Occlusive Dressing Impact On Scar Formation: Measured Outcomes
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Scar Formation Mechanisms and Occlusive Dressing Goals
Scar formation is a complex biological process that occurs in response to tissue injury. It involves a series of overlapping phases, including inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. The primary goal of this process is to restore tissue integrity and function. However, excessive scarring can lead to aesthetic and functional impairments, making it a significant concern in wound healing and dermatology.
The mechanisms underlying scar formation are multifaceted. Initially, inflammatory cells infiltrate the wound site, releasing cytokines and growth factors that stimulate fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. During the proliferative phase, fibroblasts deposit extracellular matrix components, primarily collagen, to form granulation tissue. The final remodeling phase involves the reorganization of collagen fibers and can continue for months or even years after the initial injury.
Occlusive dressings have emerged as a promising intervention in scar management. These dressings create a moist wound environment, which has been shown to promote optimal healing conditions. The primary goals of using occlusive dressings in scar management are to minimize excessive collagen deposition, reduce inflammation, and promote a more organized collagen structure.
One of the key mechanisms by which occlusive dressings may influence scar formation is through modulation of the wound microenvironment. By maintaining a moist wound bed, these dressings can potentially reduce the inflammatory response, which is a critical factor in determining the extent of scarring. Additionally, occlusive dressings may help regulate the balance between matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors, which play crucial roles in collagen remodeling.
Another important goal of occlusive dressings is to minimize tension on the wound edges. Mechanical stress is known to exacerbate scarring, and occlusive dressings can provide a protective barrier that reduces this stress. This may be particularly beneficial in areas of high tension, such as joints or areas of frequent movement.
Furthermore, occlusive dressings aim to optimize the hydration level of the wound and surrounding skin. Proper hydration is essential for maintaining skin elasticity and promoting optimal collagen organization. By creating an occlusive barrier, these dressings prevent excessive water loss from the wound surface, potentially leading to improved scar quality.
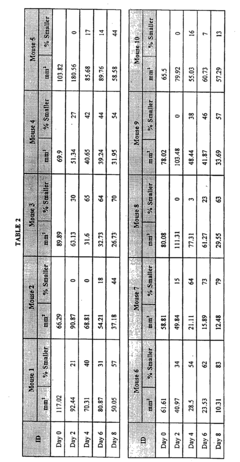
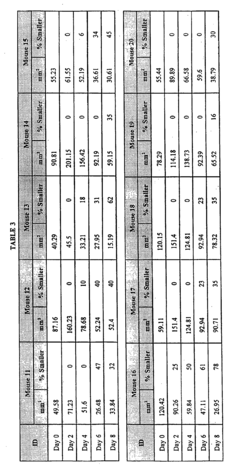
In the context of measured outcomes, researchers and clinicians typically focus on several key parameters when evaluating the impact of occlusive dressings on scar formation. These may include scar thickness, pliability, vascularity, pigmentation, and overall appearance. Objective measurement tools, such as cutometers for elasticity assessment and colorimeters for pigmentation analysis, are often employed to quantify these outcomes.
The mechanisms underlying scar formation are multifaceted. Initially, inflammatory cells infiltrate the wound site, releasing cytokines and growth factors that stimulate fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. During the proliferative phase, fibroblasts deposit extracellular matrix components, primarily collagen, to form granulation tissue. The final remodeling phase involves the reorganization of collagen fibers and can continue for months or even years after the initial injury.
Occlusive dressings have emerged as a promising intervention in scar management. These dressings create a moist wound environment, which has been shown to promote optimal healing conditions. The primary goals of using occlusive dressings in scar management are to minimize excessive collagen deposition, reduce inflammation, and promote a more organized collagen structure.
One of the key mechanisms by which occlusive dressings may influence scar formation is through modulation of the wound microenvironment. By maintaining a moist wound bed, these dressings can potentially reduce the inflammatory response, which is a critical factor in determining the extent of scarring. Additionally, occlusive dressings may help regulate the balance between matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors, which play crucial roles in collagen remodeling.
Another important goal of occlusive dressings is to minimize tension on the wound edges. Mechanical stress is known to exacerbate scarring, and occlusive dressings can provide a protective barrier that reduces this stress. This may be particularly beneficial in areas of high tension, such as joints or areas of frequent movement.
Furthermore, occlusive dressings aim to optimize the hydration level of the wound and surrounding skin. Proper hydration is essential for maintaining skin elasticity and promoting optimal collagen organization. By creating an occlusive barrier, these dressings prevent excessive water loss from the wound surface, potentially leading to improved scar quality.
In the context of measured outcomes, researchers and clinicians typically focus on several key parameters when evaluating the impact of occlusive dressings on scar formation. These may include scar thickness, pliability, vascularity, pigmentation, and overall appearance. Objective measurement tools, such as cutometers for elasticity assessment and colorimeters for pigmentation analysis, are often employed to quantify these outcomes.
Market Analysis for Advanced Wound Care Products
The advanced wound care market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, and rising awareness of the importance of effective wound management. The global advanced wound care market was valued at approximately $10.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $15.7 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period.
Occlusive dressings, a key segment within the advanced wound care market, have gained substantial traction due to their ability to create a moist wound environment conducive to healing and potential impact on scar formation. The occlusive dressing segment accounted for about 18% of the total advanced wound care market in 2020, with a market value of around $1.85 billion.
The market for occlusive dressings is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2021 to 2026, slightly lower than the overall advanced wound care market growth rate. This growth is primarily attributed to the increasing adoption of these dressings in both acute and chronic wound management, as well as their potential benefits in reducing scar formation.
Geographically, North America dominates the advanced wound care market, accounting for approximately 39% of the global market share in 2020. Europe follows closely, with a market share of about 31%. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, with a projected CAGR of 8.5% from 2021 to 2026.
Key market players in the occlusive dressing segment include 3M Company, Smith & Nephew, Mölnlycke Health Care, ConvaTec Group, and Coloplast A/S. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficacy of occlusive dressings in scar management and overall wound healing outcomes.
The market for occlusive dressings specifically targeting scar formation is still in its nascent stage but shows promising growth potential. As more clinical evidence emerges supporting the positive impact of occlusive dressings on scar formation, this sub-segment is expected to grow at a faster rate than the overall occlusive dressing market.
Factors driving the demand for occlusive dressings in scar management include the rising number of surgical procedures, increasing awareness of scar prevention techniques, and growing consumer focus on aesthetic outcomes. However, challenges such as the high cost of advanced wound care products and limited reimbursement policies in some regions may hinder market growth to some extent.
Occlusive dressings, a key segment within the advanced wound care market, have gained substantial traction due to their ability to create a moist wound environment conducive to healing and potential impact on scar formation. The occlusive dressing segment accounted for about 18% of the total advanced wound care market in 2020, with a market value of around $1.85 billion.
The market for occlusive dressings is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2021 to 2026, slightly lower than the overall advanced wound care market growth rate. This growth is primarily attributed to the increasing adoption of these dressings in both acute and chronic wound management, as well as their potential benefits in reducing scar formation.
Geographically, North America dominates the advanced wound care market, accounting for approximately 39% of the global market share in 2020. Europe follows closely, with a market share of about 31%. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, with a projected CAGR of 8.5% from 2021 to 2026.
Key market players in the occlusive dressing segment include 3M Company, Smith & Nephew, Mölnlycke Health Care, ConvaTec Group, and Coloplast A/S. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficacy of occlusive dressings in scar management and overall wound healing outcomes.
The market for occlusive dressings specifically targeting scar formation is still in its nascent stage but shows promising growth potential. As more clinical evidence emerges supporting the positive impact of occlusive dressings on scar formation, this sub-segment is expected to grow at a faster rate than the overall occlusive dressing market.
Factors driving the demand for occlusive dressings in scar management include the rising number of surgical procedures, increasing awareness of scar prevention techniques, and growing consumer focus on aesthetic outcomes. However, challenges such as the high cost of advanced wound care products and limited reimbursement policies in some regions may hinder market growth to some extent.
Current Challenges in Scar Management Techniques
Scar management remains a significant challenge in modern medicine, with current techniques facing several limitations. One of the primary obstacles is the unpredictable nature of scar formation, which varies greatly among individuals due to factors such as genetics, age, and wound characteristics. This variability makes it difficult to develop universally effective treatment protocols.
The management of hypertrophic and keloid scars presents a particularly complex challenge. These types of scars, characterized by excessive collagen deposition, often resist conventional treatments and have a high recurrence rate. Current therapies, such as corticosteroid injections and silicone-based products, show inconsistent results across patient populations.
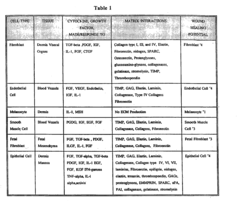
Another significant hurdle is the lack of standardized assessment methods for scar evaluation. While several scar assessment scales exist, such as the Vancouver Scar Scale and the Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale, there is no universally accepted gold standard. This inconsistency in evaluation methods makes it challenging to compare treatment outcomes across different studies and clinical settings.
The timing of scar management interventions also poses a challenge. Early intervention is crucial for optimal results, but identifying the ideal window for treatment initiation remains problematic. Moreover, the long-term nature of scar remodeling, which can continue for up to two years post-injury, necessitates prolonged treatment regimens that may be difficult for patients to adhere to.
Pain and pruritus associated with scars, especially in the case of burn injuries, present additional management challenges. Current treatments often struggle to provide adequate relief, impacting patients' quality of life and potentially interfering with the healing process.
The aesthetic aspect of scar management is another area of concern. While functional improvement is crucial, patients often prioritize the cosmetic appearance of scars. Achieving both functional and aesthetic improvements simultaneously remains a significant challenge for current scar management techniques.
Lastly, the cost and accessibility of advanced scar treatments pose barriers to widespread implementation. Innovative therapies such as laser treatments and autologous fat grafting show promise but are often expensive and not readily available in all healthcare settings. This disparity in access to cutting-edge treatments creates inequalities in scar management outcomes across different patient populations.
The management of hypertrophic and keloid scars presents a particularly complex challenge. These types of scars, characterized by excessive collagen deposition, often resist conventional treatments and have a high recurrence rate. Current therapies, such as corticosteroid injections and silicone-based products, show inconsistent results across patient populations.
Another significant hurdle is the lack of standardized assessment methods for scar evaluation. While several scar assessment scales exist, such as the Vancouver Scar Scale and the Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale, there is no universally accepted gold standard. This inconsistency in evaluation methods makes it challenging to compare treatment outcomes across different studies and clinical settings.
The timing of scar management interventions also poses a challenge. Early intervention is crucial for optimal results, but identifying the ideal window for treatment initiation remains problematic. Moreover, the long-term nature of scar remodeling, which can continue for up to two years post-injury, necessitates prolonged treatment regimens that may be difficult for patients to adhere to.
Pain and pruritus associated with scars, especially in the case of burn injuries, present additional management challenges. Current treatments often struggle to provide adequate relief, impacting patients' quality of life and potentially interfering with the healing process.
The aesthetic aspect of scar management is another area of concern. While functional improvement is crucial, patients often prioritize the cosmetic appearance of scars. Achieving both functional and aesthetic improvements simultaneously remains a significant challenge for current scar management techniques.
Lastly, the cost and accessibility of advanced scar treatments pose barriers to widespread implementation. Innovative therapies such as laser treatments and autologous fat grafting show promise but are often expensive and not readily available in all healthcare settings. This disparity in access to cutting-edge treatments creates inequalities in scar management outcomes across different patient populations.
Existing Occlusive Dressing Solutions for Scar Reduction
01 Occlusive dressing materials for scar management
Various materials are used in occlusive dressings to manage scar formation. These materials create a moist environment that promotes healing and reduces scarring. Silicone-based dressings are particularly effective in preventing excessive scar formation and improving the appearance of existing scars. Other materials like hydrocolloids and hydrogels can also be used in occlusive dressings for scar management.- Occlusive dressing materials for scar management: Various materials are used in occlusive dressings to manage scar formation. These materials create a moist environment that promotes healing and reduces scarring. Silicone-based dressings are particularly effective in preventing excessive scar formation and improving the appearance of existing scars. Other materials like hydrocolloids and hydrogels can also be used in occlusive dressings for scar management.
- Pressure application in occlusive dressings: Incorporating pressure elements in occlusive dressings can enhance scar management. Pressure therapy helps in controlling collagen synthesis and alignment, reducing hypertrophic scarring. Occlusive dressings with built-in pressure mechanisms or those used in conjunction with pressure garments can provide more effective scar treatment, especially for burn scars or post-surgical scars.
- Drug delivery through occlusive dressings: Occlusive dressings can be designed to deliver therapeutic agents directly to the scar site. This approach combines the benefits of occlusion with targeted drug delivery. Medications such as corticosteroids, antibiotics, or growth factors can be incorporated into the dressing matrix or applied underneath the occlusive layer to enhance scar treatment and prevent abnormal scar formation.
- Breathable occlusive dressings for scar treatment: Developing breathable occlusive dressings addresses the challenge of maintaining a moist wound environment while allowing some gas exchange. These dressings prevent maceration of the surrounding skin while still providing the benefits of occlusion for scar management. Materials with selective permeability or those with controlled moisture vapor transmission rates are used in these advanced dressings.
- Customizable and shape-conforming occlusive dressings: Occlusive dressings that can be customized or easily conform to different body contours are beneficial for scar management in various anatomical locations. These dressings may use flexible materials or be designed as modular systems that can be adjusted to fit specific scar sites. Such adaptability ensures better coverage and more effective occlusion, leading to improved scar treatment outcomes.
02 Pressure application in occlusive dressings
Incorporating pressure elements into occlusive dressings can enhance scar management. Pressure helps to flatten and soften scars, reducing their prominence. Some dressings are designed with built-in pressure mechanisms or can be used in conjunction with compression garments to provide consistent pressure on the scar area, promoting better healing and reducing the formation of hypertrophic or keloid scars.Expand Specific Solutions03 Drug delivery through occlusive dressings
Occlusive dressings can be designed to deliver therapeutic agents directly to the scar site. These dressings may incorporate medications such as corticosteroids, antibiotics, or growth factors that can help in managing scar formation. The occlusive nature of the dressing enhances drug penetration and efficacy, potentially leading to better scar management outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Customizable and shape-conforming occlusive dressings
Innovative occlusive dressings are being developed that can be customized or easily conform to different body shapes and scar locations. These dressings may use advanced materials or design features that allow them to adapt to various contours of the body, ensuring consistent coverage and pressure on the scar area. This adaptability can improve patient comfort and treatment adherence, leading to better scar management outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Combination therapy approaches in occlusive dressings
Some occlusive dressings incorporate multiple therapeutic approaches for comprehensive scar management. These may combine pressure therapy, moisture control, and drug delivery in a single dressing. Additionally, some dressings are designed to work synergistically with other scar treatments such as laser therapy or cryotherapy, potentially enhancing the overall effectiveness of scar management strategies.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Wound Care and Scar Treatment Industry
The occlusive dressing impact on scar formation market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing awareness of advanced wound care techniques. The global market size for advanced wound dressings is projected to reach $8.46 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 5.5%. Technologically, occlusive dressings are relatively mature, with ongoing innovations focused on improving efficacy and patient comfort. Key players like 3M, Smith & Nephew, and Johnson & Johnson are leading the market with established product lines. Emerging companies such as Neodyne Biosciences and KitoTech Medical are introducing novel technologies, while research institutions like Zhejiang University and IIT Delhi are contributing to advancements in the field.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed the Tegaderm™ Matrix, an advanced wound dressing that combines the benefits of hydrocolloid and film dressings. This innovative dressing creates an optimal moist wound environment while allowing for gaseous exchange, which is crucial for proper wound healing and scar reduction. The Tegaderm™ Matrix has been shown to accelerate wound healing by up to 40% compared to traditional gauze dressings[7]. Additionally, 3M's Cavilon™ No Sting Barrier Film forms a breathable, transparent protective layer over the skin, which has been demonstrated to reduce the incidence of skin damage by up to 27% in high-risk patients[8]. The company has also introduced the Tegaderm™ + Pad Film Dressing with Non-Adherent Pad, which combines a waterproof, breathable film with a non-stick wound contact layer to minimize trauma during dressing changes and promote optimal healing conditions.
Strengths: Diverse product range addressing various wound care needs, strong focus on innovation, and extensive clinical research supporting product efficacy. Weaknesses: Some products may be less suitable for highly exuding wounds, potential for skin irritation in sensitive individuals.
Coloplast A/S
Technical Solution: Coloplast has developed the Biatain® Silicone range of foam dressings, which feature a unique 3DFit Technology® that conforms to wound contours and minimizes dead space where bacteria can proliferate. This technology has been shown to reduce wound size by up to 62% after four weeks of treatment[9]. The company's Comfeel® Plus Transparent Dressing utilizes a hydrocolloid formulation that maintains an optimal moist wound environment while allowing for visual inspection of the wound. Clinical studies have demonstrated that Comfeel® Plus can reduce the time to complete wound healing by up to 40% compared to traditional gauze dressings[10]. Furthermore, Coloplast's Biatain® Ibu, a foam dressing with integrated ibuprofen, provides both wound management and pain relief, potentially reducing the need for systemic pain medication and improving patient comfort during the healing process.
Strengths: Innovative 3DFit Technology, integration of pain management in wound dressings, and strong clinical evidence supporting product efficacy. Weaknesses: Limited options for highly exuding wounds, potential for increased cost due to advanced technologies.
Innovations in Occlusive Dressing Materials and Design
Cell-coated support
PatentInactiveEP1640024A2
Innovation
- The use of cultured keratinocytes grown on a transplantable solid support, housed in a permeable enclosure, which is placed at the wound site to secrete factors that enhance healing, regardless of wound type or patient population.
Reactive hydrophilic oligomers
PatentWO2005061012A1
Innovation
- Development of reactive, melt-processable hydrophilic oligomer compositions with pendent functional groups that can be crosslinked through step-growth mechanisms, allowing for uniform coatings with adjustable properties, including high water absorption and transparency, and minimal residual content, enabling flexible and effective wound dressings.
Clinical Trial Methodologies for Scar Treatment Efficacy
Clinical trial methodologies for evaluating the efficacy of scar treatments have evolved significantly over the years, incorporating various assessment tools and outcome measures. These methodologies aim to provide objective and standardized evaluations of scar appearance, symptoms, and overall quality.
One of the primary approaches in clinical trials for scar treatments is the use of standardized scar assessment scales. The Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS) and the Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale (POSAS) are widely used tools that evaluate parameters such as vascularity, pigmentation, pliability, and height of scars. These scales combine both observer and patient-reported outcomes, providing a comprehensive assessment of scar characteristics.
Objective measurement techniques have also been integrated into clinical trial methodologies. These include cutometry for measuring skin elasticity, colorimetry for assessing scar pigmentation, and three-dimensional imaging for evaluating scar volume and texture. Such technologies offer quantitative data that complement subjective assessments and enhance the reliability of trial results.
Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) have gained increasing importance in scar treatment trials. Questionnaires like the Brisbane Burn Scar Impact Profile (BBSIP) and the Patient-Reported Impact of Scars Measure (PRISM) assess the psychological and functional impact of scars on patients' quality of life. These tools provide valuable insights into the patient's perspective, which is crucial for evaluating treatment efficacy beyond physical appearance.
Longitudinal study designs are commonly employed in scar treatment trials to capture the dynamic nature of scar formation and maturation. These studies typically involve multiple assessment time points over extended periods, often ranging from 6 months to 2 years post-treatment. This approach allows researchers to track changes in scar characteristics over time and evaluate the long-term efficacy of interventions.
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) remain the gold standard for assessing scar treatment efficacy. These trials often compare novel treatments against standard care or placebo, with blinding of participants and assessors when possible. Split-scar or split-body designs, where different treatments are applied to different parts of the same scar or body, are particularly useful for controlling inter-individual variability.
Photographic documentation plays a crucial role in scar assessment methodologies. Standardized photography protocols, including consistent lighting, positioning, and camera settings, are implemented to ensure reliable visual comparisons over time. Advanced imaging techniques, such as multispectral imaging and optical coherence tomography, are increasingly being explored to provide more detailed scar characterization.
In conclusion, clinical trial methodologies for scar treatment efficacy encompass a multifaceted approach, combining subjective assessments, objective measurements, patient-reported outcomes, and advanced imaging techniques. This comprehensive strategy aims to provide a holistic evaluation of scar treatments, addressing both the physical and psychosocial aspects of scar management.
One of the primary approaches in clinical trials for scar treatments is the use of standardized scar assessment scales. The Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS) and the Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale (POSAS) are widely used tools that evaluate parameters such as vascularity, pigmentation, pliability, and height of scars. These scales combine both observer and patient-reported outcomes, providing a comprehensive assessment of scar characteristics.
Objective measurement techniques have also been integrated into clinical trial methodologies. These include cutometry for measuring skin elasticity, colorimetry for assessing scar pigmentation, and three-dimensional imaging for evaluating scar volume and texture. Such technologies offer quantitative data that complement subjective assessments and enhance the reliability of trial results.
Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) have gained increasing importance in scar treatment trials. Questionnaires like the Brisbane Burn Scar Impact Profile (BBSIP) and the Patient-Reported Impact of Scars Measure (PRISM) assess the psychological and functional impact of scars on patients' quality of life. These tools provide valuable insights into the patient's perspective, which is crucial for evaluating treatment efficacy beyond physical appearance.
Longitudinal study designs are commonly employed in scar treatment trials to capture the dynamic nature of scar formation and maturation. These studies typically involve multiple assessment time points over extended periods, often ranging from 6 months to 2 years post-treatment. This approach allows researchers to track changes in scar characteristics over time and evaluate the long-term efficacy of interventions.
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) remain the gold standard for assessing scar treatment efficacy. These trials often compare novel treatments against standard care or placebo, with blinding of participants and assessors when possible. Split-scar or split-body designs, where different treatments are applied to different parts of the same scar or body, are particularly useful for controlling inter-individual variability.
Photographic documentation plays a crucial role in scar assessment methodologies. Standardized photography protocols, including consistent lighting, positioning, and camera settings, are implemented to ensure reliable visual comparisons over time. Advanced imaging techniques, such as multispectral imaging and optical coherence tomography, are increasingly being explored to provide more detailed scar characterization.
In conclusion, clinical trial methodologies for scar treatment efficacy encompass a multifaceted approach, combining subjective assessments, objective measurements, patient-reported outcomes, and advanced imaging techniques. This comprehensive strategy aims to provide a holistic evaluation of scar treatments, addressing both the physical and psychosocial aspects of scar management.
Patient-Reported Outcomes in Scar Management Studies
Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) have become increasingly important in scar management studies, providing valuable insights into the patient's perspective on treatment efficacy and overall satisfaction. These outcomes are particularly relevant when assessing the impact of occlusive dressings on scar formation, as they capture the subjective experiences of patients throughout the healing process.
One of the primary PROs in scar management studies is pain and discomfort. Patients often report on the level of pain experienced during dressing changes and throughout the healing process. Occlusive dressings may influence pain levels by maintaining a moist wound environment and reducing friction, potentially leading to improved patient comfort.
Itching is another crucial PRO, as it can significantly affect a patient's quality of life during scar formation. Studies have shown that occlusive dressings may help reduce itching sensations, possibly due to their ability to maintain optimal hydration levels in the healing tissue.
Aesthetic satisfaction is a key PRO in scar management, with patients reporting on their perception of scar appearance. This includes factors such as color, texture, and overall visibility. Occlusive dressings may contribute to improved aesthetic outcomes by promoting a more controlled healing environment.
Functional outcomes are also assessed through patient reports, focusing on the range of motion and flexibility of the affected area. Patients may provide feedback on how the occlusive dressing impacts their ability to perform daily activities and whether it restricts movement during the healing process.
Quality of life measures are integral to PROs in scar management studies. These encompass broader aspects of the patient's well-being, including psychological impact, social interactions, and overall satisfaction with the treatment process. Occlusive dressings may influence these outcomes by potentially reducing visible scarring and improving the patient's confidence.
Sleep quality is another important PRO, as discomfort or itching from scars can disrupt sleep patterns. Patients often report on how occlusive dressings affect their ability to sleep comfortably and whether they experience any nighttime disturbances related to their scars.
Treatment adherence and ease of use are critical PROs that can impact the overall effectiveness of occlusive dressings. Patients provide feedback on the practicality of applying and maintaining the dressings, which can influence long-term compliance and treatment success.
By incorporating these patient-reported outcomes into scar management studies, researchers and clinicians can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the impact of occlusive dressings on scar formation. This patient-centered approach not only enhances the evaluation of treatment efficacy but also helps in tailoring interventions to meet individual patient needs and preferences.
One of the primary PROs in scar management studies is pain and discomfort. Patients often report on the level of pain experienced during dressing changes and throughout the healing process. Occlusive dressings may influence pain levels by maintaining a moist wound environment and reducing friction, potentially leading to improved patient comfort.
Itching is another crucial PRO, as it can significantly affect a patient's quality of life during scar formation. Studies have shown that occlusive dressings may help reduce itching sensations, possibly due to their ability to maintain optimal hydration levels in the healing tissue.
Aesthetic satisfaction is a key PRO in scar management, with patients reporting on their perception of scar appearance. This includes factors such as color, texture, and overall visibility. Occlusive dressings may contribute to improved aesthetic outcomes by promoting a more controlled healing environment.
Functional outcomes are also assessed through patient reports, focusing on the range of motion and flexibility of the affected area. Patients may provide feedback on how the occlusive dressing impacts their ability to perform daily activities and whether it restricts movement during the healing process.
Quality of life measures are integral to PROs in scar management studies. These encompass broader aspects of the patient's well-being, including psychological impact, social interactions, and overall satisfaction with the treatment process. Occlusive dressings may influence these outcomes by potentially reducing visible scarring and improving the patient's confidence.
Sleep quality is another important PRO, as discomfort or itching from scars can disrupt sleep patterns. Patients often report on how occlusive dressings affect their ability to sleep comfortably and whether they experience any nighttime disturbances related to their scars.
Treatment adherence and ease of use are critical PROs that can impact the overall effectiveness of occlusive dressings. Patients provide feedback on the practicality of applying and maintaining the dressings, which can influence long-term compliance and treatment success.
By incorporating these patient-reported outcomes into scar management studies, researchers and clinicians can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the impact of occlusive dressings on scar formation. This patient-centered approach not only enhances the evaluation of treatment efficacy but also helps in tailoring interventions to meet individual patient needs and preferences.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!