products. The animal feed sector is also a significant contributor to market growth, with propionic acid being widely used as a preservative in animal feed to prevent spoilage and extend shelf life.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for propionic acid preservatives, collectively accounting for over 50% of the global market share. This dominance can be attributed to stringent food safety regulations, high consumer awareness, and the presence of major food processing industries in these regions. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, changing dietary habits, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by the presence of several key players, including BASF SE, Dow Inc., Eastman Chemical Company, and Perstorp Holding AB. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
One of the key trends shaping the market is the growing demand for natural and clean-label preservatives. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with minimal artificial additives, prompting manufacturers to explore natural alternatives to synthetic preservatives. This has led to the development of propionic acid derivatives from natural sources, such as fermentation processes using propionibacteria.
Another significant factor influencing the market is the increasing adoption of propionic acid preservatives in the pharmaceutical industry. The antimicrobial properties of propionic acid make it a valuable ingredient in various pharmaceutical formulations, particularly in topical medications and oral care products.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the propionic acid preservatives market. While the demand for packaged and processed foods with extended shelf life has increased, disruptions in the supply chain and temporary closures of food processing facilities have posed challenges to market growth. However, the long-term outlook remains positive, as the pandemic has heightened awareness about food safety and the importance of effective preservation techniques.
Current Challenges in Propionic Acid Preservation
Despite the widespread use of propionic acid in preservation techniques, several challenges persist in its application, hindering its full potential and effectiveness. One of the primary concerns is the variability in antimicrobial efficacy across different food matrices. The effectiveness of propionic acid can be significantly influenced by factors such as pH, water activity, and the presence of other preservatives, making it challenging to establish standardized dosage protocols across diverse food products.
Another significant challenge is the potential for sensory alterations in treated products. Propionic acid, especially at higher concentrations, can impart a distinct flavor and aroma that may be undesirable in certain food applications. This limitation often necessitates a delicate balance between achieving adequate preservation and maintaining the organoleptic qualities of the food product.
The development of resistance among microbial populations is an emerging concern in propionic acid preservation. Prolonged exposure to sub-lethal concentrations of the acid may lead to adaptive responses in some microorganisms, potentially reducing the long-term effectiveness of propionic acid as a preservative. This phenomenon underscores the need for more sophisticated preservation strategies that can mitigate the risk of resistance development.
Environmental and regulatory challenges also play a significant role in the current landscape of propionic acid preservation. Increasing consumer demand for "clean label" products and natural preservatives has put pressure on manufacturers to reduce or eliminate synthetic preservatives, including propionic acid. This trend, coupled with varying regulatory standards across different regions, complicates the global application of propionic acid in food preservation.
Furthermore, the interaction of propionic acid with packaging materials presents another area of concern. Some studies have reported potential migration of propionic acid into certain types of packaging, which could affect both the efficacy of preservation and the safety of the packaging material. This issue necessitates careful consideration in the selection of packaging materials for products treated with propionic acid.
Lastly, the optimization of propionic acid application methods remains a challenge. Current techniques for incorporating propionic acid into food products may not always ensure uniform distribution, potentially leading to inconsistent preservation results. Developing more efficient and precise application methods, such as microencapsulation or controlled release systems, could significantly enhance the effectiveness of propionic acid preservation while potentially addressing some of the aforementioned challenges.
Another significant challenge is the potential for sensory alterations in treated products. Propionic acid, especially at higher concentrations, can impart a distinct flavor and aroma that may be undesirable in certain food applications. This limitation often necessitates a delicate balance between achieving adequate preservation and maintaining the organoleptic qualities of the food product.
The development of resistance among microbial populations is an emerging concern in propionic acid preservation. Prolonged exposure to sub-lethal concentrations of the acid may lead to adaptive responses in some microorganisms, potentially reducing the long-term effectiveness of propionic acid as a preservative. This phenomenon underscores the need for more sophisticated preservation strategies that can mitigate the risk of resistance development.
Environmental and regulatory challenges also play a significant role in the current landscape of propionic acid preservation. Increasing consumer demand for "clean label" products and natural preservatives has put pressure on manufacturers to reduce or eliminate synthetic preservatives, including propionic acid. This trend, coupled with varying regulatory standards across different regions, complicates the global application of propionic acid in food preservation.
Furthermore, the interaction of propionic acid with packaging materials presents another area of concern. Some studies have reported potential migration of propionic acid into certain types of packaging, which could affect both the efficacy of preservation and the safety of the packaging material. This issue necessitates careful consideration in the selection of packaging materials for products treated with propionic acid.
Lastly, the optimization of propionic acid application methods remains a challenge. Current techniques for incorporating propionic acid into food products may not always ensure uniform distribution, potentially leading to inconsistent preservation results. Developing more efficient and precise application methods, such as microencapsulation or controlled release systems, could significantly enhance the effectiveness of propionic acid preservation while potentially addressing some of the aforementioned challenges.
Existing Propionic Acid Preservation Methods
01 Use of propionic acid as a preservative
Propionic acid is widely used as a preservative in various industries due to its antimicrobial properties. It effectively inhibits the growth of mold and bacteria, extending the shelf life of products. This organic acid is particularly useful in food preservation, animal feed, and pharmaceutical applications.- Use of propionic acid as a preservative: Propionic acid is widely used as a preservative in various industries due to its antimicrobial properties. It effectively inhibits the growth of mold and bacteria, extending the shelf life of products. This organic acid is particularly useful in food preservation, animal feed, and pharmaceutical applications.
- Production methods for propionic acid: Various methods have been developed for the production of propionic acid, including chemical synthesis and fermentation processes. These methods aim to improve yield, reduce costs, and enhance the purity of the final product. Innovations in production techniques contribute to the increased availability and efficiency of propionic acid as a preservative.
- Formulations containing propionic acid for preservation: Propionic acid is often incorporated into complex formulations to enhance preservation efficacy. These formulations may include other preservatives, stabilizers, or synergistic compounds that work in conjunction with propionic acid. Such combinations can provide broader spectrum antimicrobial activity and improved preservation in various products.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid and its salts are commonly used in food preservation, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and processed foods. It helps prevent mold growth and bacterial contamination, thereby extending the shelf life of food products. The use of propionic acid in food preservation is regulated and approved by various food safety authorities.
- Propionic acid preservation in animal feed: Propionic acid is extensively used in animal feed preservation, particularly in silage and grain storage. It helps prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms, maintains nutritional quality, and reduces feed spoilage. The application of propionic acid in animal feed contributes to improved livestock health and productivity.
02 Production methods for propionic acid
Various methods have been developed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes and chemical synthesis. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of the final product. Some approaches involve the use of specific microorganisms or catalysts to enhance the production process.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications in food preservation
Propionic acid and its salts are commonly used as food preservatives. They are effective in preventing mold growth in baked goods, dairy products, and other food items. The preservative action helps maintain food quality and safety by inhibiting microbial growth and extending shelf life.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use in animal feed preservation
Propionic acid is widely used in animal feed preservation to prevent mold growth and maintain nutritional quality. It is particularly effective in preserving high-moisture grains and silage. The application of propionic acid in animal feed helps reduce feed spoilage and potential health risks to livestock.Expand Specific Solutions05 Formulations and delivery systems
Various formulations and delivery systems have been developed to enhance the effectiveness and ease of use of propionic acid as a preservative. These may include encapsulation techniques, controlled release systems, or combinations with other preservatives to achieve synergistic effects. Such formulations aim to improve the stability and application of propionic acid in different products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Propionic Acid Industry
The propionic acid preservation techniques market is in a mature stage, with established players and proven applications across various industries. The global market size for propionic acid is estimated to be over $1 billion, driven by increasing demand in food preservation, animal feed, and pharmaceuticals. Technologically, the field is well-developed, with companies like BASF Corp., Dow Global Technologies LLC, and Eastman Chemical Co. leading innovation. These industry giants, along with specialized firms such as Kemin Industries and ADDCON AGRAR GmbH, are continuously refining formulations and application methods. Academic institutions like The Ohio State University and Xiamen University contribute to advancing the fundamental understanding and potential new applications of propionic acid in preservation techniques.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed advanced preservation techniques using propionic acid, focusing on its application in feed and food industries. Their approach involves optimizing the concentration and formulation of propionic acid to enhance its antimicrobial efficacy. BASF's research has shown that a combination of propionic acid with other organic acids can provide synergistic effects, improving preservation while reducing the overall acid concentration required [1]. They have also developed encapsulation technologies to control the release of propionic acid, ensuring prolonged antimicrobial activity and reducing corrosion issues in metal containers [3].
Strengths: Comprehensive research on synergistic effects and controlled release technology. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs due to complex formulations and encapsulation processes.
Purac Biochem BV
Technical Solution: Purac Biochem has focused on developing natural preservation solutions using propionic acid produced through fermentation. Their approach involves using specially selected bacterial strains to produce high-purity propionic acid with consistent quality [5]. Purac has also developed a range of propionic acid salts, such as calcium propionate and sodium propionate, which offer improved solubility and ease of use in various food applications. Their research has demonstrated that these naturally derived propionic acid products can effectively inhibit mold growth in bakery products, extending shelf life by up to 14 days [6].
Strengths: Natural, fermentation-derived propionic acid with consistent quality. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs compared to synthetic propionic acid.
Innovative Propionic Acid Applications
Improved propionibacterium strains for the production of propionic acid
PatentWO2017055932A2
Innovation
- Genome shuffling between selected Propionibacterium strains, such as P. acidipropionici ATCC 4875 and P. acidipropionici ATCC 55737, to generate novel strains with enhanced growth rates and propionic acid production, utilizing genetic material exchange to create strains with improved metabolic pathways and regulatory mechanisms.
Method for Improving Acid tolerance of Propionibacterium acdipropionici
PatentInactiveUS20140178952A1
Innovation
- Adding arginine and/or aspartic acid to the culture medium during the cultivation of Propionibacterium acdipropionici to enhance acid tolerance and propionic acid productivity.
Regulatory Framework for Food Preservatives
The regulatory framework for food preservatives, including propionic acid, is a complex and evolving system designed to ensure food safety and quality while protecting consumer health. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing the use of food preservatives. The FDA has established specific guidelines for the use of propionic acid and its salts under the Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) designation.
Under FDA regulations, propionic acid is approved for use as a preservative in various food products, with specific limitations on concentration levels. For instance, in baked goods, propionic acid can be used at levels not exceeding 0.32% by weight of the finished product. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated propionic acid and its salts, establishing an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) of 20 mg/kg body weight per day.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international food standards that many countries use as a basis for their national regulations. The Codex General Standard for Food Additives (GSFA) includes provisions for the use of propionic acid and its salts in various food categories.
In addition to concentration limits, regulations often specify labeling requirements for products containing propionic acid. In the EU, for example, propionic acid must be declared on food labels by its name or E-number (E280). Many countries also require manufacturers to follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) when using food preservatives, ensuring that the minimum quantity necessary is used to achieve the desired preservative effect.
Regulatory bodies regularly review and update their guidelines based on new scientific evidence. For instance, the EFSA periodically re-evaluates the safety of food additives, including propionic acid. This ongoing process ensures that regulations remain current with the latest scientific understanding of preservative safety and efficacy.
Compliance with these regulations is crucial for food manufacturers. Many countries have implemented strict monitoring and enforcement mechanisms, including regular inspections and product testing. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, product recalls, and damage to brand reputation.
As global trade in food products continues to grow, there is an increasing focus on harmonizing regulations across different regions. International initiatives, such as the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI), aim to promote convergence in food safety standards worldwide, which may influence future regulatory frameworks for preservatives like propionic acid.
Under FDA regulations, propionic acid is approved for use as a preservative in various food products, with specific limitations on concentration levels. For instance, in baked goods, propionic acid can be used at levels not exceeding 0.32% by weight of the finished product. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated propionic acid and its salts, establishing an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) of 20 mg/kg body weight per day.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international food standards that many countries use as a basis for their national regulations. The Codex General Standard for Food Additives (GSFA) includes provisions for the use of propionic acid and its salts in various food categories.
In addition to concentration limits, regulations often specify labeling requirements for products containing propionic acid. In the EU, for example, propionic acid must be declared on food labels by its name or E-number (E280). Many countries also require manufacturers to follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) when using food preservatives, ensuring that the minimum quantity necessary is used to achieve the desired preservative effect.
Regulatory bodies regularly review and update their guidelines based on new scientific evidence. For instance, the EFSA periodically re-evaluates the safety of food additives, including propionic acid. This ongoing process ensures that regulations remain current with the latest scientific understanding of preservative safety and efficacy.
Compliance with these regulations is crucial for food manufacturers. Many countries have implemented strict monitoring and enforcement mechanisms, including regular inspections and product testing. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, product recalls, and damage to brand reputation.
As global trade in food products continues to grow, there is an increasing focus on harmonizing regulations across different regions. International initiatives, such as the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI), aim to promote convergence in food safety standards worldwide, which may influence future regulatory frameworks for preservatives like propionic acid.
Environmental Impact of Propionic Acid Use
The use of propionic acid in preservation techniques has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. While propionic acid offers effective antimicrobial properties for food preservation, its production and application can impact various environmental aspects.
One primary concern is the potential for propionic acid to contribute to water pollution. When improperly disposed of or in the event of accidental spills, propionic acid can enter water systems, leading to increased acidity and potential harm to aquatic ecosystems. This risk necessitates stringent handling and disposal protocols to minimize environmental contamination.
Air quality is another area of environmental impact. The production of propionic acid involves chemical processes that may release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. These emissions can contribute to smog formation and air quality degradation if not properly controlled. Implementing advanced emission control technologies in production facilities is crucial to mitigate these effects.
From a lifecycle perspective, the environmental footprint of propionic acid extends beyond its immediate use. The raw materials required for its production, typically derived from petrochemical sources, contribute to resource depletion and associated environmental impacts of fossil fuel extraction and processing. This underscores the importance of exploring more sustainable production methods, such as bio-based alternatives derived from renewable resources.
Energy consumption in the production and application of propionic acid is another environmental consideration. The energy-intensive nature of chemical synthesis and the refrigeration often required for preserved foods contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Improving energy efficiency in production processes and exploring low-energy preservation techniques can help reduce this environmental burden.
Biodegradability and persistence in the environment are key factors in assessing the long-term environmental impact of propionic acid. While propionic acid is generally considered biodegradable, its rate of degradation can vary depending on environmental conditions. In some cases, it may persist long enough to affect soil and water microbial communities, potentially disrupting local ecosystems.
The use of propionic acid in food preservation also indirectly impacts the environment by reducing food waste. By extending the shelf life of various food products, propionic acid helps minimize the amount of food that spoils before consumption. This reduction in food waste translates to more efficient use of agricultural resources and a decrease in the environmental burden associated with food production and disposal.
In conclusion, while propionic acid plays a valuable role in food preservation, its environmental impact is multifaceted. Balancing its benefits with potential environmental risks requires ongoing research into more sustainable production methods, improved application techniques, and comprehensive lifecycle assessments to guide best practices in its use.
One primary concern is the potential for propionic acid to contribute to water pollution. When improperly disposed of or in the event of accidental spills, propionic acid can enter water systems, leading to increased acidity and potential harm to aquatic ecosystems. This risk necessitates stringent handling and disposal protocols to minimize environmental contamination.
Air quality is another area of environmental impact. The production of propionic acid involves chemical processes that may release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. These emissions can contribute to smog formation and air quality degradation if not properly controlled. Implementing advanced emission control technologies in production facilities is crucial to mitigate these effects.
From a lifecycle perspective, the environmental footprint of propionic acid extends beyond its immediate use. The raw materials required for its production, typically derived from petrochemical sources, contribute to resource depletion and associated environmental impacts of fossil fuel extraction and processing. This underscores the importance of exploring more sustainable production methods, such as bio-based alternatives derived from renewable resources.
Energy consumption in the production and application of propionic acid is another environmental consideration. The energy-intensive nature of chemical synthesis and the refrigeration often required for preserved foods contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Improving energy efficiency in production processes and exploring low-energy preservation techniques can help reduce this environmental burden.
Biodegradability and persistence in the environment are key factors in assessing the long-term environmental impact of propionic acid. While propionic acid is generally considered biodegradable, its rate of degradation can vary depending on environmental conditions. In some cases, it may persist long enough to affect soil and water microbial communities, potentially disrupting local ecosystems.
The use of propionic acid in food preservation also indirectly impacts the environment by reducing food waste. By extending the shelf life of various food products, propionic acid helps minimize the amount of food that spoils before consumption. This reduction in food waste translates to more efficient use of agricultural resources and a decrease in the environmental burden associated with food production and disposal.
In conclusion, while propionic acid plays a valuable role in food preservation, its environmental impact is multifaceted. Balancing its benefits with potential environmental risks requires ongoing research into more sustainable production methods, improved application techniques, and comprehensive lifecycle assessments to guide best practices in its use.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!