Occlusive Dressing Regulatory & Safety Checklist For Clinical Use
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Occlusive Dressing Evolution and Objectives
Occlusive dressings have undergone significant evolution since their inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed as simple adhesive bandages, these dressings have transformed into sophisticated medical devices designed to create and maintain a moist wound environment, crucial for optimal healing. The primary objective of occlusive dressings is to promote faster wound healing by creating a barrier that prevents contamination while maintaining a moist environment that facilitates cellular migration and proliferation.
The evolution of occlusive dressings has been driven by advancements in material science and a deeper understanding of wound healing processes. Early occlusive dressings were primarily composed of polyethylene films, which provided a basic barrier but lacked breathability. As research progressed, new materials such as hydrocolloids, hydrogels, and semi-permeable films were introduced, offering improved moisture management and gas exchange capabilities.
A significant milestone in the development of occlusive dressings was the introduction of transparent film dressings in the 1970s. These dressings allowed for visual inspection of the wound without removal, reducing the risk of contamination and minimizing patient discomfort during dressing changes. This innovation marked a shift towards more patient-centric wound care solutions.
The objectives of modern occlusive dressings have expanded beyond basic wound protection. Current goals include promoting autolytic debridement, managing exudate, reducing pain, and even incorporating antimicrobial properties to prevent infection. Advanced occlusive dressings now aim to create an ideal microenvironment that supports the body's natural healing mechanisms while addressing specific wound types and patient needs.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of smart occlusive dressings. These innovative products incorporate sensors that can monitor wound healing progress, detect infection, and even deliver therapeutic agents on-demand. The integration of nanotechnology and bioactive materials in occlusive dressings represents the cutting edge of wound care, with objectives focused on personalized treatment and improved patient outcomes.
As the field continues to evolve, the overarching goal of occlusive dressing development is to create products that not only accelerate healing but also reduce healthcare costs by minimizing complications and shortening treatment durations. Future objectives may include the development of biodegradable dressings that eliminate the need for removal, as well as dressings that can adapt to changing wound conditions autonomously.
The evolution of occlusive dressings has been driven by advancements in material science and a deeper understanding of wound healing processes. Early occlusive dressings were primarily composed of polyethylene films, which provided a basic barrier but lacked breathability. As research progressed, new materials such as hydrocolloids, hydrogels, and semi-permeable films were introduced, offering improved moisture management and gas exchange capabilities.
A significant milestone in the development of occlusive dressings was the introduction of transparent film dressings in the 1970s. These dressings allowed for visual inspection of the wound without removal, reducing the risk of contamination and minimizing patient discomfort during dressing changes. This innovation marked a shift towards more patient-centric wound care solutions.
The objectives of modern occlusive dressings have expanded beyond basic wound protection. Current goals include promoting autolytic debridement, managing exudate, reducing pain, and even incorporating antimicrobial properties to prevent infection. Advanced occlusive dressings now aim to create an ideal microenvironment that supports the body's natural healing mechanisms while addressing specific wound types and patient needs.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of smart occlusive dressings. These innovative products incorporate sensors that can monitor wound healing progress, detect infection, and even deliver therapeutic agents on-demand. The integration of nanotechnology and bioactive materials in occlusive dressings represents the cutting edge of wound care, with objectives focused on personalized treatment and improved patient outcomes.
As the field continues to evolve, the overarching goal of occlusive dressing development is to create products that not only accelerate healing but also reduce healthcare costs by minimizing complications and shortening treatment durations. Future objectives may include the development of biodegradable dressings that eliminate the need for removal, as well as dressings that can adapt to changing wound conditions autonomously.
Clinical Demand Analysis
The clinical demand for occlusive dressings has been steadily increasing due to their effectiveness in wound management and infection prevention. These dressings create a moist environment that promotes healing while providing a barrier against external contaminants. Healthcare professionals across various specialties, including surgery, dermatology, and emergency medicine, have recognized the benefits of occlusive dressings in patient care.
In acute care settings, occlusive dressings are widely used for post-operative wound care, particularly in abdominal and orthopedic surgeries. They help reduce the risk of surgical site infections and promote faster healing by maintaining optimal wound moisture levels. The demand for these dressings in surgical units has led to the development of specialized products designed for specific surgical procedures.
Chronic wound management represents another significant area of clinical demand for occlusive dressings. Patients with diabetic ulcers, pressure sores, and venous leg ulcers benefit from the protective and healing properties of these dressings. The aging population and increasing prevalence of chronic diseases have contributed to the growing need for advanced wound care solutions, including occlusive dressings.
Burns and trauma care units also rely heavily on occlusive dressings to manage complex wounds and prevent infection. The ability of these dressings to create an optimal healing environment while allowing for easy monitoring of the wound has made them indispensable in burn treatment protocols.
The demand for occlusive dressings extends beyond hospital settings to outpatient clinics and home care. As healthcare systems aim to reduce hospital stays and promote outpatient care, there is an increasing need for easy-to-use occlusive dressings that patients or caregivers can apply and manage at home. This trend has driven innovation in user-friendly designs and application methods.
In response to the diverse clinical needs, manufacturers have developed a wide range of occlusive dressing products. These include transparent film dressings, hydrocolloid dressings, and foam dressings with occlusive properties. Each type caters to specific wound characteristics and treatment goals, allowing healthcare providers to select the most appropriate dressing for individual patient needs.
The clinical demand analysis also reveals a growing emphasis on antimicrobial occlusive dressings. With the rise of antibiotic-resistant infections, healthcare facilities are seeking dressings that not only provide occlusion but also offer antimicrobial protection. This has led to the development of dressings incorporating silver, iodine, or other antimicrobial agents.
In acute care settings, occlusive dressings are widely used for post-operative wound care, particularly in abdominal and orthopedic surgeries. They help reduce the risk of surgical site infections and promote faster healing by maintaining optimal wound moisture levels. The demand for these dressings in surgical units has led to the development of specialized products designed for specific surgical procedures.
Chronic wound management represents another significant area of clinical demand for occlusive dressings. Patients with diabetic ulcers, pressure sores, and venous leg ulcers benefit from the protective and healing properties of these dressings. The aging population and increasing prevalence of chronic diseases have contributed to the growing need for advanced wound care solutions, including occlusive dressings.
Burns and trauma care units also rely heavily on occlusive dressings to manage complex wounds and prevent infection. The ability of these dressings to create an optimal healing environment while allowing for easy monitoring of the wound has made them indispensable in burn treatment protocols.
The demand for occlusive dressings extends beyond hospital settings to outpatient clinics and home care. As healthcare systems aim to reduce hospital stays and promote outpatient care, there is an increasing need for easy-to-use occlusive dressings that patients or caregivers can apply and manage at home. This trend has driven innovation in user-friendly designs and application methods.
In response to the diverse clinical needs, manufacturers have developed a wide range of occlusive dressing products. These include transparent film dressings, hydrocolloid dressings, and foam dressings with occlusive properties. Each type caters to specific wound characteristics and treatment goals, allowing healthcare providers to select the most appropriate dressing for individual patient needs.
The clinical demand analysis also reveals a growing emphasis on antimicrobial occlusive dressings. With the rise of antibiotic-resistant infections, healthcare facilities are seeking dressings that not only provide occlusion but also offer antimicrobial protection. This has led to the development of dressings incorporating silver, iodine, or other antimicrobial agents.
Regulatory Landscape and Safety Challenges
The regulatory landscape for occlusive dressings in clinical use is complex and multifaceted, involving various governing bodies and safety standards. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies occlusive dressings as medical devices, typically falling under Class I or II depending on their specific characteristics and intended use. This classification determines the level of regulatory control and the pathway for market approval.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks vary, with the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) playing significant roles. The MDR, implemented in 2021, has introduced more stringent requirements for medical devices, including occlusive dressings, emphasizing post-market surveillance and clinical evidence.
Safety challenges associated with occlusive dressings primarily revolve around infection control, skin reactions, and proper application techniques. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their products maintain a sterile barrier and do not promote microbial growth. Additionally, the potential for allergic reactions or skin irritation must be thoroughly assessed and documented.
One of the key regulatory hurdles is providing sufficient clinical evidence to support safety claims. This often requires conducting clinical trials or gathering real-world data to demonstrate the dressing's performance in various patient populations and wound types. The FDA's guidance on wound dressing products emphasizes the importance of evaluating factors such as moisture management, bacterial barrier properties, and compatibility with other wound care products.
Regulatory bodies also focus on the manufacturing processes and quality control measures employed in producing occlusive dressings. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) compliance is essential, with regular audits and inspections to ensure consistent product quality and safety. Traceability throughout the supply chain is another critical aspect, allowing for efficient recalls if safety issues arise.
Labeling and instructions for use are subject to strict regulatory scrutiny. Clear, accurate information on proper application, contraindications, and potential adverse effects must be provided to healthcare professionals and patients. This includes guidelines on the maximum duration of use and appropriate wound types for the specific dressing.
As technology advances, new challenges emerge in the regulatory landscape. Smart dressings incorporating sensors or drug delivery systems may require additional regulatory considerations, potentially crossing into combination product territory. This blurring of lines between traditional medical devices and advanced therapies necessitates a more nuanced approach to regulation and safety assessment.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks vary, with the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) playing significant roles. The MDR, implemented in 2021, has introduced more stringent requirements for medical devices, including occlusive dressings, emphasizing post-market surveillance and clinical evidence.
Safety challenges associated with occlusive dressings primarily revolve around infection control, skin reactions, and proper application techniques. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their products maintain a sterile barrier and do not promote microbial growth. Additionally, the potential for allergic reactions or skin irritation must be thoroughly assessed and documented.
One of the key regulatory hurdles is providing sufficient clinical evidence to support safety claims. This often requires conducting clinical trials or gathering real-world data to demonstrate the dressing's performance in various patient populations and wound types. The FDA's guidance on wound dressing products emphasizes the importance of evaluating factors such as moisture management, bacterial barrier properties, and compatibility with other wound care products.
Regulatory bodies also focus on the manufacturing processes and quality control measures employed in producing occlusive dressings. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) compliance is essential, with regular audits and inspections to ensure consistent product quality and safety. Traceability throughout the supply chain is another critical aspect, allowing for efficient recalls if safety issues arise.
Labeling and instructions for use are subject to strict regulatory scrutiny. Clear, accurate information on proper application, contraindications, and potential adverse effects must be provided to healthcare professionals and patients. This includes guidelines on the maximum duration of use and appropriate wound types for the specific dressing.
As technology advances, new challenges emerge in the regulatory landscape. Smart dressings incorporating sensors or drug delivery systems may require additional regulatory considerations, potentially crossing into combination product territory. This blurring of lines between traditional medical devices and advanced therapies necessitates a more nuanced approach to regulation and safety assessment.
Current Regulatory Compliance Strategies
01 Moisture-retaining occlusive dressings
Occlusive dressings are designed to create a moist environment that promotes wound healing. These dressings prevent moisture loss from the wound surface, maintain optimal hydration, and facilitate the natural healing process. They can be made from various materials such as hydrocolloids, films, or hydrogels, which form a barrier against external contaminants while allowing gaseous exchange.- Moisture-retaining occlusive dressings: Occlusive dressings are designed to create a moist environment that promotes wound healing. These dressings prevent moisture loss from the wound surface, maintain optimal hydration, and facilitate the natural healing process. They can be made from various materials such as hydrocolloids, films, or hydrogels, which form a barrier against external contaminants while allowing gaseous exchange.
- Negative pressure wound therapy dressings: Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) dressings are specialized occlusive dressings used in conjunction with vacuum systems. These dressings create a sealed environment around the wound and apply controlled negative pressure to remove excess fluids, reduce edema, and promote granulation tissue formation. NPWT dressings often incorporate foam or gauze materials to distribute negative pressure evenly across the wound bed.
- Antimicrobial occlusive dressings: Antimicrobial occlusive dressings incorporate active ingredients to prevent or treat wound infections. These dressings combine the benefits of occlusion with antimicrobial properties, creating a barrier against external pathogens while actively combating microorganisms within the wound environment. Common antimicrobial agents used in these dressings include silver, iodine, or chlorhexidine.
- Transparent film occlusive dressings: Transparent film occlusive dressings are thin, flexible, and allow visual inspection of the wound without removal. These dressings are typically made from polyurethane or similar materials that are permeable to oxygen and water vapor but impermeable to liquids and bacteria. They provide a waterproof barrier while maintaining a moist wound environment and are particularly useful for superficial wounds or as secondary dressings.
- Occlusive dressings with drug delivery capabilities: Some occlusive dressings are designed to incorporate and deliver therapeutic agents directly to the wound site. These advanced dressings combine the benefits of occlusion with controlled release of medications, growth factors, or other bioactive substances. This approach can enhance wound healing, reduce inflammation, or provide localized pain relief, depending on the incorporated agents.
02 Pressure-sensitive adhesive occlusive dressings
These dressings incorporate pressure-sensitive adhesives to ensure secure attachment to the skin. The adhesive properties allow for easy application and removal while maintaining an occlusive seal. Some designs include a non-adherent wound contact layer to prevent sticking to the wound bed, facilitating atraumatic dressing changes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Medicated occlusive dressings
Occlusive dressings can be infused with various medications or active ingredients to enhance wound healing. These may include antimicrobial agents, growth factors, or pain-relieving substances. The occlusive nature of the dressing helps to maintain the medication in close contact with the wound, potentially improving its efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions04 Transparent occlusive dressings
Transparent occlusive dressings allow for visual inspection of the wound without removing the dressing. This feature enables healthcare providers to monitor wound healing progress, detect signs of infection, and assess the need for dressing changes. These dressings are often made from thin, flexible materials that conform well to body contours.Expand Specific Solutions05 Occlusive dressings with absorption capabilities
Some occlusive dressings are designed with absorbent properties to manage wound exudate while maintaining a moist environment. These dressings can absorb excess fluid from heavily exuding wounds, reducing the risk of maceration to surrounding skin. The absorption capability is often combined with a semi-permeable outer layer to prevent leakage and maintain occlusivity.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers and Market Dynamics
The occlusive dressing market is in a mature growth stage, with a global market size expected to reach several billion dollars by 2025. The technology has evolved significantly, with major players like 3M Innovative Properties, Coloplast A/S, and Mölnlycke Health Care leading innovation. These companies, along with others such as Boston Scientific Scimed and Avery Dennison Corp., have developed advanced occlusive dressings with improved moisture management, infection control, and wound healing properties. The regulatory landscape is well-established, with stringent safety and efficacy requirements in place. Emerging trends include the integration of smart technologies and bioactive materials, driving continued research and development efforts across the industry.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed advanced occlusive dressings that incorporate their proprietary adhesive technology for enhanced wound healing. Their dressings feature a multi-layer design with a semi-permeable film that allows moisture vapor transmission while providing a barrier against external contaminants[1]. The company has implemented rigorous quality control measures to ensure compliance with FDA regulations for medical devices. Their dressings undergo extensive testing for biocompatibility, adhesion strength, and moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR) to meet safety standards for clinical use[2]. 3M also provides comprehensive documentation and labeling to support regulatory submissions and clinical applications.
Strengths: Industry-leading adhesive technology, extensive R&D capabilities, and global regulatory expertise. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to some competitors, potential for skin irritation in sensitive individuals.
Mölnlycke Health Care, AB.
Technical Solution: Mölnlycke has developed a range of advanced occlusive dressings, including their Mepilex line, which incorporates Safetac technology. This soft silicone adhesive layer minimizes pain and trauma during dressing changes while maintaining an optimal wound healing environment[3]. The company has implemented a comprehensive regulatory compliance program, including ISO 13485 certification for quality management systems in medical devices. Their dressings undergo rigorous testing for cytotoxicity, sensitization, and irritation in accordance with ISO 10993 standards[4]. Mölnlycke provides detailed clinical evidence and post-market surveillance data to support regulatory approvals and ensure ongoing safety in clinical use.
Strengths: Innovative Safetac technology, strong focus on patient comfort, extensive clinical evidence. Weaknesses: Limited product range compared to some larger competitors, potentially higher cost for specialized dressings.
Critical Safety Standards and Guidelines
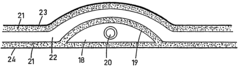
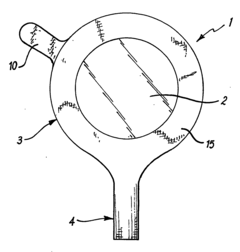
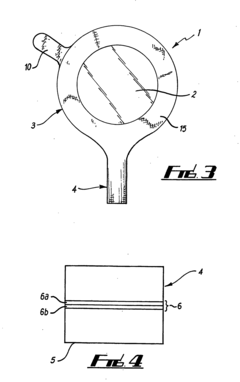
Multipurpose dynamic occlusive dressing
PatentInactiveUS7183454B1
Innovation
- An endless, flexible, adhesive barrier with an impermeable sealing film that can be configured to occlude any body area, allowing for the introduction of various substances and environmental modifications through valves and conduits, enabling the dressing to be adapted to different sizes and shapes, and allowing for the controlled exchange of materials and environments.
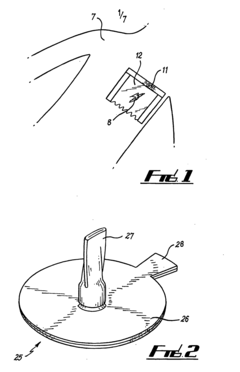
Novel Occlusive Dressing
PatentInactiveUS20070244421A1
Innovation
- A transparent, elliptical or circular bandage with a one-way flutter valve housed in a rigid casing, allowing fluid and air escape while preventing ingress, and featuring a collection bag and irrigation system, ensuring easy application and effective pressure management.
Risk Management in Clinical Application
Risk management is a critical aspect of clinical application for occlusive dressings. The implementation of a comprehensive regulatory and safety checklist is essential to ensure patient safety and compliance with healthcare standards. This process begins with a thorough assessment of potential risks associated with occlusive dressing use, including infection, skin irritation, and allergic reactions. Healthcare providers must be trained to identify and mitigate these risks through proper application techniques and regular monitoring of the dressing site.
A key component of risk management is the establishment of clear protocols for dressing selection, application, and removal. These protocols should be based on evidence-based guidelines and tailored to specific patient populations and wound types. Regular audits and quality control measures should be implemented to ensure adherence to these protocols and identify areas for improvement.
Proper documentation is crucial in risk management. A detailed record of dressing changes, wound assessment, and any adverse events should be maintained for each patient. This documentation serves as a valuable tool for tracking patient progress, identifying trends, and supporting continuous improvement of care practices.
Infection control is a primary concern in the use of occlusive dressings. Strict aseptic techniques must be employed during dressing changes, and healthcare providers should be vigilant for signs of infection. Regular monitoring of wound healing progress and early intervention in case of complications are essential components of effective risk management.
Patient education plays a significant role in minimizing risks associated with occlusive dressings. Patients and caregivers should be provided with clear instructions on how to recognize signs of complications and when to seek medical attention. This empowers patients to participate actively in their care and helps prevent adverse outcomes.
Regulatory compliance is an integral part of risk management in clinical applications. Healthcare facilities must ensure that all occlusive dressings used meet relevant regulatory standards and have appropriate certifications. Regular reviews of regulatory updates and prompt implementation of any new requirements are necessary to maintain compliance and patient safety.
Finally, a system for reporting and analyzing adverse events related to occlusive dressings should be established. This allows for the identification of patterns or recurring issues, facilitating targeted interventions and continuous improvement of risk management strategies. By implementing these comprehensive risk management measures, healthcare providers can significantly enhance patient safety and optimize the clinical application of occlusive dressings.
A key component of risk management is the establishment of clear protocols for dressing selection, application, and removal. These protocols should be based on evidence-based guidelines and tailored to specific patient populations and wound types. Regular audits and quality control measures should be implemented to ensure adherence to these protocols and identify areas for improvement.
Proper documentation is crucial in risk management. A detailed record of dressing changes, wound assessment, and any adverse events should be maintained for each patient. This documentation serves as a valuable tool for tracking patient progress, identifying trends, and supporting continuous improvement of care practices.
Infection control is a primary concern in the use of occlusive dressings. Strict aseptic techniques must be employed during dressing changes, and healthcare providers should be vigilant for signs of infection. Regular monitoring of wound healing progress and early intervention in case of complications are essential components of effective risk management.
Patient education plays a significant role in minimizing risks associated with occlusive dressings. Patients and caregivers should be provided with clear instructions on how to recognize signs of complications and when to seek medical attention. This empowers patients to participate actively in their care and helps prevent adverse outcomes.
Regulatory compliance is an integral part of risk management in clinical applications. Healthcare facilities must ensure that all occlusive dressings used meet relevant regulatory standards and have appropriate certifications. Regular reviews of regulatory updates and prompt implementation of any new requirements are necessary to maintain compliance and patient safety.
Finally, a system for reporting and analyzing adverse events related to occlusive dressings should be established. This allows for the identification of patterns or recurring issues, facilitating targeted interventions and continuous improvement of risk management strategies. By implementing these comprehensive risk management measures, healthcare providers can significantly enhance patient safety and optimize the clinical application of occlusive dressings.
Biocompatibility and Material Advancements
Biocompatibility and material advancements have become crucial factors in the development of occlusive dressings for clinical use. The evolution of these dressings has been driven by the need for improved patient comfort, enhanced wound healing, and reduced risk of infection. Recent advancements in material science have led to the creation of innovative polymers and composites that offer superior biocompatibility and functionality.
One of the key areas of focus has been the development of materials that mimic the properties of human skin. These biomimetic materials are designed to provide an optimal environment for wound healing while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions. Researchers have made significant progress in creating synthetic polymers that closely resemble the extracellular matrix, promoting cell adhesion and proliferation.
Nanotechnology has played a pivotal role in enhancing the biocompatibility of occlusive dressings. Nanostructured materials, such as nanofibers and nanoparticles, have been incorporated into dressing designs to improve their antimicrobial properties and promote tissue regeneration. These nanomaterials can be engineered to release therapeutic agents in a controlled manner, further enhancing their clinical efficacy.
Another notable advancement is the development of smart materials that respond to changes in the wound environment. These materials can adapt their properties based on factors such as pH, temperature, or the presence of specific biomarkers. This dynamic response allows for more personalized and effective wound management, potentially reducing healing times and improving patient outcomes.
Biodegradable materials have gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential to reduce environmental impact and minimize the need for dressing changes. Researchers have made substantial progress in developing biodegradable polymers that maintain their structural integrity during the healing process but gradually break down into non-toxic components over time.
The integration of bioactive compounds into occlusive dressing materials has opened up new possibilities for enhanced wound healing. Growth factors, antimicrobial peptides, and other bioactive molecules can be incorporated into the dressing matrix, providing a sustained release of therapeutic agents directly to the wound site. This approach has shown promising results in accelerating healing and reducing the risk of infection.
As the field of material science continues to advance, we can expect to see further innovations in occlusive dressing technologies. The development of hybrid materials that combine the benefits of different material classes, such as synthetic polymers and natural biopolymers, holds great promise for creating next-generation wound care solutions. These advancements will likely lead to more effective, comfortable, and safer occlusive dressings for clinical use.
One of the key areas of focus has been the development of materials that mimic the properties of human skin. These biomimetic materials are designed to provide an optimal environment for wound healing while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions. Researchers have made significant progress in creating synthetic polymers that closely resemble the extracellular matrix, promoting cell adhesion and proliferation.
Nanotechnology has played a pivotal role in enhancing the biocompatibility of occlusive dressings. Nanostructured materials, such as nanofibers and nanoparticles, have been incorporated into dressing designs to improve their antimicrobial properties and promote tissue regeneration. These nanomaterials can be engineered to release therapeutic agents in a controlled manner, further enhancing their clinical efficacy.
Another notable advancement is the development of smart materials that respond to changes in the wound environment. These materials can adapt their properties based on factors such as pH, temperature, or the presence of specific biomarkers. This dynamic response allows for more personalized and effective wound management, potentially reducing healing times and improving patient outcomes.
Biodegradable materials have gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential to reduce environmental impact and minimize the need for dressing changes. Researchers have made substantial progress in developing biodegradable polymers that maintain their structural integrity during the healing process but gradually break down into non-toxic components over time.
The integration of bioactive compounds into occlusive dressing materials has opened up new possibilities for enhanced wound healing. Growth factors, antimicrobial peptides, and other bioactive molecules can be incorporated into the dressing matrix, providing a sustained release of therapeutic agents directly to the wound site. This approach has shown promising results in accelerating healing and reducing the risk of infection.
As the field of material science continues to advance, we can expect to see further innovations in occlusive dressing technologies. The development of hybrid materials that combine the benefits of different material classes, such as synthetic polymers and natural biopolymers, holds great promise for creating next-generation wound care solutions. These advancements will likely lead to more effective, comfortable, and safer occlusive dressings for clinical use.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!