Ammonium Hydroxide in Hair Dye Formulations: Efficacy and Safety
JUL 22, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ammonia in Hair Dye: History and Objectives
The use of ammonia in hair dye formulations has a rich history dating back to the early 20th century. In 1907, Eugene Schueller, the founder of L'Oréal, developed the first synthetic hair dye using para-phenylenediamine (PPD) and ammonia. This breakthrough marked the beginning of modern hair coloring techniques and set the stage for the widespread use of ammonia in hair dye formulations.
Ammonia, or more specifically ammonium hydroxide, plays a crucial role in the hair dyeing process. It acts as an alkalizing agent, raising the pH of the hair shaft and causing the cuticle to swell and open. This allows the dye molecules to penetrate deeper into the hair structure, resulting in more effective and longer-lasting color. Additionally, ammonia facilitates the oxidation of the dye precursors, enabling the formation of larger, colored molecules within the hair shaft.
Throughout the 20th century, the hair dye industry experienced significant growth and technological advancements. The development of new dye molecules and improved formulations led to a wider range of color options and enhanced performance. However, the use of ammonia remained a constant in most permanent hair dye products due to its effectiveness in color development and penetration.
In recent decades, there has been a growing focus on the potential health and safety concerns associated with ammonia in hair dyes. Consumers and regulatory bodies have raised questions about the irritation and sensitization potential of ammonia, as well as its strong odor. This has led to increased research efforts aimed at developing ammonia-free or low-ammonia alternatives that can deliver comparable coloring results.
The primary objectives of current research and development in this field are twofold. First, there is a push to optimize the efficacy of ammonia-based hair dye formulations, seeking to maximize color performance while minimizing the concentration of ammonia required. This involves exploring synergistic combinations of alkalizing agents and developing more efficient dye molecules that can achieve desired results with lower ammonia levels.
Secondly, there is a significant focus on developing alternative alkalizing agents that can replace or reduce the need for ammonia in hair dye formulations. These alternatives aim to provide similar or superior color results while addressing the safety concerns and sensory issues associated with ammonia. Potential candidates include various organic bases, amino acids, and innovative delivery systems that can achieve the necessary pH elevation without the drawbacks of traditional ammonia-based formulations.
Ammonia, or more specifically ammonium hydroxide, plays a crucial role in the hair dyeing process. It acts as an alkalizing agent, raising the pH of the hair shaft and causing the cuticle to swell and open. This allows the dye molecules to penetrate deeper into the hair structure, resulting in more effective and longer-lasting color. Additionally, ammonia facilitates the oxidation of the dye precursors, enabling the formation of larger, colored molecules within the hair shaft.
Throughout the 20th century, the hair dye industry experienced significant growth and technological advancements. The development of new dye molecules and improved formulations led to a wider range of color options and enhanced performance. However, the use of ammonia remained a constant in most permanent hair dye products due to its effectiveness in color development and penetration.
In recent decades, there has been a growing focus on the potential health and safety concerns associated with ammonia in hair dyes. Consumers and regulatory bodies have raised questions about the irritation and sensitization potential of ammonia, as well as its strong odor. This has led to increased research efforts aimed at developing ammonia-free or low-ammonia alternatives that can deliver comparable coloring results.
The primary objectives of current research and development in this field are twofold. First, there is a push to optimize the efficacy of ammonia-based hair dye formulations, seeking to maximize color performance while minimizing the concentration of ammonia required. This involves exploring synergistic combinations of alkalizing agents and developing more efficient dye molecules that can achieve desired results with lower ammonia levels.
Secondly, there is a significant focus on developing alternative alkalizing agents that can replace or reduce the need for ammonia in hair dye formulations. These alternatives aim to provide similar or superior color results while addressing the safety concerns and sensory issues associated with ammonia. Potential candidates include various organic bases, amino acids, and innovative delivery systems that can achieve the necessary pH elevation without the drawbacks of traditional ammonia-based formulations.
Market Analysis of Ammonia-based Hair Dyes
The global hair dye market has experienced significant growth in recent years, with ammonia-based hair dyes playing a crucial role in this expansion. The market for ammonia-based hair dyes is driven by several factors, including the increasing desire for personal grooming, changing fashion trends, and the growing aging population seeking to cover gray hair.
Ammonia-based hair dyes dominate a substantial portion of the hair coloring market due to their effectiveness in penetrating the hair shaft and providing long-lasting color results. These products are particularly popular among consumers looking for permanent hair color solutions, as the ammonia helps to open the hair cuticle and allow the dye to penetrate deeply.
The market for ammonia-based hair dyes is segmented based on product type, distribution channel, and region. Product types include permanent, semi-permanent, and temporary hair dyes, with permanent dyes containing ammonia being the largest segment. Distribution channels encompass professional salons, retail stores, and online platforms, with professional salons holding a significant market share due to the expertise required in applying these products.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for ammonia-based hair dyes, owing to high consumer awareness and disposable income. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by changing lifestyles, increasing urbanization, and a growing middle-class population.
Key players in the ammonia-based hair dye market include L'Oréal, Henkel, Kao Corporation, Coty, and Revlon. These companies are continuously investing in research and development to improve product formulations and address consumer concerns regarding the safety and potential health impacts of ammonia in hair dyes.
Despite the dominance of ammonia-based hair dyes, there is a growing trend towards ammonia-free and natural hair coloring products. This shift is driven by increasing consumer awareness of potential health risks associated with chemical hair dyes and a preference for more environmentally friendly options. As a result, manufacturers are exploring alternative alkalizing agents and developing innovative formulations to meet this demand while maintaining color efficacy.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the ammonia-based hair dye market. While salon closures during lockdowns negatively affected professional hair coloring services, there was an increase in at-home hair coloring, boosting retail sales of hair dye products. This trend has led to a shift in consumer behavior and product preferences, with many opting for DIY hair coloring solutions.
Ammonia-based hair dyes dominate a substantial portion of the hair coloring market due to their effectiveness in penetrating the hair shaft and providing long-lasting color results. These products are particularly popular among consumers looking for permanent hair color solutions, as the ammonia helps to open the hair cuticle and allow the dye to penetrate deeply.
The market for ammonia-based hair dyes is segmented based on product type, distribution channel, and region. Product types include permanent, semi-permanent, and temporary hair dyes, with permanent dyes containing ammonia being the largest segment. Distribution channels encompass professional salons, retail stores, and online platforms, with professional salons holding a significant market share due to the expertise required in applying these products.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for ammonia-based hair dyes, owing to high consumer awareness and disposable income. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by changing lifestyles, increasing urbanization, and a growing middle-class population.
Key players in the ammonia-based hair dye market include L'Oréal, Henkel, Kao Corporation, Coty, and Revlon. These companies are continuously investing in research and development to improve product formulations and address consumer concerns regarding the safety and potential health impacts of ammonia in hair dyes.
Despite the dominance of ammonia-based hair dyes, there is a growing trend towards ammonia-free and natural hair coloring products. This shift is driven by increasing consumer awareness of potential health risks associated with chemical hair dyes and a preference for more environmentally friendly options. As a result, manufacturers are exploring alternative alkalizing agents and developing innovative formulations to meet this demand while maintaining color efficacy.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the ammonia-based hair dye market. While salon closures during lockdowns negatively affected professional hair coloring services, there was an increase in at-home hair coloring, boosting retail sales of hair dye products. This trend has led to a shift in consumer behavior and product preferences, with many opting for DIY hair coloring solutions.
Current Challenges in Ammonia Hair Dye Technology
The current challenges in ammonia hair dye technology primarily revolve around safety concerns, efficacy issues, and environmental impact. Ammonium hydroxide, a key component in many hair dye formulations, has long been used for its ability to effectively open the hair cuticle and facilitate color penetration. However, its use is not without drawbacks.
One of the main challenges is the potential health risks associated with ammonia exposure. Inhalation of ammonia fumes can cause respiratory irritation, headaches, and in severe cases, lung damage. Skin contact may lead to irritation, burns, or allergic reactions. These safety concerns have led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and a growing demand for safer alternatives.
Efficacy remains a critical challenge in ammonia-based hair dyes. While ammonia effectively raises the pH of the hair, allowing for better color penetration, it can also lead to excessive hair damage. The high alkalinity can cause cuticle swelling and porosity, resulting in weakened hair structure, increased brittleness, and reduced color longevity. Balancing the need for effective color deposition with minimal hair damage is an ongoing challenge for formulators.
Another significant issue is the strong, unpleasant odor associated with ammonia-based hair dyes. This odor can be off-putting for consumers and salon professionals alike, leading to a negative user experience. Developing effective odor-masking technologies or reducing ammonia concentrations without compromising efficacy is a key area of focus for many manufacturers.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges for ammonia hair dye technology. The release of ammonia into wastewater systems can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, the production and transportation of ammonia contribute to carbon emissions, raising sustainability concerns in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Regulatory compliance presents another hurdle for manufacturers. Different countries and regions have varying regulations regarding ammonia content in hair dyes, necessitating the development of formulations that can meet diverse regulatory requirements while maintaining consistent performance across markets.
Lastly, there is a growing consumer demand for more natural and gentle hair coloring options. This shift in consumer preferences challenges manufacturers to develop ammonia-free or low-ammonia formulations that can match the performance of traditional ammonia-based dyes. Achieving comparable color lift, gray coverage, and long-lasting results without relying on high ammonia concentrations remains a significant technical challenge in the industry.
One of the main challenges is the potential health risks associated with ammonia exposure. Inhalation of ammonia fumes can cause respiratory irritation, headaches, and in severe cases, lung damage. Skin contact may lead to irritation, burns, or allergic reactions. These safety concerns have led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and a growing demand for safer alternatives.
Efficacy remains a critical challenge in ammonia-based hair dyes. While ammonia effectively raises the pH of the hair, allowing for better color penetration, it can also lead to excessive hair damage. The high alkalinity can cause cuticle swelling and porosity, resulting in weakened hair structure, increased brittleness, and reduced color longevity. Balancing the need for effective color deposition with minimal hair damage is an ongoing challenge for formulators.
Another significant issue is the strong, unpleasant odor associated with ammonia-based hair dyes. This odor can be off-putting for consumers and salon professionals alike, leading to a negative user experience. Developing effective odor-masking technologies or reducing ammonia concentrations without compromising efficacy is a key area of focus for many manufacturers.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges for ammonia hair dye technology. The release of ammonia into wastewater systems can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, the production and transportation of ammonia contribute to carbon emissions, raising sustainability concerns in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Regulatory compliance presents another hurdle for manufacturers. Different countries and regions have varying regulations regarding ammonia content in hair dyes, necessitating the development of formulations that can meet diverse regulatory requirements while maintaining consistent performance across markets.
Lastly, there is a growing consumer demand for more natural and gentle hair coloring options. This shift in consumer preferences challenges manufacturers to develop ammonia-free or low-ammonia formulations that can match the performance of traditional ammonia-based dyes. Achieving comparable color lift, gray coverage, and long-lasting results without relying on high ammonia concentrations remains a significant technical challenge in the industry.
Existing Ammonia-based Hair Dye Formulations
01 Efficacy in chemical processes
Ammonium hydroxide is widely used in various chemical processes due to its effectiveness as a base and reactant. It plays a crucial role in neutralization reactions, pH adjustment, and as a catalyst in organic synthesis. Its ability to readily donate hydroxide ions makes it valuable in industrial applications.- Efficacy in chemical processes: Ammonium hydroxide is widely used in various chemical processes due to its effectiveness as a base and reactant. It plays a crucial role in neutralization reactions, pH adjustment, and as a catalyst in organic synthesis. Its ability to readily donate hydroxide ions makes it valuable in industrial applications.
- Safety considerations and handling: While ammonium hydroxide is a useful chemical, proper safety measures are essential when handling it. It can cause irritation to skin, eyes, and respiratory system. Adequate ventilation, personal protective equipment, and proper storage are crucial to ensure safe usage. Safety data sheets and handling guidelines should be strictly followed.
- Environmental impact and regulations: The use of ammonium hydroxide is subject to environmental regulations due to its potential impact on aquatic ecosystems and air quality. Proper disposal methods and emission control measures are necessary to minimize environmental harm. Compliance with local and international environmental standards is crucial for industries using this chemical.
- Applications in cleaning and surface treatment: Ammonium hydroxide is effective in cleaning and surface treatment applications. It is used in household cleaners, industrial degreasers, and as a component in metal surface treatment processes. Its alkaline nature helps in removing grease, oils, and other contaminants from various surfaces.
- Use in agricultural and pharmaceutical industries: Ammonium hydroxide finds applications in both agricultural and pharmaceutical sectors. In agriculture, it is used as a nitrogen source in fertilizers. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is utilized in the production of certain medications and as a pH adjuster in drug formulations. Its efficacy in these fields is balanced with safety considerations specific to each application.
02 Safety considerations and handling
While ammonium hydroxide is a useful chemical, proper safety measures are essential when handling it. It can cause irritation to skin, eyes, and respiratory system. Adequate ventilation, personal protective equipment, and proper storage are crucial to minimize risks associated with its use. Safety data sheets and handling guidelines should be strictly followed.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications in cleaning and disinfection
Ammonium hydroxide is effective in cleaning and disinfection processes. Its alkaline nature helps in breaking down grease and grime, making it useful in household and industrial cleaning products. It also exhibits antimicrobial properties, contributing to its use in disinfectants and sanitizers.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental impact and regulations
The use of ammonium hydroxide is subject to environmental regulations due to its potential impact on aquatic ecosystems and air quality. Proper disposal methods and emission controls are necessary to minimize environmental harm. Compliance with local and international environmental standards is crucial for industries using this chemical.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial applications and alternatives
Ammonium hydroxide finds applications in various industries, including textiles, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. However, due to safety and environmental concerns, research is ongoing to find safer alternatives or optimize its use. Some industries are exploring the use of other alkaline compounds or developing new processes that reduce or eliminate the need for ammonium hydroxide.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Ammonia Hair Dye Industry
The market for ammonium hydroxide in hair dye formulations is in a mature stage, with established players dominating the industry. The global hair color market, valued at over $20 billion, continues to grow steadily. Major companies like L'Oréal, Henkel, and Kao Corporation have advanced research capabilities and extensive product portfolios. These industry leaders, along with emerging players such as Hoyu and Arimino, are focusing on developing safer and more effective formulations. The technology is well-established, but ongoing innovation aims to address safety concerns and improve product performance. Regulatory scrutiny and consumer demand for natural alternatives are driving research into new ingredients and application methods.
L'Oréal SA
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has developed innovative hair dye formulations utilizing ammonium hydroxide as a key ingredient. Their approach involves a controlled-release system that gradually releases ammonia during the coloring process, reducing scalp irritation while maintaining color efficacy[1]. The company has also introduced ammonia-free hair color options using monoethanolamine (MEA) as an alternative alkalizing agent, catering to consumers seeking gentler formulations[2]. L'Oréal's research focuses on optimizing the pH balance in hair dye products to ensure effective color penetration while minimizing damage to the hair structure[3].
Strengths: Advanced controlled-release technology, diverse product range including ammonia-free options, strong R&D capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential consumer concerns about ammonia use, need for continuous innovation to stay competitive.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed a range of hair dye formulations that utilize ammonium hydroxide in conjunction with other ingredients to enhance color performance and hair protection. Their approach includes the use of specialized polymer technologies that work synergistically with ammonium hydroxide to improve color penetration and longevity[4]. Henkel has also invested in research to optimize the concentration of ammonium hydroxide in their formulations, balancing efficacy with safety considerations[5]. The company has introduced innovative conditioning agents that help mitigate potential damage caused by the alkaline nature of ammonium hydroxide, ensuring better hair health post-coloration[6].
Strengths: Advanced polymer technologies, focus on hair health preservation, balanced approach to efficacy and safety. Weaknesses: Ongoing challenge to address consumer preferences for natural ingredients, potential regulatory hurdles in certain markets.
Innovations in Ammonia Hair Dye Chemistry
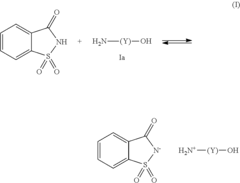
Ammonium hydroxide-free hair dye compositions containing a buffer system
PatentInactiveUS8834580B2
Innovation
- A buffer system comprising saccharine and at least one alkanolamine is used in oxidative hair color compositions to achieve a lightening effect similar to ammonium hydroxide-based systems while minimizing odors and irritation, with a pH range of 8 to 11, enhancing stability and compatibility.
Hair-dyeing composition for minimizing ammonium hydroxide content and odor and method of producing the same
PatentWO2020010128A1
Innovation
- A hair-dyeing composition using amino propanol as the alkalizing agent, such as 2-Dimethylamino-2-methylpropanol, with a dyeing agent and oxidizing agent ratio of 1:1 to 1:3, which minimizes ammonium hydroxide content and eliminates the characteristic malodor, achieving equivalent color coverage to ammonium hydroxide-based compositions without the associated harm.
Safety Regulations for Hair Dye Ingredients
Safety regulations for hair dye ingredients are crucial in ensuring consumer protection and product quality in the cosmetics industry. These regulations are typically established and enforced by governmental bodies and international organizations to maintain high standards of safety and efficacy.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in regulating hair dye ingredients. The FDA classifies hair dyes as cosmetics and requires manufacturers to ensure their products are safe for intended use. However, it's important to note that the FDA does not have the authority to approve hair dye ingredients before they are marketed, except for color additives.
The European Union (EU) has implemented more stringent regulations through the European Commission's Cosmetic Regulation. This regulation includes a list of prohibited substances in cosmetic products, including certain hair dye ingredients. The EU also requires safety assessments for all cosmetic products before they can be placed on the market.
Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cosmetics, including hair dyes, under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. This law sets standards for ingredients, labeling, and manufacturing practices to ensure product safety.
International organizations, such as the Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS) in the EU, provide scientific opinions on the safety of cosmetic ingredients. These opinions often inform regulatory decisions and industry practices globally.
Specific to ammonium hydroxide in hair dye formulations, regulations typically focus on concentration limits and proper labeling. Many jurisdictions require warning labels for products containing ammonia or its derivatives, highlighting potential skin irritation or allergic reactions.
Safety regulations also extend to manufacturing practices. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) guidelines are often mandated to ensure consistent product quality and safety. These practices cover aspects such as ingredient sourcing, production processes, and quality control measures.
Regulatory bodies frequently update their guidelines based on new scientific evidence. For instance, the EU periodically reviews and updates its list of allowed, restricted, and prohibited substances in cosmetics, including hair dye ingredients.
Compliance with these regulations is mandatory for manufacturers and importers. Non-compliance can result in product recalls, fines, or legal action. Therefore, companies invest significantly in research and development to ensure their products meet or exceed regulatory requirements while maintaining efficacy.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in regulating hair dye ingredients. The FDA classifies hair dyes as cosmetics and requires manufacturers to ensure their products are safe for intended use. However, it's important to note that the FDA does not have the authority to approve hair dye ingredients before they are marketed, except for color additives.
The European Union (EU) has implemented more stringent regulations through the European Commission's Cosmetic Regulation. This regulation includes a list of prohibited substances in cosmetic products, including certain hair dye ingredients. The EU also requires safety assessments for all cosmetic products before they can be placed on the market.
Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cosmetics, including hair dyes, under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. This law sets standards for ingredients, labeling, and manufacturing practices to ensure product safety.
International organizations, such as the Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS) in the EU, provide scientific opinions on the safety of cosmetic ingredients. These opinions often inform regulatory decisions and industry practices globally.
Specific to ammonium hydroxide in hair dye formulations, regulations typically focus on concentration limits and proper labeling. Many jurisdictions require warning labels for products containing ammonia or its derivatives, highlighting potential skin irritation or allergic reactions.
Safety regulations also extend to manufacturing practices. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) guidelines are often mandated to ensure consistent product quality and safety. These practices cover aspects such as ingredient sourcing, production processes, and quality control measures.
Regulatory bodies frequently update their guidelines based on new scientific evidence. For instance, the EU periodically reviews and updates its list of allowed, restricted, and prohibited substances in cosmetics, including hair dye ingredients.
Compliance with these regulations is mandatory for manufacturers and importers. Non-compliance can result in product recalls, fines, or legal action. Therefore, companies invest significantly in research and development to ensure their products meet or exceed regulatory requirements while maintaining efficacy.
Environmental Impact of Ammonia in Hair Dyes
The environmental impact of ammonia in hair dyes is a significant concern that warrants careful consideration. Ammonia, a key component in many hair dye formulations, plays a crucial role in the coloring process but also poses potential risks to the environment. When hair dyes containing ammonia are rinsed off, they enter wastewater systems and can ultimately find their way into natural water bodies.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ammonia in hair dyes is its potential to contribute to eutrophication. Eutrophication occurs when excessive nutrients, including nitrogen compounds like ammonia, accumulate in water bodies. This process can lead to algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and disruption of aquatic ecosystems. The increased nitrogen load from ammonia-containing hair dyes can exacerbate this problem, particularly in areas with inadequate wastewater treatment facilities.
Furthermore, ammonia can be toxic to aquatic life at high concentrations. Fish and other aquatic organisms are particularly sensitive to ammonia, which can cause gill damage, impair growth, and even lead to mortality. The continuous release of ammonia-containing hair dyes into water systems may contribute to chronic low-level exposure, potentially affecting the long-term health and biodiversity of aquatic ecosystems.
The volatility of ammonia also raises concerns about air quality. During the hair dyeing process, ammonia vapors are released into the air, contributing to indoor air pollution in salons and homes. These vapors can then be vented to the outdoor environment, potentially impacting local air quality and contributing to the formation of particulate matter.
In response to these environmental concerns, there is a growing trend towards the development of ammonia-free hair dye formulations. These alternative products often use ethanolamine or other less volatile alkaline agents to achieve similar results. While these substitutes may address some of the environmental issues associated with ammonia, their long-term environmental impacts are still being studied.
The cosmetics industry is increasingly recognizing the need for more sustainable practices. Some manufacturers are exploring biodegradable formulations and implementing closed-loop systems to minimize the environmental footprint of hair dye production and use. Additionally, there is ongoing research into novel dyeing technologies that could reduce or eliminate the need for alkaline agents altogether, potentially offering more environmentally friendly solutions in the future.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ammonia in hair dyes is its potential to contribute to eutrophication. Eutrophication occurs when excessive nutrients, including nitrogen compounds like ammonia, accumulate in water bodies. This process can lead to algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and disruption of aquatic ecosystems. The increased nitrogen load from ammonia-containing hair dyes can exacerbate this problem, particularly in areas with inadequate wastewater treatment facilities.
Furthermore, ammonia can be toxic to aquatic life at high concentrations. Fish and other aquatic organisms are particularly sensitive to ammonia, which can cause gill damage, impair growth, and even lead to mortality. The continuous release of ammonia-containing hair dyes into water systems may contribute to chronic low-level exposure, potentially affecting the long-term health and biodiversity of aquatic ecosystems.
The volatility of ammonia also raises concerns about air quality. During the hair dyeing process, ammonia vapors are released into the air, contributing to indoor air pollution in salons and homes. These vapors can then be vented to the outdoor environment, potentially impacting local air quality and contributing to the formation of particulate matter.
In response to these environmental concerns, there is a growing trend towards the development of ammonia-free hair dye formulations. These alternative products often use ethanolamine or other less volatile alkaline agents to achieve similar results. While these substitutes may address some of the environmental issues associated with ammonia, their long-term environmental impacts are still being studied.
The cosmetics industry is increasingly recognizing the need for more sustainable practices. Some manufacturers are exploring biodegradable formulations and implementing closed-loop systems to minimize the environmental footprint of hair dye production and use. Additionally, there is ongoing research into novel dyeing technologies that could reduce or eliminate the need for alkaline agents altogether, potentially offering more environmentally friendly solutions in the future.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!