Application of Ammonium Hydroxide in Developing Eco-Friendly Detergents
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
NH4OH in Detergents: Background and Objectives
Ammonium hydroxide, a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen, has been a subject of increasing interest in the detergent industry due to its potential as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional cleaning agents. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 20th century when the Haber-Bosch process revolutionized ammonia production. However, it is only in recent decades that its application in detergents has gained significant attention.
The primary objective of incorporating ammonium hydroxide in detergent formulations is to develop cleaning products that are both effective and environmentally sustainable. This aligns with the growing global demand for green technologies and the increasing regulatory pressure on manufacturers to reduce the environmental impact of their products. The use of ammonium hydroxide in detergents aims to address several key challenges in the industry, including the reduction of phosphates, the minimization of toxic residues, and the improvement of biodegradability.
From a technical perspective, ammonium hydroxide offers unique properties that make it suitable for detergent applications. Its alkaline nature provides excellent cleaning power, particularly for removing grease and oil-based stains. Additionally, it can act as a buffering agent, helping to maintain optimal pH levels during the cleaning process. These characteristics have led to its exploration in various types of detergents, including laundry detergents, dishwashing liquids, and all-purpose cleaners.
The development trajectory of ammonium hydroxide in detergents has been influenced by advancements in chemical engineering and formulation technologies. Researchers have focused on optimizing the concentration and stability of ammonium hydroxide in detergent formulations, as well as exploring synergistic effects with other eco-friendly ingredients. This has led to the creation of novel detergent compositions that leverage the benefits of ammonium hydroxide while mitigating potential drawbacks such as odor and volatility.
As the detergent industry continues to evolve, the role of ammonium hydroxide is expected to expand. Current research is aimed at enhancing its efficacy, improving its stability in various formulations, and exploring new applications. The ultimate goal is to develop a new generation of detergents that not only clean effectively but also contribute to environmental conservation and sustainable development.
In conclusion, the application of ammonium hydroxide in developing eco-friendly detergents represents a significant technological trend in the cleaning products industry. It embodies the intersection of chemical innovation, environmental consciousness, and consumer demand for sustainable solutions. As research progresses, ammonium hydroxide-based detergents are poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of green cleaning technologies.
The primary objective of incorporating ammonium hydroxide in detergent formulations is to develop cleaning products that are both effective and environmentally sustainable. This aligns with the growing global demand for green technologies and the increasing regulatory pressure on manufacturers to reduce the environmental impact of their products. The use of ammonium hydroxide in detergents aims to address several key challenges in the industry, including the reduction of phosphates, the minimization of toxic residues, and the improvement of biodegradability.
From a technical perspective, ammonium hydroxide offers unique properties that make it suitable for detergent applications. Its alkaline nature provides excellent cleaning power, particularly for removing grease and oil-based stains. Additionally, it can act as a buffering agent, helping to maintain optimal pH levels during the cleaning process. These characteristics have led to its exploration in various types of detergents, including laundry detergents, dishwashing liquids, and all-purpose cleaners.
The development trajectory of ammonium hydroxide in detergents has been influenced by advancements in chemical engineering and formulation technologies. Researchers have focused on optimizing the concentration and stability of ammonium hydroxide in detergent formulations, as well as exploring synergistic effects with other eco-friendly ingredients. This has led to the creation of novel detergent compositions that leverage the benefits of ammonium hydroxide while mitigating potential drawbacks such as odor and volatility.
As the detergent industry continues to evolve, the role of ammonium hydroxide is expected to expand. Current research is aimed at enhancing its efficacy, improving its stability in various formulations, and exploring new applications. The ultimate goal is to develop a new generation of detergents that not only clean effectively but also contribute to environmental conservation and sustainable development.
In conclusion, the application of ammonium hydroxide in developing eco-friendly detergents represents a significant technological trend in the cleaning products industry. It embodies the intersection of chemical innovation, environmental consciousness, and consumer demand for sustainable solutions. As research progresses, ammonium hydroxide-based detergents are poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of green cleaning technologies.
Market Analysis for Green Cleaning Products
The global market for green cleaning products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and health concerns. This trend is particularly evident in the eco-friendly detergent sector, where ammonium hydroxide is gaining traction as a key ingredient. The market size for green cleaning products was valued at approximately $3.9 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach $11.6 billion by 2029, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.8% during the forecast period.
Consumer demand for environmentally friendly cleaning solutions has been steadily rising, with a notable shift towards products that are biodegradable, non-toxic, and derived from renewable resources. This shift is largely attributed to growing concerns over the environmental impact of traditional cleaning products and their potential health risks. Ammonium hydroxide, when used in eco-friendly detergents, addresses these concerns by offering effective cleaning power while minimizing environmental harm.
The market for green cleaning products featuring ammonium hydroxide is segmented by product type, including laundry detergents, dishwashing detergents, and all-purpose cleaners. Among these, laundry detergents hold the largest market share, accounting for over 40% of the total green cleaning products market. This dominance is expected to continue due to the high frequency of use and the increasing adoption of eco-friendly laundry solutions in both residential and commercial sectors.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for green cleaning products, with the United States and Germany being the largest individual markets. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and growing environmental consciousness among consumers in countries like China and India.
Key market players in the eco-friendly detergent sector include Seventh Generation, Method Products, Ecover, and Procter & Gamble's eco-friendly product lines. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficacy of their products while maintaining their environmental credentials. The use of ammonium hydroxide in their formulations is seen as a strategic move to enhance cleaning performance without compromising on sustainability.
Consumer preferences within the green cleaning products market are evolving, with a growing demand for multi-functional products that offer convenience alongside environmental benefits. Products that incorporate ammonium hydroxide are well-positioned to meet this demand, as they can provide effective cleaning across various applications while maintaining an eco-friendly profile.
Consumer demand for environmentally friendly cleaning solutions has been steadily rising, with a notable shift towards products that are biodegradable, non-toxic, and derived from renewable resources. This shift is largely attributed to growing concerns over the environmental impact of traditional cleaning products and their potential health risks. Ammonium hydroxide, when used in eco-friendly detergents, addresses these concerns by offering effective cleaning power while minimizing environmental harm.
The market for green cleaning products featuring ammonium hydroxide is segmented by product type, including laundry detergents, dishwashing detergents, and all-purpose cleaners. Among these, laundry detergents hold the largest market share, accounting for over 40% of the total green cleaning products market. This dominance is expected to continue due to the high frequency of use and the increasing adoption of eco-friendly laundry solutions in both residential and commercial sectors.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for green cleaning products, with the United States and Germany being the largest individual markets. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and growing environmental consciousness among consumers in countries like China and India.
Key market players in the eco-friendly detergent sector include Seventh Generation, Method Products, Ecover, and Procter & Gamble's eco-friendly product lines. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficacy of their products while maintaining their environmental credentials. The use of ammonium hydroxide in their formulations is seen as a strategic move to enhance cleaning performance without compromising on sustainability.
Consumer preferences within the green cleaning products market are evolving, with a growing demand for multi-functional products that offer convenience alongside environmental benefits. Products that incorporate ammonium hydroxide are well-positioned to meet this demand, as they can provide effective cleaning across various applications while maintaining an eco-friendly profile.
Current Challenges in Eco-Friendly Detergent Formulation
The development of eco-friendly detergents faces several significant challenges, primarily stemming from the need to balance environmental sustainability with cleaning efficacy and consumer expectations. One of the key hurdles is the formulation of products that maintain high cleaning performance while using biodegradable and non-toxic ingredients. Traditional detergents often rely on petrochemical-based surfactants, which are effective but environmentally problematic. Replacing these with plant-based alternatives can lead to reduced cleaning power or stability issues in the final product.
Another major challenge lies in creating formulations that work effectively in cold water. Many eco-friendly detergents struggle to perform well at lower temperatures, which is crucial for reducing energy consumption during washing. This limitation often forces consumers to choose between environmental consciousness and cleaning effectiveness, potentially hindering widespread adoption of green detergents.
The use of enzymes in eco-friendly detergents presents both opportunities and challenges. While enzymes can enhance cleaning power without harsh chemicals, they are sensitive to temperature and pH, making formulation and storage more complex. Additionally, some consumers have concerns about potential allergic reactions to enzyme-containing products, necessitating careful consideration in product development and marketing.
Packaging remains a significant hurdle in the eco-friendly detergent sector. While many companies are moving towards recyclable or biodegradable packaging, finding materials that are both environmentally friendly and capable of safely containing liquid detergents without leakage or degradation is an ongoing challenge. The industry is also grappling with the need to reduce water content in detergents to minimize packaging and transportation costs, which in turn affects formulation strategies.
Cost-effectiveness is another critical challenge. Eco-friendly ingredients and sustainable production processes often come at a higher price point, making it difficult for manufacturers to compete with conventional detergents on cost. This price disparity can limit market penetration, particularly in price-sensitive segments.
Lastly, there's the challenge of consumer perception and education. Many consumers are skeptical about the cleaning power of eco-friendly detergents or are unaware of their environmental benefits. Overcoming these perceptions and educating consumers about the importance of sustainable cleaning products requires significant marketing efforts and clear, transparent communication about product ingredients and their environmental impact.
Another major challenge lies in creating formulations that work effectively in cold water. Many eco-friendly detergents struggle to perform well at lower temperatures, which is crucial for reducing energy consumption during washing. This limitation often forces consumers to choose between environmental consciousness and cleaning effectiveness, potentially hindering widespread adoption of green detergents.
The use of enzymes in eco-friendly detergents presents both opportunities and challenges. While enzymes can enhance cleaning power without harsh chemicals, they are sensitive to temperature and pH, making formulation and storage more complex. Additionally, some consumers have concerns about potential allergic reactions to enzyme-containing products, necessitating careful consideration in product development and marketing.
Packaging remains a significant hurdle in the eco-friendly detergent sector. While many companies are moving towards recyclable or biodegradable packaging, finding materials that are both environmentally friendly and capable of safely containing liquid detergents without leakage or degradation is an ongoing challenge. The industry is also grappling with the need to reduce water content in detergents to minimize packaging and transportation costs, which in turn affects formulation strategies.
Cost-effectiveness is another critical challenge. Eco-friendly ingredients and sustainable production processes often come at a higher price point, making it difficult for manufacturers to compete with conventional detergents on cost. This price disparity can limit market penetration, particularly in price-sensitive segments.
Lastly, there's the challenge of consumer perception and education. Many consumers are skeptical about the cleaning power of eco-friendly detergents or are unaware of their environmental benefits. Overcoming these perceptions and educating consumers about the importance of sustainable cleaning products requires significant marketing efforts and clear, transparent communication about product ingredients and their environmental impact.
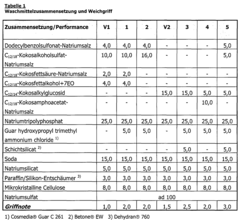
Existing NH4OH Detergent Formulations
01 Eco-friendly production methods
Developing environmentally friendly production methods for ammonium hydroxide, focusing on reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste. These methods may involve using renewable energy sources, optimizing reaction conditions, and implementing closed-loop systems to recycle byproducts.- Eco-friendly production methods: Some patents describe environmentally friendly methods for producing ammonium hydroxide, including processes that reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. These methods aim to make the production of ammonium hydroxide more sustainable and less harmful to the environment.
- Use in green chemical processes: Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in various eco-friendly chemical processes as a reagent or catalyst. These applications demonstrate its potential in supporting more sustainable industrial practices and reducing environmental impact in chemical manufacturing.
- Waste treatment and pollution control: Several patents focus on using ammonium hydroxide in waste treatment and pollution control applications. These include processes for treating industrial effluents, reducing air pollution, and managing hazardous waste, showcasing its potential in environmental remediation.
- Biodegradable and non-toxic formulations: Some inventions describe formulations containing ammonium hydroxide that are biodegradable and non-toxic. These formulations are designed to minimize environmental impact and reduce potential harm to ecosystems when released into the environment.
- Recycling and recovery processes: Patents in this category detail methods for recycling and recovering ammonium hydroxide from various industrial processes. These techniques aim to reduce waste and promote circular economy principles, enhancing the overall eco-friendliness of ammonium hydroxide use in industry.
02 Sustainable applications in agriculture
Utilizing ammonium hydroxide in sustainable agricultural practices, such as eco-friendly fertilizers and soil amendments. This approach aims to improve crop yields while minimizing environmental impact through controlled release formulations and precision application techniques.Expand Specific Solutions03 Green chemistry alternatives
Exploring green chemistry alternatives to traditional ammonium hydroxide production and use. This includes developing bio-based precursors, using catalysts to improve reaction efficiency, and investigating novel synthesis routes that reduce environmental footprint.Expand Specific Solutions04 Waste treatment and recycling
Implementing waste treatment and recycling processes for ammonium hydroxide-containing effluents. These methods focus on recovering and reusing ammonium hydroxide, reducing water pollution, and converting waste streams into valuable byproducts.Expand Specific Solutions05 Emission reduction technologies
Developing technologies to reduce ammonia emissions associated with ammonium hydroxide use. This includes designing improved storage and handling systems, implementing vapor recovery techniques, and creating low-emission application methods for various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Green Detergent Industry
The application of ammonium hydroxide in eco-friendly detergents is gaining traction in a maturing industry, with the global green cleaning products market expected to reach $11.6 billion by 2029. Major players like Henkel, Unilever, and Kao Corp. are investing heavily in R&D to develop sustainable formulations. The technology is approaching maturity, with companies like Aekyung Industrial and Surface Technologies GmbH focusing on optimizing production processes and improving product efficacy. Smaller firms such as SACHEM, Inc. and Amicogen (China) Biopharm Co. Ltd. are also contributing to innovation in this space, particularly in specialized applications and bio-based alternatives.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed an innovative approach to eco-friendly detergents using ammonium hydroxide. Their technology involves a unique formulation that combines ammonium hydroxide with biodegradable surfactants and enzymes. This combination enhances cleaning power while reducing environmental impact. The ammonium hydroxide acts as a pH regulator and helps in breaking down tough stains[1]. Henkel's process also includes a controlled release mechanism for the ammonium hydroxide, ensuring optimal cleaning performance throughout the wash cycle while minimizing potential irritation[3]. Additionally, they have implemented a closed-loop manufacturing system that recycles and reuses ammonium hydroxide, significantly reducing waste and emissions[5].
Strengths: Enhanced cleaning power, reduced environmental impact, and efficient use of resources. Weaknesses: Potential for ammonia odor if not properly formulated, and higher production costs compared to traditional detergents.
Unilever NV
Technical Solution: Unilever has pioneered a novel approach to incorporating ammonium hydroxide in eco-friendly detergents. Their technology utilizes a micro-encapsulation technique that allows for the controlled release of ammonium hydroxide during the washing process[2]. This method ensures optimal cleaning efficiency while minimizing environmental impact. The encapsulated ammonium hydroxide is combined with plant-based surfactants and enzymes, creating a powerful yet eco-friendly cleaning solution. Unilever's process also includes a proprietary stabilization method that extends the shelf life of the product without compromising its eco-friendly properties[4]. Furthermore, they have developed a water-efficient manufacturing process that reduces the overall water footprint of the detergent production[6].
Strengths: Controlled release technology, extended shelf life, and reduced water consumption in production. Weaknesses: Higher production costs and potential challenges in scaling up the micro-encapsulation process.
Innovations in NH4OH Application for Cleaning
Quaternary ammonium composition
PatentInactiveUS7348303B2
Innovation
- A quaternary ammonium composition with less than 20% water by weight, comprising a cationic compound, a non-ionic solvent, and minimal by-products, is developed, allowing for concentrated detergent formulations with improved handling and reduced transportation, storage, and packaging costs.
Detergent tablets
PatentInactiveEP1186649A1
Innovation
- Detergent tablets comprising anionic, nonionic, and/or amphoteric surfactants, cationic polymers, phosphates, disintegrants, and optionally phyllosilicates, which provide a stable, eco-friendly, and effective softening effect without cationic surfactants, leveraging the chemical stability and finishing properties of cationic polymers.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of ammonium hydroxide in eco-friendly detergents is a critical aspect of their development and application. Ammonium hydroxide, while effective as a cleaning agent, poses potential risks to aquatic ecosystems if not properly managed.
When released into water bodies, ammonium hydroxide can lead to increased ammonia levels, which can be toxic to fish and other aquatic organisms. Even at low concentrations, ammonia can cause stress, reduced growth rates, and impaired reproduction in aquatic life. However, the impact is generally localized and short-term due to the rapid dilution and natural breakdown of ammonia in water.
The use of ammonium hydroxide in detergents may contribute to eutrophication, a process where excess nutrients in water bodies lead to algal blooms and oxygen depletion. This can have cascading effects on aquatic ecosystems, potentially disrupting food chains and biodiversity. Nevertheless, the extent of this impact is typically less severe compared to phosphate-based detergents.
On the positive side, ammonium hydroxide-based detergents have a lower environmental footprint compared to many traditional cleaning agents. They are biodegradable and do not persist in the environment for extended periods. This characteristic aligns well with the principles of eco-friendly product development.
The production process of ammonium hydroxide for detergents also needs consideration. While it can be synthesized using renewable resources, industrial production may still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting cleaner production methods to mitigate these impacts.
Soil contamination is another potential concern, particularly in cases of improper disposal or accidental spills. However, the impact on soil is generally less severe than that of more persistent chemical compounds, as ammonium hydroxide tends to volatilize or be neutralized in soil environments.
Air quality impacts are minimal when ammonium hydroxide is used in detergents, as the compound is not highly volatile at room temperature. However, proper ventilation should be ensured during use to prevent localized accumulation of ammonia vapors.
In terms of human health, while ammonium hydroxide in detergents poses lower risks compared to harsher chemicals, proper handling and use instructions are crucial to prevent skin irritation or respiratory issues from prolonged exposure.
Overall, the environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide in eco-friendly detergents is relatively low when compared to traditional cleaning agents. Its biodegradability and lower persistence in the environment make it a promising component for sustainable cleaning solutions. However, ongoing research and monitoring are essential to fully understand and mitigate any long-term ecological effects, ensuring that the development of these detergents truly aligns with environmental sustainability goals.
When released into water bodies, ammonium hydroxide can lead to increased ammonia levels, which can be toxic to fish and other aquatic organisms. Even at low concentrations, ammonia can cause stress, reduced growth rates, and impaired reproduction in aquatic life. However, the impact is generally localized and short-term due to the rapid dilution and natural breakdown of ammonia in water.
The use of ammonium hydroxide in detergents may contribute to eutrophication, a process where excess nutrients in water bodies lead to algal blooms and oxygen depletion. This can have cascading effects on aquatic ecosystems, potentially disrupting food chains and biodiversity. Nevertheless, the extent of this impact is typically less severe compared to phosphate-based detergents.
On the positive side, ammonium hydroxide-based detergents have a lower environmental footprint compared to many traditional cleaning agents. They are biodegradable and do not persist in the environment for extended periods. This characteristic aligns well with the principles of eco-friendly product development.
The production process of ammonium hydroxide for detergents also needs consideration. While it can be synthesized using renewable resources, industrial production may still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting cleaner production methods to mitigate these impacts.
Soil contamination is another potential concern, particularly in cases of improper disposal or accidental spills. However, the impact on soil is generally less severe than that of more persistent chemical compounds, as ammonium hydroxide tends to volatilize or be neutralized in soil environments.
Air quality impacts are minimal when ammonium hydroxide is used in detergents, as the compound is not highly volatile at room temperature. However, proper ventilation should be ensured during use to prevent localized accumulation of ammonia vapors.
In terms of human health, while ammonium hydroxide in detergents poses lower risks compared to harsher chemicals, proper handling and use instructions are crucial to prevent skin irritation or respiratory issues from prolonged exposure.
Overall, the environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide in eco-friendly detergents is relatively low when compared to traditional cleaning agents. Its biodegradability and lower persistence in the environment make it a promising component for sustainable cleaning solutions. However, ongoing research and monitoring are essential to fully understand and mitigate any long-term ecological effects, ensuring that the development of these detergents truly aligns with environmental sustainability goals.
Regulatory Framework for Green Cleaning Products
The regulatory framework for green cleaning products is a critical aspect of the eco-friendly detergent industry, particularly in the context of ammonium hydroxide applications. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide have established stringent guidelines to ensure the safety and environmental sustainability of cleaning products.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a pivotal role in regulating green cleaning products through its Safer Choice program. This voluntary initiative encourages manufacturers to develop and market products that meet strict human health and environmental criteria. Products containing ammonium hydroxide must adhere to specific concentration limits and safety standards to qualify for the Safer Choice label.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which governs the use of chemical substances in various products, including detergents. Under REACH, manufacturers must register ammonium hydroxide and provide detailed safety information if used in significant quantities. Additionally, the EU Ecolabel scheme sets criteria for environmentally friendly cleaning products, promoting the use of less harmful alternatives to traditional chemicals.
In Canada, the Environmental Choice Program, operated by Environment Canada, certifies environmentally preferable products. The program includes specific criteria for cleaning products, addressing issues such as toxicity, biodegradability, and packaging. Manufacturers using ammonium hydroxide in their formulations must demonstrate compliance with these standards to obtain certification.
Many countries have adopted the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), which standardizes hazard communication for chemical products. This system requires clear labeling of ammonium hydroxide-containing products, including hazard pictograms, signal words, and safety data sheets.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards relevant to green cleaning products, such as ISO 14024 for environmental labeling. These standards provide a framework for assessing the environmental impact of products throughout their lifecycle, influencing the formulation and marketing of eco-friendly detergents.
As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, many countries have introduced regulations mandating the disclosure of product ingredients. This transparency allows consumers to make informed choices and encourages manufacturers to develop safer, more sustainable formulations. The use of ammonium hydroxide in eco-friendly detergents must be clearly communicated in accordance with these disclosure requirements.
Regulatory bodies also focus on the biodegradability of cleaning products. For instance, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has established guidelines for testing the biodegradability of surfactants and other detergent components. Products containing ammonium hydroxide must demonstrate compliance with these biodegradability standards to be marketed as environmentally friendly.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a pivotal role in regulating green cleaning products through its Safer Choice program. This voluntary initiative encourages manufacturers to develop and market products that meet strict human health and environmental criteria. Products containing ammonium hydroxide must adhere to specific concentration limits and safety standards to qualify for the Safer Choice label.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which governs the use of chemical substances in various products, including detergents. Under REACH, manufacturers must register ammonium hydroxide and provide detailed safety information if used in significant quantities. Additionally, the EU Ecolabel scheme sets criteria for environmentally friendly cleaning products, promoting the use of less harmful alternatives to traditional chemicals.
In Canada, the Environmental Choice Program, operated by Environment Canada, certifies environmentally preferable products. The program includes specific criteria for cleaning products, addressing issues such as toxicity, biodegradability, and packaging. Manufacturers using ammonium hydroxide in their formulations must demonstrate compliance with these standards to obtain certification.
Many countries have adopted the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), which standardizes hazard communication for chemical products. This system requires clear labeling of ammonium hydroxide-containing products, including hazard pictograms, signal words, and safety data sheets.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards relevant to green cleaning products, such as ISO 14024 for environmental labeling. These standards provide a framework for assessing the environmental impact of products throughout their lifecycle, influencing the formulation and marketing of eco-friendly detergents.
As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, many countries have introduced regulations mandating the disclosure of product ingredients. This transparency allows consumers to make informed choices and encourages manufacturers to develop safer, more sustainable formulations. The use of ammonium hydroxide in eco-friendly detergents must be clearly communicated in accordance with these disclosure requirements.
Regulatory bodies also focus on the biodegradability of cleaning products. For instance, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has established guidelines for testing the biodegradability of surfactants and other detergent components. Products containing ammonium hydroxide must demonstrate compliance with these biodegradability standards to be marketed as environmentally friendly.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!