Occlusive Dressing vs Semi-Permeable Films: Healing Rate Comparison
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Wound Healing Tech Evolution
The evolution of wound healing technology has seen significant advancements over the past few decades, with a particular focus on the development of advanced dressings. The journey from traditional gauze dressings to modern occlusive and semi-permeable films represents a paradigm shift in wound care management.
In the 1960s, the concept of moist wound healing was introduced, challenging the conventional wisdom of keeping wounds dry. This breakthrough led to the development of occlusive dressings, which create a moist environment conducive to healing. The 1970s saw the introduction of hydrocolloid dressings, marking a significant milestone in occlusive wound care technology.
The 1980s brought about the advent of semi-permeable films, offering a balance between moisture retention and gas exchange. These films allowed oxygen to reach the wound while maintaining a moist environment and protecting against external contaminants. This period also saw the development of advanced foam dressings, combining absorption capabilities with moisture retention.
The 1990s and early 2000s witnessed a surge in research comparing the efficacy of occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films. Studies began to emerge, evaluating healing rates, patient comfort, and cost-effectiveness. This era marked the beginning of evidence-based practice in wound care, with clinicians increasingly relying on scientific data to guide their treatment decisions.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards bioactive dressings and smart wound care technologies. These innovations incorporate growth factors, antimicrobial agents, and even sensors to monitor wound healing progress. The comparison between occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films has evolved to include these advanced materials, considering not only healing rates but also factors such as infection prevention and wound assessment capabilities.
The current landscape of wound healing technology reflects a nuanced understanding of wound types and patient needs. While occlusive dressings continue to play a crucial role in managing heavily exuding wounds, semi-permeable films have found their niche in protecting wounds that require less moisture management. The ongoing research aims to optimize the balance between occlusion and permeability, tailoring dressing choices to specific wound characteristics and healing stages.
In the 1960s, the concept of moist wound healing was introduced, challenging the conventional wisdom of keeping wounds dry. This breakthrough led to the development of occlusive dressings, which create a moist environment conducive to healing. The 1970s saw the introduction of hydrocolloid dressings, marking a significant milestone in occlusive wound care technology.
The 1980s brought about the advent of semi-permeable films, offering a balance between moisture retention and gas exchange. These films allowed oxygen to reach the wound while maintaining a moist environment and protecting against external contaminants. This period also saw the development of advanced foam dressings, combining absorption capabilities with moisture retention.
The 1990s and early 2000s witnessed a surge in research comparing the efficacy of occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films. Studies began to emerge, evaluating healing rates, patient comfort, and cost-effectiveness. This era marked the beginning of evidence-based practice in wound care, with clinicians increasingly relying on scientific data to guide their treatment decisions.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards bioactive dressings and smart wound care technologies. These innovations incorporate growth factors, antimicrobial agents, and even sensors to monitor wound healing progress. The comparison between occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films has evolved to include these advanced materials, considering not only healing rates but also factors such as infection prevention and wound assessment capabilities.
The current landscape of wound healing technology reflects a nuanced understanding of wound types and patient needs. While occlusive dressings continue to play a crucial role in managing heavily exuding wounds, semi-permeable films have found their niche in protecting wounds that require less moisture management. The ongoing research aims to optimize the balance between occlusion and permeability, tailoring dressing choices to specific wound characteristics and healing stages.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for advanced wound care solutions, particularly in the comparison between occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films, has been steadily increasing. This growth is driven by several factors, including the rising prevalence of chronic wounds, an aging population, and the increasing incidence of diabetes and obesity worldwide.
The global advanced wound care market, which encompasses both occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films, has been experiencing significant growth. This market segment is expected to continue expanding due to the growing awareness of the benefits of these advanced wound healing technologies among healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Occlusive dressings have gained popularity due to their ability to create a moist wound environment, which is crucial for optimal healing. These dressings are particularly effective in managing exudate and protecting the wound from external contaminants. The demand for occlusive dressings is especially high in the treatment of chronic wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers and pressure sores.
Semi-permeable films, on the other hand, have carved out a significant market share due to their unique properties. These films allow for gas exchange while maintaining a barrier against bacteria and external moisture. This characteristic makes them particularly suitable for surgical wounds and superficial burns. The demand for semi-permeable films has been growing in both hospital and outpatient settings.
The comparison of healing rates between occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films has become a focal point for healthcare providers and payers. As healthcare systems worldwide strive for cost-effectiveness and improved patient outcomes, there is an increasing demand for evidence-based solutions that can demonstrate superior healing rates and reduced treatment durations.
The market demand is further influenced by the shift towards home healthcare and the need for easy-to-use wound care products. Both occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films offer advantages in this regard, as they often require less frequent changes and can be managed by patients or caregivers with minimal training.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for advanced wound care products, including occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show rapid growth in demand due to improving healthcare infrastructure and increasing awareness of advanced wound care techniques.
In conclusion, the market demand for both occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films remains strong, with a growing emphasis on comparative effectiveness. As research continues to elucidate the specific advantages of each technology in different wound types and patient populations, the market is likely to see further segmentation and specialization in product offerings to meet diverse clinical needs.
The global advanced wound care market, which encompasses both occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films, has been experiencing significant growth. This market segment is expected to continue expanding due to the growing awareness of the benefits of these advanced wound healing technologies among healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Occlusive dressings have gained popularity due to their ability to create a moist wound environment, which is crucial for optimal healing. These dressings are particularly effective in managing exudate and protecting the wound from external contaminants. The demand for occlusive dressings is especially high in the treatment of chronic wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers and pressure sores.
Semi-permeable films, on the other hand, have carved out a significant market share due to their unique properties. These films allow for gas exchange while maintaining a barrier against bacteria and external moisture. This characteristic makes them particularly suitable for surgical wounds and superficial burns. The demand for semi-permeable films has been growing in both hospital and outpatient settings.
The comparison of healing rates between occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films has become a focal point for healthcare providers and payers. As healthcare systems worldwide strive for cost-effectiveness and improved patient outcomes, there is an increasing demand for evidence-based solutions that can demonstrate superior healing rates and reduced treatment durations.
The market demand is further influenced by the shift towards home healthcare and the need for easy-to-use wound care products. Both occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films offer advantages in this regard, as they often require less frequent changes and can be managed by patients or caregivers with minimal training.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for advanced wound care products, including occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show rapid growth in demand due to improving healthcare infrastructure and increasing awareness of advanced wound care techniques.
In conclusion, the market demand for both occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films remains strong, with a growing emphasis on comparative effectiveness. As research continues to elucidate the specific advantages of each technology in different wound types and patient populations, the market is likely to see further segmentation and specialization in product offerings to meet diverse clinical needs.
Current Dressing Challenges
The current landscape of wound dressing presents several challenges that hinder optimal healing rates and patient comfort. One of the primary issues is the balance between moisture retention and breathability. Occlusive dressings, while effective in maintaining a moist wound environment, can sometimes lead to maceration of surrounding healthy tissue due to excessive moisture accumulation. Conversely, semi-permeable films may not provide sufficient moisture retention for certain wound types, potentially leading to desiccation and delayed healing.
Another significant challenge is the management of wound exudate. Excessive exudate can lead to skin breakdown and increased risk of infection, while insufficient exudate management can impede the healing process. Both occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films have limitations in this regard, with occlusive dressings sometimes struggling to handle high levels of exudate and semi-permeable films occasionally failing to absorb enough moisture.
The prevention of bacterial contamination remains a critical concern in wound management. While occlusive dressings provide a barrier against external contaminants, they can also create an environment conducive to bacterial growth if not managed properly. Semi-permeable films offer some level of protection but may not be as effective in highly contaminated wounds.
Adhesion and removal of dressings pose additional challenges. Strong adhesives are necessary to keep dressings in place, especially in areas of high movement or moisture. However, these can cause trauma to the wound bed or surrounding skin upon removal. Semi-permeable films often offer gentler removal but may not adhere as effectively in challenging locations.
The diversity of wound types and locations further complicates dressing selection. What works well for a surgical incision may not be suitable for a pressure ulcer or burn wound. This variability necessitates a wide range of dressing options, making it challenging for healthcare providers to select the most appropriate dressing for each unique situation.
Cost-effectiveness and accessibility of advanced wound dressings remain ongoing issues, particularly in resource-limited settings. While both occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films offer advantages, their higher cost compared to traditional gauze dressings can limit widespread adoption.
Lastly, the lack of standardized protocols for dressing changes and wound assessment complicates the comparison of healing rates between different dressing types. This inconsistency in practice makes it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the superiority of one dressing type over another in various wound scenarios.
Another significant challenge is the management of wound exudate. Excessive exudate can lead to skin breakdown and increased risk of infection, while insufficient exudate management can impede the healing process. Both occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films have limitations in this regard, with occlusive dressings sometimes struggling to handle high levels of exudate and semi-permeable films occasionally failing to absorb enough moisture.
The prevention of bacterial contamination remains a critical concern in wound management. While occlusive dressings provide a barrier against external contaminants, they can also create an environment conducive to bacterial growth if not managed properly. Semi-permeable films offer some level of protection but may not be as effective in highly contaminated wounds.
Adhesion and removal of dressings pose additional challenges. Strong adhesives are necessary to keep dressings in place, especially in areas of high movement or moisture. However, these can cause trauma to the wound bed or surrounding skin upon removal. Semi-permeable films often offer gentler removal but may not adhere as effectively in challenging locations.
The diversity of wound types and locations further complicates dressing selection. What works well for a surgical incision may not be suitable for a pressure ulcer or burn wound. This variability necessitates a wide range of dressing options, making it challenging for healthcare providers to select the most appropriate dressing for each unique situation.
Cost-effectiveness and accessibility of advanced wound dressings remain ongoing issues, particularly in resource-limited settings. While both occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films offer advantages, their higher cost compared to traditional gauze dressings can limit widespread adoption.
Lastly, the lack of standardized protocols for dressing changes and wound assessment complicates the comparison of healing rates between different dressing types. This inconsistency in practice makes it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the superiority of one dressing type over another in various wound scenarios.
Occlusive vs Semi-Permeable
01 Occlusive dressings for enhanced wound healing
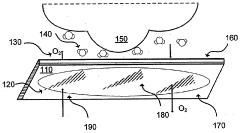
Occlusive dressings create a moist environment that promotes faster wound healing by preventing moisture loss and protecting the wound from external contaminants. These dressings can be made from various materials and may incorporate additional features such as adhesive borders for secure attachment.- Occlusive dressings for wound healing: Occlusive dressings create a moist environment that promotes faster wound healing. These dressings prevent water loss from the wound surface, maintain optimal moisture levels, and protect the wound from external contaminants. They can also help reduce pain and scarring while promoting the formation of new tissue.
- Semi-permeable films for wound management: Semi-permeable films allow for gas exchange while maintaining a moist wound environment. These films are breathable, preventing maceration of the surrounding skin while still protecting the wound from external contaminants. They can be used for various wound types and are often transparent, allowing for easy wound monitoring without dressing removal.
- Combination of occlusive and semi-permeable materials: Some dressings combine occlusive and semi-permeable materials to optimize wound healing. These hybrid dressings provide the benefits of both occlusion and breathability, allowing for customized wound management based on the specific needs of the wound. They can help balance moisture levels and promote faster healing rates.
- Incorporation of active ingredients in dressings: Wound dressings can be enhanced by incorporating active ingredients such as antimicrobials, growth factors, or pain-relieving agents. These advanced dressings not only provide a protective barrier but also actively contribute to the wound healing process, potentially increasing healing rates and reducing the risk of infection.
- Smart dressings with monitoring capabilities: Innovative smart dressings incorporate sensors or indicators to monitor wound healing progress. These advanced dressings can provide real-time information on wound status, such as pH levels, temperature, or moisture content, allowing for more informed decision-making in wound management and potentially improving healing rates.
02 Semi-permeable films for controlled moisture management
Semi-permeable films allow for controlled moisture vapor transmission while still providing a barrier against external contaminants. These films can be used in wound dressings to maintain an optimal moisture balance, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of maceration.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination of occlusive and semi-permeable materials
Dressings that combine occlusive and semi-permeable materials can provide the benefits of both types, offering enhanced moisture management and wound protection. These hybrid dressings can be designed with multiple layers or zones to optimize healing conditions for different wound types.Expand Specific Solutions04 Incorporation of active ingredients for accelerated healing
Wound dressings can be enhanced by incorporating active ingredients such as antimicrobials, growth factors, or pain-relieving agents. These additives can work synergistically with the occlusive or semi-permeable properties of the dressing to further accelerate the healing process.Expand Specific Solutions05 Smart dressings with healing rate monitoring capabilities
Advanced wound dressings incorporating sensors or indicators can monitor the healing rate and provide real-time feedback on wound status. These smart dressings can help healthcare professionals optimize treatment plans and adjust dressing changes based on objective data.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Wound Care Players
The competition landscape for occlusive dressing and semi-permeable films technology is characterized by a mature market with established players and ongoing innovation. The global wound dressing market, valued at over $7 billion, is expected to grow steadily due to increasing chronic wounds and surgical procedures. Key players like 3M, Smith & Nephew, and Coloplast dominate with advanced product portfolios. These companies, along with emerging firms like ConvaTec and BSN medical, are investing in R&D to improve healing rates and patient comfort. The technology's maturity is evident in widespread clinical adoption, but there's continuous development in materials and designs to enhance performance and cost-effectiveness.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed advanced occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films for wound healing. Their Tegaderm™ line includes both occlusive and semi-permeable options. The occlusive dressings create a moist environment that promotes faster healing and reduces pain[1]. Their semi-permeable films allow oxygen exchange while maintaining a barrier against external contaminants[2]. 3M's dressings incorporate adhesive technology that allows for secure attachment while being gentle on the skin, reducing the risk of further damage during dressing changes[3]. The company has also introduced antimicrobial versions of both types of dressings to prevent infection in high-risk wounds[4].
Strengths: Wide range of products for different wound types, strong adhesive technology, antimicrobial options. Weaknesses: May be more expensive than some competitors, potential for skin irritation in sensitive individuals.
Convatec, Inc.
Technical Solution: Convatec specializes in advanced wound care solutions, offering both occlusive and semi-permeable dressings. Their DuoDERM® line of occlusive dressings uses hydrocolloid technology to create a moist healing environment, which has been shown to accelerate healing rates by up to 50% compared to traditional dry dressings[5]. For semi-permeable films, Convatec's AQUACEL® technology allows for moisture management while providing a bacterial barrier[6]. The company has also developed dressings with silver ions for antimicrobial protection in chronic wounds[7]. Convatec's dressings are designed to minimize dressing changes, reducing disruption to the healing process and lowering overall treatment costs.
Strengths: Hydrocolloid technology for moist wound healing, moisture management in semi-permeable films, cost-effective due to reduced dressing changes. Weaknesses: May not be suitable for all wound types, potential for maceration in highly exuding wounds.
Core Dressing Innovations
Herpes treatment and dressing
PatentWO2009062144A2
Innovation
- A semi-permeable film dressing made of materials like polyvinyl ethyl ether, polymethyl vinyl ether, and polyacrylic ester, which is adhesive, water vapor permeable, and impermeable to liquid, is applied to herpes lesions to promote healing and prevent transmission by creating a barrier against bacteria and viruses.
Wound dressing for promoting moist wound healing
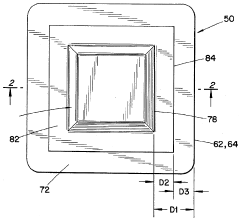
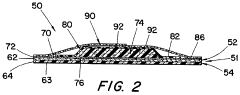
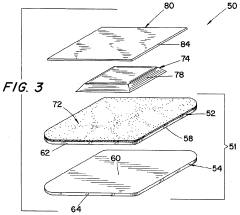
PatentInactiveUS5512041A
Innovation
- A wound dressing with a multi-layer backing sheet comprising a stretchable, vapor-permeable non-woven fabric and a semi-occlusive polyurethane film, where the film is externally positioned to provide a low-friction surface and ensure uniform MVTR across different sizes, reducing handling issues and shear forces.
Clinical Trial Regulations
Clinical trials comparing healing rates between occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films are subject to stringent regulatory oversight. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) governs these trials under the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, specifically parts 50, 56, and 312. These regulations ensure the protection of human subjects, ethical conduct of research, and scientific integrity of the data collected.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides similar guidance for clinical trials conducted within the European Union, as outlined in the Clinical Trials Regulation (EU) No 536/2014. This regulation harmonizes the assessment and supervision processes for clinical trials throughout the EU, streamlining the application procedure and enhancing transparency.
Investigators must obtain approval from an Institutional Review Board (IRB) or Ethics Committee before initiating any clinical trial. This process involves submitting a detailed protocol outlining the study design, participant selection criteria, and safety monitoring procedures. For trials comparing wound healing technologies, special attention must be given to the risk-benefit analysis and the potential for adverse events related to infection or delayed healing.
Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, as established by the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH), provide an international ethical and scientific quality standard for designing, conducting, and reporting clinical trials. Adherence to GCP is crucial for ensuring that the data and reported results are credible and accurate.
Informed consent is a cornerstone of clinical trial regulations. Participants must be fully informed about the nature of the study, potential risks and benefits, and their rights as research subjects. In wound healing studies, this includes clear explanations of the different dressing types and any potential discomfort or complications associated with their use.
Data management and privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the US and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, play a significant role in clinical trials. These regulations dictate how patient information is collected, stored, and protected throughout the study and beyond.
Reporting requirements for adverse events and serious adverse events are strictly defined by regulatory bodies. Investigators must promptly report any unexpected or severe reactions to the dressings or films, ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Post-trial obligations include the dissemination of results, regardless of the outcome. ClinicalTrials.gov and the EU Clinical Trials Register are platforms where trial information and results must be published, promoting transparency and preventing publication bias.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides similar guidance for clinical trials conducted within the European Union, as outlined in the Clinical Trials Regulation (EU) No 536/2014. This regulation harmonizes the assessment and supervision processes for clinical trials throughout the EU, streamlining the application procedure and enhancing transparency.
Investigators must obtain approval from an Institutional Review Board (IRB) or Ethics Committee before initiating any clinical trial. This process involves submitting a detailed protocol outlining the study design, participant selection criteria, and safety monitoring procedures. For trials comparing wound healing technologies, special attention must be given to the risk-benefit analysis and the potential for adverse events related to infection or delayed healing.
Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, as established by the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH), provide an international ethical and scientific quality standard for designing, conducting, and reporting clinical trials. Adherence to GCP is crucial for ensuring that the data and reported results are credible and accurate.
Informed consent is a cornerstone of clinical trial regulations. Participants must be fully informed about the nature of the study, potential risks and benefits, and their rights as research subjects. In wound healing studies, this includes clear explanations of the different dressing types and any potential discomfort or complications associated with their use.
Data management and privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the US and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, play a significant role in clinical trials. These regulations dictate how patient information is collected, stored, and protected throughout the study and beyond.
Reporting requirements for adverse events and serious adverse events are strictly defined by regulatory bodies. Investigators must promptly report any unexpected or severe reactions to the dressings or films, ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Post-trial obligations include the dissemination of results, regardless of the outcome. ClinicalTrials.gov and the EU Clinical Trials Register are platforms where trial information and results must be published, promoting transparency and preventing publication bias.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Cost-effectiveness analysis is a crucial aspect when comparing healing rates between occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films. This analysis provides valuable insights into the economic implications of using these different wound care approaches, helping healthcare providers and policymakers make informed decisions.
To conduct a comprehensive cost-effectiveness analysis, it is essential to consider both direct and indirect costs associated with each dressing type. Direct costs include the purchase price of the dressings, frequency of dressing changes, and labor costs for healthcare professionals. Indirect costs may encompass factors such as patient discomfort, potential complications, and the overall impact on quality of life.
One key factor in the analysis is the healing time. Occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films may exhibit different healing rates, which can significantly influence the overall cost-effectiveness. A faster healing rate can lead to reduced treatment duration, fewer dressing changes, and potentially lower overall costs. However, it is crucial to balance these benefits against the initial cost of the dressing materials.
Another important consideration is the incidence of complications or adverse events associated with each dressing type. Complications can lead to extended treatment periods, additional interventions, and increased healthcare costs. By comparing the complication rates between occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films, we can better understand their long-term cost implications.
The analysis should also take into account the specific wound types and patient populations for which each dressing is most effective. Some dressings may be more cost-effective for certain wound types or patient demographics, while others may offer better value in different scenarios. This nuanced approach allows for a more accurate assessment of the overall cost-effectiveness.
Furthermore, it is important to consider the impact of dressing choice on healthcare resource utilization. This includes factors such as the frequency of outpatient visits, the need for specialized care, and the potential for reducing hospital stays. A dressing that requires fewer changes or allows for easier self-management by patients may lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness analysis should incorporate quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) or other relevant health outcome measures. This approach allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of the overall value provided by each dressing type, taking into account both the clinical outcomes and the impact on patient quality of life.
By conducting a thorough cost-effectiveness analysis, healthcare providers and policymakers can make evidence-based decisions regarding the use of occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films. This analysis not only helps optimize resource allocation but also ensures that patients receive the most appropriate and cost-effective wound care treatment.
To conduct a comprehensive cost-effectiveness analysis, it is essential to consider both direct and indirect costs associated with each dressing type. Direct costs include the purchase price of the dressings, frequency of dressing changes, and labor costs for healthcare professionals. Indirect costs may encompass factors such as patient discomfort, potential complications, and the overall impact on quality of life.
One key factor in the analysis is the healing time. Occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films may exhibit different healing rates, which can significantly influence the overall cost-effectiveness. A faster healing rate can lead to reduced treatment duration, fewer dressing changes, and potentially lower overall costs. However, it is crucial to balance these benefits against the initial cost of the dressing materials.
Another important consideration is the incidence of complications or adverse events associated with each dressing type. Complications can lead to extended treatment periods, additional interventions, and increased healthcare costs. By comparing the complication rates between occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films, we can better understand their long-term cost implications.
The analysis should also take into account the specific wound types and patient populations for which each dressing is most effective. Some dressings may be more cost-effective for certain wound types or patient demographics, while others may offer better value in different scenarios. This nuanced approach allows for a more accurate assessment of the overall cost-effectiveness.
Furthermore, it is important to consider the impact of dressing choice on healthcare resource utilization. This includes factors such as the frequency of outpatient visits, the need for specialized care, and the potential for reducing hospital stays. A dressing that requires fewer changes or allows for easier self-management by patients may lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness analysis should incorporate quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) or other relevant health outcome measures. This approach allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of the overall value provided by each dressing type, taking into account both the clinical outcomes and the impact on patient quality of life.
By conducting a thorough cost-effectiveness analysis, healthcare providers and policymakers can make evidence-based decisions regarding the use of occlusive dressings and semi-permeable films. This analysis not only helps optimize resource allocation but also ensures that patients receive the most appropriate and cost-effective wound care treatment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!