How To Integrate Drug-Releasing Occlusive Dressings In Wound Care
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Drug-Releasing Dressings: Background and Objectives
Drug-releasing occlusive dressings represent a significant advancement in wound care technology, combining the protective properties of traditional dressings with the therapeutic benefits of controlled drug delivery. This innovative approach has evolved from the need to address complex wound healing challenges, particularly in chronic wounds and infections. The development of these dressings can be traced back to the late 20th century, with significant progress made in the past two decades due to advancements in material science and drug delivery systems.
The primary objective of integrating drug-releasing occlusive dressings in wound care is to enhance healing outcomes while reducing the frequency of dressing changes and minimizing the risk of infection. These dressings aim to create an optimal wound healing environment by maintaining moisture balance, protecting against external contaminants, and delivering targeted therapeutic agents directly to the wound site. The controlled release of drugs allows for sustained treatment, potentially improving patient compliance and reducing overall healthcare costs.
The evolution of drug-releasing dressings has been driven by a growing understanding of wound healing physiology and the role of various growth factors, antimicrobials, and other therapeutic agents in the healing process. Early iterations focused primarily on antimicrobial agents, but recent developments have expanded to include a wide range of bioactive compounds, including growth factors, anti-inflammatory drugs, and pain relievers.
A key technological trend in this field is the development of smart dressings that can respond to changes in the wound environment, such as pH or bacterial load, to trigger drug release. This approach aims to provide more precise and timely treatment, potentially accelerating healing and reducing the risk of complications. Another emerging trend is the use of nanotechnology to enhance drug delivery and improve the overall efficacy of these dressings.
The integration of drug-releasing occlusive dressings in wound care faces several challenges, including ensuring consistent drug release profiles, maintaining dressing integrity over time, and addressing potential issues of drug resistance. Additionally, regulatory considerations and the need for extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy pose significant hurdles to widespread adoption.
Looking forward, the field of drug-releasing occlusive dressings is expected to continue evolving, with a focus on personalized wound care solutions, biodegradable materials, and advanced drug delivery mechanisms. The ultimate goal is to develop dressings that can adapt to individual patient needs, providing optimal healing conditions while minimizing the need for frequent interventions.
The primary objective of integrating drug-releasing occlusive dressings in wound care is to enhance healing outcomes while reducing the frequency of dressing changes and minimizing the risk of infection. These dressings aim to create an optimal wound healing environment by maintaining moisture balance, protecting against external contaminants, and delivering targeted therapeutic agents directly to the wound site. The controlled release of drugs allows for sustained treatment, potentially improving patient compliance and reducing overall healthcare costs.
The evolution of drug-releasing dressings has been driven by a growing understanding of wound healing physiology and the role of various growth factors, antimicrobials, and other therapeutic agents in the healing process. Early iterations focused primarily on antimicrobial agents, but recent developments have expanded to include a wide range of bioactive compounds, including growth factors, anti-inflammatory drugs, and pain relievers.
A key technological trend in this field is the development of smart dressings that can respond to changes in the wound environment, such as pH or bacterial load, to trigger drug release. This approach aims to provide more precise and timely treatment, potentially accelerating healing and reducing the risk of complications. Another emerging trend is the use of nanotechnology to enhance drug delivery and improve the overall efficacy of these dressings.
The integration of drug-releasing occlusive dressings in wound care faces several challenges, including ensuring consistent drug release profiles, maintaining dressing integrity over time, and addressing potential issues of drug resistance. Additionally, regulatory considerations and the need for extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy pose significant hurdles to widespread adoption.
Looking forward, the field of drug-releasing occlusive dressings is expected to continue evolving, with a focus on personalized wound care solutions, biodegradable materials, and advanced drug delivery mechanisms. The ultimate goal is to develop dressings that can adapt to individual patient needs, providing optimal healing conditions while minimizing the need for frequent interventions.
Wound Care Market Analysis
The global wound care market has been experiencing significant growth, driven by an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, and advancements in wound care technologies. As of 2021, the market was valued at approximately $20 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% through 2026. This growth is particularly evident in the advanced wound care segment, which includes drug-releasing occlusive dressings.
The demand for innovative wound care solutions, such as drug-releasing occlusive dressings, is on the rise due to their potential to improve healing outcomes and reduce treatment duration. These advanced dressings combine the benefits of occlusive wound healing with controlled drug delivery, addressing both moisture management and infection control simultaneously. The market for such products is expected to grow at a faster rate than the overall wound care market, with some estimates suggesting a CAGR of 6-7% for this specific segment.
Geographically, North America currently holds the largest market share in advanced wound care products, followed by Europe. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, increasing awareness of advanced wound care techniques, and rising disposable incomes.
Key factors influencing market growth include the increasing incidence of chronic wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers. The global prevalence of diabetes, a major contributor to chronic wounds, is expected to reach 578 million by 2030, further driving the demand for advanced wound care solutions.
The market is characterized by intense competition among major players, including 3M, Smith & Nephew, Mölnlycke Health Care, and ConvaTec Group. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products and gain a competitive edge. The integration of drug-releasing occlusive dressings in wound care represents a significant opportunity for market expansion and differentiation.
Challenges in the market include the high cost of advanced wound care products, which may limit adoption in price-sensitive regions, and the need for clinical evidence to support the efficacy of drug-releasing occlusive dressings in various wound types. Additionally, regulatory hurdles and reimbursement issues in some countries may impact market growth.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for drug-releasing occlusive dressings in the wound care market remains positive. The increasing focus on personalized medicine and the potential for these dressings to reduce healthcare costs through faster healing and fewer complications are expected to drive continued innovation and market expansion in this sector.
The demand for innovative wound care solutions, such as drug-releasing occlusive dressings, is on the rise due to their potential to improve healing outcomes and reduce treatment duration. These advanced dressings combine the benefits of occlusive wound healing with controlled drug delivery, addressing both moisture management and infection control simultaneously. The market for such products is expected to grow at a faster rate than the overall wound care market, with some estimates suggesting a CAGR of 6-7% for this specific segment.
Geographically, North America currently holds the largest market share in advanced wound care products, followed by Europe. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, increasing awareness of advanced wound care techniques, and rising disposable incomes.
Key factors influencing market growth include the increasing incidence of chronic wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers. The global prevalence of diabetes, a major contributor to chronic wounds, is expected to reach 578 million by 2030, further driving the demand for advanced wound care solutions.
The market is characterized by intense competition among major players, including 3M, Smith & Nephew, Mölnlycke Health Care, and ConvaTec Group. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products and gain a competitive edge. The integration of drug-releasing occlusive dressings in wound care represents a significant opportunity for market expansion and differentiation.
Challenges in the market include the high cost of advanced wound care products, which may limit adoption in price-sensitive regions, and the need for clinical evidence to support the efficacy of drug-releasing occlusive dressings in various wound types. Additionally, regulatory hurdles and reimbursement issues in some countries may impact market growth.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for drug-releasing occlusive dressings in the wound care market remains positive. The increasing focus on personalized medicine and the potential for these dressings to reduce healthcare costs through faster healing and fewer complications are expected to drive continued innovation and market expansion in this sector.
Current Challenges in Occlusive Dressing Technology
Occlusive dressings have revolutionized wound care by creating a moist environment conducive to healing. However, integrating drug-releasing capabilities into these dressings presents several significant challenges. One of the primary obstacles is maintaining the occlusive properties of the dressing while simultaneously allowing for controlled drug release. The barrier function of occlusive dressings, which is crucial for preventing external contamination and maintaining moisture, can potentially hinder the effective delivery of therapeutic agents to the wound site.
Another challenge lies in the stability and longevity of the incorporated drugs within the dressing matrix. The moist environment created by occlusive dressings, while beneficial for wound healing, can accelerate drug degradation or alter its release kinetics. This necessitates careful consideration of drug formulation and delivery mechanisms to ensure sustained and effective release over the intended duration of dressing application.
The diversity of wound types and healing stages further complicates the development of universally applicable drug-releasing occlusive dressings. Different wounds may require varying drug concentrations, release rates, and treatment durations, making it challenging to design a one-size-fits-all solution. Additionally, the dynamic nature of the wound environment, including changes in pH, exudate levels, and microbial load, can impact drug efficacy and release patterns.
Biocompatibility and potential adverse reactions pose another significant hurdle. The introduction of drugs into occlusive dressings increases the risk of skin irritation, allergic responses, or other undesired effects, particularly in patients with sensitive skin or compromised immune systems. Ensuring the safety and tolerability of these advanced dressings across diverse patient populations is crucial but complex.
Manufacturing and scalability present technical challenges in producing drug-releasing occlusive dressings consistently and cost-effectively. The integration of pharmaceutical components into traditional dressing materials requires specialized production processes and quality control measures. Achieving uniform drug distribution and maintaining dressing integrity during manufacturing and storage are critical considerations that impact product reliability and shelf life.
Regulatory hurdles also pose significant challenges in bringing drug-releasing occlusive dressings to market. These products often straddle the line between medical devices and pharmaceuticals, potentially requiring more complex regulatory pathways and extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Navigating these regulatory requirements while balancing innovation and market demands adds another layer of complexity to the development process.
Another challenge lies in the stability and longevity of the incorporated drugs within the dressing matrix. The moist environment created by occlusive dressings, while beneficial for wound healing, can accelerate drug degradation or alter its release kinetics. This necessitates careful consideration of drug formulation and delivery mechanisms to ensure sustained and effective release over the intended duration of dressing application.
The diversity of wound types and healing stages further complicates the development of universally applicable drug-releasing occlusive dressings. Different wounds may require varying drug concentrations, release rates, and treatment durations, making it challenging to design a one-size-fits-all solution. Additionally, the dynamic nature of the wound environment, including changes in pH, exudate levels, and microbial load, can impact drug efficacy and release patterns.
Biocompatibility and potential adverse reactions pose another significant hurdle. The introduction of drugs into occlusive dressings increases the risk of skin irritation, allergic responses, or other undesired effects, particularly in patients with sensitive skin or compromised immune systems. Ensuring the safety and tolerability of these advanced dressings across diverse patient populations is crucial but complex.
Manufacturing and scalability present technical challenges in producing drug-releasing occlusive dressings consistently and cost-effectively. The integration of pharmaceutical components into traditional dressing materials requires specialized production processes and quality control measures. Achieving uniform drug distribution and maintaining dressing integrity during manufacturing and storage are critical considerations that impact product reliability and shelf life.
Regulatory hurdles also pose significant challenges in bringing drug-releasing occlusive dressings to market. These products often straddle the line between medical devices and pharmaceuticals, potentially requiring more complex regulatory pathways and extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Navigating these regulatory requirements while balancing innovation and market demands adds another layer of complexity to the development process.
Existing Drug-Releasing Occlusive Dressing Systems
01 Controlled drug release mechanisms
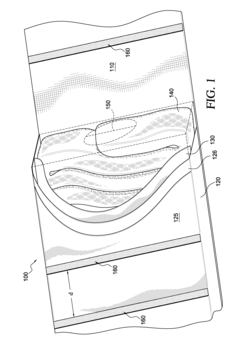
Occlusive dressings can be designed with various mechanisms to control drug release, such as using specific polymers, matrices, or layered structures. These mechanisms allow for sustained and targeted delivery of medications to the wound site, improving therapeutic efficacy and reducing the need for frequent dressing changes.- Controlled drug release mechanisms in occlusive dressings: Occlusive dressings are designed with specific mechanisms to control the release of drugs. These mechanisms may include the use of polymeric matrices, microencapsulation, or layered structures that regulate the diffusion of active ingredients. The controlled release helps maintain therapeutic levels of medication over extended periods, improving treatment efficacy and patient compliance.
- Incorporation of active pharmaceutical ingredients in dressing materials: Various active pharmaceutical ingredients can be incorporated directly into the materials used to construct occlusive dressings. This may involve impregnating the dressing fabric or adhesive with drugs, or creating drug-loaded fibers or films. The choice of dressing material and drug incorporation method affects the release profile and overall effectiveness of the treatment.
- Moisture-activated drug release systems: Some occlusive dressings utilize moisture-activated drug release systems. These dressings are designed to release medication when exposed to wound exudate or other bodily fluids. The moisture triggers the dissolution or activation of the drug, allowing for targeted delivery to the wound site. This approach can be particularly useful for managing chronic wounds or infections.
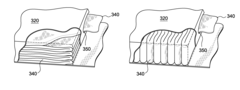
- Multi-layer dressings for sustained drug release: Multi-layer occlusive dressings are developed to provide sustained drug release over time. These dressings typically consist of different layers with varying drug concentrations or release properties. The layered structure allows for initial rapid release followed by a more controlled, prolonged delivery of medication, optimizing the therapeutic effect and reducing the frequency of dressing changes.
- Smart drug-releasing occlusive dressings: Advanced occlusive dressings incorporate smart technologies for drug release. These may include stimuli-responsive materials that can release drugs in response to changes in pH, temperature, or other environmental factors. Some smart dressings also feature integrated sensors or indicators to monitor drug release or wound healing progress, allowing for more personalized and efficient treatment.
02 Integration of drug reservoirs
Drug-releasing occlusive dressings can incorporate reservoirs or compartments that store and gradually release medications. These reservoirs can be designed to respond to specific stimuli or environmental conditions, enabling precise control over drug release rates and duration.Expand Specific Solutions03 Smart materials for responsive drug release
Advanced occlusive dressings may utilize smart materials that respond to changes in wound environment, such as pH, temperature, or bacterial presence. These materials can trigger or modulate drug release based on the wound's healing status, optimizing treatment efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nanotech-enhanced drug delivery
Nanotechnology can be incorporated into occlusive dressings to enhance drug delivery. Nanoparticles or nanofibers can be used to encapsulate drugs, improve their stability, and control their release, potentially increasing the effectiveness of wound treatment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Multi-layer dressing designs
Occlusive dressings can be designed with multiple layers, each serving a specific function in drug release and wound healing. These layers may include adhesive components, drug-containing matrices, barrier layers, and absorption layers, working together to optimize drug delivery and wound management.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Advanced Wound Care Industry
The integration of drug-releasing occlusive dressings in wound care represents a growing market in the advanced wound management sector. This technology is in a mature development stage, with several key players driving innovation. The global advanced wound dressing market is expected to reach $8.3 billion by 2026, with drug-releasing dressings contributing significantly. Companies like 3M Innovative Properties Co., ConvaTec, Inc., and Smith & Nephew plc are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in materials science and wound care to develop sophisticated drug-delivery systems. Coloplast A/S and Mölnlycke Health Care AB are also making significant strides in this field, focusing on patient-centric solutions that combine wound healing with targeted drug release.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed advanced drug-releasing occlusive dressings for wound care, leveraging their expertise in adhesive technologies and material science. Their Tegaderm CHG (Chlorhexidine Gluconate) IV Securement Dressing combines a transparent film dressing with a CHG gel pad[9]. This integrated approach provides both antimicrobial protection and a barrier against external contaminants. The CHG is gradually released into the wound area, providing sustained antimicrobial activity for up to 7 days. 3M has also introduced the Tegaderm Matrix, a unique dressing that combines an absorbent polyurethane matrix with a breathable film backing. This dressing can be impregnated with various active ingredients, allowing for customized drug delivery based on specific wound care needs[10]. The company's Coban 2 Layer Compression System incorporates zinc oxide into the inner comfort layer, providing both compression therapy and topical zinc delivery for venous leg ulcers.
Strengths: Innovative combination of adhesive technology and drug delivery. Customizable drug delivery options. Weaknesses: Some products may be more suitable for specific applications (e.g., IV sites) rather than general wound care. Higher cost compared to basic dressings.
Convatec, Inc.
Technical Solution: Convatec has pioneered the integration of drug-releasing occlusive dressings in wound care with their AQUACEL Ag+ Extra dressing. This advanced dressing combines Hydrofiber Technology with ionic silver and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and benzethonium chloride (BeCl) to create a synergistic antimicrobial effect[4]. The dressing forms a cohesive gel when in contact with wound fluid, allowing for controlled release of silver ions. The addition of EDTA and BeCl enhances the dressing's ability to penetrate and disrupt biofilms, a common barrier to wound healing[5]. Convatec's dressing can absorb up to 50 times its weight in fluid, maintaining a moist wound environment while managing exudate effectively. The company has also developed the Granuflex drug-delivery system, which allows for the incorporation of various active ingredients into hydrocolloid dressings[6].
Strengths: Synergistic antimicrobial action with biofilm-disrupting capabilities. High fluid absorption capacity. Weaknesses: May not be suitable for dry wounds. Higher cost compared to standard dressings.
Innovative Drug Delivery Mechanisms for Wound Care
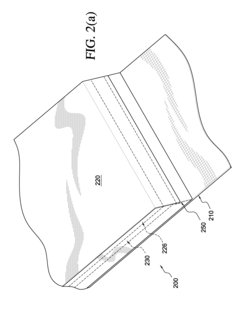
Modifiable Occlusive Skin Dressing
PatentActiveUS20210030597A1
Innovation
- The development of occlusive dressings with a liquid sealant applied to create an air-tight seal at the dressing-skin and tube-dressing interfaces, using a drape made of elastomeric material with biocompatible adhesive and a fast-drying sealant to maintain a sealed environment for up to 72 hours without external power, and incorporating a mechanical vacuum source connected via a flexible tube.
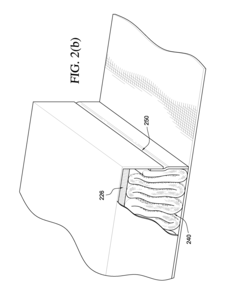
Integrated wound dressing system
PatentActiveUS8163973B2
Innovation
- An integrated wound dressing system that includes a bandage with a receptacle containing treatment material, such as gauze or a blood coagulant, and a pressure member for controlled application and compression, reducing the need for separate components and simplifying the treatment process.
Regulatory Framework for Drug-Device Combination Products
The regulatory framework for drug-device combination products, such as drug-releasing occlusive dressings, is complex and multifaceted. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval and regulation of these products through its Office of Combination Products (OCP). The primary mode of action determines whether the product is regulated as a drug, device, or biological product.
For drug-releasing occlusive dressings, the regulatory pathway often falls under the medical device regulations, with additional considerations for the drug component. The FDA's Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) typically takes the lead in reviewing these products, collaborating with the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) for the drug component.
Manufacturers must navigate various regulatory requirements, including premarket approval (PMA) or 510(k) clearance for the device aspect, and New Drug Application (NDA) or Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) for the drug component. The choice between these pathways depends on the novelty and risk profile of the product.
Quality control and manufacturing standards are crucial aspects of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for both the device and drug components. This includes maintaining appropriate documentation, implementing quality management systems, and ensuring consistent production processes.
Clinical trials for drug-releasing occlusive dressings often require a comprehensive approach that addresses both the wound healing efficacy of the dressing and the pharmacological effects of the drug. The FDA may require separate studies to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of each component, as well as their combined action.
Post-market surveillance is another critical element of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must implement systems for adverse event reporting, conduct post-approval studies if required, and maintain ongoing compliance with regulatory standards. This ensures the continued safety and effectiveness of the product throughout its lifecycle.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks for combination products vary. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) in the European Union and the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) in Japan have their own guidelines for these products. Manufacturers aiming for global markets must navigate these diverse regulatory landscapes, often requiring separate submissions and approvals for different regions.
For drug-releasing occlusive dressings, the regulatory pathway often falls under the medical device regulations, with additional considerations for the drug component. The FDA's Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) typically takes the lead in reviewing these products, collaborating with the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) for the drug component.
Manufacturers must navigate various regulatory requirements, including premarket approval (PMA) or 510(k) clearance for the device aspect, and New Drug Application (NDA) or Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) for the drug component. The choice between these pathways depends on the novelty and risk profile of the product.
Quality control and manufacturing standards are crucial aspects of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for both the device and drug components. This includes maintaining appropriate documentation, implementing quality management systems, and ensuring consistent production processes.
Clinical trials for drug-releasing occlusive dressings often require a comprehensive approach that addresses both the wound healing efficacy of the dressing and the pharmacological effects of the drug. The FDA may require separate studies to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of each component, as well as their combined action.
Post-market surveillance is another critical element of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must implement systems for adverse event reporting, conduct post-approval studies if required, and maintain ongoing compliance with regulatory standards. This ensures the continued safety and effectiveness of the product throughout its lifecycle.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks for combination products vary. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) in the European Union and the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) in Japan have their own guidelines for these products. Manufacturers aiming for global markets must navigate these diverse regulatory landscapes, often requiring separate submissions and approvals for different regions.
Cost-Effectiveness of Integrated Wound Care Solutions
The integration of drug-releasing occlusive dressings in wound care represents a significant advancement in treatment strategies, offering potential cost savings and improved patient outcomes. This analysis examines the cost-effectiveness of these integrated wound care solutions compared to traditional methods.
Initial investment in drug-releasing occlusive dressings may be higher than conventional dressings. However, their long-term cost-effectiveness becomes apparent when considering reduced frequency of dressing changes, decreased risk of complications, and potentially shorter healing times.
Studies have shown that occlusive dressings with controlled drug release can reduce the need for frequent dressing changes by up to 50%. This reduction translates to significant savings in nursing time and materials. For example, a typical chronic wound might require dressing changes every 1-2 days with traditional methods, while drug-releasing occlusive dressings may extend this interval to 3-7 days.
The incorporation of antimicrobial agents or growth factors directly into the dressing matrix can lead to more efficient drug delivery and potentially faster wound healing. This targeted approach minimizes the need for systemic medications, reducing the risk of side effects and associated treatment costs.
Furthermore, the occlusive nature of these dressings creates an optimal wound healing environment, maintaining moisture balance and protecting against external contaminants. This environment promotes faster epithelialization and reduces the risk of infection, potentially shortening the overall treatment duration and associated costs.
A comprehensive cost analysis must also consider the reduced risk of complications. By providing a controlled release of antimicrobial agents, these dressings can significantly lower the incidence of wound infections. Given that wound infections can increase treatment costs by 2-4 times, prevention through advanced dressing technology offers substantial economic benefits.
Long-term cost savings extend beyond direct medical expenses. Patients treated with integrated wound care solutions often experience less pain and discomfort, leading to improved quality of life and potentially faster return to work or normal activities. This indirect economic benefit, while challenging to quantify precisely, contributes to the overall cost-effectiveness of the approach.
However, it is crucial to note that the cost-effectiveness of drug-releasing occlusive dressings may vary depending on the specific wound type, patient characteristics, and healthcare setting. Tailored approaches considering these factors are essential for maximizing the economic benefits of integrated wound care solutions.
Initial investment in drug-releasing occlusive dressings may be higher than conventional dressings. However, their long-term cost-effectiveness becomes apparent when considering reduced frequency of dressing changes, decreased risk of complications, and potentially shorter healing times.
Studies have shown that occlusive dressings with controlled drug release can reduce the need for frequent dressing changes by up to 50%. This reduction translates to significant savings in nursing time and materials. For example, a typical chronic wound might require dressing changes every 1-2 days with traditional methods, while drug-releasing occlusive dressings may extend this interval to 3-7 days.
The incorporation of antimicrobial agents or growth factors directly into the dressing matrix can lead to more efficient drug delivery and potentially faster wound healing. This targeted approach minimizes the need for systemic medications, reducing the risk of side effects and associated treatment costs.
Furthermore, the occlusive nature of these dressings creates an optimal wound healing environment, maintaining moisture balance and protecting against external contaminants. This environment promotes faster epithelialization and reduces the risk of infection, potentially shortening the overall treatment duration and associated costs.
A comprehensive cost analysis must also consider the reduced risk of complications. By providing a controlled release of antimicrobial agents, these dressings can significantly lower the incidence of wound infections. Given that wound infections can increase treatment costs by 2-4 times, prevention through advanced dressing technology offers substantial economic benefits.
Long-term cost savings extend beyond direct medical expenses. Patients treated with integrated wound care solutions often experience less pain and discomfort, leading to improved quality of life and potentially faster return to work or normal activities. This indirect economic benefit, while challenging to quantify precisely, contributes to the overall cost-effectiveness of the approach.
However, it is crucial to note that the cost-effectiveness of drug-releasing occlusive dressings may vary depending on the specific wound type, patient characteristics, and healthcare setting. Tailored approaches considering these factors are essential for maximizing the economic benefits of integrated wound care solutions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!