Occlusive Dressing Materials: Hydrogel Vs Silicone Barrier Performance
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Occlusive Dressing Evolution and Objectives
Occlusive dressings have undergone significant evolution since their inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed to provide a moist wound healing environment, these dressings have transformed from simple adhesive films to advanced, multi-functional materials. The journey began with the recognition that maintaining a moist wound bed accelerates healing, reduces pain, and minimizes scarring.
Early occlusive dressings were primarily composed of polyurethane films, which provided a barrier against external contaminants while allowing some moisture vapor transmission. However, these early versions had limitations in terms of fluid handling capacity and conformability to complex wound surfaces. As research progressed, new materials and technologies were incorporated to address these shortcomings.
The introduction of hydrocolloid dressings in the 1980s marked a significant milestone. These dressings combined occlusive properties with the ability to absorb wound exudate, maintaining an optimal moisture balance. This development paved the way for more advanced occlusive materials, including hydrogels and silicone-based dressings.
Hydrogels emerged as a promising material due to their high water content and ability to donate moisture to dry wounds while absorbing excess exudate. Silicone, on the other hand, gained popularity for its gentle adhesion and minimal trauma upon removal. Both materials offered unique advantages in occlusive wound care, leading to their widespread adoption and continued refinement.
The objectives of modern occlusive dressing research focus on enhancing the performance of these materials, particularly in terms of their barrier properties. Key goals include improving moisture vapor transmission rates, optimizing adhesion strength, and enhancing biocompatibility. Researchers aim to develop dressings that can maintain an ideal wound microenvironment while adapting to various wound types and healing stages.
Another critical objective is to compare and evaluate the efficacy of different occlusive materials, such as hydrogels and silicone barriers. This involves assessing their respective strengths in preventing bacterial infiltration, managing wound exudate, and promoting optimal healing conditions. The ultimate aim is to provide healthcare professionals with evidence-based options for selecting the most appropriate occlusive dressing for specific wound care scenarios.
As technology advances, there is a growing emphasis on developing smart occlusive dressings that can respond to changes in the wound environment. This includes incorporating sensors for real-time monitoring of wound healing progress and integrating controlled release mechanisms for targeted drug delivery. These innovations seek to revolutionize wound care by enabling personalized treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Early occlusive dressings were primarily composed of polyurethane films, which provided a barrier against external contaminants while allowing some moisture vapor transmission. However, these early versions had limitations in terms of fluid handling capacity and conformability to complex wound surfaces. As research progressed, new materials and technologies were incorporated to address these shortcomings.
The introduction of hydrocolloid dressings in the 1980s marked a significant milestone. These dressings combined occlusive properties with the ability to absorb wound exudate, maintaining an optimal moisture balance. This development paved the way for more advanced occlusive materials, including hydrogels and silicone-based dressings.
Hydrogels emerged as a promising material due to their high water content and ability to donate moisture to dry wounds while absorbing excess exudate. Silicone, on the other hand, gained popularity for its gentle adhesion and minimal trauma upon removal. Both materials offered unique advantages in occlusive wound care, leading to their widespread adoption and continued refinement.
The objectives of modern occlusive dressing research focus on enhancing the performance of these materials, particularly in terms of their barrier properties. Key goals include improving moisture vapor transmission rates, optimizing adhesion strength, and enhancing biocompatibility. Researchers aim to develop dressings that can maintain an ideal wound microenvironment while adapting to various wound types and healing stages.
Another critical objective is to compare and evaluate the efficacy of different occlusive materials, such as hydrogels and silicone barriers. This involves assessing their respective strengths in preventing bacterial infiltration, managing wound exudate, and promoting optimal healing conditions. The ultimate aim is to provide healthcare professionals with evidence-based options for selecting the most appropriate occlusive dressing for specific wound care scenarios.
As technology advances, there is a growing emphasis on developing smart occlusive dressings that can respond to changes in the wound environment. This includes incorporating sensors for real-time monitoring of wound healing progress and integrating controlled release mechanisms for targeted drug delivery. These innovations seek to revolutionize wound care by enabling personalized treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Market Analysis for Advanced Wound Care
The advanced wound care market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, and rising awareness of the importance of effective wound management. This market segment encompasses a wide range of products, including occlusive dressing materials such as hydrogels and silicone-based dressings.
The global advanced wound care market was valued at approximately $9.4 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $14.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 8.2% during the forecast period. Occlusive dressings, including hydrogels and silicone-based products, represent a substantial portion of this market, with an estimated share of 35-40%.
Hydrogel dressings have gained popularity due to their ability to maintain a moist wound environment, promote autolytic debridement, and provide cooling and pain relief. The hydrogel segment of the advanced wound care market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2021 to 2028, driven by increasing adoption in chronic wound management.
Silicone-based dressings, on the other hand, have seen rapid growth due to their non-adherent properties, ability to minimize trauma during dressing changes, and effectiveness in scar management. The silicone dressings market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2021 to 2028, with increasing applications in post-surgical wound care and burn treatment.
Geographically, North America dominates the advanced wound care market, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market share. Europe follows closely, with a market share of around 30%. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure and rising awareness of advanced wound care products.
Key market players in the occlusive dressing segment include 3M Company, Smith & Nephew, Mölnlycke Health Care, ConvaTec Group, and Coloplast A/S. These companies are actively investing in research and development to improve the performance of hydrogel and silicone-based dressings, focusing on enhanced moisture management, antimicrobial properties, and ease of application.
The market for occlusive dressing materials is influenced by several trends, including the shift towards outpatient and home healthcare settings, increasing demand for combination dressings that incorporate multiple technologies, and growing emphasis on cost-effective wound care solutions. Additionally, there is a rising interest in smart wound dressings that can monitor wound healing progress and provide real-time data to healthcare providers.
The global advanced wound care market was valued at approximately $9.4 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $14.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 8.2% during the forecast period. Occlusive dressings, including hydrogels and silicone-based products, represent a substantial portion of this market, with an estimated share of 35-40%.
Hydrogel dressings have gained popularity due to their ability to maintain a moist wound environment, promote autolytic debridement, and provide cooling and pain relief. The hydrogel segment of the advanced wound care market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2021 to 2028, driven by increasing adoption in chronic wound management.
Silicone-based dressings, on the other hand, have seen rapid growth due to their non-adherent properties, ability to minimize trauma during dressing changes, and effectiveness in scar management. The silicone dressings market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2021 to 2028, with increasing applications in post-surgical wound care and burn treatment.
Geographically, North America dominates the advanced wound care market, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market share. Europe follows closely, with a market share of around 30%. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure and rising awareness of advanced wound care products.
Key market players in the occlusive dressing segment include 3M Company, Smith & Nephew, Mölnlycke Health Care, ConvaTec Group, and Coloplast A/S. These companies are actively investing in research and development to improve the performance of hydrogel and silicone-based dressings, focusing on enhanced moisture management, antimicrobial properties, and ease of application.
The market for occlusive dressing materials is influenced by several trends, including the shift towards outpatient and home healthcare settings, increasing demand for combination dressings that incorporate multiple technologies, and growing emphasis on cost-effective wound care solutions. Additionally, there is a rising interest in smart wound dressings that can monitor wound healing progress and provide real-time data to healthcare providers.
Hydrogel and Silicone Barrier Technologies: Current Status
Hydrogel and silicone barrier technologies have emerged as two prominent solutions in the field of occlusive dressing materials. Both technologies have made significant strides in recent years, offering unique advantages in wound care and skin protection applications.
Hydrogel technology has seen substantial advancements, with current formulations providing excellent moisture retention and cooling properties. These gels, typically composed of cross-linked polymers, can absorb and retain large amounts of water, creating an ideal moist environment for wound healing. Recent developments have focused on improving the mechanical strength and durability of hydrogels, addressing previous limitations in their structural integrity.
Innovations in hydrogel technology include the incorporation of antimicrobial agents, growth factors, and other bioactive compounds. These additions enhance the wound healing process and provide additional protection against infections. Some cutting-edge hydrogels now feature stimuli-responsive properties, allowing for controlled release of therapeutic agents in response to changes in pH, temperature, or other environmental factors.
Silicone barrier technology, on the other hand, has evolved to offer superior breathability and flexibility. Modern silicone-based dressings provide an effective barrier against external contaminants while allowing for gaseous exchange. This balance is crucial for maintaining optimal wound healing conditions without causing maceration of the surrounding skin.
Recent advancements in silicone technology have focused on improving adhesion properties and reducing the risk of skin trauma upon removal. Some silicone dressings now incorporate soft silicone adhesive layers that can adhere gently to the peri-wound skin without adhering to the wound bed itself, minimizing pain and damage during dressing changes.
Both technologies have seen improvements in their ability to conform to complex body contours, enhancing patient comfort and ensuring consistent coverage. Manufacturers have developed thinner, more flexible variants of both hydrogel and silicone dressings, allowing for better adaptation to joint areas and other challenging anatomical sites.
In terms of performance comparison, hydrogels generally excel in providing a moist wound environment and promoting autolytic debridement. They are particularly effective in managing dry to moderately exuding wounds. Silicone barriers, conversely, offer superior protection against external contaminants and are often preferred for their ease of application and removal, especially in fragile skin situations.
Current research is exploring hybrid solutions that combine the benefits of both technologies. These composite dressings aim to leverage the moisture-retaining properties of hydrogels with the protective barrier function of silicone. Such innovations promise to address a broader range of wound care needs and potentially improve overall healing outcomes.
As the field continues to evolve, both hydrogel and silicone barrier technologies are expected to see further refinements. Future developments may focus on enhancing biocompatibility, improving long-term wear time, and incorporating smart materials that can respond dynamically to wound healing stages.
Hydrogel technology has seen substantial advancements, with current formulations providing excellent moisture retention and cooling properties. These gels, typically composed of cross-linked polymers, can absorb and retain large amounts of water, creating an ideal moist environment for wound healing. Recent developments have focused on improving the mechanical strength and durability of hydrogels, addressing previous limitations in their structural integrity.
Innovations in hydrogel technology include the incorporation of antimicrobial agents, growth factors, and other bioactive compounds. These additions enhance the wound healing process and provide additional protection against infections. Some cutting-edge hydrogels now feature stimuli-responsive properties, allowing for controlled release of therapeutic agents in response to changes in pH, temperature, or other environmental factors.
Silicone barrier technology, on the other hand, has evolved to offer superior breathability and flexibility. Modern silicone-based dressings provide an effective barrier against external contaminants while allowing for gaseous exchange. This balance is crucial for maintaining optimal wound healing conditions without causing maceration of the surrounding skin.
Recent advancements in silicone technology have focused on improving adhesion properties and reducing the risk of skin trauma upon removal. Some silicone dressings now incorporate soft silicone adhesive layers that can adhere gently to the peri-wound skin without adhering to the wound bed itself, minimizing pain and damage during dressing changes.
Both technologies have seen improvements in their ability to conform to complex body contours, enhancing patient comfort and ensuring consistent coverage. Manufacturers have developed thinner, more flexible variants of both hydrogel and silicone dressings, allowing for better adaptation to joint areas and other challenging anatomical sites.
In terms of performance comparison, hydrogels generally excel in providing a moist wound environment and promoting autolytic debridement. They are particularly effective in managing dry to moderately exuding wounds. Silicone barriers, conversely, offer superior protection against external contaminants and are often preferred for their ease of application and removal, especially in fragile skin situations.
Current research is exploring hybrid solutions that combine the benefits of both technologies. These composite dressings aim to leverage the moisture-retaining properties of hydrogels with the protective barrier function of silicone. Such innovations promise to address a broader range of wound care needs and potentially improve overall healing outcomes.
As the field continues to evolve, both hydrogel and silicone barrier technologies are expected to see further refinements. Future developments may focus on enhancing biocompatibility, improving long-term wear time, and incorporating smart materials that can respond dynamically to wound healing stages.
Comparative Analysis: Hydrogel vs Silicone Barriers
01 Multilayer occlusive dressing materials
Occlusive dressings with multiple layers are designed to enhance barrier performance. These dressings typically include a moisture-permeable outer layer, an absorbent middle layer, and a non-adherent wound contact layer. The combination of layers provides effective protection against external contaminants while maintaining a moist wound environment conducive to healing.- Multilayer occlusive dressing materials: Occlusive dressings with multiple layers enhance barrier performance. These dressings typically include a breathable outer layer, an absorbent middle layer, and a non-adherent wound contact layer. The combination of layers provides improved protection against external contaminants while maintaining a moist wound environment.
- Hydrocolloid-based occlusive dressings: Hydrocolloid dressings offer excellent barrier properties by forming a gel-like substance when in contact with wound exudate. This gel creates a moist environment that promotes healing while preventing external contamination. These dressings are particularly effective for managing moderate to high exuding wounds.
- Silicone-based occlusive dressings: Silicone-based dressings provide superior barrier performance due to their ability to conform closely to the wound surface. These dressings create an effective seal against external contaminants while allowing for easy, pain-free removal. They are particularly useful for patients with fragile skin or those prone to adhesive-related injuries.
- Antimicrobial occlusive dressings: Occlusive dressings incorporating antimicrobial agents offer enhanced barrier performance by actively preventing bacterial colonization. These dressings typically contain substances such as silver, iodine, or chlorhexidine, which provide an additional layer of protection against infection while maintaining the occlusive properties of the dressing.
- Smart occlusive dressings with moisture management: Advanced occlusive dressings with moisture management capabilities offer improved barrier performance by dynamically regulating the wound environment. These dressings can absorb excess exudate while maintaining optimal moisture levels, preventing maceration and reducing the risk of bacterial penetration. Some incorporate indicators to signal when dressing changes are necessary.
02 Hydrocolloid-based occlusive dressings
Hydrocolloid dressings are occlusive materials that form a gel-like barrier when in contact with wound exudate. These dressings provide excellent barrier performance by creating a moist environment that promotes healing while protecting the wound from external contamination. They also have the ability to absorb excess exudate, maintaining an optimal wound healing environment.Expand Specific Solutions03 Antimicrobial occlusive dressings
Occlusive dressings incorporating antimicrobial agents enhance barrier performance by actively preventing microbial penetration. These dressings often contain silver, iodine, or other antimicrobial substances that create an inhospitable environment for pathogens, reducing the risk of infection while maintaining the occlusive properties of the dressing.Expand Specific Solutions04 Breathable film occlusive dressings
Breathable film dressings provide occlusive properties while allowing for gas exchange. These thin, transparent films create a barrier against external contaminants and moisture while permitting oxygen to reach the wound. This balance of occlusion and breathability helps maintain an optimal wound healing environment and reduces the risk of maceration.Expand Specific Solutions05 Smart occlusive dressings with sensing capabilities
Advanced occlusive dressings incorporate sensing technologies to monitor wound healing progress and maintain barrier integrity. These smart dressings can detect changes in pH, temperature, or moisture levels, allowing for early detection of potential complications. Some designs also include drug delivery systems that can be activated based on the sensed wound conditions, enhancing the overall barrier performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers in Occlusive Dressing Industry
The competitive landscape for occlusive dressing materials, particularly hydrogel vs silicone barrier performance, is in a mature stage with established players and ongoing innovation. The market size is substantial, driven by growing demand in wound care and surgical applications. Technologically, both hydrogel and silicone-based dressings are well-developed, with companies like Bausch & Lomb, Ethicon, and Hollister leading in innovation. Emerging players such as Quick-Med Technologies and Corium are introducing novel formulations, while research institutions like the University of Florida contribute to advancing the field. The competition focuses on enhancing performance, biocompatibility, and cost-effectiveness of these materials.
Ethicon, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ethicon has developed advanced occlusive dressing materials combining hydrogel and silicone technologies. Their approach involves a multi-layer dressing with a silicone contact layer for gentle adhesion and a hydrogel layer for moisture management. The silicone layer provides a barrier against external contaminants while allowing for easy, pain-free removal. The hydrogel component maintains a moist wound environment, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection[1][3]. Ethicon's dressings also incorporate controlled release of antimicrobial agents to further enhance wound protection[5].
Strengths: Combines benefits of both hydrogel and silicone, excellent moisture management, gentle on skin, antimicrobial properties. Weaknesses: May be more expensive than single-technology dressings, potential for overhydration in certain wound types.
Hollister, Inc.
Technical Solution: Hollister has innovated in the field of occlusive dressing materials with their advanced hydrocolloid technology. Their dressings feature a hydrocolloid layer that absorbs wound exudate and forms a gel, maintaining an optimal moist environment for healing. This is combined with a breathable outer layer that provides a barrier against external contaminants. Hollister's dressings are designed to be flexible and conform to body contours, enhancing patient comfort[2]. The company has also developed dressings with tapered edges to prevent edge lift and extend wear time, addressing a common issue with occlusive dressings[4].
Strengths: Excellent exudate management, conformability to body contours, extended wear time. Weaknesses: May not be suitable for heavily exuding wounds, potential for maceration if not changed appropriately.
Innovative Approaches in Occlusive Dressing Materials
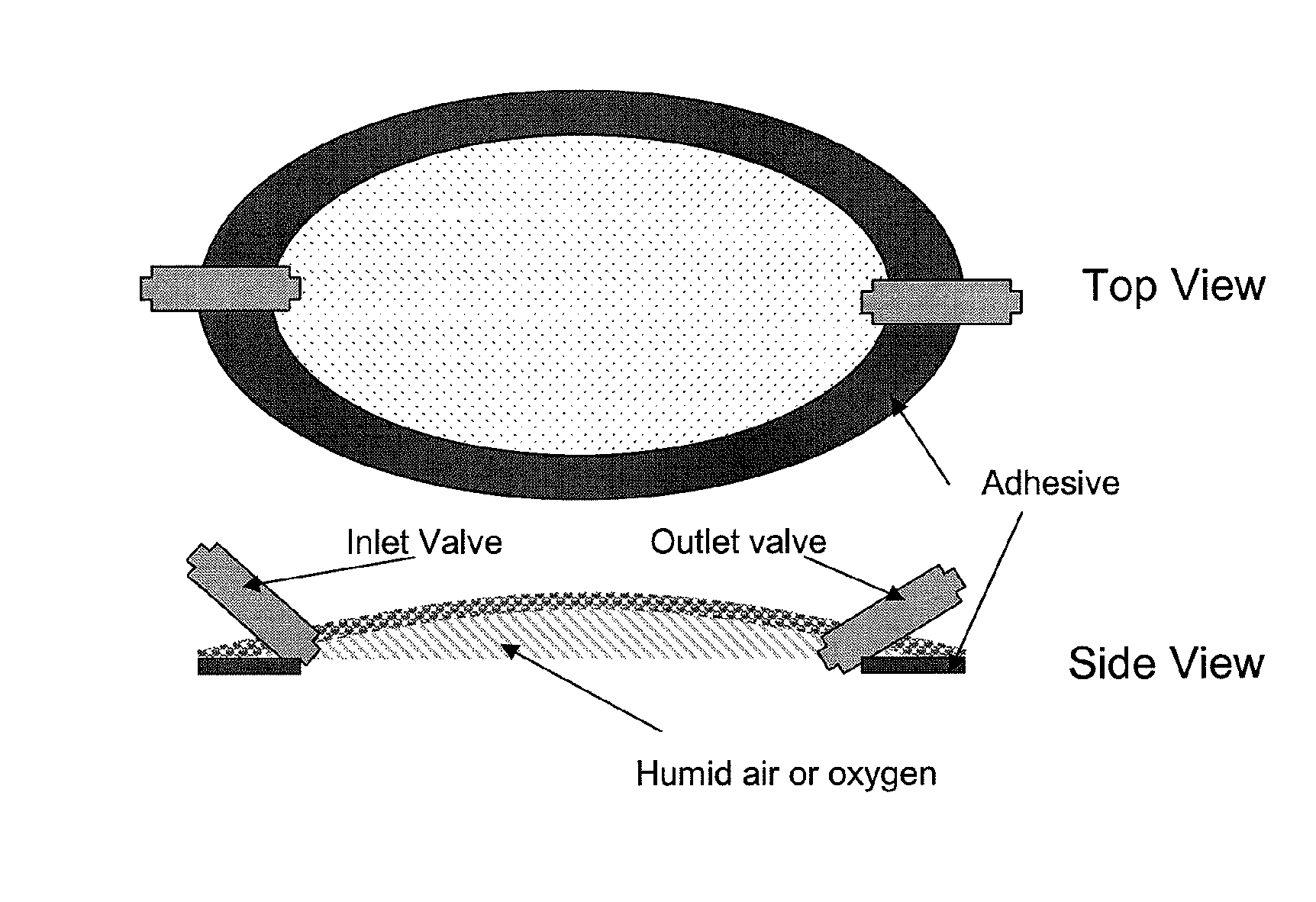
Silicone hydrogels for tissue adhesives and tissue dressing applications
PatentInactiveUS20110086077A1
Innovation
- Silicone hydrogels with high oxygen permeability and water content, formulated as films or sprays, are used to create a biocompatible dressing that maintains a moist environment while allowing for controlled drug release and antimicrobial functionality, tailored for different wound types and healing stages through variations in hydrophilic content and silicone concentration.
Silicone hydrogels for tissue adhesives and tissue dressing applications
PatentInactiveEP2217290A2
Innovation
- Silicone hydrogels with high oxygen permeability and water content, formulated as films or sprays, are used to create dressings that promote wound healing by allowing controlled moisture and oxygen transmission, while also incorporating antimicrobial agents and biocompatible components for infection prevention and tissue adhesion.
Regulatory Framework for Wound Care Products
The regulatory framework for wound care products, including occlusive dressing materials such as hydrogels and silicone barriers, is complex and multifaceted. In the United States, these products are primarily regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under the Medical Device Regulations. The FDA classifies wound dressings into different categories based on their intended use and risk level, with most occlusive dressings falling under Class I or Class II devices.
Class I devices are generally subject to the least regulatory control and are often exempt from premarket notification requirements. However, manufacturers must still register their establishment and list their devices with the FDA. Class II devices, which may include more advanced occlusive dressings, typically require a 510(k) premarket notification submission to demonstrate substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device.
In the European Union, wound care products are regulated under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745. This regulation, which replaced the previous Medical Device Directive (MDD), imposes stricter requirements for clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and traceability. Occlusive dressings are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb devices under the MDR, depending on their specific characteristics and intended use.
The regulatory framework also encompasses quality management systems, such as ISO 13485, which is specifically designed for medical device manufacturers. Compliance with this standard is often required or strongly recommended by regulatory bodies worldwide. It ensures that manufacturers have robust processes in place for design, development, production, and post-market surveillance of their products.
Safety and performance standards play a crucial role in the regulatory landscape for wound care products. Standards such as ISO 10993 for biocompatibility testing and ASTM F2258 for absorbent wound dressings provide guidelines for evaluating the safety and efficacy of these materials. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with these standards as part of their regulatory submissions.
Post-market surveillance is an integral part of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers are required to monitor the performance and safety of their products after they have been placed on the market. This includes collecting and analyzing data on adverse events, implementing corrective actions when necessary, and reporting significant incidents to regulatory authorities.
The regulatory landscape for wound care products is continually evolving, with increasing emphasis on clinical evidence and real-world performance data. Regulatory bodies are also focusing more on unique device identification (UDI) systems to enhance traceability and facilitate efficient recalls if needed. As new technologies emerge in the field of occlusive dressings, including advanced hydrogels and silicone barriers, regulatory frameworks may need to adapt to address novel materials and their potential risks and benefits.
Class I devices are generally subject to the least regulatory control and are often exempt from premarket notification requirements. However, manufacturers must still register their establishment and list their devices with the FDA. Class II devices, which may include more advanced occlusive dressings, typically require a 510(k) premarket notification submission to demonstrate substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device.
In the European Union, wound care products are regulated under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745. This regulation, which replaced the previous Medical Device Directive (MDD), imposes stricter requirements for clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and traceability. Occlusive dressings are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb devices under the MDR, depending on their specific characteristics and intended use.
The regulatory framework also encompasses quality management systems, such as ISO 13485, which is specifically designed for medical device manufacturers. Compliance with this standard is often required or strongly recommended by regulatory bodies worldwide. It ensures that manufacturers have robust processes in place for design, development, production, and post-market surveillance of their products.
Safety and performance standards play a crucial role in the regulatory landscape for wound care products. Standards such as ISO 10993 for biocompatibility testing and ASTM F2258 for absorbent wound dressings provide guidelines for evaluating the safety and efficacy of these materials. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with these standards as part of their regulatory submissions.
Post-market surveillance is an integral part of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers are required to monitor the performance and safety of their products after they have been placed on the market. This includes collecting and analyzing data on adverse events, implementing corrective actions when necessary, and reporting significant incidents to regulatory authorities.
The regulatory landscape for wound care products is continually evolving, with increasing emphasis on clinical evidence and real-world performance data. Regulatory bodies are also focusing more on unique device identification (UDI) systems to enhance traceability and facilitate efficient recalls if needed. As new technologies emerge in the field of occlusive dressings, including advanced hydrogels and silicone barriers, regulatory frameworks may need to adapt to address novel materials and their potential risks and benefits.
Cost-Effectiveness of Occlusive Dressing Materials
When evaluating the cost-effectiveness of occlusive dressing materials, particularly comparing hydrogel and silicone barrier dressings, several factors must be considered. These include material costs, application frequency, healing time, and overall treatment outcomes.
Hydrogel dressings are generally less expensive per unit compared to silicone barrier dressings. However, they often require more frequent changes, which can increase the total cost of treatment over time. Hydrogels typically need replacement every 1-3 days, depending on the wound condition and exudate levels.
Silicone barrier dressings, while initially more expensive, can remain in place for up to 7 days. This reduced frequency of dressing changes can lead to lower overall treatment costs, especially in terms of nursing time and resources. Additionally, silicone dressings are often associated with less skin trauma during removal, potentially reducing the need for additional treatments.
The healing time associated with each dressing type is a crucial factor in cost-effectiveness analysis. Some studies suggest that silicone dressings may promote faster wound healing in certain types of wounds, which could result in shorter overall treatment duration and, consequently, lower total costs.
It's important to consider the specific wound type when assessing cost-effectiveness. For highly exudative wounds, hydrogels may require more frequent changes, potentially increasing costs. In contrast, silicone dressings may be more cost-effective for wounds with moderate to low exudate levels.
Patient comfort and ease of use also play a role in cost-effectiveness. Silicone dressings are often preferred by patients due to their gentle adhesion and easy removal, which can improve treatment adherence and potentially reduce complications that could extend treatment time and increase costs.
The impact on nursing time is another significant factor. Silicone dressings, with their less frequent change requirements, can reduce the time nurses spend on wound care, allowing for more efficient allocation of healthcare resources.
In terms of long-term cost-effectiveness, the potential for reduced scarring and improved wound outcomes associated with silicone dressings may lead to fewer follow-up treatments and better overall patient satisfaction, which can translate to cost savings for healthcare systems.
While the upfront costs of silicone barrier dressings are higher, their potential for less frequent changes, faster healing times, and improved patient outcomes may result in greater cost-effectiveness over the course of treatment compared to hydrogel dressings. However, a comprehensive cost-effectiveness analysis should consider the specific wound characteristics, treatment duration, and individual patient factors to determine the most appropriate and cost-effective dressing choice.
Hydrogel dressings are generally less expensive per unit compared to silicone barrier dressings. However, they often require more frequent changes, which can increase the total cost of treatment over time. Hydrogels typically need replacement every 1-3 days, depending on the wound condition and exudate levels.
Silicone barrier dressings, while initially more expensive, can remain in place for up to 7 days. This reduced frequency of dressing changes can lead to lower overall treatment costs, especially in terms of nursing time and resources. Additionally, silicone dressings are often associated with less skin trauma during removal, potentially reducing the need for additional treatments.
The healing time associated with each dressing type is a crucial factor in cost-effectiveness analysis. Some studies suggest that silicone dressings may promote faster wound healing in certain types of wounds, which could result in shorter overall treatment duration and, consequently, lower total costs.
It's important to consider the specific wound type when assessing cost-effectiveness. For highly exudative wounds, hydrogels may require more frequent changes, potentially increasing costs. In contrast, silicone dressings may be more cost-effective for wounds with moderate to low exudate levels.
Patient comfort and ease of use also play a role in cost-effectiveness. Silicone dressings are often preferred by patients due to their gentle adhesion and easy removal, which can improve treatment adherence and potentially reduce complications that could extend treatment time and increase costs.
The impact on nursing time is another significant factor. Silicone dressings, with their less frequent change requirements, can reduce the time nurses spend on wound care, allowing for more efficient allocation of healthcare resources.
In terms of long-term cost-effectiveness, the potential for reduced scarring and improved wound outcomes associated with silicone dressings may lead to fewer follow-up treatments and better overall patient satisfaction, which can translate to cost savings for healthcare systems.
While the upfront costs of silicone barrier dressings are higher, their potential for less frequent changes, faster healing times, and improved patient outcomes may result in greater cost-effectiveness over the course of treatment compared to hydrogel dressings. However, a comprehensive cost-effectiveness analysis should consider the specific wound characteristics, treatment duration, and individual patient factors to determine the most appropriate and cost-effective dressing choice.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!