Occlusive Dressing Wear Time: Testing Adhesion And Skin Irritation
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Occlusive Dressing Evolution and Objectives
Occlusive dressings have undergone significant evolution since their inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for wound management, these dressings have become integral to various medical applications, including post-operative care, burn treatment, and chronic wound management. The primary objective of occlusive dressings is to create a moist wound environment that promotes healing while protecting the wound from external contaminants.
The evolution of occlusive dressings has been driven by advancements in material science and a deeper understanding of wound healing processes. Early occlusive dressings were simple plastic films, which, while effective in maintaining moisture, lacked breathability and often led to maceration of the surrounding skin. This limitation prompted research into more advanced materials that could balance moisture retention with gas exchange.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the introduction of semi-permeable films marked a significant milestone. These materials allowed for the passage of oxygen and water vapor while still maintaining a barrier against bacteria and external moisture. This development greatly improved the wearability and effectiveness of occlusive dressings, reducing the risk of skin irritation and improving overall patient comfort.
The turn of the millennium saw the emergence of "intelligent" occlusive dressings. These advanced products incorporated features such as antimicrobial agents, growth factors, and even sensors to monitor wound healing progress. The integration of nanotechnology has further enhanced the capabilities of occlusive dressings, allowing for more precise control of moisture levels and the targeted delivery of therapeutic agents.
Current research in occlusive dressings focuses on several key objectives. Firstly, there is a push towards developing materials with improved adhesion properties that can maintain a secure seal for extended periods without causing skin irritation. This is particularly crucial for patients requiring long-term dressing applications or those with sensitive skin.
Secondly, researchers are exploring ways to enhance the breathability of occlusive dressings while maintaining their protective properties. This involves developing new polymer blends and manufacturing techniques that allow for optimal gas exchange without compromising the dressing's barrier function.
Another important objective is the creation of "smart" dressings that can adapt to the changing needs of the wound environment. This includes dressings that can adjust their permeability based on wound exudate levels or release therapeutic agents in response to specific wound conditions.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability in occlusive dressing development. Researchers are investigating biodegradable materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes to reduce the environmental impact of these medical devices.
The evolution of occlusive dressings has been driven by advancements in material science and a deeper understanding of wound healing processes. Early occlusive dressings were simple plastic films, which, while effective in maintaining moisture, lacked breathability and often led to maceration of the surrounding skin. This limitation prompted research into more advanced materials that could balance moisture retention with gas exchange.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the introduction of semi-permeable films marked a significant milestone. These materials allowed for the passage of oxygen and water vapor while still maintaining a barrier against bacteria and external moisture. This development greatly improved the wearability and effectiveness of occlusive dressings, reducing the risk of skin irritation and improving overall patient comfort.
The turn of the millennium saw the emergence of "intelligent" occlusive dressings. These advanced products incorporated features such as antimicrobial agents, growth factors, and even sensors to monitor wound healing progress. The integration of nanotechnology has further enhanced the capabilities of occlusive dressings, allowing for more precise control of moisture levels and the targeted delivery of therapeutic agents.
Current research in occlusive dressings focuses on several key objectives. Firstly, there is a push towards developing materials with improved adhesion properties that can maintain a secure seal for extended periods without causing skin irritation. This is particularly crucial for patients requiring long-term dressing applications or those with sensitive skin.
Secondly, researchers are exploring ways to enhance the breathability of occlusive dressings while maintaining their protective properties. This involves developing new polymer blends and manufacturing techniques that allow for optimal gas exchange without compromising the dressing's barrier function.
Another important objective is the creation of "smart" dressings that can adapt to the changing needs of the wound environment. This includes dressings that can adjust their permeability based on wound exudate levels or release therapeutic agents in response to specific wound conditions.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability in occlusive dressing development. Researchers are investigating biodegradable materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes to reduce the environmental impact of these medical devices.
Market Analysis for Extended-Wear Dressings
The market for extended-wear dressings has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for advanced wound care solutions and the rising prevalence of chronic wounds. This segment of the wound care market is particularly attractive due to its potential to reduce healthcare costs, improve patient outcomes, and enhance overall quality of life for individuals with chronic wounds or those recovering from surgical procedures.
Extended-wear dressings offer several advantages over traditional dressings, including longer wear times, reduced frequency of dressing changes, and improved moisture management. These benefits have led to a growing adoption rate among healthcare providers and patients alike. The global market for advanced wound dressings, which includes extended-wear options, was valued at approximately $7 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach over $10 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6%.
Key factors driving market growth include the aging population, increasing incidence of chronic diseases such as diabetes and obesity, and advancements in wound care technologies. The rise in surgical procedures worldwide has also contributed to the expanding market for extended-wear dressings, as these products are often used in post-operative care to promote healing and reduce the risk of infection.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the extended-wear dressing market, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness of advanced wound care products.
The market landscape is characterized by intense competition among major players such as 3M, Smith & Nephew, Mölnlycke Health Care, and ConvaTec. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products with enhanced adhesion properties and reduced skin irritation. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards the development of antimicrobial extended-wear dressings to address the rising concern of healthcare-associated infections.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of advanced wound care products and reimbursement issues in some regions. However, the increasing focus on value-based healthcare and the potential for extended-wear dressings to reduce overall treatment costs are expected to drive continued market expansion. As healthcare systems worldwide seek to optimize patient care while managing costs, the demand for extended-wear dressings that can demonstrate improved clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness is likely to grow substantially in the coming years.
Extended-wear dressings offer several advantages over traditional dressings, including longer wear times, reduced frequency of dressing changes, and improved moisture management. These benefits have led to a growing adoption rate among healthcare providers and patients alike. The global market for advanced wound dressings, which includes extended-wear options, was valued at approximately $7 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach over $10 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6%.
Key factors driving market growth include the aging population, increasing incidence of chronic diseases such as diabetes and obesity, and advancements in wound care technologies. The rise in surgical procedures worldwide has also contributed to the expanding market for extended-wear dressings, as these products are often used in post-operative care to promote healing and reduce the risk of infection.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the extended-wear dressing market, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness of advanced wound care products.
The market landscape is characterized by intense competition among major players such as 3M, Smith & Nephew, Mölnlycke Health Care, and ConvaTec. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products with enhanced adhesion properties and reduced skin irritation. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards the development of antimicrobial extended-wear dressings to address the rising concern of healthcare-associated infections.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of advanced wound care products and reimbursement issues in some regions. However, the increasing focus on value-based healthcare and the potential for extended-wear dressings to reduce overall treatment costs are expected to drive continued market expansion. As healthcare systems worldwide seek to optimize patient care while managing costs, the demand for extended-wear dressings that can demonstrate improved clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness is likely to grow substantially in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Adhesion and Skin Compatibility
The development of occlusive dressings has significantly improved wound care management, but challenges persist in achieving optimal adhesion and skin compatibility. One of the primary issues is balancing strong adhesion with minimal skin irritation. Dressings that adhere too strongly can cause trauma upon removal, while those with weak adhesion may fail to maintain a proper seal, compromising wound healing.
Skin irritation remains a significant concern, particularly for patients with sensitive skin or those requiring long-term dressing use. The occlusive nature of these dressings can create a moist environment that, while beneficial for wound healing, may also promote skin maceration and increase the risk of irritation or allergic reactions. This is especially problematic in areas with high moisture or movement, such as joints or skin folds.
Another challenge lies in the variability of skin types and conditions across patients. A dressing that performs well on one individual may cause irritation or poor adhesion on another, making it difficult to develop a universally effective solution. This variability extends to different body areas, with some locations proving more challenging for dressing adherence than others.
The duration of wear time presents a complex problem. Longer wear times are desirable for reducing dressing changes and associated costs, but they also increase the risk of skin damage and irritation. Achieving an optimal balance between extended wear time and skin health is a key focus of current research and development efforts.
Environmental factors further complicate adhesion and skin compatibility. Exposure to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and physical stress can all impact dressing performance. Developing adhesives that maintain their properties under various conditions while remaining gentle on the skin is an ongoing challenge.
Lastly, there is a growing demand for dressings that not only adhere well and minimize irritation but also actively contribute to wound healing. Incorporating bioactive components or drug delivery systems into dressings without compromising their adhesive properties or increasing skin irritation potential presents a significant technical hurdle.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in materials science, bioengineering, and clinical research. Innovations in adhesive technologies, such as silicone-based adhesives and intelligent polymers, show promise in improving both adhesion and skin compatibility. However, further research is needed to optimize these solutions for diverse patient populations and wound types.
Skin irritation remains a significant concern, particularly for patients with sensitive skin or those requiring long-term dressing use. The occlusive nature of these dressings can create a moist environment that, while beneficial for wound healing, may also promote skin maceration and increase the risk of irritation or allergic reactions. This is especially problematic in areas with high moisture or movement, such as joints or skin folds.
Another challenge lies in the variability of skin types and conditions across patients. A dressing that performs well on one individual may cause irritation or poor adhesion on another, making it difficult to develop a universally effective solution. This variability extends to different body areas, with some locations proving more challenging for dressing adherence than others.
The duration of wear time presents a complex problem. Longer wear times are desirable for reducing dressing changes and associated costs, but they also increase the risk of skin damage and irritation. Achieving an optimal balance between extended wear time and skin health is a key focus of current research and development efforts.
Environmental factors further complicate adhesion and skin compatibility. Exposure to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and physical stress can all impact dressing performance. Developing adhesives that maintain their properties under various conditions while remaining gentle on the skin is an ongoing challenge.
Lastly, there is a growing demand for dressings that not only adhere well and minimize irritation but also actively contribute to wound healing. Incorporating bioactive components or drug delivery systems into dressings without compromising their adhesive properties or increasing skin irritation potential presents a significant technical hurdle.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in materials science, bioengineering, and clinical research. Innovations in adhesive technologies, such as silicone-based adhesives and intelligent polymers, show promise in improving both adhesion and skin compatibility. However, further research is needed to optimize these solutions for diverse patient populations and wound types.
Existing Methods for Adhesion and Irritation Testing
01 Adhesive composition for occlusive dressings
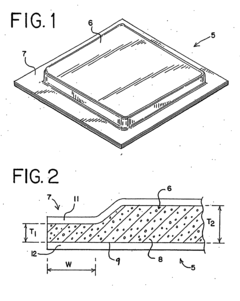
Specialized adhesive compositions are developed for occlusive dressings to improve adhesion while minimizing skin irritation. These compositions often include skin-friendly polymers and additives that provide strong adhesion but allow for gentle removal. The formulations may incorporate moisture-absorbing components to manage wound exudate and maintain a moist healing environment.- Adhesive composition for occlusive dressings: Specialized adhesive compositions are developed for occlusive dressings to improve adhesion while minimizing skin irritation. These compositions often include skin-friendly polymers, tackifiers, and plasticizers that provide strong adhesion but allow for gentle removal. Some formulations incorporate moisture-absorbing components to manage wound exudate and maintain a moist healing environment.
- Skin-friendly backing materials: The choice of backing material for occlusive dressings plays a crucial role in reducing skin irritation. Breathable films, non-woven fabrics, and silicone-based materials are used to allow moisture vapor transmission while maintaining an occlusive environment. These materials help prevent maceration of the skin and reduce the risk of irritation caused by trapped moisture or heat.
- Incorporation of skin-soothing agents: To address skin irritation concerns, occlusive dressings may incorporate various skin-soothing agents. These can include natural extracts, anti-inflammatory compounds, and moisturizing ingredients. Such additives help to calm the skin, reduce redness, and maintain skin health during prolonged dressing wear.
- Controlled release of active ingredients: Advanced occlusive dressings feature controlled release mechanisms for active ingredients. This approach allows for the gradual delivery of antimicrobial agents, growth factors, or other therapeutic compounds directly to the wound site. By controlling the release rate, these dressings can provide sustained benefits while minimizing potential skin irritation from high concentrations of active ingredients.
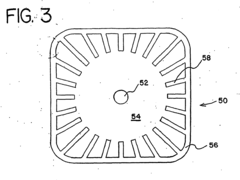
- Innovative dressing designs for reduced irritation: Novel dressing designs are developed to minimize skin irritation while maintaining occlusion. These may include multi-layer structures, perforated films, or dressings with specialized edge designs. Some innovations focus on creating dressings that conform better to body contours or incorporate stress-distributing elements to reduce mechanical irritation during movement.
02 Skin-friendly backing materials
The choice of backing materials for occlusive dressings plays a crucial role in reducing skin irritation. Breathable films, non-woven fabrics, and silicone-based materials are used to allow moisture vapor transmission while maintaining an occlusive environment. These materials help prevent maceration of the skin and reduce the risk of irritation caused by trapped moisture or heat.Expand Specific Solutions03 Incorporation of skin-soothing agents
Occlusive dressings may incorporate skin-soothing agents to reduce irritation and promote comfort. These agents can include natural extracts, anti-inflammatory compounds, or moisturizing ingredients that help maintain skin integrity. The addition of these components aims to minimize adverse skin reactions while supporting the healing process.Expand Specific Solutions04 Controlled release of active ingredients
Advanced occlusive dressings may feature controlled release mechanisms for active ingredients. This approach allows for the gradual delivery of therapeutic agents, such as antimicrobials or growth factors, directly to the wound site. By controlling the release rate, these dressings can maintain effective treatment levels while minimizing potential skin irritation from high concentrations of active ingredients.Expand Specific Solutions05 Improved dressing design for reduced skin stress
Innovative dressing designs focus on reducing mechanical stress on the skin to minimize irritation. These designs may include tapered edges, multi-layer constructions, or flexible materials that conform to body contours. Some dressings incorporate stress-distributing elements or allow for partial removal and reapplication, further reducing the risk of skin damage during wear or removal.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers and Market Competitors
The occlusive dressing wear time market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for advanced wound care solutions. The market size is expanding due to rising chronic wounds and surgical procedures globally. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Coloplast A/S, 3M Innovative Properties Co., and DuPont de Nemours, Inc. leading innovation in adhesive technologies and skin-friendly materials. These industry leaders are focusing on developing dressings with improved wear time, adhesion, and reduced skin irritation. Emerging players like Worldwide Innovative Healthcare, Inc. are also contributing to market dynamism by introducing novel, cost-effective solutions. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and specialized wound care firms, all striving to enhance product performance and patient comfort.
Coloplast A/S
Technical Solution: Coloplast A/S has developed advanced occlusive dressings with enhanced adhesion and reduced skin irritation. Their technology incorporates a unique multi-layer design that combines a breathable top film with a skin-friendly adhesive layer. This structure allows for extended wear time while maintaining skin integrity. The company's dressings utilize a proprietary adhesive formulation that balances strong adherence with gentle removal, minimizing trauma to periwound skin. Additionally, Coloplast has implemented a moisture management system within their dressings, which helps control exudate levels and creates an optimal healing environment[1][3]. Their latest innovations include incorporating silicone-based adhesives and hydrocolloid materials to further improve wear time and reduce the risk of maceration[5].
Strengths: Extended wear time, reduced skin irritation, and effective moisture management. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to basic dressings and may require more careful application technique.
Nitto Denko Corp.
Technical Solution: Nitto Denko Corp. has pioneered occlusive dressing technology with a focus on long-term wear and minimal skin irritation. Their approach involves the use of advanced polymer science to create breathable films that maintain a moist wound environment while allowing gaseous exchange. The company's dressings feature a gradient adhesive system, where adhesive strength varies across the surface to optimize both secure attachment and easy removal[2]. Nitto Denko has also developed a novel microporous structure in their adhesives, which allows for better conformability to skin contours and reduces shear forces that can lead to irritation[4]. Recent advancements include the integration of nanoparticle technology to enhance antimicrobial properties without compromising skin compatibility[6].
Strengths: Excellent conformability, balanced adhesion for secure attachment and easy removal, and advanced antimicrobial properties. Weaknesses: May be more expensive than traditional dressings and could require specialized training for optimal application.
Innovative Approaches in Dressing Materials
Extended stay-on wound dressing
PatentInactiveHK1115337A
Innovation
- A dressing layer comprising 20-60% water-absorbable material, 5-60% hot melt acrylic adhesive, 5-40% tackifier, 5-30% elastomers, and 5-30% extender, which combines hydrocolloid adhesive with acrylic to provide extended stay-on time without pain or irritation during removal.
Adhesive patch and patch preparation
PatentInactiveUS20120027840A1
Innovation
- Regulating the logarithmic decrement and maximum shear displacement of the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer, determined by the rigid-pendulum free-damped oscillation method, to achieve a range of 0.03 to 0.35 and 18 μm to 1,000 μm respectively, along with a percentage recovery of 85% or higher, which reduces skin irritation and prevents peeling.
Regulatory Framework for Medical Dressings
The regulatory framework for medical dressings plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of occlusive dressings, particularly in relation to wear time, adhesion, and skin irritation. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of medical dressings under the Medical Device Regulations.
The FDA classifies medical dressings into different categories based on their intended use and risk level. Occlusive dressings are typically classified as Class II medical devices, requiring a 510(k) premarket notification submission. This process involves demonstrating substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device in terms of safety and effectiveness.
For occlusive dressings, manufacturers must provide evidence of biocompatibility, adhesion performance, and skin irritation potential. The ISO 10993 series of standards is commonly used to evaluate the biocompatibility of medical devices, including dressings. Specifically, ISO 10993-10 addresses tests for irritation and skin sensitization.
Adhesion testing for occlusive dressings often follows ASTM D3330 or similar standards, which measure peel adhesion strength. The FDA may require data on adhesion performance over the intended wear time to ensure the dressing remains in place throughout its use.
Skin irritation testing typically involves in vitro methods or controlled human studies. The OECD Test Guideline 439 for in vitro skin irritation is widely accepted, while human patch tests may be conducted following ISO 10993-10 guidelines.
In the European Union, medical dressings fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). The MDR requires manufacturers to demonstrate compliance with Essential Requirements, including biocompatibility and performance characteristics. The CE marking process involves a conformity assessment, which may require involvement of a Notified Body for Class II devices.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) regulates medical dressings under the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act. The approval process involves submitting data on safety, efficacy, and quality, with specific requirements for skin-contacting devices.
Globally, the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) works to harmonize regulatory approaches across different regions. Their guidance documents often influence national regulations and can provide valuable insights for manufacturers developing occlusive dressings.
Regulatory bodies increasingly emphasize post-market surveillance and real-world evidence. Manufacturers are expected to monitor the performance of their dressings after market release, including any adverse events related to wear time, adhesion failures, or skin irritation.
The FDA classifies medical dressings into different categories based on their intended use and risk level. Occlusive dressings are typically classified as Class II medical devices, requiring a 510(k) premarket notification submission. This process involves demonstrating substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device in terms of safety and effectiveness.
For occlusive dressings, manufacturers must provide evidence of biocompatibility, adhesion performance, and skin irritation potential. The ISO 10993 series of standards is commonly used to evaluate the biocompatibility of medical devices, including dressings. Specifically, ISO 10993-10 addresses tests for irritation and skin sensitization.
Adhesion testing for occlusive dressings often follows ASTM D3330 or similar standards, which measure peel adhesion strength. The FDA may require data on adhesion performance over the intended wear time to ensure the dressing remains in place throughout its use.
Skin irritation testing typically involves in vitro methods or controlled human studies. The OECD Test Guideline 439 for in vitro skin irritation is widely accepted, while human patch tests may be conducted following ISO 10993-10 guidelines.
In the European Union, medical dressings fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). The MDR requires manufacturers to demonstrate compliance with Essential Requirements, including biocompatibility and performance characteristics. The CE marking process involves a conformity assessment, which may require involvement of a Notified Body for Class II devices.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) regulates medical dressings under the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act. The approval process involves submitting data on safety, efficacy, and quality, with specific requirements for skin-contacting devices.
Globally, the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) works to harmonize regulatory approaches across different regions. Their guidance documents often influence national regulations and can provide valuable insights for manufacturers developing occlusive dressings.
Regulatory bodies increasingly emphasize post-market surveillance and real-world evidence. Manufacturers are expected to monitor the performance of their dressings after market release, including any adverse events related to wear time, adhesion failures, or skin irritation.
Patient Comfort and Compliance Factors
Patient comfort and compliance are critical factors in the successful implementation of occlusive dressings, particularly when testing adhesion and skin irritation. The wear time of these dressings is directly influenced by how comfortable patients find them and their willingness to adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen.
One of the primary considerations in patient comfort is the flexibility and conformability of the dressing material. Occlusive dressings that can adapt to the contours of the body and allow for natural movement are more likely to be tolerated for extended periods. Materials that mimic the elasticity of skin, such as silicone-based adhesives, have shown promise in improving patient comfort and reducing the likelihood of premature dressing removal.
The breathability of the dressing also plays a crucial role in patient comfort. While occlusive dressings are designed to create a barrier, those that allow some degree of moisture vapor transmission can help prevent maceration of the skin and reduce the sensation of heat and humidity that patients often report as uncomfortable. Balancing occlusion with breathability is an ongoing challenge in dressing design.
Skin sensitivity is another key factor affecting patient compliance. Hypoallergenic materials and adhesives that minimize the risk of allergic reactions or skin irritation are essential for prolonged wear times. Some advanced dressings incorporate skin-friendly components such as aloe vera or other soothing agents to reduce irritation and improve overall comfort.
The ease of application and removal of the dressing can significantly impact patient compliance. Dressings that are simple to apply correctly and remove with minimal discomfort are more likely to be used as directed. This is particularly important for patients who may need to change dressings themselves or have them changed by non-professional caregivers.
Pain management during dressing wear and removal is another critical aspect of patient comfort. Dressings that incorporate pain-reducing technologies, such as silicone interfaces or controlled adhesion strength, can greatly enhance patient experience and willingness to continue treatment.
Education and clear communication about the expected sensations and proper care of the dressing site can also improve compliance. Patients who understand the importance of maintaining the dressing and are prepared for potential discomfort are more likely to persevere with the prescribed wear time.
Lastly, the psychological impact of wearing an occlusive dressing should not be underestimated. Dressings that are discreet and do not significantly alter the patient's appearance or lifestyle are more likely to be accepted for longer periods. This includes considerations such as the visual appearance of the dressing and its impact on daily activities and clothing choices.
One of the primary considerations in patient comfort is the flexibility and conformability of the dressing material. Occlusive dressings that can adapt to the contours of the body and allow for natural movement are more likely to be tolerated for extended periods. Materials that mimic the elasticity of skin, such as silicone-based adhesives, have shown promise in improving patient comfort and reducing the likelihood of premature dressing removal.
The breathability of the dressing also plays a crucial role in patient comfort. While occlusive dressings are designed to create a barrier, those that allow some degree of moisture vapor transmission can help prevent maceration of the skin and reduce the sensation of heat and humidity that patients often report as uncomfortable. Balancing occlusion with breathability is an ongoing challenge in dressing design.
Skin sensitivity is another key factor affecting patient compliance. Hypoallergenic materials and adhesives that minimize the risk of allergic reactions or skin irritation are essential for prolonged wear times. Some advanced dressings incorporate skin-friendly components such as aloe vera or other soothing agents to reduce irritation and improve overall comfort.
The ease of application and removal of the dressing can significantly impact patient compliance. Dressings that are simple to apply correctly and remove with minimal discomfort are more likely to be used as directed. This is particularly important for patients who may need to change dressings themselves or have them changed by non-professional caregivers.
Pain management during dressing wear and removal is another critical aspect of patient comfort. Dressings that incorporate pain-reducing technologies, such as silicone interfaces or controlled adhesion strength, can greatly enhance patient experience and willingness to continue treatment.
Education and clear communication about the expected sensations and proper care of the dressing site can also improve compliance. Patients who understand the importance of maintaining the dressing and are prepared for potential discomfort are more likely to persevere with the prescribed wear time.
Lastly, the psychological impact of wearing an occlusive dressing should not be underestimated. Dressings that are discreet and do not significantly alter the patient's appearance or lifestyle are more likely to be accepted for longer periods. This includes considerations such as the visual appearance of the dressing and its impact on daily activities and clothing choices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!