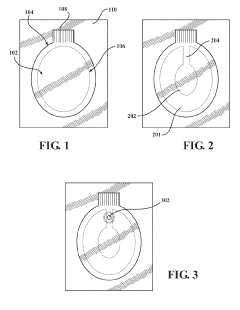
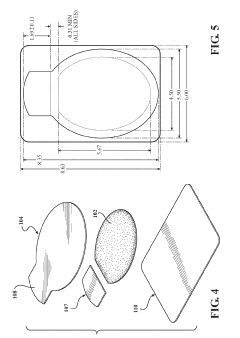
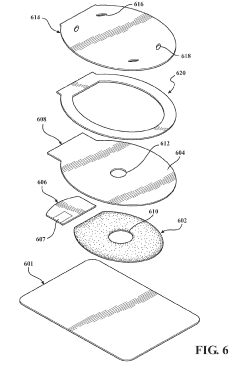
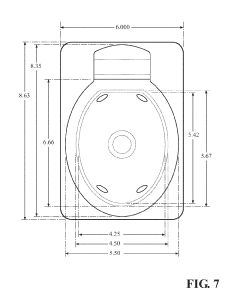
How To Select Occlusive Dressings For Battlefield Emergency Care
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Battlefield Dressing Evolution and Objectives
The evolution of battlefield dressings has been driven by the need for more effective and efficient emergency care in combat situations. From the early days of simple cloth bandages to modern advanced occlusive dressings, the development has been marked by significant improvements in materials, design, and functionality.
In the past, battlefield medics relied on basic gauze and cotton dressings, which were often inadequate for severe injuries and challenging environmental conditions. These traditional dressings lacked the ability to create an airtight seal, which is crucial for treating penetrating chest wounds and preventing tension pneumothorax.
The introduction of plastic wrap as an improvised occlusive dressing in the 1960s marked a turning point. This innovation highlighted the importance of creating an airtight seal over wounds, particularly for thoracic injuries. However, these early makeshift solutions were far from ideal, as they lacked proper adhesion and could easily be compromised in field conditions.
The 1990s saw the development of purpose-designed occlusive dressings for military use. These dressings incorporated advanced adhesives and moisture-resistant materials, significantly improving their effectiveness in battlefield conditions. The focus shifted towards creating dressings that could withstand the rigors of combat environments while providing superior wound protection.
Recent advancements have led to the creation of multi-functional occlusive dressings. These modern dressings not only provide an airtight seal but also incorporate features such as hemostatic agents to control bleeding, antimicrobial properties to prevent infection, and venting systems to allow for the release of excess air or fluids.
The primary objectives of contemporary battlefield dressing evolution are multifaceted. First and foremost is the enhancement of survival rates by providing immediate and effective wound management. This includes rapid hemorrhage control, prevention of contamination, and mitigation of life-threatening conditions such as tension pneumothorax.
Another key objective is to improve the ease of application and effectiveness in challenging combat situations. Dressings must be designed for quick and straightforward use by both trained medical personnel and soldiers with basic first aid training. This necessitates intuitive designs and clear instructions that can be followed under high-stress conditions.
Durability and versatility are also crucial objectives. Modern battlefield dressings aim to remain effective for extended periods, even in extreme environmental conditions such as high humidity, extreme temperatures, and exposure to various contaminants. Additionally, they should be adaptable to a wide range of wound types and body locations.
In the past, battlefield medics relied on basic gauze and cotton dressings, which were often inadequate for severe injuries and challenging environmental conditions. These traditional dressings lacked the ability to create an airtight seal, which is crucial for treating penetrating chest wounds and preventing tension pneumothorax.
The introduction of plastic wrap as an improvised occlusive dressing in the 1960s marked a turning point. This innovation highlighted the importance of creating an airtight seal over wounds, particularly for thoracic injuries. However, these early makeshift solutions were far from ideal, as they lacked proper adhesion and could easily be compromised in field conditions.
The 1990s saw the development of purpose-designed occlusive dressings for military use. These dressings incorporated advanced adhesives and moisture-resistant materials, significantly improving their effectiveness in battlefield conditions. The focus shifted towards creating dressings that could withstand the rigors of combat environments while providing superior wound protection.
Recent advancements have led to the creation of multi-functional occlusive dressings. These modern dressings not only provide an airtight seal but also incorporate features such as hemostatic agents to control bleeding, antimicrobial properties to prevent infection, and venting systems to allow for the release of excess air or fluids.
The primary objectives of contemporary battlefield dressing evolution are multifaceted. First and foremost is the enhancement of survival rates by providing immediate and effective wound management. This includes rapid hemorrhage control, prevention of contamination, and mitigation of life-threatening conditions such as tension pneumothorax.
Another key objective is to improve the ease of application and effectiveness in challenging combat situations. Dressings must be designed for quick and straightforward use by both trained medical personnel and soldiers with basic first aid training. This necessitates intuitive designs and clear instructions that can be followed under high-stress conditions.
Durability and versatility are also crucial objectives. Modern battlefield dressings aim to remain effective for extended periods, even in extreme environmental conditions such as high humidity, extreme temperatures, and exposure to various contaminants. Additionally, they should be adaptable to a wide range of wound types and body locations.
Market Analysis for Military Medical Supplies
The military medical supplies market, particularly for battlefield emergency care, has been experiencing significant growth due to ongoing global conflicts and increased focus on soldier safety. The demand for occlusive dressings, a critical component in treating penetrating chest wounds and other battlefield injuries, has seen a substantial rise in recent years. These specialized dressings are designed to create an airtight seal over wounds, preventing air from entering the chest cavity and reducing the risk of tension pneumothorax.
Market analysis indicates that the global military medical supplies market is projected to expand at a steady rate, driven by technological advancements in wound care products and increased defense spending by various nations. The occlusive dressings segment within this market is expected to grow at an above-average rate due to their crucial role in preventing life-threatening conditions on the battlefield.
Key factors influencing the market include the development of more advanced, lightweight, and easy-to-apply occlusive dressings that can withstand harsh battlefield conditions. There is a growing demand for dressings that offer improved adhesion, flexibility, and durability while maintaining their occlusive properties in extreme environments. Additionally, there is an increasing emphasis on dressings that can be quickly and easily applied by non-medical personnel, as immediate care is often critical in combat situations.
The market for occlusive dressings in military applications is characterized by a mix of established medical supply companies and specialized military equipment manufacturers. Competition in this sector is intensifying as companies invest in research and development to create innovative products that meet the specific needs of modern warfare medicine.
Geographically, North America dominates the market for military medical supplies, including occlusive dressings, due to its high defense budget and ongoing military operations. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East are showing rapid growth as these regions increase their defense spending and modernize their military medical capabilities.
The selection of occlusive dressings for battlefield emergency care is influenced by several factors, including effectiveness, ease of use, durability, and cost. Military procurement agencies are increasingly looking for products that offer a balance between performance and value, driving manufacturers to innovate and optimize their offerings.
Market analysis indicates that the global military medical supplies market is projected to expand at a steady rate, driven by technological advancements in wound care products and increased defense spending by various nations. The occlusive dressings segment within this market is expected to grow at an above-average rate due to their crucial role in preventing life-threatening conditions on the battlefield.
Key factors influencing the market include the development of more advanced, lightweight, and easy-to-apply occlusive dressings that can withstand harsh battlefield conditions. There is a growing demand for dressings that offer improved adhesion, flexibility, and durability while maintaining their occlusive properties in extreme environments. Additionally, there is an increasing emphasis on dressings that can be quickly and easily applied by non-medical personnel, as immediate care is often critical in combat situations.
The market for occlusive dressings in military applications is characterized by a mix of established medical supply companies and specialized military equipment manufacturers. Competition in this sector is intensifying as companies invest in research and development to create innovative products that meet the specific needs of modern warfare medicine.
Geographically, North America dominates the market for military medical supplies, including occlusive dressings, due to its high defense budget and ongoing military operations. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East are showing rapid growth as these regions increase their defense spending and modernize their military medical capabilities.
The selection of occlusive dressings for battlefield emergency care is influenced by several factors, including effectiveness, ease of use, durability, and cost. Military procurement agencies are increasingly looking for products that offer a balance between performance and value, driving manufacturers to innovate and optimize their offerings.
Current Occlusive Dressing Technologies and Challenges
The current landscape of occlusive dressing technologies for battlefield emergency care presents both innovative solutions and significant challenges. Advanced materials such as hydrocolloids, hydrogels, and transparent film dressings have revolutionized wound management, offering improved moisture control, infection prevention, and ease of application in high-stress environments.
Hydrocolloid dressings, composed of gel-forming agents, provide excellent moisture retention and create an optimal healing environment. These dressings are particularly effective for partial-thickness wounds and abrasions commonly encountered in combat situations. However, their opaque nature can hinder wound monitoring, presenting a challenge in battlefield scenarios where frequent wound assessment is crucial.
Transparent film dressings, made from thin polyurethane membranes, offer the advantage of wound visibility while maintaining a moist environment. These dressings are highly conformable and allow for easy application on irregular surfaces, making them suitable for various battlefield injuries. Nevertheless, their limited absorption capacity can be problematic for heavily exuding wounds, potentially compromising their occlusive properties.
Hydrogel dressings, consisting of water-based gels, excel in providing a cooling effect and pain relief, which is particularly beneficial for burn injuries. Their ability to donate moisture to dry wounds while absorbing excess exudate from moist wounds makes them versatile for different wound types. However, their relatively weak adhesive properties may pose challenges in maintaining a secure seal during patient transport or prolonged field operations.
One of the primary challenges in occlusive dressing technology for battlefield care is balancing the need for robust adhesion with easy removal for wound inspection and redressing. Current adhesives may not always withstand the extreme conditions of combat environments, leading to potential dressing failure and increased risk of wound contamination.
Another significant challenge is the development of dressings that can effectively manage heavily contaminated wounds often encountered in battlefield scenarios. While some advanced dressings incorporate antimicrobial agents, there is still a need for more effective solutions that can rapidly decontaminate wounds without compromising the healing process or causing adverse effects on healthy tissue.
The integration of smart technologies into occlusive dressings represents both an opportunity and a challenge. Emerging concepts such as dressings with embedded sensors for real-time wound monitoring show promise but face hurdles in terms of durability, cost-effectiveness, and practical implementation in austere battlefield conditions.
In conclusion, while current occlusive dressing technologies offer significant advancements in battlefield wound care, there remain substantial challenges in developing solutions that can fully meet the unique demands of combat medicine. Addressing these challenges will require continued innovation in materials science, adhesive technology, and the integration of smart systems tailored specifically for military medical applications.
Hydrocolloid dressings, composed of gel-forming agents, provide excellent moisture retention and create an optimal healing environment. These dressings are particularly effective for partial-thickness wounds and abrasions commonly encountered in combat situations. However, their opaque nature can hinder wound monitoring, presenting a challenge in battlefield scenarios where frequent wound assessment is crucial.
Transparent film dressings, made from thin polyurethane membranes, offer the advantage of wound visibility while maintaining a moist environment. These dressings are highly conformable and allow for easy application on irregular surfaces, making them suitable for various battlefield injuries. Nevertheless, their limited absorption capacity can be problematic for heavily exuding wounds, potentially compromising their occlusive properties.
Hydrogel dressings, consisting of water-based gels, excel in providing a cooling effect and pain relief, which is particularly beneficial for burn injuries. Their ability to donate moisture to dry wounds while absorbing excess exudate from moist wounds makes them versatile for different wound types. However, their relatively weak adhesive properties may pose challenges in maintaining a secure seal during patient transport or prolonged field operations.
One of the primary challenges in occlusive dressing technology for battlefield care is balancing the need for robust adhesion with easy removal for wound inspection and redressing. Current adhesives may not always withstand the extreme conditions of combat environments, leading to potential dressing failure and increased risk of wound contamination.
Another significant challenge is the development of dressings that can effectively manage heavily contaminated wounds often encountered in battlefield scenarios. While some advanced dressings incorporate antimicrobial agents, there is still a need for more effective solutions that can rapidly decontaminate wounds without compromising the healing process or causing adverse effects on healthy tissue.
The integration of smart technologies into occlusive dressings represents both an opportunity and a challenge. Emerging concepts such as dressings with embedded sensors for real-time wound monitoring show promise but face hurdles in terms of durability, cost-effectiveness, and practical implementation in austere battlefield conditions.
In conclusion, while current occlusive dressing technologies offer significant advancements in battlefield wound care, there remain substantial challenges in developing solutions that can fully meet the unique demands of combat medicine. Addressing these challenges will require continued innovation in materials science, adhesive technology, and the integration of smart systems tailored specifically for military medical applications.
Existing Occlusive Dressing Selection Criteria
01 Composition of occlusive dressings
Occlusive dressings are designed with specific materials and compositions to create a barrier over wounds. These dressings may include polymeric materials, adhesives, and moisture-retaining components to promote healing and protect the wound from external contaminants. The composition can be tailored to provide optimal occlusion and moisture management for different wound types.- Composition of occlusive dressings: Occlusive dressings are typically composed of materials that create a barrier to prevent moisture loss and protect wounds. These may include polymers, adhesives, and moisture-absorbing substances. The composition is designed to maintain a moist wound environment, which is conducive to healing.
- Application methods for occlusive dressings: Various methods are used to apply occlusive dressings, including adhesive backing, spray-on formulations, and hydrogel applications. These methods aim to ensure proper coverage and adherence to the wound site, maximizing the occlusive effect and promoting optimal healing conditions.
- Wound healing enhancement features: Occlusive dressings often incorporate features to enhance wound healing. These may include antimicrobial agents, growth factors, or oxygen-permeable layers. Such additions aim to create an ideal environment for tissue regeneration while preventing infection.
- Smart occlusive dressing technologies: Advanced occlusive dressings incorporate smart technologies such as sensors for monitoring wound healing progress, temperature regulation systems, or controlled release mechanisms for medication delivery. These innovations aim to provide real-time wound assessment and optimize treatment.
- Specialized occlusive dressings for specific applications: Certain occlusive dressings are designed for specific medical applications, such as burn treatment, surgical incisions, or chronic wounds. These specialized dressings may have unique properties tailored to the particular needs of different wound types or healing stages.
02 Application methods for occlusive dressings
Various techniques and devices are used to apply occlusive dressings effectively. These may include specialized applicators, adhesive systems, or methods for ensuring proper placement and adherence to the skin. The application process is designed to minimize discomfort, ensure complete coverage, and facilitate easy removal when necessary.Expand Specific Solutions03 Wound healing properties of occlusive dressings
Occlusive dressings are formulated to enhance wound healing by creating an optimal environment. They maintain moisture balance, promote autolytic debridement, and may incorporate active ingredients that stimulate tissue regeneration. These dressings can accelerate healing, reduce scarring, and minimize the risk of infection in various wound types.Expand Specific Solutions04 Specialized occlusive dressings for specific medical conditions
Certain occlusive dressings are developed for particular medical conditions or wound types. These may include dressings for burn treatment, post-surgical care, or chronic wounds. The dressings are tailored in terms of materials, absorption capacity, and incorporated medications to address the unique needs of each condition.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of technology in occlusive dressings
Advanced occlusive dressings incorporate various technologies to enhance their effectiveness. This may include smart materials that respond to wound conditions, sensors for monitoring healing progress, or systems for controlled release of therapeutic agents. These innovations aim to improve treatment outcomes and provide real-time data on wound status.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers in Military Medical Equipment
The battlefield emergency care occlusive dressing market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing military conflicts and disaster response needs. The market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, occlusive dressings are evolving rapidly, with companies like 3M Innovative Properties Co., ConvaTec Inc., and TacMed Solutions LLC leading innovation. These firms are developing advanced materials and designs to enhance wound sealing, infection prevention, and ease of application in challenging field conditions. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established medical device manufacturers and specialized tactical medical equipment providers, each striving to improve product efficacy and usability for military and emergency responders.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed advanced occlusive dressings for battlefield emergency care, utilizing their proprietary Tegaderm technology. These dressings feature a transparent, semi-permeable film that allows for visual wound assessment while maintaining a moist wound environment. The dressings incorporate a unique adhesive system that provides strong adherence even in challenging battlefield conditions, yet allows for gentle removal to minimize trauma to healing tissue. 3M's occlusive dressings also integrate antimicrobial agents to reduce the risk of infection, which is crucial in battlefield settings where immediate access to sterile environments may be limited[1][3]. The company has further enhanced their dressings with a multi-layer design that includes an absorbent pad to manage exudate, improving overall wound healing outcomes.
Strengths: Strong adherence in challenging conditions, allows visual wound assessment, antimicrobial properties. Weaknesses: May require additional training for proper application, potential for moisture build-up in certain wound types.
Convatec, Inc.
Technical Solution: Convatec has developed a range of advanced occlusive dressings specifically designed for battlefield emergency care. Their AQUACEL Ag+ Extra dressing combines the company's Hydrofiber Technology with ionic silver and anti-biofilm agents. This innovative combination provides rapid absorption of wound exudate, forms a gel-like covering over the wound, and offers broad-spectrum antimicrobial protection[2]. The dressing is designed to conform closely to wound contours, minimizing dead space where bacteria can proliferate. Convatec's occlusive dressings also feature easy-to-use application systems, crucial for quick deployment in high-stress battlefield situations. The company has incorporated moisture vapor transmission technology into their dressings, allowing excess fluid to evaporate while maintaining an optimal moist wound environment[4].
Strengths: Rapid exudate absorption, antimicrobial properties, conformability to wound contours. Weaknesses: May be more expensive than basic dressings, requires proper storage to maintain effectiveness.
Innovative Materials for Battlefield Dressings
Vented emergency wound dressings with Anti-thrombogenic layers
PatentInactiveUS20190298578A1
Innovation
- A wound dressing combining an adhesive backing layer with a hydrogel layer and an anti-thrombogenic cover layer, featuring a central aperture and vent passages for pressure release, and an optional pull-tab for easy removal, using thermoplastic polyurethane films to prevent clotting and ensure effective sealing and venting.
Wound care polymer compositions and methods for use thereof
PatentInactiveUS20060188486A1
Innovation
- Development of biodegradable polymer compositions, including poly(ester amide), poly(ester urethane), and poly(ester urea) polymers, that release wound healing agents to restore the natural healing process by promoting endothelialization and inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation, used in wound dressings, implants, and stent coatings.
Regulatory Standards for Combat Medical Devices
The regulatory landscape for combat medical devices, including occlusive dressings for battlefield emergency care, is complex and multifaceted. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating these devices. The FDA classifies medical devices into three categories based on their risk level and the regulatory controls necessary to ensure their safety and effectiveness. Occlusive dressings for battlefield use typically fall under Class II, requiring special controls in addition to general controls.
Military medical devices must comply with stringent standards set by the Department of Defense (DoD). These standards often exceed civilian requirements due to the extreme conditions and high-stakes scenarios in which they are used. The DoD's medical materiel standardization program ensures that all medical devices used in combat situations meet specific performance criteria, durability standards, and compatibility requirements with other military equipment.
International standards also play a significant role in the regulation of combat medical devices. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards relevant to occlusive dressings, such as ISO 13485 for quality management systems in medical device manufacturing. Additionally, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) has established Standardization Agreements (STANAGs) that define processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures among member countries.
Regulatory bodies emphasize the importance of sterility, biocompatibility, and shelf life for occlusive dressings. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with standards such as ISO 11607 for packaging of terminally sterilized medical devices and ISO 10993 for biological evaluation of medical devices. These standards ensure that the dressings remain sterile and effective under various environmental conditions encountered in battlefield scenarios.
Environmental considerations are also critical in the regulatory framework for combat medical devices. Occlusive dressings must be able to withstand extreme temperatures, humidity, and altitude changes without compromising their performance. Regulatory standards often require extensive testing to simulate these conditions and validate the product's resilience.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape is continually evolving to keep pace with technological advancements and emerging threats. Recent focus areas include the integration of smart technologies in medical devices and enhanced protection against chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear (CBRN) agents. Manufacturers and researchers must stay abreast of these developments to ensure their products meet the latest regulatory requirements and provide optimal care for wounded soldiers in battlefield environments.
Military medical devices must comply with stringent standards set by the Department of Defense (DoD). These standards often exceed civilian requirements due to the extreme conditions and high-stakes scenarios in which they are used. The DoD's medical materiel standardization program ensures that all medical devices used in combat situations meet specific performance criteria, durability standards, and compatibility requirements with other military equipment.
International standards also play a significant role in the regulation of combat medical devices. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards relevant to occlusive dressings, such as ISO 13485 for quality management systems in medical device manufacturing. Additionally, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) has established Standardization Agreements (STANAGs) that define processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures among member countries.
Regulatory bodies emphasize the importance of sterility, biocompatibility, and shelf life for occlusive dressings. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with standards such as ISO 11607 for packaging of terminally sterilized medical devices and ISO 10993 for biological evaluation of medical devices. These standards ensure that the dressings remain sterile and effective under various environmental conditions encountered in battlefield scenarios.
Environmental considerations are also critical in the regulatory framework for combat medical devices. Occlusive dressings must be able to withstand extreme temperatures, humidity, and altitude changes without compromising their performance. Regulatory standards often require extensive testing to simulate these conditions and validate the product's resilience.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape is continually evolving to keep pace with technological advancements and emerging threats. Recent focus areas include the integration of smart technologies in medical devices and enhanced protection against chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear (CBRN) agents. Manufacturers and researchers must stay abreast of these developments to ensure their products meet the latest regulatory requirements and provide optimal care for wounded soldiers in battlefield environments.
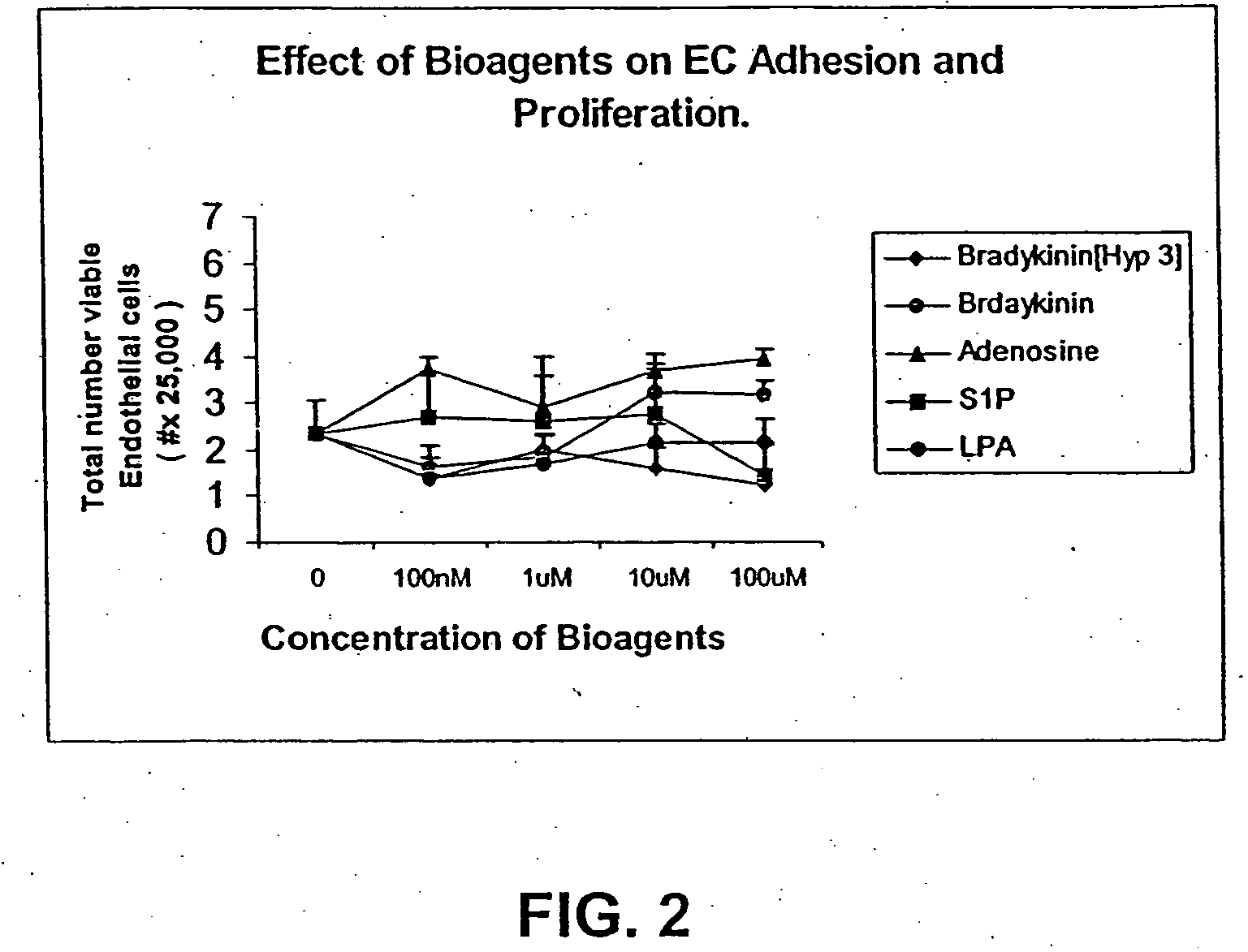
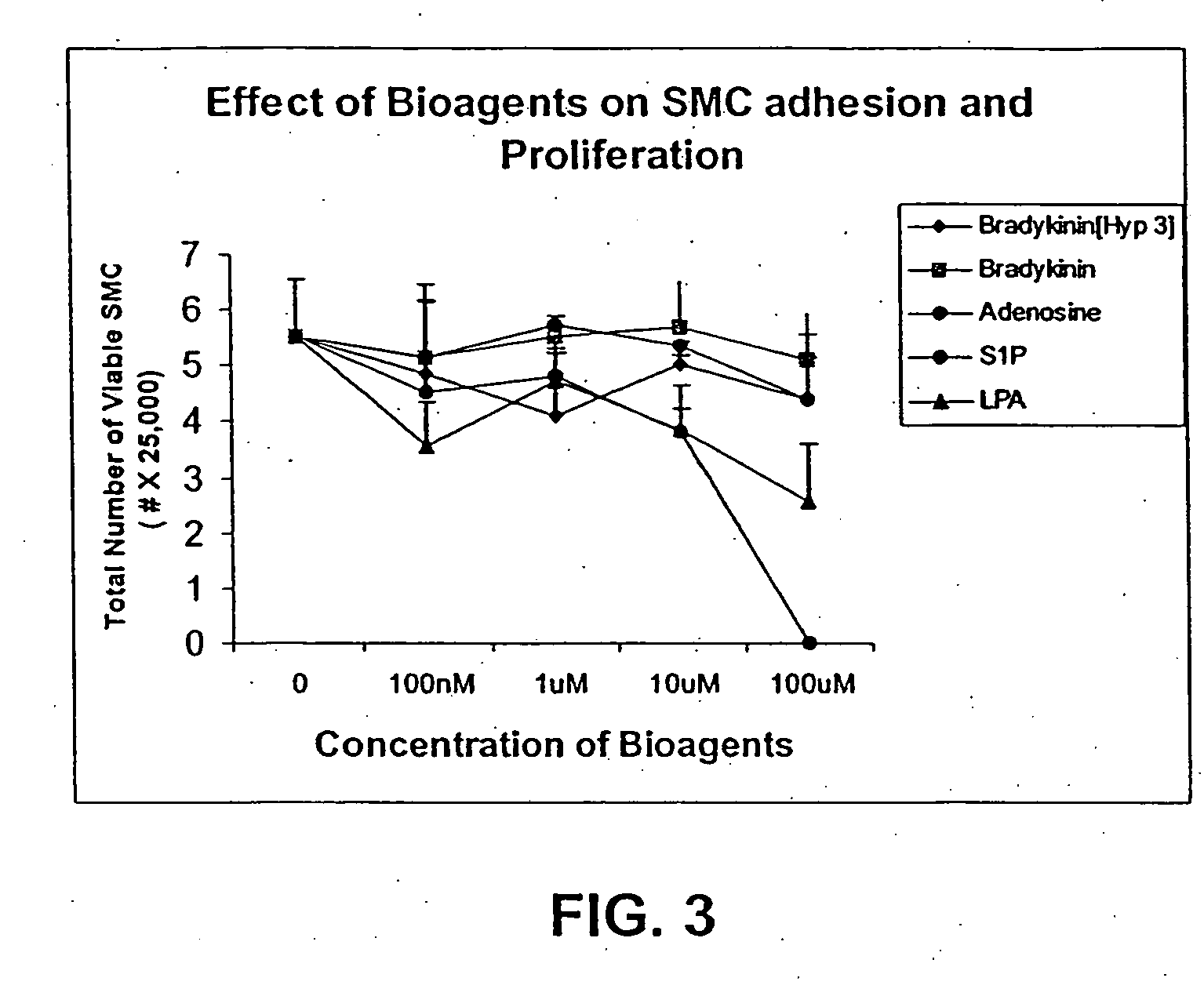
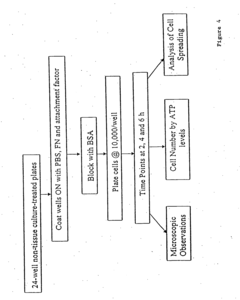
Field Testing and Performance Evaluation
Field testing and performance evaluation are crucial steps in selecting occlusive dressings for battlefield emergency care. These processes involve rigorous assessment of dressing materials under simulated combat conditions to ensure their efficacy and reliability in high-stress environments.
The evaluation typically begins with laboratory testing, where dressings are subjected to controlled conditions mimicking battlefield scenarios. This includes exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity levels, and contaminants commonly encountered in combat zones. Dressings are tested for their ability to maintain adhesion, flexibility, and barrier properties under these challenging conditions.
Following laboratory assessments, field trials are conducted to evaluate the dressings' performance in more realistic settings. These trials often involve military personnel or medical professionals simulating emergency care scenarios in outdoor environments. Factors such as ease of application, speed of deployment, and durability during patient transport are carefully observed and documented.
One critical aspect of field testing is the assessment of the dressings' occlusive properties. This involves evaluating their ability to create an airtight seal over wounds, preventing the ingress of contaminants and maintaining a sterile environment. The effectiveness of the seal is tested under various movement conditions to ensure it remains intact during patient evacuation and transport.
Performance evaluation also includes an analysis of the dressings' impact on wound healing and infection prevention. This may involve monitoring treated injuries over time, comparing healing rates and infection incidence with control groups. Additionally, the dressings' compatibility with other medical equipment and treatments commonly used in battlefield medicine is evaluated to ensure seamless integration into existing care protocols.
Feedback from end-users, including combat medics and field surgeons, plays a vital role in the evaluation process. Their insights on the practicality, ease of use, and perceived effectiveness of the dressings in real-world scenarios are invaluable for refining selection criteria and improving product design.
The data collected from these field tests and performance evaluations is meticulously analyzed to identify the most suitable occlusive dressings for battlefield emergency care. This analysis considers factors such as wound coverage efficacy, durability, ease of use, and compatibility with various wound types and locations. The results inform evidence-based recommendations for dressing selection and guide future improvements in battlefield medical supplies.
The evaluation typically begins with laboratory testing, where dressings are subjected to controlled conditions mimicking battlefield scenarios. This includes exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity levels, and contaminants commonly encountered in combat zones. Dressings are tested for their ability to maintain adhesion, flexibility, and barrier properties under these challenging conditions.
Following laboratory assessments, field trials are conducted to evaluate the dressings' performance in more realistic settings. These trials often involve military personnel or medical professionals simulating emergency care scenarios in outdoor environments. Factors such as ease of application, speed of deployment, and durability during patient transport are carefully observed and documented.
One critical aspect of field testing is the assessment of the dressings' occlusive properties. This involves evaluating their ability to create an airtight seal over wounds, preventing the ingress of contaminants and maintaining a sterile environment. The effectiveness of the seal is tested under various movement conditions to ensure it remains intact during patient evacuation and transport.
Performance evaluation also includes an analysis of the dressings' impact on wound healing and infection prevention. This may involve monitoring treated injuries over time, comparing healing rates and infection incidence with control groups. Additionally, the dressings' compatibility with other medical equipment and treatments commonly used in battlefield medicine is evaluated to ensure seamless integration into existing care protocols.
Feedback from end-users, including combat medics and field surgeons, plays a vital role in the evaluation process. Their insights on the practicality, ease of use, and perceived effectiveness of the dressings in real-world scenarios are invaluable for refining selection criteria and improving product design.
The data collected from these field tests and performance evaluations is meticulously analyzed to identify the most suitable occlusive dressings for battlefield emergency care. This analysis considers factors such as wound coverage efficacy, durability, ease of use, and compatibility with various wound types and locations. The results inform evidence-based recommendations for dressing selection and guide future improvements in battlefield medical supplies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!