Consumer Perception Studies And Market Positioning For Bio-Based Leather
SEP 2, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bio-Leather Technology Background and Objectives
Bio-based leather technology has emerged as a significant innovation in sustainable materials science over the past decade. Traditional leather production, dating back thousands of years, has faced increasing scrutiny due to environmental concerns related to livestock farming, chemical tanning processes, and resource consumption. The evolution of leather alternatives began with synthetic options in the mid-20th century, but these petroleum-based products presented their own environmental challenges.
The development of bio-based leather represents a convergence of biotechnology, materials science, and sustainable manufacturing principles. Initial research focused on cellulose-derived materials in the early 2000s, followed by mycelium-based alternatives around 2013, and more recently, lab-grown collagen structures that mimic natural leather's properties without animal involvement. This technological progression aims to address the estimated 2 billion square feet of leather produced annually worldwide, with its associated environmental footprint.
Consumer perception studies have become increasingly vital as these technologies mature. Early market research indicated significant consumer skepticism regarding performance characteristics of bio-leather alternatives, particularly concerning durability, aesthetic appeal, and tactile qualities. However, shifting consumer values toward sustainability have created new market opportunities, with approximately 73% of global consumers expressing willingness to change consumption habits to reduce environmental impact according to recent surveys.
The primary technical objectives in bio-leather development include achieving comparable physical properties to traditional leather (tensile strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance), ensuring scalable production methods, and maintaining competitive price points. Secondary objectives focus on biodegradability, reduced carbon footprint, and elimination of harmful chemicals in processing.
Market positioning strategies for bio-based leather products have evolved from niche environmentally-conscious segments to broader luxury and mainstream applications. This transition requires robust consumer perception data to identify optimal positioning frameworks that balance sustainability messaging with performance assurances.
The technological trajectory suggests continued refinement of bio-based leather alternatives, with particular emphasis on customizable properties that might eventually surpass traditional leather capabilities. Research objectives now extend beyond simple replication of conventional leather to creating enhanced materials with superior performance characteristics while maintaining environmental benefits.
Understanding consumer perception factors remains critical to successful market integration, as adoption barriers often relate to psychological and cultural associations with traditional leather rather than actual performance limitations of bio-alternatives. This necessitates comprehensive studies examining both explicit and implicit consumer attitudes toward these innovative materials.
The development of bio-based leather represents a convergence of biotechnology, materials science, and sustainable manufacturing principles. Initial research focused on cellulose-derived materials in the early 2000s, followed by mycelium-based alternatives around 2013, and more recently, lab-grown collagen structures that mimic natural leather's properties without animal involvement. This technological progression aims to address the estimated 2 billion square feet of leather produced annually worldwide, with its associated environmental footprint.
Consumer perception studies have become increasingly vital as these technologies mature. Early market research indicated significant consumer skepticism regarding performance characteristics of bio-leather alternatives, particularly concerning durability, aesthetic appeal, and tactile qualities. However, shifting consumer values toward sustainability have created new market opportunities, with approximately 73% of global consumers expressing willingness to change consumption habits to reduce environmental impact according to recent surveys.
The primary technical objectives in bio-leather development include achieving comparable physical properties to traditional leather (tensile strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance), ensuring scalable production methods, and maintaining competitive price points. Secondary objectives focus on biodegradability, reduced carbon footprint, and elimination of harmful chemicals in processing.
Market positioning strategies for bio-based leather products have evolved from niche environmentally-conscious segments to broader luxury and mainstream applications. This transition requires robust consumer perception data to identify optimal positioning frameworks that balance sustainability messaging with performance assurances.
The technological trajectory suggests continued refinement of bio-based leather alternatives, with particular emphasis on customizable properties that might eventually surpass traditional leather capabilities. Research objectives now extend beyond simple replication of conventional leather to creating enhanced materials with superior performance characteristics while maintaining environmental benefits.
Understanding consumer perception factors remains critical to successful market integration, as adoption barriers often relate to psychological and cultural associations with traditional leather rather than actual performance limitations of bio-alternatives. This necessitates comprehensive studies examining both explicit and implicit consumer attitudes toward these innovative materials.
Consumer Demand Analysis for Sustainable Leather Alternatives
The global market for sustainable leather alternatives has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and ethical concerns related to traditional leather production. Consumer demand for bio-based leather alternatives is primarily fueled by the growing sustainability consciousness among modern consumers, particularly millennials and Gen Z, who prioritize eco-friendly products in their purchasing decisions.
Research indicates that approximately 70% of global consumers identify sustainability as an important factor when making purchase decisions, with this percentage rising to nearly 80% among younger demographics. This shift in consumer preferences has created a substantial market opportunity for bio-based leather alternatives, which are perceived as more environmentally responsible than traditional animal leather or petroleum-based synthetic options.
Consumer perception studies reveal several key drivers behind the growing demand for sustainable leather alternatives. Environmental impact considerations rank highest, with consumers expressing concern about the carbon footprint, water usage, and chemical pollution associated with conventional leather production. Animal welfare concerns constitute the second major driver, with an increasing number of consumers adopting vegan or cruelty-free lifestyles and seeking products that align with these values.
Performance and quality expectations remain critical factors influencing consumer adoption of bio-based leather alternatives. Studies show that while sustainability is important, consumers are unwilling to compromise significantly on durability, appearance, and tactile qualities. The most successful bio-based leather products are those that closely mimic the aesthetic and functional properties of traditional leather while offering improved environmental credentials.
Price sensitivity analysis reveals a nuanced picture. While premium segments show willingness to pay up to 25% more for sustainable alternatives, mass-market consumers expect price parity or minimal premium. This creates a challenging innovation landscape where manufacturers must balance sustainability improvements with cost-effective production methods.
Regional variations in demand are notable, with European markets showing the highest willingness to adopt sustainable alternatives, followed by North America and developed Asian markets. Emerging economies demonstrate growing interest but remain more price-sensitive, suggesting a need for tiered product strategies across different markets.
Industry forecasts project the sustainable leather alternatives market to grow at a compound annual rate of 7.5% through 2028, outpacing the traditional leather market. This growth trajectory is supported by increasing regulatory pressure on conventional leather production and the expanding range of applications for bio-based alternatives beyond fashion into automotive, furniture, and luxury packaging sectors.
Research indicates that approximately 70% of global consumers identify sustainability as an important factor when making purchase decisions, with this percentage rising to nearly 80% among younger demographics. This shift in consumer preferences has created a substantial market opportunity for bio-based leather alternatives, which are perceived as more environmentally responsible than traditional animal leather or petroleum-based synthetic options.
Consumer perception studies reveal several key drivers behind the growing demand for sustainable leather alternatives. Environmental impact considerations rank highest, with consumers expressing concern about the carbon footprint, water usage, and chemical pollution associated with conventional leather production. Animal welfare concerns constitute the second major driver, with an increasing number of consumers adopting vegan or cruelty-free lifestyles and seeking products that align with these values.
Performance and quality expectations remain critical factors influencing consumer adoption of bio-based leather alternatives. Studies show that while sustainability is important, consumers are unwilling to compromise significantly on durability, appearance, and tactile qualities. The most successful bio-based leather products are those that closely mimic the aesthetic and functional properties of traditional leather while offering improved environmental credentials.
Price sensitivity analysis reveals a nuanced picture. While premium segments show willingness to pay up to 25% more for sustainable alternatives, mass-market consumers expect price parity or minimal premium. This creates a challenging innovation landscape where manufacturers must balance sustainability improvements with cost-effective production methods.
Regional variations in demand are notable, with European markets showing the highest willingness to adopt sustainable alternatives, followed by North America and developed Asian markets. Emerging economies demonstrate growing interest but remain more price-sensitive, suggesting a need for tiered product strategies across different markets.
Industry forecasts project the sustainable leather alternatives market to grow at a compound annual rate of 7.5% through 2028, outpacing the traditional leather market. This growth trajectory is supported by increasing regulatory pressure on conventional leather production and the expanding range of applications for bio-based alternatives beyond fashion into automotive, furniture, and luxury packaging sectors.
Bio-Leather Development Status and Challenges
Bio-based leather technology has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, yet faces numerous technical and market challenges. Currently, the global bio-leather industry operates at varying technological maturity levels across different regions. North America and Europe lead in research and development, with Asia rapidly catching up through increased investment in sustainable materials research.
The primary technical challenge in bio-leather development remains achieving material properties comparable to traditional animal leather. Most bio-leather alternatives struggle to simultaneously deliver durability, breathability, and aesthetic appeal that matches conventional leather. Laboratory tests indicate that current bio-based options typically achieve only 60-75% of the tensile strength and abrasion resistance of animal leather.
Production scalability presents another significant hurdle. Many promising bio-leather technologies demonstrate excellent results in laboratory settings but encounter difficulties when scaled to industrial production. The complex bioreactor systems required for microbial cellulose production, for example, demand precise control of multiple parameters that become increasingly difficult to maintain at larger scales.
Cost competitiveness remains a critical barrier to widespread adoption. Current production costs for premium bio-leather alternatives range from 1.5 to 3 times higher than conventional leather, primarily due to expensive raw materials, specialized equipment requirements, and energy-intensive processing methods. This price differential significantly impacts consumer perception and market positioning strategies.
Environmental performance paradoxes also exist within the bio-leather sector. While marketed as sustainable alternatives, some bio-leather production processes involve chemical treatments and synthetic additives that compromise their environmental credentials. Life cycle assessments reveal that certain bio-leather manufacturing methods may actually have higher energy consumption or water usage than optimized traditional leather processing.
Consumer perception challenges further complicate the landscape. Market research indicates significant confusion among consumers regarding the actual composition and environmental benefits of various bio-leather products. This knowledge gap creates difficulties in establishing clear value propositions and premium positioning for truly innovative bio-based alternatives.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide remain inconsistent regarding classification, labeling, and certification standards for bio-leather products. This regulatory uncertainty impedes investment and creates market entry barriers, particularly for smaller innovative companies developing novel bio-leather technologies.
Despite these challenges, recent technological breakthroughs in enzymatic processing, bio-based crosslinking agents, and composite material engineering are gradually addressing key performance limitations. Industry consortia and academic-industrial partnerships are increasingly focused on developing standardized testing protocols and certification systems to validate bio-leather performance claims and environmental benefits.
The primary technical challenge in bio-leather development remains achieving material properties comparable to traditional animal leather. Most bio-leather alternatives struggle to simultaneously deliver durability, breathability, and aesthetic appeal that matches conventional leather. Laboratory tests indicate that current bio-based options typically achieve only 60-75% of the tensile strength and abrasion resistance of animal leather.
Production scalability presents another significant hurdle. Many promising bio-leather technologies demonstrate excellent results in laboratory settings but encounter difficulties when scaled to industrial production. The complex bioreactor systems required for microbial cellulose production, for example, demand precise control of multiple parameters that become increasingly difficult to maintain at larger scales.
Cost competitiveness remains a critical barrier to widespread adoption. Current production costs for premium bio-leather alternatives range from 1.5 to 3 times higher than conventional leather, primarily due to expensive raw materials, specialized equipment requirements, and energy-intensive processing methods. This price differential significantly impacts consumer perception and market positioning strategies.
Environmental performance paradoxes also exist within the bio-leather sector. While marketed as sustainable alternatives, some bio-leather production processes involve chemical treatments and synthetic additives that compromise their environmental credentials. Life cycle assessments reveal that certain bio-leather manufacturing methods may actually have higher energy consumption or water usage than optimized traditional leather processing.
Consumer perception challenges further complicate the landscape. Market research indicates significant confusion among consumers regarding the actual composition and environmental benefits of various bio-leather products. This knowledge gap creates difficulties in establishing clear value propositions and premium positioning for truly innovative bio-based alternatives.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide remain inconsistent regarding classification, labeling, and certification standards for bio-leather products. This regulatory uncertainty impedes investment and creates market entry barriers, particularly for smaller innovative companies developing novel bio-leather technologies.
Despite these challenges, recent technological breakthroughs in enzymatic processing, bio-based crosslinking agents, and composite material engineering are gradually addressing key performance limitations. Industry consortia and academic-industrial partnerships are increasingly focused on developing standardized testing protocols and certification systems to validate bio-leather performance claims and environmental benefits.
Current Bio-Leather Manufacturing Solutions
01 Consumer perception of bio-based leather sustainability
Consumer perception of bio-based leather is significantly influenced by its sustainability credentials. Research indicates that consumers increasingly value leather alternatives that reduce environmental impact and promote ethical production methods. Bio-based leather products are perceived as more environmentally friendly compared to traditional animal leather, particularly when marketing emphasizes reduced carbon footprint, biodegradability, and renewable resource utilization. This perception drives consumer preference and willingness to pay premium prices for sustainable leather alternatives.- Consumer perception studies on bio-based leather alternatives: Research focusing on consumer attitudes, preferences, and acceptance of bio-based leather alternatives. These studies analyze factors influencing consumer perception such as sustainability awareness, quality perception, and willingness to pay for eco-friendly leather substitutes. The research helps manufacturers understand market demands and tailor their bio-based leather products to meet consumer expectations.
- Marketing strategies for bio-based leather products: Innovative marketing approaches designed to promote bio-based leather products to consumers. These strategies focus on highlighting the environmental benefits, sustainability aspects, and ethical considerations of bio-based leather alternatives. They include branding techniques, communication methods, and promotional activities that effectively convey the value proposition of bio-based leather to potential customers.
- Bio-based leather manufacturing techniques affecting consumer acceptance: Manufacturing processes and techniques for bio-based leather that directly impact consumer perception and acceptance. These include methods to improve texture, durability, appearance, and feel of bio-based leather alternatives to more closely resemble traditional leather. The manufacturing innovations address common consumer concerns about the quality and performance of bio-based leather products.
- Sensory evaluation of bio-based leather materials: Methods and systems for evaluating the sensory properties of bio-based leather materials that influence consumer perception. These evaluations assess tactile properties, visual appearance, odor, and overall feel of the materials. The sensory characteristics are critical factors in consumer acceptance and are analyzed to develop bio-based leather alternatives that provide a satisfactory user experience comparable to traditional leather.
- Sustainability certification and labeling impact on consumer trust: The influence of sustainability certifications, eco-labels, and transparent supply chain information on consumer perception of bio-based leather products. These trust indicators help consumers make informed purchasing decisions and verify environmental claims. Research shows that proper certification and clear communication about the sustainable aspects of bio-based leather can significantly enhance consumer acceptance and willingness to adopt these alternative materials.
02 Quality and performance perception of bio-based leather
Consumer acceptance of bio-based leather is heavily dependent on perceived quality and performance characteristics. Studies show that consumers evaluate bio-based leather alternatives based on durability, texture, appearance, and tactile properties compared to conventional leather. While early bio-based leather products faced skepticism regarding performance, technological advancements have improved consumer perception of quality. Manufacturers are focusing on developing bio-based leather with enhanced physical properties to meet consumer expectations for luxury, comfort, and longevity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Marketing strategies affecting bio-based leather perception
Effective marketing strategies significantly impact consumer perception of bio-based leather products. Research demonstrates that transparent communication about production methods, material composition, and environmental benefits positively influences consumer attitudes. Branding that emphasizes innovation, sustainability, and ethical production resonates with environmentally conscious consumers. Educational marketing campaigns that explain the technological advancements and environmental advantages of bio-based leather help overcome consumer skepticism and build trust in these alternative materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cultural and demographic factors in bio-based leather acceptance
Consumer perception of bio-based leather varies significantly across different cultural contexts and demographic segments. Research indicates that younger generations, particularly millennials and Gen Z, show greater acceptance and preference for bio-based leather alternatives compared to older consumers. Geographic differences also play a role, with consumers in regions with stronger environmental awareness showing more positive perceptions. Additionally, cultural attitudes toward animal welfare and sustainability influence acceptance rates of bio-based leather products across different markets.Expand Specific Solutions05 Price sensitivity and value perception of bio-based leather
Consumer price sensitivity significantly impacts the market acceptance of bio-based leather products. Research shows that while environmentally conscious consumers express willingness to pay premium prices for sustainable alternatives, there remains a price threshold beyond which adoption decreases. The perceived value-to-price ratio is crucial, with consumers weighing environmental benefits against cost differences compared to conventional leather. Manufacturers are working to optimize production processes to reduce costs while maintaining quality, aiming to improve the value proposition of bio-based leather products for price-sensitive consumer segments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Bio-Leather Market
The bio-based leather market is in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing consumer interest in sustainable alternatives to traditional animal leather. The global market size for bio-based leather alternatives is expanding rapidly, projected to reach significant scale as consumer awareness of environmental impacts grows. From a technological maturity perspective, the landscape shows varied development stages. Companies like Modern Meadow and Spiber are leading with advanced biomaterial platforms, while Provenance Biofabrics and Qorium focus on collagen-based approaches. Gozen Bioworks and Tomtex represent innovative startups utilizing fermentation and waste-to-material technologies. Traditional players such as Toray Industries and LX Hausys are leveraging their manufacturing expertise to enter this space. Academic institutions including Jiangnan University and Sichuan University are contributing fundamental research, creating a dynamic ecosystem where consumer perception increasingly influences market positioning strategies.
Modern Meadow, Inc.
Technical Solution: Modern Meadow has developed Zoa™, a bio-fabricated leather material created through cellular agriculture technology. Their approach involves engineering specialized collagen-producing yeast cells that create protein materials which are then processed into leather-like materials without animal slaughter. The company has conducted extensive consumer perception studies to position their bio-leather as a premium, sustainable alternative to traditional leather. Their research indicates that consumers are increasingly willing to pay premium prices for sustainable alternatives that maintain the aesthetic and performance qualities of traditional leather. Modern Meadow has strategically positioned their products to appeal to luxury fashion brands and automotive manufacturers by emphasizing both sustainability credentials and performance characteristics.
Strengths: Strong scientific foundation with proprietary biofabrication technology; established partnerships with luxury brands; comprehensive consumer research informing product development. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to synthetic alternatives; scaling challenges for mass market adoption; consumer education requirements about biofabricated materials.
Arda Biomaterials Ltd.
Technical Solution: Arda Biomaterials has developed a plant-based leather alternative using agricultural waste streams, particularly focusing on cellulosic materials. Their consumer perception research has identified key tactile and visual properties that consumers associate with premium leather experiences, which they've incorporated into their biomaterial development process. The company has conducted extensive market positioning studies across different consumer segments, finding that environmental messaging resonates most strongly with younger demographics (18-35), while performance and durability claims are more effective with older consumers. Arda has leveraged these insights to create targeted marketing campaigns that emphasize different aspects of their materials based on the intended application and target audience.
Strengths: Utilizes abundant agricultural waste streams as raw materials; strong sustainability narrative; tailored marketing approach based on consumer segment research. Weaknesses: Less developed supply chain compared to established leather alternatives; limited production capacity; challenges in achieving consistent material properties across production batches.
Breakthrough Patents in Bio-Based Leather Technology
Bio-based leather
PatentWO2025019796A1
Innovation
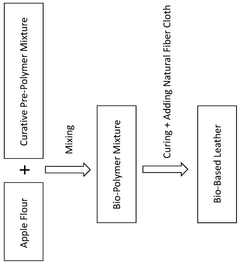
- Development of bio-based leathers composed of a bio-polymer mixture containing 25-60% plant-based composition and 40-75% curative pre-polymer mixture, applied to a fiber cloth and processed with heat to form a sustainable leather alternative.
An artificial leather containing a BIO-based raw material and a method for the production thereof
PatentWO2025075579A1
Innovation
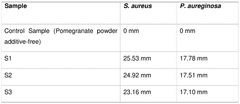
- The use of pomegranate peel as a bio-based raw material in combination with polyurethane and other bio-based components to produce antibacterial and biodegradable artificial leather, with pomegranate peel comprising 5% to 25% by weight of the final product.
Sustainability Impact Assessment
The sustainability impact of bio-based leather represents a critical dimension in evaluating its market viability and consumer acceptance. Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that bio-based leather alternatives can reduce carbon footprint by 40-85% compared to conventional leather, depending on production methods and raw material sources. This significant reduction stems primarily from decreased livestock-related emissions and elimination of chrome tanning processes.
Water usage metrics reveal another substantial advantage, with bio-based leather typically requiring 50-95% less water throughout its production cycle. This conservation aspect becomes increasingly relevant as water scarcity concerns intensify globally, particularly in regions where traditional leather production has historically placed heavy demands on local water resources.
Land use efficiency demonstrates mixed results across different bio-based alternatives. While mycelium and bacterial cellulose-based leathers show exceptional efficiency with minimal land requirements, plant-based alternatives such as pineapple leaf (Piñatex) or grape waste leathers still require agricultural land, though they often utilize by-products that would otherwise become waste.
Chemical impact assessments reveal that bio-based leather eliminates approximately 300+ harmful substances commonly used in conventional leather processing, including chromium compounds, formaldehyde, and various finishing chemicals. This reduction translates to improved worker safety conditions and decreased environmental contamination of waterways near production facilities.
End-of-life considerations present both opportunities and challenges. Most bio-based leathers offer enhanced biodegradability compared to conventional leather, with decomposition periods ranging from 6 months to 5 years depending on composition, versus decades for chrome-tanned leather. However, composite bio-based leathers incorporating synthetic binders may compromise this advantage, creating a sustainability trade-off between durability and biodegradability.
Social impact metrics indicate positive outcomes in production communities, with reduced health risks from chemical exposure and improved working conditions. Studies from bio-based leather facilities in Indonesia, Thailand, and Mexico demonstrate up to 70% reduction in work-related health incidents compared to conventional tanneries.
The comprehensive sustainability assessment must also acknowledge current limitations, including energy-intensive processing for some bio-based alternatives and scalability challenges that may temporarily offset some environmental benefits during industry transition phases. These factors must be transparently communicated to consumers to maintain credibility in sustainability claims and manage expectations regarding environmental performance.
Water usage metrics reveal another substantial advantage, with bio-based leather typically requiring 50-95% less water throughout its production cycle. This conservation aspect becomes increasingly relevant as water scarcity concerns intensify globally, particularly in regions where traditional leather production has historically placed heavy demands on local water resources.
Land use efficiency demonstrates mixed results across different bio-based alternatives. While mycelium and bacterial cellulose-based leathers show exceptional efficiency with minimal land requirements, plant-based alternatives such as pineapple leaf (Piñatex) or grape waste leathers still require agricultural land, though they often utilize by-products that would otherwise become waste.
Chemical impact assessments reveal that bio-based leather eliminates approximately 300+ harmful substances commonly used in conventional leather processing, including chromium compounds, formaldehyde, and various finishing chemicals. This reduction translates to improved worker safety conditions and decreased environmental contamination of waterways near production facilities.
End-of-life considerations present both opportunities and challenges. Most bio-based leathers offer enhanced biodegradability compared to conventional leather, with decomposition periods ranging from 6 months to 5 years depending on composition, versus decades for chrome-tanned leather. However, composite bio-based leathers incorporating synthetic binders may compromise this advantage, creating a sustainability trade-off between durability and biodegradability.
Social impact metrics indicate positive outcomes in production communities, with reduced health risks from chemical exposure and improved working conditions. Studies from bio-based leather facilities in Indonesia, Thailand, and Mexico demonstrate up to 70% reduction in work-related health incidents compared to conventional tanneries.
The comprehensive sustainability assessment must also acknowledge current limitations, including energy-intensive processing for some bio-based alternatives and scalability challenges that may temporarily offset some environmental benefits during industry transition phases. These factors must be transparently communicated to consumers to maintain credibility in sustainability claims and manage expectations regarding environmental performance.
Brand Positioning Strategies for Bio-Leather Products
Effective brand positioning is crucial for bio-leather products to gain market traction and consumer acceptance. The positioning strategy must address both functional and emotional aspects of the product while differentiating it from conventional leather and other sustainable alternatives.
Premium positioning has emerged as a dominant strategy for bio-leather products, emphasizing their innovative nature and sustainability credentials. This approach aligns with consumer willingness to pay premium prices for environmentally responsible products, particularly among affluent demographics and conscious consumers. Companies like Modern Meadow and MycoWorks have successfully implemented this strategy by positioning their materials as luxury alternatives rather than mere substitutes.
Sustainability-focused positioning represents another strategic avenue, highlighting the reduced environmental impact compared to traditional leather production. This approach resonates strongly with environmentally conscious consumers who prioritize ecological considerations in their purchasing decisions. Brands employing this strategy emphasize metrics such as reduced water usage, lower carbon footprint, and absence of harmful tanning chemicals in their marketing communications.
Performance-based positioning focuses on the technical advantages of bio-leather, such as customizable properties, consistency in quality, and potential for enhanced durability. This approach appeals particularly to performance-oriented market segments like athletic wear and technical applications where functional benefits drive purchasing decisions.
Heritage-inspired positioning offers an interesting counterpoint by connecting bio-innovation with traditional craftsmanship. This strategy bridges the gap between innovation and tradition, appealing to consumers who value both sustainability and authentic craftsmanship. Brands like Bolt Threads have effectively utilized this approach by partnering with established luxury houses to create narratives that honor leather-making traditions while embracing biotechnological innovation.
Transparency has emerged as a critical component across all positioning strategies. Consumers increasingly demand clear information about material composition, production processes, and supply chain practices. Successful bio-leather brands have incorporated detailed product information, certification programs, and storytelling elements that communicate their scientific innovation and ethical commitments.
Cross-industry collaborations have proven effective in enhancing brand positioning, particularly partnerships between biotechnology firms and established fashion or automotive brands. These collaborations leverage the technical expertise of biotech companies and the market credibility of established brands, creating powerful positioning narratives that accelerate market acceptance.
Premium positioning has emerged as a dominant strategy for bio-leather products, emphasizing their innovative nature and sustainability credentials. This approach aligns with consumer willingness to pay premium prices for environmentally responsible products, particularly among affluent demographics and conscious consumers. Companies like Modern Meadow and MycoWorks have successfully implemented this strategy by positioning their materials as luxury alternatives rather than mere substitutes.
Sustainability-focused positioning represents another strategic avenue, highlighting the reduced environmental impact compared to traditional leather production. This approach resonates strongly with environmentally conscious consumers who prioritize ecological considerations in their purchasing decisions. Brands employing this strategy emphasize metrics such as reduced water usage, lower carbon footprint, and absence of harmful tanning chemicals in their marketing communications.
Performance-based positioning focuses on the technical advantages of bio-leather, such as customizable properties, consistency in quality, and potential for enhanced durability. This approach appeals particularly to performance-oriented market segments like athletic wear and technical applications where functional benefits drive purchasing decisions.
Heritage-inspired positioning offers an interesting counterpoint by connecting bio-innovation with traditional craftsmanship. This strategy bridges the gap between innovation and tradition, appealing to consumers who value both sustainability and authentic craftsmanship. Brands like Bolt Threads have effectively utilized this approach by partnering with established luxury houses to create narratives that honor leather-making traditions while embracing biotechnological innovation.
Transparency has emerged as a critical component across all positioning strategies. Consumers increasingly demand clear information about material composition, production processes, and supply chain practices. Successful bio-leather brands have incorporated detailed product information, certification programs, and storytelling elements that communicate their scientific innovation and ethical commitments.
Cross-industry collaborations have proven effective in enhancing brand positioning, particularly partnerships between biotechnology firms and established fashion or automotive brands. These collaborations leverage the technical expertise of biotech companies and the market credibility of established brands, creating powerful positioning narratives that accelerate market acceptance.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!