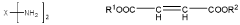Examining the Workforce Impacts of Isocyanate Innovations
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Evolution and Objectives
Isocyanates have played a pivotal role in the chemical industry since their discovery in the early 20th century. These highly reactive compounds, characterized by their -N=C=O functional group, have undergone significant evolution in terms of production methods, applications, and safety considerations. The journey of isocyanates began with their synthesis by Wurtz in 1848, but it wasn't until the 1930s that their commercial potential was realized.
The primary objective in the field of isocyanate technology has been to enhance their versatility while mitigating associated health and environmental risks. Over the decades, researchers and industry professionals have focused on developing more efficient production processes, exploring novel applications, and improving the safety profile of these compounds. This has led to a continuous refinement of isocyanate chemistry, resulting in a wide array of products that have transformed various sectors, including automotive, construction, and consumer goods.
One of the key trends in isocyanate evolution has been the shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods. Traditional processes often involved the use of phosgene, a highly toxic compound. However, recent innovations have aimed at developing phosgene-free routes for isocyanate synthesis, aligning with global sustainability goals and stricter environmental regulations.
Another significant objective in isocyanate development has been to expand their application range. While initially used primarily in polyurethane production, isocyanates have found their way into diverse fields such as coatings, adhesives, elastomers, and foams. This expansion has driven research into tailoring isocyanate properties for specific end-uses, leading to the development of specialized variants like aliphatic isocyanates for UV-resistant coatings.
The workforce impact of these innovations has been substantial. As isocyanate technology has advanced, it has necessitated the development of new skills and knowledge among workers in the chemical industry. This has led to changes in training programs, safety protocols, and job roles, reflecting the evolving nature of isocyanate handling and application.
Looking ahead, the objectives for isocyanate technology continue to focus on sustainability, safety, and performance enhancement. Researchers are exploring bio-based isocyanates, aiming to reduce reliance on petrochemical feedstocks. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on developing isocyanates with lower volatility and reactivity, which could significantly improve worker safety without compromising product performance.
The primary objective in the field of isocyanate technology has been to enhance their versatility while mitigating associated health and environmental risks. Over the decades, researchers and industry professionals have focused on developing more efficient production processes, exploring novel applications, and improving the safety profile of these compounds. This has led to a continuous refinement of isocyanate chemistry, resulting in a wide array of products that have transformed various sectors, including automotive, construction, and consumer goods.
One of the key trends in isocyanate evolution has been the shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods. Traditional processes often involved the use of phosgene, a highly toxic compound. However, recent innovations have aimed at developing phosgene-free routes for isocyanate synthesis, aligning with global sustainability goals and stricter environmental regulations.
Another significant objective in isocyanate development has been to expand their application range. While initially used primarily in polyurethane production, isocyanates have found their way into diverse fields such as coatings, adhesives, elastomers, and foams. This expansion has driven research into tailoring isocyanate properties for specific end-uses, leading to the development of specialized variants like aliphatic isocyanates for UV-resistant coatings.
The workforce impact of these innovations has been substantial. As isocyanate technology has advanced, it has necessitated the development of new skills and knowledge among workers in the chemical industry. This has led to changes in training programs, safety protocols, and job roles, reflecting the evolving nature of isocyanate handling and application.
Looking ahead, the objectives for isocyanate technology continue to focus on sustainability, safety, and performance enhancement. Researchers are exploring bio-based isocyanates, aiming to reduce reliance on petrochemical feedstocks. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on developing isocyanates with lower volatility and reactivity, which could significantly improve worker safety without compromising product performance.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for isocyanate innovations is driven by several key factors, including the growing construction industry, automotive sector expansion, and increasing awareness of energy efficiency. Isocyanates, as essential components in polyurethane production, play a crucial role in various applications such as insulation materials, coatings, adhesives, and sealants.
In the construction sector, the demand for high-performance insulation materials continues to rise due to stringent energy efficiency regulations and the push for sustainable building practices. Isocyanate-based polyurethane foams offer superior thermal insulation properties, contributing to reduced energy consumption in both residential and commercial buildings. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed countries where retrofitting existing structures for improved energy efficiency is becoming increasingly common.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for isocyanate innovations. As vehicle manufacturers strive to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency, the use of polyurethane components in car interiors, seating, and structural parts has increased. Additionally, the growing electric vehicle market has created new opportunities for isocyanate-based materials in battery encapsulation and thermal management systems.
The global polyurethane market, which heavily relies on isocyanates, is expected to experience steady growth in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the expanding middle class in emerging economies, leading to increased consumer spending on furniture, bedding, and automotive products. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is anticipated to be a major driver of market demand due to rapid industrialization and urbanization.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures are shaping the market demand for isocyanate innovations. There is a growing emphasis on developing more sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional isocyanates. This has led to research into bio-based isocyanates and low-emission formulations, creating new market opportunities for companies that can successfully innovate in this space.
The healthcare sector presents another area of potential growth for isocyanate-based products. Medical-grade polyurethanes are increasingly used in various applications, including wound dressings, medical tubing, and prosthetics. The aging population in many developed countries is expected to drive demand for these specialized materials in the coming years.
However, the market demand analysis must also consider potential challenges. Occupational health and safety concerns related to isocyanate exposure have led to stricter regulations in many countries. This has created a need for safer handling practices and innovative product formulations that minimize worker exposure risks. Companies that can address these safety concerns while maintaining product performance are likely to gain a competitive edge in the market.
In the construction sector, the demand for high-performance insulation materials continues to rise due to stringent energy efficiency regulations and the push for sustainable building practices. Isocyanate-based polyurethane foams offer superior thermal insulation properties, contributing to reduced energy consumption in both residential and commercial buildings. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed countries where retrofitting existing structures for improved energy efficiency is becoming increasingly common.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for isocyanate innovations. As vehicle manufacturers strive to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency, the use of polyurethane components in car interiors, seating, and structural parts has increased. Additionally, the growing electric vehicle market has created new opportunities for isocyanate-based materials in battery encapsulation and thermal management systems.
The global polyurethane market, which heavily relies on isocyanates, is expected to experience steady growth in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the expanding middle class in emerging economies, leading to increased consumer spending on furniture, bedding, and automotive products. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is anticipated to be a major driver of market demand due to rapid industrialization and urbanization.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures are shaping the market demand for isocyanate innovations. There is a growing emphasis on developing more sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional isocyanates. This has led to research into bio-based isocyanates and low-emission formulations, creating new market opportunities for companies that can successfully innovate in this space.
The healthcare sector presents another area of potential growth for isocyanate-based products. Medical-grade polyurethanes are increasingly used in various applications, including wound dressings, medical tubing, and prosthetics. The aging population in many developed countries is expected to drive demand for these specialized materials in the coming years.
However, the market demand analysis must also consider potential challenges. Occupational health and safety concerns related to isocyanate exposure have led to stricter regulations in many countries. This has created a need for safer handling practices and innovative product formulations that minimize worker exposure risks. Companies that can address these safety concerns while maintaining product performance are likely to gain a competitive edge in the market.
Current Challenges
The isocyanate industry is currently facing several significant challenges that impact its workforce and overall development. One of the primary concerns is the ongoing health and safety risks associated with isocyanate exposure. Despite advancements in protective equipment and handling procedures, workers in manufacturing and application processes remain at risk of respiratory issues, skin irritation, and potential long-term health effects. This necessitates continuous improvement in safety protocols and protective measures, which can be resource-intensive for companies.
Environmental regulations pose another substantial challenge for the isocyanate sector. Stricter emission controls and waste management requirements are forcing companies to invest heavily in new technologies and processes to comply with evolving standards. This regulatory pressure not only affects production costs but also requires workforce retraining and adaptation to new operational procedures.
The volatility of raw material prices, particularly for key ingredients like toluene and propylene, presents a significant economic challenge. Price fluctuations can impact production costs and, consequently, workforce stability. Companies may need to adjust their workforce in response to market conditions, leading to potential job insecurity and the need for flexible staffing strategies.
Technological advancements in isocyanate production and application are creating a skills gap within the industry. As new, more efficient, and environmentally friendly processes are developed, there is an increasing demand for workers with specialized knowledge in areas such as green chemistry, advanced process control, and automation. This shift requires significant investment in workforce training and development, as well as potential restructuring of job roles and responsibilities.
Global competition, particularly from emerging markets with lower production costs, is putting pressure on established isocyanate manufacturers. This competitive landscape is driving companies to seek cost-cutting measures, which can sometimes lead to workforce reductions or relocations. Balancing competitiveness with maintaining a skilled and experienced workforce remains a critical challenge for many organizations in the sector.
The industry is also grappling with public perception issues related to the environmental and health impacts of isocyanates. This can affect recruitment efforts and employee morale, as workers may be hesitant to join or remain in an industry perceived as potentially harmful. Addressing these perception challenges requires ongoing public education and transparency efforts, which can strain resources and impact workforce engagement.
Lastly, the push for sustainable alternatives to traditional isocyanate-based products is creating uncertainty within the industry. As research into bio-based and less toxic alternatives progresses, companies must navigate the potential for disruptive changes in their product lines and manufacturing processes. This uncertainty can lead to hesitation in long-term workforce planning and investment in skills development, as the future direction of the industry becomes less clear.
Environmental regulations pose another substantial challenge for the isocyanate sector. Stricter emission controls and waste management requirements are forcing companies to invest heavily in new technologies and processes to comply with evolving standards. This regulatory pressure not only affects production costs but also requires workforce retraining and adaptation to new operational procedures.
The volatility of raw material prices, particularly for key ingredients like toluene and propylene, presents a significant economic challenge. Price fluctuations can impact production costs and, consequently, workforce stability. Companies may need to adjust their workforce in response to market conditions, leading to potential job insecurity and the need for flexible staffing strategies.
Technological advancements in isocyanate production and application are creating a skills gap within the industry. As new, more efficient, and environmentally friendly processes are developed, there is an increasing demand for workers with specialized knowledge in areas such as green chemistry, advanced process control, and automation. This shift requires significant investment in workforce training and development, as well as potential restructuring of job roles and responsibilities.
Global competition, particularly from emerging markets with lower production costs, is putting pressure on established isocyanate manufacturers. This competitive landscape is driving companies to seek cost-cutting measures, which can sometimes lead to workforce reductions or relocations. Balancing competitiveness with maintaining a skilled and experienced workforce remains a critical challenge for many organizations in the sector.
The industry is also grappling with public perception issues related to the environmental and health impacts of isocyanates. This can affect recruitment efforts and employee morale, as workers may be hesitant to join or remain in an industry perceived as potentially harmful. Addressing these perception challenges requires ongoing public education and transparency efforts, which can strain resources and impact workforce engagement.
Lastly, the push for sustainable alternatives to traditional isocyanate-based products is creating uncertainty within the industry. As research into bio-based and less toxic alternatives progresses, companies must navigate the potential for disruptive changes in their product lines and manufacturing processes. This uncertainty can lead to hesitation in long-term workforce planning and investment in skills development, as the future direction of the industry becomes less clear.
Existing Workforce Solutions
01 Workforce management and scheduling
Systems and methods for managing workforce schedules in industries dealing with isocyanates. This includes optimizing shift assignments, tracking employee availability, and ensuring proper staffing levels to handle isocyanate-related tasks safely and efficiently.- Workforce management and scheduling: Systems and methods for managing workforce schedules, particularly in industries dealing with hazardous materials like isocyanates. These solutions optimize employee allocation, track working hours, and ensure compliance with safety regulations specific to chemical handling.
- Health and safety monitoring: Technologies for monitoring and assessing the health impacts of isocyanate exposure on workers. This includes real-time health tracking, risk assessment tools, and systems for managing occupational health data to mitigate long-term effects of chemical exposure.
- Training and competency management: Platforms and methodologies for training workforce in safe handling of isocyanates and other hazardous materials. These systems track employee competencies, certifications, and provide ongoing education to ensure a skilled and safety-conscious workforce.
- Workplace environmental monitoring: Systems for continuous monitoring of workplace environments where isocyanates are present. These solutions include air quality sensors, exposure level tracking, and alert systems to ensure safe working conditions and compliance with occupational safety standards.
- Impact assessment and reporting: Tools and methods for assessing and reporting the overall impact of isocyanate exposure on workforce productivity, health, and organizational performance. These systems help in decision-making regarding workforce policies, protective measures, and long-term strategies for minimizing negative impacts.
02 Health and safety monitoring
Implementation of health and safety protocols for workers exposed to isocyanates. This involves real-time monitoring of exposure levels, providing personal protective equipment, and conducting regular health assessments to mitigate risks associated with isocyanate handling.Expand Specific Solutions03 Training and skill development
Development of comprehensive training programs for workers handling isocyanates. This includes education on proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and continuous skill development to ensure a competent and safety-conscious workforce.Expand Specific Solutions04 Performance evaluation and productivity analysis
Systems for evaluating worker performance and analyzing productivity in isocyanate-related tasks. This involves setting performance metrics, conducting regular assessments, and identifying areas for improvement to optimize workforce efficiency while maintaining safety standards.Expand Specific Solutions05 Compliance and regulatory management
Tools and processes for ensuring compliance with regulations related to isocyanate handling in the workplace. This includes tracking and reporting on regulatory requirements, managing documentation, and implementing changes in response to evolving standards to protect the workforce.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The isocyanate innovations market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in various industries. The global market size is expanding, with key players like Wanhua Chemical, Covestro, BASF, and Dow leading technological advancements. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to improve product performance and sustainability. The technology is relatively mature but evolving, with a focus on developing eco-friendly alternatives and enhancing efficiency. Emerging players such as Asahi Kasei and Mitsui Chemicals are also contributing to market dynamics, intensifying competition and driving further innovation in isocyanate technologies.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has developed innovative isocyanate technologies that focus on improving worker safety and reducing environmental impact. Their approach includes the development of low-free monomer technology for TDI and MDI production, which significantly reduces worker exposure to harmful isocyanate vapors[1]. They have also implemented advanced containment systems and automated handling processes to minimize direct contact between workers and isocyanate materials[2]. Additionally, Wanhua has invested in the development of water-based polyurethane systems that reduce the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and improve air quality in manufacturing environments[3].
Strengths: Enhanced worker safety, reduced environmental impact, and improved production efficiency. Weaknesses: Potential higher initial implementation costs and the need for worker retraining.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro has pioneered the development of novel isocyanate-free polyurethane technologies, which aim to eliminate the use of traditional isocyanates in certain applications. Their INSQIN® technology for textile coating uses waterborne polyurethane dispersions that do not require isocyanates during the coating process[4]. This innovation significantly reduces worker exposure to hazardous chemicals and improves overall workplace safety. Covestro has also developed partially bio-based isocyanates, derived from renewable resources, which reduce the carbon footprint of polyurethane production while maintaining performance characteristics[5]. These advancements have led to changes in workforce requirements, with a shift towards more specialized roles in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing processes.
Strengths: Elimination of isocyanate exposure in certain applications, reduced environmental impact, and alignment with sustainability trends. Weaknesses: Limited applicability to all polyurethane products and potential higher production costs.
Innovative Isocyanate Developments
Two-component coating composition
PatentWO2022002679A1
Innovation
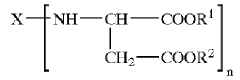
- A two-component coating composition comprising a polyaspartic ester A-component and a polyether-modified polyisocyanate B-component with a molar ratio of isocyanate groups to amino groups of 0.8:1-4:1, where the polyether-modified polyisocyanate is obtained by reacting a polyisocyanate with hexamethylene diisocyanate trimer and polyoxyalkylene monoether alcohol, providing a long working time and short surface-drying time without the need for special equipment.
Isocyanate composition
PatentPendingKR1020240058767A
Innovation
- An isocyanate composition comprising an isocyanate-based compound and a phosphonate-based compound, along with optional polyfunctional thiol-, alcohol-, or episulfide-based compounds, to suppress oligomerization and improve storage stability and workability.
Occupational Safety Regulations
Occupational safety regulations play a crucial role in addressing the workforce impacts of isocyanate innovations. These regulations are designed to protect workers from the potential health hazards associated with exposure to isocyanates, which are widely used in various industries, including automotive, construction, and manufacturing.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States has established specific standards for isocyanate exposure in the workplace. These standards set permissible exposure limits (PELs) for different types of isocyanates, such as toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene bisphenyl isocyanate (MDI). The current PELs for most isocyanates are set at 0.02 parts per million (ppm) for an 8-hour time-weighted average.
In addition to exposure limits, occupational safety regulations mandate the implementation of engineering controls and personal protective equipment (PPE) to minimize worker exposure to isocyanates. These measures include the use of ventilation systems, enclosed processes, and respiratory protection. Employers are required to provide appropriate PPE, such as chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, and respirators, to workers handling isocyanates.
Worker training and education are also essential components of occupational safety regulations. Employers must ensure that workers are properly trained on the hazards of isocyanates, safe handling procedures, and emergency response protocols. This includes providing information on the signs and symptoms of isocyanate exposure, as well as proper decontamination procedures.
Regulatory bodies also require employers to conduct regular workplace monitoring and health surveillance programs. These programs involve periodic air sampling to assess isocyanate levels in the work environment and medical examinations to detect early signs of isocyanate-related health effects in workers.
As isocyanate innovations continue to evolve, occupational safety regulations must adapt to address new challenges. This includes updating exposure limits and control measures based on the latest scientific evidence and technological advancements. Regulatory agencies work closely with industry stakeholders and research institutions to ensure that safety standards remain effective and relevant.
The implementation of these regulations has led to significant improvements in worker safety and health outcomes related to isocyanate exposure. However, ongoing vigilance and compliance are necessary to maintain these positive trends and address emerging concerns associated with new isocyanate formulations and applications.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States has established specific standards for isocyanate exposure in the workplace. These standards set permissible exposure limits (PELs) for different types of isocyanates, such as toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene bisphenyl isocyanate (MDI). The current PELs for most isocyanates are set at 0.02 parts per million (ppm) for an 8-hour time-weighted average.
In addition to exposure limits, occupational safety regulations mandate the implementation of engineering controls and personal protective equipment (PPE) to minimize worker exposure to isocyanates. These measures include the use of ventilation systems, enclosed processes, and respiratory protection. Employers are required to provide appropriate PPE, such as chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, and respirators, to workers handling isocyanates.
Worker training and education are also essential components of occupational safety regulations. Employers must ensure that workers are properly trained on the hazards of isocyanates, safe handling procedures, and emergency response protocols. This includes providing information on the signs and symptoms of isocyanate exposure, as well as proper decontamination procedures.
Regulatory bodies also require employers to conduct regular workplace monitoring and health surveillance programs. These programs involve periodic air sampling to assess isocyanate levels in the work environment and medical examinations to detect early signs of isocyanate-related health effects in workers.
As isocyanate innovations continue to evolve, occupational safety regulations must adapt to address new challenges. This includes updating exposure limits and control measures based on the latest scientific evidence and technological advancements. Regulatory agencies work closely with industry stakeholders and research institutions to ensure that safety standards remain effective and relevant.
The implementation of these regulations has led to significant improvements in worker safety and health outcomes related to isocyanate exposure. However, ongoing vigilance and compliance are necessary to maintain these positive trends and address emerging concerns associated with new isocyanate formulations and applications.
Economic Impact Assessment
The economic impact of isocyanate innovations on the workforce is multifaceted and far-reaching. These advancements have led to significant changes in various industries, particularly in manufacturing, construction, and automotive sectors. The introduction of new isocyanate-based materials and processes has resulted in a shift in labor demand, requiring workers to adapt to new technologies and acquire new skills.
In the manufacturing sector, the adoption of innovative isocyanate products has led to increased productivity and efficiency. This has resulted in a reduction of labor-intensive tasks and a growing demand for workers with specialized knowledge in handling and processing these advanced materials. The automotive industry, in particular, has seen a surge in the use of isocyanate-based polyurethanes for lightweight components, leading to the creation of new job roles focused on material engineering and application.
The construction industry has also experienced significant changes due to isocyanate innovations. The widespread use of spray polyurethane foam insulation has created a niche market for skilled applicators and technicians. This has led to the emergence of specialized training programs and certifications, contributing to the development of a more skilled workforce in the construction sector.
However, the economic impact is not without challenges. The transition to new isocyanate technologies has resulted in job displacement in some traditional manufacturing roles. Workers in industries relying on older materials and processes have faced the need to retrain or risk obsolescence. This has put pressure on educational institutions and vocational training centers to develop curricula that address the evolving needs of the industry.
The health and safety considerations associated with isocyanate handling have also influenced the workforce landscape. Stricter regulations and safety standards have necessitated the creation of new roles focused on environmental health and safety compliance. This has led to increased demand for professionals specializing in occupational health, industrial hygiene, and regulatory affairs.
From an economic perspective, the innovations in isocyanate technology have contributed to the growth of ancillary industries. The development of specialized equipment for isocyanate processing and application has stimulated job creation in the machinery and equipment manufacturing sector. Additionally, the research and development efforts driving these innovations have bolstered employment opportunities in scientific and technical fields.
The global nature of the isocyanate market has also had implications for workforce distribution. As production capabilities expand in emerging economies, there has been a shift in the geographical distribution of jobs related to isocyanate manufacturing and application. This has led to both challenges and opportunities for workers in different regions, influencing patterns of labor migration and skill transfer across borders.
In the manufacturing sector, the adoption of innovative isocyanate products has led to increased productivity and efficiency. This has resulted in a reduction of labor-intensive tasks and a growing demand for workers with specialized knowledge in handling and processing these advanced materials. The automotive industry, in particular, has seen a surge in the use of isocyanate-based polyurethanes for lightweight components, leading to the creation of new job roles focused on material engineering and application.
The construction industry has also experienced significant changes due to isocyanate innovations. The widespread use of spray polyurethane foam insulation has created a niche market for skilled applicators and technicians. This has led to the emergence of specialized training programs and certifications, contributing to the development of a more skilled workforce in the construction sector.
However, the economic impact is not without challenges. The transition to new isocyanate technologies has resulted in job displacement in some traditional manufacturing roles. Workers in industries relying on older materials and processes have faced the need to retrain or risk obsolescence. This has put pressure on educational institutions and vocational training centers to develop curricula that address the evolving needs of the industry.
The health and safety considerations associated with isocyanate handling have also influenced the workforce landscape. Stricter regulations and safety standards have necessitated the creation of new roles focused on environmental health and safety compliance. This has led to increased demand for professionals specializing in occupational health, industrial hygiene, and regulatory affairs.
From an economic perspective, the innovations in isocyanate technology have contributed to the growth of ancillary industries. The development of specialized equipment for isocyanate processing and application has stimulated job creation in the machinery and equipment manufacturing sector. Additionally, the research and development efforts driving these innovations have bolstered employment opportunities in scientific and technical fields.
The global nature of the isocyanate market has also had implications for workforce distribution. As production capabilities expand in emerging economies, there has been a shift in the geographical distribution of jobs related to isocyanate manufacturing and application. This has led to both challenges and opportunities for workers in different regions, influencing patterns of labor migration and skill transfer across borders.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!