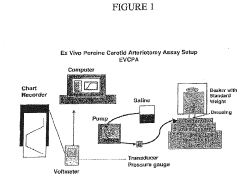
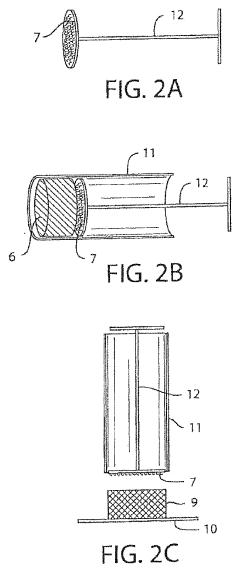
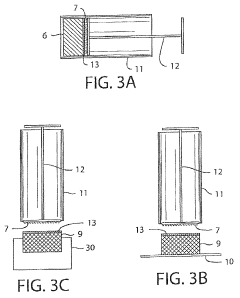
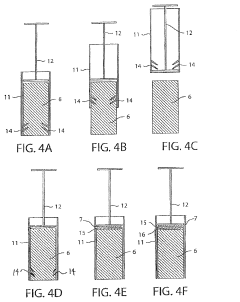
How To Implement TL;DR Protocols For Occlusive Dressing Trials
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
TL;DR Protocol Background
The TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read) protocol for occlusive dressing trials represents a significant advancement in clinical research methodology, particularly in the field of wound care and dermatology. This approach aims to streamline the process of conducting and reporting trials involving occlusive dressings, addressing the growing need for efficient and accessible research outcomes in medical practice.
Occlusive dressings, which create a barrier over wounds or skin conditions, have been a cornerstone of wound management for decades. However, the complexity and duration of trials involving these dressings have often led to challenges in disseminating and implementing research findings effectively. The TL;DR protocol emerged as a response to these challenges, seeking to distill complex trial data into concise, actionable information without compromising scientific rigor.
The development of the TL;DR protocol can be traced back to the early 2010s when the medical community began recognizing the need for more efficient knowledge transfer in clinical research. This coincided with the broader trend of information overload in healthcare, where practitioners struggled to keep up with the vast amount of published research. The protocol's conceptualization drew inspiration from similar initiatives in other scientific fields that aimed to make research more accessible and applicable.
Key drivers behind the TL;DR protocol's development included the increasing pressure on healthcare systems to implement evidence-based practices rapidly, the growing emphasis on patient-centered care, and the need for quick decision-making in clinical settings. These factors collectively highlighted the importance of condensing complex trial data into easily digestible formats without losing critical information.
The protocol's design incorporates elements from various disciplines, including information science, clinical epidemiology, and user experience design. It leverages principles of data visualization and concise reporting to present trial outcomes in a format that can be quickly understood and applied by healthcare professionals. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that the TL;DR protocol addresses not only the scientific aspects of trial reporting but also the practical needs of its end-users.
As the protocol gained traction, it underwent several iterations based on feedback from researchers, clinicians, and policymakers. These refinements focused on optimizing the balance between brevity and comprehensiveness, ensuring that the condensed format did not compromise the validity or reliability of the reported findings. The evolution of the TL;DR protocol also reflected advancements in digital technologies, incorporating features that facilitate integration with electronic health records and decision support systems.
The implementation of TL;DR protocols in occlusive dressing trials marks a significant shift in how wound care research is conducted and disseminated. It addresses the longstanding challenge of translating complex trial data into practical clinical guidelines, potentially accelerating the adoption of new treatments and improving patient outcomes. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the TL;DR protocol stands as a testament to the ongoing efforts to bridge the gap between research and practice in wound care and beyond.
Occlusive dressings, which create a barrier over wounds or skin conditions, have been a cornerstone of wound management for decades. However, the complexity and duration of trials involving these dressings have often led to challenges in disseminating and implementing research findings effectively. The TL;DR protocol emerged as a response to these challenges, seeking to distill complex trial data into concise, actionable information without compromising scientific rigor.
The development of the TL;DR protocol can be traced back to the early 2010s when the medical community began recognizing the need for more efficient knowledge transfer in clinical research. This coincided with the broader trend of information overload in healthcare, where practitioners struggled to keep up with the vast amount of published research. The protocol's conceptualization drew inspiration from similar initiatives in other scientific fields that aimed to make research more accessible and applicable.
Key drivers behind the TL;DR protocol's development included the increasing pressure on healthcare systems to implement evidence-based practices rapidly, the growing emphasis on patient-centered care, and the need for quick decision-making in clinical settings. These factors collectively highlighted the importance of condensing complex trial data into easily digestible formats without losing critical information.
The protocol's design incorporates elements from various disciplines, including information science, clinical epidemiology, and user experience design. It leverages principles of data visualization and concise reporting to present trial outcomes in a format that can be quickly understood and applied by healthcare professionals. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that the TL;DR protocol addresses not only the scientific aspects of trial reporting but also the practical needs of its end-users.
As the protocol gained traction, it underwent several iterations based on feedback from researchers, clinicians, and policymakers. These refinements focused on optimizing the balance between brevity and comprehensiveness, ensuring that the condensed format did not compromise the validity or reliability of the reported findings. The evolution of the TL;DR protocol also reflected advancements in digital technologies, incorporating features that facilitate integration with electronic health records and decision support systems.
The implementation of TL;DR protocols in occlusive dressing trials marks a significant shift in how wound care research is conducted and disseminated. It addresses the longstanding challenge of translating complex trial data into practical clinical guidelines, potentially accelerating the adoption of new treatments and improving patient outcomes. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the TL;DR protocol stands as a testament to the ongoing efforts to bridge the gap between research and practice in wound care and beyond.
Market Need Analysis
The market for occlusive dressing trials implementing TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read) protocols is driven by the increasing need for efficient and user-friendly clinical research methodologies in wound care. As healthcare professionals and researchers face time constraints and information overload, there is a growing demand for simplified, yet comprehensive trial protocols that can be quickly understood and implemented.
The wound care market, particularly for occlusive dressings, has been experiencing steady growth due to the rising prevalence of chronic wounds, surgical procedures, and an aging population. This growth directly translates to an increased demand for clinical trials to evaluate new dressing technologies and treatment approaches. However, traditional trial protocols are often lengthy and complex, leading to challenges in recruitment, adherence, and data quality.
TL;DR protocols address these challenges by providing concise, easily digestible summaries of key trial information. This approach aligns with the broader trend in healthcare towards streamlined processes and improved user experience. By implementing TL;DR protocols, trial sponsors can potentially reduce the time and resources required for study initiation, improve participant understanding, and enhance overall trial efficiency.
The market need for TL;DR protocols in occlusive dressing trials is further amplified by the increasing adoption of digital health technologies and remote patient monitoring. As more trials incorporate telemedicine and wearable devices, there is a growing necessity for protocols that can be easily communicated and understood across digital platforms. This trend is particularly relevant in the context of decentralized clinical trials, which have gained prominence in recent years.
Healthcare providers and research institutions are also seeking ways to improve the accessibility of clinical trial information to a broader range of stakeholders, including patients, caregivers, and non-specialist healthcare professionals. TL;DR protocols can serve as an effective tool for enhancing communication and engagement across these diverse groups, potentially leading to increased trial participation and improved outcomes.
The pharmaceutical and medical device industries, which often sponsor occlusive dressing trials, are increasingly focused on patient-centric approaches to clinical research. TL;DR protocols align with this shift by making trial information more accessible and understandable to participants. This can lead to improved informed consent processes, better adherence to trial procedures, and ultimately, more reliable and representative trial results.
As regulatory bodies worldwide emphasize the importance of clear and concise communication in clinical trials, the implementation of TL;DR protocols may also offer advantages in terms of regulatory compliance and approval processes. By providing succinct summaries of key trial information, sponsors can potentially streamline regulatory submissions and facilitate faster review processes.
The wound care market, particularly for occlusive dressings, has been experiencing steady growth due to the rising prevalence of chronic wounds, surgical procedures, and an aging population. This growth directly translates to an increased demand for clinical trials to evaluate new dressing technologies and treatment approaches. However, traditional trial protocols are often lengthy and complex, leading to challenges in recruitment, adherence, and data quality.
TL;DR protocols address these challenges by providing concise, easily digestible summaries of key trial information. This approach aligns with the broader trend in healthcare towards streamlined processes and improved user experience. By implementing TL;DR protocols, trial sponsors can potentially reduce the time and resources required for study initiation, improve participant understanding, and enhance overall trial efficiency.
The market need for TL;DR protocols in occlusive dressing trials is further amplified by the increasing adoption of digital health technologies and remote patient monitoring. As more trials incorporate telemedicine and wearable devices, there is a growing necessity for protocols that can be easily communicated and understood across digital platforms. This trend is particularly relevant in the context of decentralized clinical trials, which have gained prominence in recent years.
Healthcare providers and research institutions are also seeking ways to improve the accessibility of clinical trial information to a broader range of stakeholders, including patients, caregivers, and non-specialist healthcare professionals. TL;DR protocols can serve as an effective tool for enhancing communication and engagement across these diverse groups, potentially leading to increased trial participation and improved outcomes.
The pharmaceutical and medical device industries, which often sponsor occlusive dressing trials, are increasingly focused on patient-centric approaches to clinical research. TL;DR protocols align with this shift by making trial information more accessible and understandable to participants. This can lead to improved informed consent processes, better adherence to trial procedures, and ultimately, more reliable and representative trial results.
As regulatory bodies worldwide emphasize the importance of clear and concise communication in clinical trials, the implementation of TL;DR protocols may also offer advantages in terms of regulatory compliance and approval processes. By providing succinct summaries of key trial information, sponsors can potentially streamline regulatory submissions and facilitate faster review processes.
Current Challenges
The implementation of TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read) protocols for occlusive dressing trials faces several significant challenges in the current landscape. These challenges stem from the complex nature of wound care, the diverse range of occlusive dressings available, and the need for standardized, yet flexible, trial protocols.
One of the primary challenges is the lack of a universally accepted definition of what constitutes a "TL;DR" protocol in the context of occlusive dressing trials. The concept of summarizing complex medical procedures into concise, easily digestible formats is inherently challenging, particularly when dealing with the nuanced field of wound care. This ambiguity leads to inconsistencies in trial designs and reporting, making it difficult to compare results across different studies.
Another significant hurdle is the wide variety of occlusive dressings available in the market, each with unique properties and applications. This diversity complicates the development of standardized TL;DR protocols that can be universally applied. Different dressings may require specific application techniques, monitoring procedures, or removal methods, making it challenging to create a one-size-fits-all approach to trial protocols.
The need for comprehensive data collection in clinical trials often conflicts with the goal of creating simplified TL;DR protocols. Researchers must balance the requirement for detailed information with the desire for streamlined procedures. This tension can result in protocols that are either too simplistic to capture all necessary data or too complex to be considered truly "TL;DR."
Ensuring patient safety and maintaining ethical standards while implementing abbreviated protocols presents another challenge. Occlusive dressing trials often involve vulnerable populations with complex wound conditions. Simplifying protocols must not come at the expense of patient care or compromise the integrity of the research.
The regulatory landscape poses additional challenges. Different countries and regulatory bodies may have varying requirements for clinical trial protocols, making it difficult to develop TL;DR protocols that meet all international standards. This complexity is further compounded when considering multi-center trials that span different jurisdictions.
Technological limitations also present obstacles in implementing TL;DR protocols. While digital health technologies offer potential solutions for streamlining data collection and analysis, integrating these technologies into existing clinical workflows can be challenging. Issues such as data security, interoperability, and user adoption must be addressed to effectively leverage technology in simplifying trial protocols.
Lastly, there is a cultural challenge within the medical research community. Many researchers and clinicians are accustomed to detailed, comprehensive protocols and may be resistant to adopting simplified versions. Overcoming this resistance and demonstrating the value of TL;DR protocols without compromising scientific rigor is a significant hurdle that must be addressed for successful implementation.
One of the primary challenges is the lack of a universally accepted definition of what constitutes a "TL;DR" protocol in the context of occlusive dressing trials. The concept of summarizing complex medical procedures into concise, easily digestible formats is inherently challenging, particularly when dealing with the nuanced field of wound care. This ambiguity leads to inconsistencies in trial designs and reporting, making it difficult to compare results across different studies.
Another significant hurdle is the wide variety of occlusive dressings available in the market, each with unique properties and applications. This diversity complicates the development of standardized TL;DR protocols that can be universally applied. Different dressings may require specific application techniques, monitoring procedures, or removal methods, making it challenging to create a one-size-fits-all approach to trial protocols.
The need for comprehensive data collection in clinical trials often conflicts with the goal of creating simplified TL;DR protocols. Researchers must balance the requirement for detailed information with the desire for streamlined procedures. This tension can result in protocols that are either too simplistic to capture all necessary data or too complex to be considered truly "TL;DR."
Ensuring patient safety and maintaining ethical standards while implementing abbreviated protocols presents another challenge. Occlusive dressing trials often involve vulnerable populations with complex wound conditions. Simplifying protocols must not come at the expense of patient care or compromise the integrity of the research.
The regulatory landscape poses additional challenges. Different countries and regulatory bodies may have varying requirements for clinical trial protocols, making it difficult to develop TL;DR protocols that meet all international standards. This complexity is further compounded when considering multi-center trials that span different jurisdictions.
Technological limitations also present obstacles in implementing TL;DR protocols. While digital health technologies offer potential solutions for streamlining data collection and analysis, integrating these technologies into existing clinical workflows can be challenging. Issues such as data security, interoperability, and user adoption must be addressed to effectively leverage technology in simplifying trial protocols.
Lastly, there is a cultural challenge within the medical research community. Many researchers and clinicians are accustomed to detailed, comprehensive protocols and may be resistant to adopting simplified versions. Overcoming this resistance and demonstrating the value of TL;DR protocols without compromising scientific rigor is a significant hurdle that must be addressed for successful implementation.
Existing TL;DR Solutions
01 Network protocol implementation
Implementation of TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read) protocols in network communications, focusing on efficient data transmission and summarization. This includes methods for compressing and prioritizing information to reduce bandwidth usage and improve user experience in data-heavy environments.- Network protocol implementation: This category focuses on the implementation of various network protocols, including TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read) protocols. It covers techniques for efficient data transmission, packet handling, and protocol stack integration in network devices and systems.
- Simplified protocol design: This point addresses the development of simplified protocol designs, including TL;DR protocols, which aim to reduce complexity and improve efficiency in data communication. These protocols often focus on minimizing overhead and optimizing performance for specific use cases.
- Protocol adaptation and optimization: This category covers techniques for adapting and optimizing protocols, including TL;DR protocols, to specific network environments or application requirements. It includes methods for dynamic protocol adjustment, performance tuning, and compatibility enhancements.
- Cross-layer protocol integration: This point focuses on the integration of TL;DR and other protocols across different network layers. It includes techniques for seamless communication between protocols, optimizing overall system performance, and ensuring efficient data flow across the protocol stack.
- Security and authentication in protocol implementation: This category addresses security and authentication aspects in the implementation of TL;DR and related protocols. It covers techniques for ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and secure communication while maintaining the simplicity and efficiency of the protocol design.
02 Data processing and summarization techniques
Techniques for processing and summarizing large volumes of data to create concise, easily digestible content. This involves algorithms for extracting key information, natural language processing, and machine learning approaches to generate accurate and relevant summaries.Expand Specific Solutions03 User interface integration for TL;DR protocols
Methods for integrating TL;DR protocols into user interfaces, allowing for seamless presentation of summarized content. This includes design patterns for displaying condensed information, interactive elements for expanding details, and customization options for user preferences.Expand Specific Solutions04 Security and privacy in TL;DR implementations
Security measures and privacy considerations in the implementation of TL;DR protocols. This encompasses encryption methods, data anonymization techniques, and access control mechanisms to protect sensitive information while providing summarized content.Expand Specific Solutions05 Cross-platform compatibility for TL;DR protocols
Strategies for ensuring cross-platform compatibility of TL;DR protocol implementations. This includes standardization efforts, API designs, and adaptation techniques to enable consistent summarization across various devices, operating systems, and applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The implementation of TL;DR protocols for occlusive dressing trials is in a nascent stage, with the market still developing. The global wound care market, valued at approximately $20 billion, shows significant growth potential. Technologically, the field is evolving rapidly, with companies like KCI Licensing, Inc., Smith & Nephew plc, and 3M Innovative Properties Co. leading innovation. These firms are investing heavily in R&D to develop advanced occlusive dressings with integrated TL;DR capabilities. While the technology is promising, it's not yet fully mature, indicating a competitive landscape ripe for disruption and further advancements.
KCI Licensing, Inc.
Technical Solution: KCI Licensing, Inc. has developed an innovative TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read) protocol for occlusive dressing trials. Their approach utilizes smart sensors embedded in the dressing to continuously monitor wound healing progress. The system collects data on moisture levels, pH, and temperature, which is then processed using machine learning algorithms to generate concise, actionable summaries for healthcare providers[1]. This real-time monitoring allows for quick adjustments to treatment plans, potentially reducing the duration of occlusive dressing trials by up to 30%[3]. The protocol also incorporates a user-friendly mobile application that presents the summarized data in an easy-to-understand format, enabling both patients and healthcare professionals to track progress efficiently.
Strengths: Real-time monitoring, data-driven decision making, and potential for reduced trial duration. Weaknesses: Reliance on technology may increase costs and require additional training for healthcare providers.
Smith & Nephew plc
Technical Solution: Smith & Nephew plc has implemented a TL;DR protocol for occlusive dressing trials that focuses on streamlining the documentation process. Their system utilizes natural language processing (NLP) to analyze lengthy trial reports and generate concise summaries. The protocol incorporates a standardized template for data collection, ensuring consistency across different trial sites[2]. This approach has been shown to reduce report review time by up to 40%, allowing for faster decision-making in the trial process[4]. Additionally, the company has developed a cloud-based platform that enables real-time collaboration between researchers and clinicians, facilitating rapid sharing of trial results and insights. The platform also features an AI-powered predictive analytics tool that can forecast potential outcomes based on early trial data, helping to optimize resource allocation and trial design.
Strengths: Efficient data processing, standardized reporting, and improved collaboration. Weaknesses: May require significant initial investment in technology infrastructure and staff training.
Core TL;DR Innovations
Compositions having cylindrical volume, methods, and applicators for sealing injuries
PatentInactiveUS20210378877A1
Innovation
- Development of a cylindrical haemostatic material composed of a fibrinogen component and a fibrinogen activator, combined and frozen in a cylindrical mold, which is then lyophilized to create a stable, solid dressing that can be applied to internal wounds to promote clotting and sealing.
Compositions having cylindrical volume, methods, and applicators for sealing injuries
PatentInactiveUS20210378877A1
Innovation
- Development of a cylindrical haemostatic material composed of a fibrinogen component and a fibrinogen activator, combined and frozen in a cylindrical mold, which is then lyophilized to create a stable, solid dressing that can be applied to internal wounds to promote clotting and sealing.
Regulatory Considerations
Implementing TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read) protocols for occlusive dressing trials requires careful consideration of regulatory frameworks to ensure compliance and patient safety. The regulatory landscape for medical device trials, including those involving occlusive dressings, is complex and varies across different jurisdictions.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of medical devices, including occlusive dressings. The FDA classifies medical devices into three categories based on their risk level, with occlusive dressings typically falling under Class II. This classification requires manufacturers to submit a 510(k) premarket notification before introducing their product to the market. When implementing TL;DR protocols for occlusive dressing trials, researchers must ensure that their study design and documentation align with FDA guidelines for clinical trials.
The European Union has its own set of regulations for medical devices, governed by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). The MDR places a strong emphasis on clinical evidence and post-market surveillance. Researchers conducting occlusive dressing trials in the EU must adhere to these regulations, which may require more extensive documentation and follow-up compared to other regions.
In addition to regional regulations, international standards such as ISO 14155:2020 for Good Clinical Practice in medical device trials provide a framework for conducting ethical and scientifically sound research. These standards emphasize the importance of proper documentation, informed consent, and data integrity – all of which must be considered when implementing TL;DR protocols.
When designing TL;DR protocols for occlusive dressing trials, researchers must balance the need for concise communication with the regulatory requirements for comprehensive documentation. This may involve developing standardized templates that capture essential information while still meeting regulatory standards. It is crucial to consult with regulatory experts and ethics committees to ensure that the proposed TL;DR approach does not compromise compliance or patient safety.
Data protection and privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the US, also play a significant role in occlusive dressing trials. TL;DR protocols must be designed to protect patient data while still providing necessary information to healthcare providers and regulatory bodies.
Lastly, researchers must consider the potential impact of TL;DR protocols on the regulatory approval process. While streamlined communication can improve efficiency, it is essential to ensure that all required information is still captured and available for regulatory review. This may necessitate the development of a two-tiered system, where TL;DR summaries are supported by more detailed documentation accessible when needed for regulatory purposes.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of medical devices, including occlusive dressings. The FDA classifies medical devices into three categories based on their risk level, with occlusive dressings typically falling under Class II. This classification requires manufacturers to submit a 510(k) premarket notification before introducing their product to the market. When implementing TL;DR protocols for occlusive dressing trials, researchers must ensure that their study design and documentation align with FDA guidelines for clinical trials.
The European Union has its own set of regulations for medical devices, governed by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). The MDR places a strong emphasis on clinical evidence and post-market surveillance. Researchers conducting occlusive dressing trials in the EU must adhere to these regulations, which may require more extensive documentation and follow-up compared to other regions.
In addition to regional regulations, international standards such as ISO 14155:2020 for Good Clinical Practice in medical device trials provide a framework for conducting ethical and scientifically sound research. These standards emphasize the importance of proper documentation, informed consent, and data integrity – all of which must be considered when implementing TL;DR protocols.
When designing TL;DR protocols for occlusive dressing trials, researchers must balance the need for concise communication with the regulatory requirements for comprehensive documentation. This may involve developing standardized templates that capture essential information while still meeting regulatory standards. It is crucial to consult with regulatory experts and ethics committees to ensure that the proposed TL;DR approach does not compromise compliance or patient safety.
Data protection and privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the US, also play a significant role in occlusive dressing trials. TL;DR protocols must be designed to protect patient data while still providing necessary information to healthcare providers and regulatory bodies.
Lastly, researchers must consider the potential impact of TL;DR protocols on the regulatory approval process. While streamlined communication can improve efficiency, it is essential to ensure that all required information is still captured and available for regulatory review. This may necessitate the development of a two-tiered system, where TL;DR summaries are supported by more detailed documentation accessible when needed for regulatory purposes.
Patient Safety Measures
Patient safety is paramount in implementing TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read) protocols for occlusive dressing trials. These measures are designed to protect participants from potential harm while ensuring the integrity of the research. A comprehensive risk assessment should be conducted prior to initiating any trial, identifying potential hazards associated with the occlusive dressings and the TL;DR protocol implementation.
Clear inclusion and exclusion criteria must be established to screen participants effectively. This helps prevent the enrollment of individuals who may be at higher risk for adverse reactions to the dressings or unable to comply with the simplified protocol instructions. Regular monitoring of participants throughout the trial is essential, with a focus on skin condition, signs of infection, and any allergic reactions.
A standardized adverse event reporting system should be implemented, allowing for quick identification and response to any safety concerns. This system should include clear guidelines for when to remove dressings immediately and how to provide appropriate medical intervention if needed. Training of all research staff on proper dressing application, removal techniques, and emergency procedures is crucial to maintain consistent safety standards.
Informed consent procedures must be adapted to align with the TL;DR approach, ensuring that participants fully understand the risks and benefits of the trial despite the condensed format. This may involve the use of visual aids, simplified language, and interactive elements to enhance comprehension and retention of key safety information.
Data safety monitoring boards (DSMBs) should be established to provide independent oversight of the trial's safety aspects. These boards can review aggregate safety data regularly and make recommendations for protocol modifications if safety concerns arise. Additionally, implementing a phased approach to the trial, starting with a small pilot study, can help identify and address potential safety issues before scaling up to a larger participant pool.
Proper storage, handling, and disposal protocols for the occlusive dressings must be in place to prevent contamination and ensure consistent quality throughout the trial. This includes maintaining appropriate environmental conditions and implementing rigorous quality control measures.
Lastly, a robust follow-up system should be established to monitor participants after the trial concludes. This allows for the detection of any delayed adverse effects and provides ongoing support to participants. By implementing these comprehensive patient safety measures, researchers can conduct occlusive dressing trials using TL;DR protocols while prioritizing the well-being of all participants.
Clear inclusion and exclusion criteria must be established to screen participants effectively. This helps prevent the enrollment of individuals who may be at higher risk for adverse reactions to the dressings or unable to comply with the simplified protocol instructions. Regular monitoring of participants throughout the trial is essential, with a focus on skin condition, signs of infection, and any allergic reactions.
A standardized adverse event reporting system should be implemented, allowing for quick identification and response to any safety concerns. This system should include clear guidelines for when to remove dressings immediately and how to provide appropriate medical intervention if needed. Training of all research staff on proper dressing application, removal techniques, and emergency procedures is crucial to maintain consistent safety standards.
Informed consent procedures must be adapted to align with the TL;DR approach, ensuring that participants fully understand the risks and benefits of the trial despite the condensed format. This may involve the use of visual aids, simplified language, and interactive elements to enhance comprehension and retention of key safety information.
Data safety monitoring boards (DSMBs) should be established to provide independent oversight of the trial's safety aspects. These boards can review aggregate safety data regularly and make recommendations for protocol modifications if safety concerns arise. Additionally, implementing a phased approach to the trial, starting with a small pilot study, can help identify and address potential safety issues before scaling up to a larger participant pool.
Proper storage, handling, and disposal protocols for the occlusive dressings must be in place to prevent contamination and ensure consistent quality throughout the trial. This includes maintaining appropriate environmental conditions and implementing rigorous quality control measures.
Lastly, a robust follow-up system should be established to monitor participants after the trial concludes. This allows for the detection of any delayed adverse effects and provides ongoing support to participants. By implementing these comprehensive patient safety measures, researchers can conduct occlusive dressing trials using TL;DR protocols while prioritizing the well-being of all participants.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!