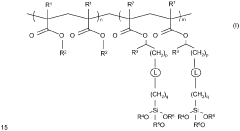
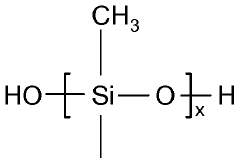
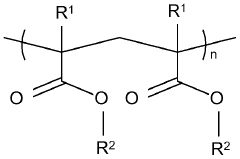
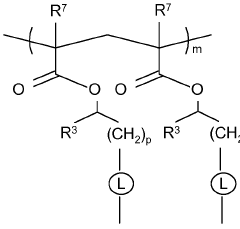
Exploring Polysilane's Compatibility With Other Polymers
JUL 11, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Background
Polysilanes, a class of inorganic polymers with a silicon backbone, have garnered significant attention in materials science and polymer chemistry over the past few decades. These unique macromolecules consist of repeating units of silicon atoms bonded to organic side groups, typically alkyl or aryl substituents. The discovery of polysilanes dates back to the early 20th century, but their potential as functional materials was not fully recognized until the 1970s.
The structural characteristics of polysilanes contribute to their distinctive properties. The silicon-silicon backbone allows for σ-electron delocalization, resulting in interesting electronic and optical properties. This feature sets polysilanes apart from their carbon-based counterparts and opens up possibilities for applications in optoelectronics, photoresists, and preceramic materials.
Historically, the synthesis of polysilanes has been challenging due to the instability of Si-Si bonds. The breakthrough came with the development of the Wurtz-type coupling reaction, which involves the reductive coupling of dichlorosilanes using alkali metals. This method, while effective, has limitations in terms of molecular weight control and side reactions. Subsequent research has focused on developing alternative synthetic routes, including catalytic dehydrogenative coupling and ring-opening polymerization of cyclic silanes.
The unique electronic structure of polysilanes gives rise to their photophysical properties. They exhibit strong UV absorption and photoluminescence, making them attractive for various optical applications. Additionally, polysilanes can undergo photoinduced degradation, a property that has been exploited in the development of photoresists for microlithography.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in exploring the compatibility of polysilanes with other polymers. This research direction stems from the potential to combine the unique properties of polysilanes with the diverse characteristics of organic polymers. The goal is to create hybrid materials that leverage the strengths of both components, potentially leading to novel materials with enhanced performance in various applications.
The exploration of polysilane compatibility with other polymers presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, the incorporation of polysilanes into conventional polymer systems could impart new functionalities, such as improved thermal stability, enhanced optical properties, or unique electronic characteristics. On the other hand, the inherent differences in chemical structure and properties between polysilanes and organic polymers pose significant challenges in achieving seamless integration and maintaining desired material properties.
As research in this area progresses, scientists are investigating various approaches to enhance compatibility, including the development of copolymers, blending techniques, and surface modification strategies. The ultimate aim is to create a new generation of hybrid materials that combine the best attributes of polysilanes and organic polymers, opening up new avenues for technological advancements in fields ranging from electronics to biomedicine.
The structural characteristics of polysilanes contribute to their distinctive properties. The silicon-silicon backbone allows for σ-electron delocalization, resulting in interesting electronic and optical properties. This feature sets polysilanes apart from their carbon-based counterparts and opens up possibilities for applications in optoelectronics, photoresists, and preceramic materials.
Historically, the synthesis of polysilanes has been challenging due to the instability of Si-Si bonds. The breakthrough came with the development of the Wurtz-type coupling reaction, which involves the reductive coupling of dichlorosilanes using alkali metals. This method, while effective, has limitations in terms of molecular weight control and side reactions. Subsequent research has focused on developing alternative synthetic routes, including catalytic dehydrogenative coupling and ring-opening polymerization of cyclic silanes.
The unique electronic structure of polysilanes gives rise to their photophysical properties. They exhibit strong UV absorption and photoluminescence, making them attractive for various optical applications. Additionally, polysilanes can undergo photoinduced degradation, a property that has been exploited in the development of photoresists for microlithography.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in exploring the compatibility of polysilanes with other polymers. This research direction stems from the potential to combine the unique properties of polysilanes with the diverse characteristics of organic polymers. The goal is to create hybrid materials that leverage the strengths of both components, potentially leading to novel materials with enhanced performance in various applications.
The exploration of polysilane compatibility with other polymers presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, the incorporation of polysilanes into conventional polymer systems could impart new functionalities, such as improved thermal stability, enhanced optical properties, or unique electronic characteristics. On the other hand, the inherent differences in chemical structure and properties between polysilanes and organic polymers pose significant challenges in achieving seamless integration and maintaining desired material properties.
As research in this area progresses, scientists are investigating various approaches to enhance compatibility, including the development of copolymers, blending techniques, and surface modification strategies. The ultimate aim is to create a new generation of hybrid materials that combine the best attributes of polysilanes and organic polymers, opening up new avenues for technological advancements in fields ranging from electronics to biomedicine.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for polysilane-compatible polymers has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by the increasing need for advanced materials in various industries. Polysilanes, known for their unique electronic and optical properties, have shown promising potential in applications ranging from photoresists and semiconductors to optoelectronic devices and solar cells. The compatibility of polysilanes with other polymers opens up new possibilities for creating hybrid materials with enhanced performance characteristics.
In the electronics industry, there is a significant demand for materials that can improve the efficiency and durability of electronic components. Polysilane-polymer blends have demonstrated potential in this area, particularly in the development of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and photovoltaic cells. The market for these applications is expected to expand as consumer electronics and renewable energy sectors continue to grow.
The automotive industry has also shown interest in polysilane-compatible polymers for their potential use in lightweight, high-strength materials. As vehicle manufacturers strive to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, there is a growing demand for innovative materials that can replace traditional metal components without compromising safety or performance. Polysilane-polymer composites could offer a solution to this challenge, potentially driving market growth in the automotive sector.
In the field of coatings and adhesives, polysilane-compatible polymers are gaining attention for their ability to enhance UV resistance and thermal stability. This has led to increased demand in industries such as construction, aerospace, and marine applications, where materials are often exposed to harsh environmental conditions. The market for these specialized coatings is expected to expand as manufacturers seek to improve the longevity and performance of their products.
The medical and healthcare sectors represent another area of potential growth for polysilane-compatible polymers. These materials show promise in applications such as drug delivery systems, biocompatible implants, and advanced wound dressings. As the global population ages and healthcare needs increase, the demand for innovative biomaterials is likely to rise, creating new opportunities for polysilane-polymer hybrids.
Despite the promising market outlook, challenges remain in scaling up production and reducing costs associated with polysilane-compatible polymers. Current market penetration is limited, primarily due to the relatively high cost of production and the need for further research to optimize material properties. However, as research progresses and manufacturing processes improve, it is anticipated that these barriers will be gradually overcome, leading to wider adoption across various industries.
In the electronics industry, there is a significant demand for materials that can improve the efficiency and durability of electronic components. Polysilane-polymer blends have demonstrated potential in this area, particularly in the development of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and photovoltaic cells. The market for these applications is expected to expand as consumer electronics and renewable energy sectors continue to grow.
The automotive industry has also shown interest in polysilane-compatible polymers for their potential use in lightweight, high-strength materials. As vehicle manufacturers strive to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, there is a growing demand for innovative materials that can replace traditional metal components without compromising safety or performance. Polysilane-polymer composites could offer a solution to this challenge, potentially driving market growth in the automotive sector.
In the field of coatings and adhesives, polysilane-compatible polymers are gaining attention for their ability to enhance UV resistance and thermal stability. This has led to increased demand in industries such as construction, aerospace, and marine applications, where materials are often exposed to harsh environmental conditions. The market for these specialized coatings is expected to expand as manufacturers seek to improve the longevity and performance of their products.
The medical and healthcare sectors represent another area of potential growth for polysilane-compatible polymers. These materials show promise in applications such as drug delivery systems, biocompatible implants, and advanced wound dressings. As the global population ages and healthcare needs increase, the demand for innovative biomaterials is likely to rise, creating new opportunities for polysilane-polymer hybrids.
Despite the promising market outlook, challenges remain in scaling up production and reducing costs associated with polysilane-compatible polymers. Current market penetration is limited, primarily due to the relatively high cost of production and the need for further research to optimize material properties. However, as research progresses and manufacturing processes improve, it is anticipated that these barriers will be gradually overcome, leading to wider adoption across various industries.
Polymer Compatibility
Polymer compatibility is a critical factor in the development of new materials and the optimization of existing ones. In the context of exploring polysilane's compatibility with other polymers, it is essential to understand the fundamental principles that govern polymer blending and the specific characteristics of polysilanes that influence their interactions with other polymeric materials.
Polysilanes, characterized by their silicon-silicon backbone, exhibit unique electronic and optical properties that make them attractive for various applications. However, their compatibility with other polymers is often limited due to their distinct chemical structure and physical properties. The primary challenge in blending polysilanes with other polymers lies in overcoming the inherent differences in polarity, molecular weight, and chain flexibility.
One of the key factors affecting polymer compatibility is the miscibility of the components at the molecular level. For polysilanes, this is particularly challenging due to their rigid backbone structure, which can lead to phase separation when mixed with more flexible polymers. The degree of miscibility is often determined by the balance between enthalpic and entropic contributions to the free energy of mixing.
To enhance the compatibility of polysilanes with other polymers, several strategies have been explored. One approach involves the modification of polysilane structures through the incorporation of functional groups that can interact favorably with the target polymer. For instance, the introduction of polar side groups can improve compatibility with more polar polymers, while the addition of aromatic moieties may enhance interactions with aromatic-containing polymers.
Another strategy focuses on the use of compatibilizers or coupling agents that can act as intermediaries between polysilanes and other polymers. These additives typically contain segments that are compatible with both components, effectively reducing interfacial tension and promoting better mixing. Block copolymers containing polysilane segments have also been investigated as potential compatibilizers for polysilane blends.
The processing conditions play a crucial role in determining the final compatibility and properties of polysilane-containing polymer blends. Factors such as temperature, shear rate, and solvent selection can significantly influence the morphology and distribution of components within the blend. Careful optimization of these parameters is often necessary to achieve the desired level of compatibility and performance.
Characterization techniques such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), and microscopy methods are commonly employed to assess the compatibility of polysilane blends. These techniques provide valuable insights into the thermal behavior, mechanical properties, and morphology of the blended systems, allowing researchers to evaluate the effectiveness of various compatibility strategies.
In conclusion, while the compatibility of polysilanes with other polymers presents significant challenges, ongoing research continues to uncover new approaches and solutions. The development of novel compatibilization techniques and the tailoring of polysilane structures offer promising avenues for expanding the range of compatible polymer systems, ultimately leading to new materials with enhanced properties and broader applications.
Polysilanes, characterized by their silicon-silicon backbone, exhibit unique electronic and optical properties that make them attractive for various applications. However, their compatibility with other polymers is often limited due to their distinct chemical structure and physical properties. The primary challenge in blending polysilanes with other polymers lies in overcoming the inherent differences in polarity, molecular weight, and chain flexibility.
One of the key factors affecting polymer compatibility is the miscibility of the components at the molecular level. For polysilanes, this is particularly challenging due to their rigid backbone structure, which can lead to phase separation when mixed with more flexible polymers. The degree of miscibility is often determined by the balance between enthalpic and entropic contributions to the free energy of mixing.
To enhance the compatibility of polysilanes with other polymers, several strategies have been explored. One approach involves the modification of polysilane structures through the incorporation of functional groups that can interact favorably with the target polymer. For instance, the introduction of polar side groups can improve compatibility with more polar polymers, while the addition of aromatic moieties may enhance interactions with aromatic-containing polymers.
Another strategy focuses on the use of compatibilizers or coupling agents that can act as intermediaries between polysilanes and other polymers. These additives typically contain segments that are compatible with both components, effectively reducing interfacial tension and promoting better mixing. Block copolymers containing polysilane segments have also been investigated as potential compatibilizers for polysilane blends.
The processing conditions play a crucial role in determining the final compatibility and properties of polysilane-containing polymer blends. Factors such as temperature, shear rate, and solvent selection can significantly influence the morphology and distribution of components within the blend. Careful optimization of these parameters is often necessary to achieve the desired level of compatibility and performance.
Characterization techniques such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), and microscopy methods are commonly employed to assess the compatibility of polysilane blends. These techniques provide valuable insights into the thermal behavior, mechanical properties, and morphology of the blended systems, allowing researchers to evaluate the effectiveness of various compatibility strategies.
In conclusion, while the compatibility of polysilanes with other polymers presents significant challenges, ongoing research continues to uncover new approaches and solutions. The development of novel compatibilization techniques and the tailoring of polysilane structures offer promising avenues for expanding the range of compatible polymer systems, ultimately leading to new materials with enhanced properties and broader applications.
Current Solutions
01 Compatibility with organic solvents
Polysilanes can be made compatible with various organic solvents through chemical modifications or by selecting appropriate side groups. This compatibility allows for better processing and integration in different applications, such as coatings or composite materials.- Compatibility with organic solvents: Polysilanes can be made compatible with organic solvents through various modifications and formulations. This compatibility is crucial for their use in coatings, films, and other applications where solvent-based processing is required. Techniques may include the incorporation of specific functional groups or the use of compatibilizing agents to improve solubility and dispersion in organic media.
- Compatibility with polymers and resins: Polysilanes can be made compatible with various polymers and resins to create composite materials with enhanced properties. This compatibility is achieved through careful selection of polysilane structures, molecular weights, and functionalization. The resulting composites may exhibit improved thermal stability, optical properties, or mechanical strength compared to the base polymers.
- Photosensitive polysilane compositions: Polysilanes can be formulated into photosensitive compositions for use in photolithography and other light-sensitive applications. These compositions often include photoinitiators, sensitizers, or other additives to enhance their responsiveness to light. The compatibility of polysilanes with these components is crucial for achieving the desired photochemical properties and patterning capabilities.
- Compatibility with inorganic materials: Polysilanes can be made compatible with inorganic materials such as silica, metal oxides, or ceramics. This compatibility is important for creating hybrid organic-inorganic materials with unique properties. Techniques may include surface modification of inorganic particles or the use of coupling agents to improve the interfacial adhesion between the polysilane and inorganic components.
- Compatibility in electronic and optoelectronic applications: Polysilanes can be formulated to be compatible with various electronic and optoelectronic materials and devices. This includes their use in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photovoltaic cells, and other semiconductor applications. The compatibility of polysilanes with charge transport materials, emissive layers, and electrode materials is crucial for optimizing device performance and stability.
02 Compatibility with polymers and resins
Polysilanes can be designed to be compatible with different polymers and resins, enabling the creation of hybrid materials with enhanced properties. This compatibility is achieved through careful selection of polysilane structures and functionalization.Expand Specific Solutions03 Photosensitivity and lithographic applications
Polysilanes exhibit photosensitivity, making them compatible with photolithographic processes. This property allows for their use in the fabrication of microelectronic devices and other patterned structures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thermal stability and high-temperature applications
Certain polysilane structures demonstrate compatibility with high-temperature environments, making them suitable for applications requiring thermal stability. This property is particularly useful in the development of heat-resistant materials and coatings.Expand Specific Solutions05 Compatibility with inorganic materials
Polysilanes can be designed to be compatible with various inorganic materials, such as metals or ceramics. This compatibility enables the creation of hybrid organic-inorganic materials with unique properties and applications in fields like electronics and materials science.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The exploration of polysilane's compatibility with other polymers is currently in an early development stage, with significant potential for growth. The market size is relatively small but expanding as researchers and companies recognize the unique properties of polysilanes. Technologically, the field is still maturing, with companies like Wacker Chemie AG, Momentive Performance Materials, Inc., and Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. leading the way in research and development. These firms are leveraging their expertise in silicone chemistry to advance polysilane technology. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies and specialized materials firms, each working to unlock the full potential of polysilane-polymer combinations for various industrial applications.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed innovative polysilane-based polymer blends for enhanced material properties. Their approach involves grafting polysilanes onto other polymer backbones, creating hybrid materials with improved thermal stability and optical properties[1]. The company has successfully incorporated polysilanes into silicone rubber formulations, resulting in materials with enhanced UV resistance and electrical conductivity[2]. Wacker's research also focuses on using polysilanes as precursors for silicon carbide ceramics, exploring their compatibility with various ceramic precursor polymers[3]. Their latest developments include polysilane-modified epoxy resins for advanced coating applications, demonstrating improved adhesion and weatherability[4].
Strengths: Extensive experience in silicone chemistry, strong R&D capabilities, and a diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Potential high production costs and limited commercial scale production of polysilane-based materials.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has made significant strides in exploring polysilane compatibility with other polymers, particularly focusing on nanocomposite materials. Their research involves incorporating polysilanes into various polymer matrices, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, to enhance mechanical and thermal properties[1]. Evonik has developed a proprietary process for synthesizing high-molecular-weight polysilanes with controlled structures, allowing for better integration with other polymers[2]. The company has also explored the use of polysilanes as compatibilizers in polymer blends, improving the miscibility of otherwise immiscible polymer systems[3]. Recent advancements include the development of polysilane-based additives for improving the flame retardancy and electrical conductivity of thermoplastic polymers[4].
Strengths: Strong expertise in specialty chemicals, extensive polymer research facilities, and a global presence in various markets. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges and the need for substantial investment in scaling up new technologies.
Core Innovations
Novel polyacrylate-polysilane block copolymers
PatentWO2018019642A1
Innovation
- Development of polyacrylate-polysilane block copolymers with specific molecular structures and polymerization processes to create a stable hybrid polymer system that combines the benefits of both acrylate and silane polymers, including low surface energy and thermo-oxidative stability, while maintaining compatibility with other polymers.
Cross-linkable polymer blends containing alkoxysilane-terminated polymers
PatentInactiveUS20050119421A1
Innovation
- The development of alkoxysilane-terminated polymer blends using isocyanatomethylalkoxysilanes with prepolymers containing reactive HO, NH, or SH endgroups, allowing for high reactivity with moisture and enabling the preparation of low-modulus elastomers with high chain lengths and molecular weights, even with small amounts of catalysts or none at all, and achieving rapid curing and low tack-free times.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of exploring polysilane's compatibility with other polymers is a crucial aspect to consider in the development and application of these materials. Polysilanes, being silicon-based polymers, have unique properties that can potentially offer environmental benefits when combined with other polymers. However, their production, use, and disposal also present challenges that need to be carefully evaluated.
One of the primary environmental advantages of polysilane-polymer blends is their potential to enhance the durability and longevity of materials. By improving the mechanical and thermal properties of conventional polymers, these blends can lead to products with extended lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and ultimately decreasing waste generation. This aspect is particularly relevant in industries such as construction, automotive, and electronics, where material longevity is a key factor in sustainability.
The production of polysilanes and their integration with other polymers may have both positive and negative environmental implications. On one hand, the synthesis of polysilanes often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. This could result in increased energy consumption and the generation of harmful byproducts. On the other hand, if the production methods can be optimized and made more efficient, the overall environmental footprint of these materials could be reduced compared to traditional polymer production.
When considering the end-of-life phase of polysilane-polymer blends, recycling and disposal become important environmental considerations. The compatibility of polysilanes with other polymers may affect the recyclability of the resulting materials. If the blends can be easily separated or recycled as a whole, it could contribute to a more circular economy approach. However, if the presence of polysilanes complicates the recycling process, it may lead to increased waste and environmental burden.
The potential for biodegradability or environmental persistence of polysilane-polymer blends is another critical factor. Depending on the specific combinations and chemical structures, these materials may exhibit varying degrees of biodegradability. If designed properly, they could offer improved environmental outcomes compared to conventional non-biodegradable polymers. Conversely, if the materials are resistant to degradation, they may contribute to long-term environmental pollution, particularly in marine environments.
The use of polysilane-polymer blends in various applications can also have indirect environmental impacts. For instance, in photovoltaic technologies, these materials could potentially enhance the efficiency and durability of solar panels, contributing to increased renewable energy production and reduced carbon emissions. Similarly, in packaging applications, improved barrier properties could lead to better food preservation and reduced food waste.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of exploring polysilane's compatibility with other polymers is multifaceted and requires comprehensive assessment. While there are potential benefits in terms of material longevity, energy efficiency, and enhanced performance in sustainable technologies, challenges related to production processes, recyclability, and end-of-life management need to be carefully addressed to ensure a net positive environmental outcome.
One of the primary environmental advantages of polysilane-polymer blends is their potential to enhance the durability and longevity of materials. By improving the mechanical and thermal properties of conventional polymers, these blends can lead to products with extended lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and ultimately decreasing waste generation. This aspect is particularly relevant in industries such as construction, automotive, and electronics, where material longevity is a key factor in sustainability.
The production of polysilanes and their integration with other polymers may have both positive and negative environmental implications. On one hand, the synthesis of polysilanes often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. This could result in increased energy consumption and the generation of harmful byproducts. On the other hand, if the production methods can be optimized and made more efficient, the overall environmental footprint of these materials could be reduced compared to traditional polymer production.
When considering the end-of-life phase of polysilane-polymer blends, recycling and disposal become important environmental considerations. The compatibility of polysilanes with other polymers may affect the recyclability of the resulting materials. If the blends can be easily separated or recycled as a whole, it could contribute to a more circular economy approach. However, if the presence of polysilanes complicates the recycling process, it may lead to increased waste and environmental burden.
The potential for biodegradability or environmental persistence of polysilane-polymer blends is another critical factor. Depending on the specific combinations and chemical structures, these materials may exhibit varying degrees of biodegradability. If designed properly, they could offer improved environmental outcomes compared to conventional non-biodegradable polymers. Conversely, if the materials are resistant to degradation, they may contribute to long-term environmental pollution, particularly in marine environments.
The use of polysilane-polymer blends in various applications can also have indirect environmental impacts. For instance, in photovoltaic technologies, these materials could potentially enhance the efficiency and durability of solar panels, contributing to increased renewable energy production and reduced carbon emissions. Similarly, in packaging applications, improved barrier properties could lead to better food preservation and reduced food waste.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of exploring polysilane's compatibility with other polymers is multifaceted and requires comprehensive assessment. While there are potential benefits in terms of material longevity, energy efficiency, and enhanced performance in sustainable technologies, challenges related to production processes, recyclability, and end-of-life management need to be carefully addressed to ensure a net positive environmental outcome.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding polysilane's compatibility with other polymers is complex and evolving. As research in this field progresses, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the safety, environmental impact, and performance standards of polymer blends containing polysilanes.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating new chemical substances, including novel polymer blends. Under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), manufacturers must submit premanufacture notices (PMNs) for new chemical substances, which would include polysilane-polymer composites. The EPA evaluates these materials for potential risks to human health and the environment, potentially requiring additional testing or imposing restrictions on their use.
The European Union's regulatory framework is equally stringent, with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governing the introduction of new chemical substances. Polysilane-polymer blends would need to undergo thorough safety assessments and registration processes before being approved for commercial use within the EU market.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have their own chemical substance control laws, which would apply to polysilane-polymer composites. The Japanese Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and Korea's Act on Registration and Evaluation of Chemical Substances (K-REACH) both require rigorous safety evaluations and registrations for new chemical substances.
Globally, there is an increasing trend towards harmonization of chemical regulations, as evidenced by initiatives like the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). This system aims to standardize hazard communication across different countries, which would affect how polysilane-polymer blends are classified and labeled internationally.
Specific to polymer compatibility, regulatory bodies are particularly concerned with the potential for leaching of harmful substances from polymer blends. As such, regulations often focus on migration limits for various compounds, especially in applications that involve food contact or medical devices. For polysilane-polymer blends, this could mean extensive testing to ensure compliance with these migration limits.
The regulatory landscape also extends to end-of-life considerations for polymer products. With growing emphasis on circular economy principles, regulations are increasingly addressing the recyclability and biodegradability of polymer materials. This trend may influence the development of polysilane-polymer blends, pushing researchers to consider not only compatibility during use but also compatibility with recycling processes or environmental degradation pathways.
As research in polysilane-polymer compatibility advances, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will evolve to address any unique properties or potential risks associated with these novel materials. This may include the development of new testing protocols or the adaptation of existing standards to accurately assess the safety and performance of polysilane-containing polymer blends.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating new chemical substances, including novel polymer blends. Under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), manufacturers must submit premanufacture notices (PMNs) for new chemical substances, which would include polysilane-polymer composites. The EPA evaluates these materials for potential risks to human health and the environment, potentially requiring additional testing or imposing restrictions on their use.
The European Union's regulatory framework is equally stringent, with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governing the introduction of new chemical substances. Polysilane-polymer blends would need to undergo thorough safety assessments and registration processes before being approved for commercial use within the EU market.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have their own chemical substance control laws, which would apply to polysilane-polymer composites. The Japanese Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and Korea's Act on Registration and Evaluation of Chemical Substances (K-REACH) both require rigorous safety evaluations and registrations for new chemical substances.
Globally, there is an increasing trend towards harmonization of chemical regulations, as evidenced by initiatives like the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). This system aims to standardize hazard communication across different countries, which would affect how polysilane-polymer blends are classified and labeled internationally.
Specific to polymer compatibility, regulatory bodies are particularly concerned with the potential for leaching of harmful substances from polymer blends. As such, regulations often focus on migration limits for various compounds, especially in applications that involve food contact or medical devices. For polysilane-polymer blends, this could mean extensive testing to ensure compliance with these migration limits.
The regulatory landscape also extends to end-of-life considerations for polymer products. With growing emphasis on circular economy principles, regulations are increasingly addressing the recyclability and biodegradability of polymer materials. This trend may influence the development of polysilane-polymer blends, pushing researchers to consider not only compatibility during use but also compatibility with recycling processes or environmental degradation pathways.
As research in polysilane-polymer compatibility advances, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will evolve to address any unique properties or potential risks associated with these novel materials. This may include the development of new testing protocols or the adaptation of existing standards to accurately assess the safety and performance of polysilane-containing polymer blends.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!