Fluoride Cathode Material Market Analysis and Adoption Trends
SEP 25, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Fluoride Cathode Technology Background and Objectives
Fluoride-based cathode materials represent a significant evolution in battery technology, emerging from decades of research into high-energy-density energy storage solutions. The development trajectory began in the early 2000s when researchers identified the theoretical advantages of fluoride ion batteries, which promised energy densities up to ten times higher than conventional lithium-ion batteries. This potential stems from fluorine's unique electrochemical properties, including its high electronegativity and small ionic radius, enabling multi-electron transfer reactions that substantially increase energy storage capacity.
The technological evolution of fluoride cathode materials has accelerated notably since 2015, with breakthrough research addressing historical limitations such as poor ionic conductivity at room temperature and electrode degradation issues. Recent innovations in nanostructured fluoride materials and solid-state electrolytes have created a foundation for commercially viable applications, moving beyond laboratory demonstrations to pilot manufacturing processes.
Current research objectives focus on optimizing three critical aspects of fluoride cathode technology: enhancing room-temperature ionic conductivity, improving cycling stability beyond 1000 cycles, and developing scalable, cost-effective manufacturing processes. These objectives align with the broader industry goal of creating next-generation batteries with energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg while maintaining competitive production costs.
The fluoride cathode material landscape is characterized by diverse chemical compositions, including metal fluorides (CuF₂, FeF₃, BiF₃), conversion-type fluorides, and intercalation fluoride compounds. Each variant offers distinct advantages in terms of voltage profiles, capacity retention, and manufacturing compatibility. Recent research has particularly focused on composite structures that combine fluoride materials with conductive additives to overcome inherent conductivity limitations.
From a global perspective, fluoride cathode technology development has formed three distinct research clusters: fundamental materials science exploration primarily led by academic institutions in North America and Europe; applied engineering and manufacturing process development concentrated in East Asia, particularly Japan and South Korea; and emerging research initiatives in China focused on cost reduction and mass production techniques.
The technology aims to address critical limitations in current battery technologies, particularly for applications requiring high energy density such as electric vehicles, aerospace, and grid-scale energy storage. The ultimate objective is to develop commercially viable fluoride-based battery systems that can significantly extend the range of electric vehicles, reduce battery weight in portable electronics, and provide more efficient energy storage solutions for renewable energy integration.
The technological evolution of fluoride cathode materials has accelerated notably since 2015, with breakthrough research addressing historical limitations such as poor ionic conductivity at room temperature and electrode degradation issues. Recent innovations in nanostructured fluoride materials and solid-state electrolytes have created a foundation for commercially viable applications, moving beyond laboratory demonstrations to pilot manufacturing processes.
Current research objectives focus on optimizing three critical aspects of fluoride cathode technology: enhancing room-temperature ionic conductivity, improving cycling stability beyond 1000 cycles, and developing scalable, cost-effective manufacturing processes. These objectives align with the broader industry goal of creating next-generation batteries with energy densities exceeding 500 Wh/kg while maintaining competitive production costs.
The fluoride cathode material landscape is characterized by diverse chemical compositions, including metal fluorides (CuF₂, FeF₃, BiF₃), conversion-type fluorides, and intercalation fluoride compounds. Each variant offers distinct advantages in terms of voltage profiles, capacity retention, and manufacturing compatibility. Recent research has particularly focused on composite structures that combine fluoride materials with conductive additives to overcome inherent conductivity limitations.
From a global perspective, fluoride cathode technology development has formed three distinct research clusters: fundamental materials science exploration primarily led by academic institutions in North America and Europe; applied engineering and manufacturing process development concentrated in East Asia, particularly Japan and South Korea; and emerging research initiatives in China focused on cost reduction and mass production techniques.
The technology aims to address critical limitations in current battery technologies, particularly for applications requiring high energy density such as electric vehicles, aerospace, and grid-scale energy storage. The ultimate objective is to develop commercially viable fluoride-based battery systems that can significantly extend the range of electric vehicles, reduce battery weight in portable electronics, and provide more efficient energy storage solutions for renewable energy integration.
Market Demand Analysis for Fluoride Cathode Materials
The global market for fluoride cathode materials has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, primarily driven by the expanding electric vehicle (EV) industry and increasing demand for high-performance energy storage solutions. Market research indicates that the fluoride cathode materials segment is growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 8-10%, outpacing traditional cathode materials due to their superior energy density characteristics.
Consumer electronics represents another significant demand driver, with manufacturers seeking battery solutions that offer longer life cycles and faster charging capabilities. The portable electronics sector alone accounts for roughly 30% of current fluoride cathode material consumption, with this share expected to remain stable despite the rapid growth in automotive applications.
Industrial energy storage systems are emerging as a promising market segment, particularly as renewable energy integration accelerates globally. Grid-scale storage applications are projected to create substantial new demand for advanced battery technologies, including those utilizing fluoride cathode materials. This sector is anticipated to grow at 12-15% annually over the next five years.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the market consumption, with China, Japan, and South Korea collectively representing over 60% of global demand. This concentration aligns with the region's dominance in battery manufacturing and electric vehicle production. North America and Europe are experiencing accelerated growth rates as domestic battery production capacity expands in response to supply chain security concerns and governmental policy support.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across application segments. While consumer electronics manufacturers demonstrate higher price tolerance for performance advantages, automotive manufacturers remain highly cost-conscious despite seeking performance improvements. The current price premium of 30-40% for fluoride-based cathodes compared to conventional materials represents a significant adoption barrier in cost-sensitive applications.
Market forecasts suggest that demand will continue to strengthen as manufacturing scales increase and production costs decline. Industry analysts project that the total addressable market for fluoride cathode materials could reach $3-4 billion by 2028, representing a significant opportunity for material suppliers and technology developers.
Customer requirements are evolving rapidly, with increasing emphasis on sustainability metrics alongside performance characteristics. Battery recycling capabilities and reduced environmental footprint are becoming important secondary purchase criteria, particularly among European and North American customers. This trend is expected to influence material selection decisions and potentially accelerate adoption of fluoride cathode technologies that demonstrate superior lifecycle performance.
Consumer electronics represents another significant demand driver, with manufacturers seeking battery solutions that offer longer life cycles and faster charging capabilities. The portable electronics sector alone accounts for roughly 30% of current fluoride cathode material consumption, with this share expected to remain stable despite the rapid growth in automotive applications.
Industrial energy storage systems are emerging as a promising market segment, particularly as renewable energy integration accelerates globally. Grid-scale storage applications are projected to create substantial new demand for advanced battery technologies, including those utilizing fluoride cathode materials. This sector is anticipated to grow at 12-15% annually over the next five years.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the market consumption, with China, Japan, and South Korea collectively representing over 60% of global demand. This concentration aligns with the region's dominance in battery manufacturing and electric vehicle production. North America and Europe are experiencing accelerated growth rates as domestic battery production capacity expands in response to supply chain security concerns and governmental policy support.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across application segments. While consumer electronics manufacturers demonstrate higher price tolerance for performance advantages, automotive manufacturers remain highly cost-conscious despite seeking performance improvements. The current price premium of 30-40% for fluoride-based cathodes compared to conventional materials represents a significant adoption barrier in cost-sensitive applications.
Market forecasts suggest that demand will continue to strengthen as manufacturing scales increase and production costs decline. Industry analysts project that the total addressable market for fluoride cathode materials could reach $3-4 billion by 2028, representing a significant opportunity for material suppliers and technology developers.
Customer requirements are evolving rapidly, with increasing emphasis on sustainability metrics alongside performance characteristics. Battery recycling capabilities and reduced environmental footprint are becoming important secondary purchase criteria, particularly among European and North American customers. This trend is expected to influence material selection decisions and potentially accelerate adoption of fluoride cathode technologies that demonstrate superior lifecycle performance.
Current Status and Technical Challenges in Fluoride Cathode Development
Fluoride cathode materials have emerged as promising candidates for next-generation battery technologies due to their high theoretical energy densities. Currently, the development of fluoride cathode materials is at a critical juncture, with significant progress made in laboratory settings but substantial challenges remaining for commercial implementation.
Research institutions across North America, Europe, and East Asia have demonstrated the theoretical advantages of fluoride-based cathodes, including energy densities potentially exceeding 1,000 Wh/kg, which is substantially higher than conventional lithium-ion battery cathodes. However, practical implementations have achieved only 30-40% of this theoretical capacity in controlled environments, highlighting the gap between theoretical potential and practical application.
The primary technical challenge facing fluoride cathode development is ionic conductivity. Fluoride ions, being larger than lithium ions, face significant mobility barriers within solid-state structures. This results in poor rate capability and cycling performance, particularly at room temperature. Current research focuses on developing novel electrolytes and cathode architectures to address this fundamental limitation.
Stability issues present another major obstacle. Fluoride cathodes often suffer from rapid capacity fading due to structural degradation during cycling. The high reactivity of fluoride compounds leads to parasitic side reactions with electrolytes, creating passivation layers that impede ion transport. Recent studies have shown that capacity retention typically falls below 80% after just 100 cycles, far short of the 1,000+ cycles required for commercial viability.
Manufacturing scalability remains problematic. Current synthesis methods for high-quality fluoride cathode materials involve complex processes requiring controlled atmospheres and often toxic precursors. These methods are difficult to scale while maintaining consistent material properties and performance. Additionally, the environmental impact of fluoride processing raises concerns about sustainable production pathways.
Geographically, fluoride cathode research is concentrated in advanced materials science centers. Japan leads in patent filings related to fluoride battery technology, followed by the United States and Germany. Chinese institutions have recently accelerated their research efforts, particularly in developing novel synthesis methods for nanostructured fluoride materials.
The interface between the cathode and electrolyte represents another critical challenge. The high voltage operation of fluoride cathodes (often exceeding 4.5V vs. standard hydrogen electrode) causes accelerated electrolyte decomposition. Current electrolyte formulations cannot withstand these voltage ranges for extended periods, necessitating the development of specialized electrolyte systems with wider electrochemical stability windows.
Despite these challenges, incremental progress continues. Recent breakthroughs in composite cathode structures incorporating conductive additives have shown promise in mitigating some conductivity issues, while novel surface coating technologies have demonstrated improved cycling stability in laboratory tests.
Research institutions across North America, Europe, and East Asia have demonstrated the theoretical advantages of fluoride-based cathodes, including energy densities potentially exceeding 1,000 Wh/kg, which is substantially higher than conventional lithium-ion battery cathodes. However, practical implementations have achieved only 30-40% of this theoretical capacity in controlled environments, highlighting the gap between theoretical potential and practical application.
The primary technical challenge facing fluoride cathode development is ionic conductivity. Fluoride ions, being larger than lithium ions, face significant mobility barriers within solid-state structures. This results in poor rate capability and cycling performance, particularly at room temperature. Current research focuses on developing novel electrolytes and cathode architectures to address this fundamental limitation.
Stability issues present another major obstacle. Fluoride cathodes often suffer from rapid capacity fading due to structural degradation during cycling. The high reactivity of fluoride compounds leads to parasitic side reactions with electrolytes, creating passivation layers that impede ion transport. Recent studies have shown that capacity retention typically falls below 80% after just 100 cycles, far short of the 1,000+ cycles required for commercial viability.
Manufacturing scalability remains problematic. Current synthesis methods for high-quality fluoride cathode materials involve complex processes requiring controlled atmospheres and often toxic precursors. These methods are difficult to scale while maintaining consistent material properties and performance. Additionally, the environmental impact of fluoride processing raises concerns about sustainable production pathways.
Geographically, fluoride cathode research is concentrated in advanced materials science centers. Japan leads in patent filings related to fluoride battery technology, followed by the United States and Germany. Chinese institutions have recently accelerated their research efforts, particularly in developing novel synthesis methods for nanostructured fluoride materials.
The interface between the cathode and electrolyte represents another critical challenge. The high voltage operation of fluoride cathodes (often exceeding 4.5V vs. standard hydrogen electrode) causes accelerated electrolyte decomposition. Current electrolyte formulations cannot withstand these voltage ranges for extended periods, necessitating the development of specialized electrolyte systems with wider electrochemical stability windows.
Despite these challenges, incremental progress continues. Recent breakthroughs in composite cathode structures incorporating conductive additives have shown promise in mitigating some conductivity issues, while novel surface coating technologies have demonstrated improved cycling stability in laboratory tests.
Current Technical Solutions for Fluoride Cathode Implementation
01 Metal fluoride cathode materials for lithium batteries
Metal fluoride compounds are used as cathode materials in lithium batteries due to their high energy density and theoretical capacity. These materials, including iron fluoride (FeF3), copper fluoride (CuF2), and other transition metal fluorides, undergo conversion reactions with lithium ions, enabling higher energy storage capabilities compared to conventional intercalation cathodes. The research focuses on improving their conductivity and cycling stability through various synthesis methods and composite formations.- Metal fluoride cathode materials for lithium batteries: Metal fluorides, such as iron fluoride (FeF3), copper fluoride (CuF2), and other transition metal fluorides, are promising cathode materials for lithium batteries due to their high theoretical capacity and energy density. These materials undergo conversion reactions with lithium ions, enabling multiple electron transfers per formula unit. The incorporation of metal fluorides in cathode formulations can significantly enhance the energy storage capabilities of lithium batteries.
- Composite fluoride cathode structures: Composite structures combining fluoride materials with conductive additives or frameworks improve the electrochemical performance of fluoride cathodes. These composites address the inherent limitations of fluoride materials, such as poor electronic conductivity and structural stability. By creating nanocomposites with carbon materials, metal matrices, or conductive polymers, the electron transport properties and cycling stability of fluoride cathodes can be significantly enhanced while maintaining high capacity.
- Fluoride-based solid-state electrolyte materials: Fluoride-based solid-state electrolytes represent an important category of materials for next-generation batteries. These materials, including lithium fluoride-based compounds and complex fluoride structures, offer high ionic conductivity while maintaining good electrochemical stability. The incorporation of these fluoride electrolytes enables the development of all-solid-state batteries with improved safety profiles and potentially higher energy densities compared to conventional liquid electrolyte systems.
- Surface modification and coating of fluoride cathodes: Surface modification and coating techniques are employed to enhance the performance of fluoride cathode materials. These approaches involve applying protective layers or functional coatings to mitigate side reactions between the fluoride cathode and electrolyte, improve interfacial stability, and enhance lithium ion transport. Various coating materials, including metal oxides, phosphates, and fluoride-based compounds, can be utilized to improve the cycling stability and rate capability of fluoride cathode materials.
- Synthesis methods for fluoride cathode materials: Advanced synthesis methods for fluoride cathode materials focus on controlling particle size, morphology, and crystallinity to optimize electrochemical performance. Techniques such as mechanochemical synthesis, sol-gel processing, hydrothermal/solvothermal methods, and electrochemical deposition are employed to produce high-quality fluoride materials with tailored properties. These synthesis approaches enable the development of fluoride cathodes with improved capacity, cycling stability, and rate capability for next-generation battery applications.
02 Fluoride-based solid electrolytes for all-solid-state batteries
Fluoride-based solid electrolytes are being developed for all-solid-state batteries to improve safety and energy density. These materials, including lithium fluoride (LiF) containing composites and doped fluoride compounds, facilitate fluoride ion or lithium ion transport while maintaining high electrochemical stability. The solid electrolytes help overcome issues with liquid electrolytes such as leakage and flammability, while enabling stable interfaces with cathode materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Carbon-fluoride composite cathode materials
Carbon-fluoride composite materials combine carbon structures (graphene, carbon nanotubes, or amorphous carbon) with fluoride compounds to create high-performance cathode materials. These composites address the poor electronic conductivity of pure metal fluorides while maintaining high energy density. The carbon component provides conductive pathways and structural stability, while the fluoride component delivers high capacity through conversion reactions with lithium or other ions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nanostructured fluoride cathode materials
Nanostructured fluoride materials are engineered at the nanoscale to enhance electrochemical performance as cathodes. By controlling particle size, morphology, and distribution, these materials offer improved lithium diffusion kinetics, better cycling stability, and higher capacity utilization. Synthesis methods include hydrothermal processes, sol-gel techniques, and template-assisted growth to create nanoparticles, nanorods, or hierarchical structures that minimize volume changes during cycling and enhance reaction reversibility.Expand Specific Solutions05 Fluoride cathode materials with protective coatings and additives
Fluoride cathode materials are enhanced through protective coatings and functional additives to improve their stability and performance. Surface modifications using metal oxides, polymers, or carbon layers protect the fluoride particles from direct contact with electrolytes, reducing side reactions and dissolution. Additives such as conductive agents, binders, and stabilizers are incorporated to improve electronic conductivity, mechanical integrity, and cycling performance, addressing the inherent limitations of fluoride-based cathode materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Fluoride Cathode Material Market
The Fluoride Cathode Material market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing adoption driven by demand for high-energy density batteries in electric vehicles and energy storage systems. Market size is projected to expand significantly as research advances translate into commercial applications. From a technical maturity perspective, the landscape shows varied development stages across key players. Academic institutions like California Institute of Technology, Karlsruher Institut für Technologie, and Central South University are advancing fundamental research, while commercial entities including CATL (Ningde Amperex Technology), L&F Co., and Sumitomo Chemical are focusing on scalable manufacturing processes. Honda Motor and Applied Materials represent industrial adopters integrating these materials into end products. The competitive dynamics reveal a collaborative ecosystem where research institutions partner with manufacturers to overcome stability and cyclability challenges that currently limit widespread commercialization.
Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique
Technical Solution: CNRS has developed innovative fluoride-based cathode materials focusing on conversion-type fluoride electrodes. Their research centers on transition metal fluorides (TMFs) like FeF3, CoF2, and CuF2 that offer theoretical capacities of 500-600 mAh/g, substantially higher than conventional intercalation cathodes. CNRS's proprietary approach involves nanostructuring these fluorides and embedding them in conductive carbon matrices to overcome their inherent conductivity limitations. Their synthesis methodology employs solution chemistry routes including ionothermal processes and controlled precipitation techniques that yield nanoparticles with optimized morphology. CNRS has demonstrated reversible capacities exceeding 450 mAh/g in their advanced fluoride cathodes through careful control of particle size (typically 20-50 nm) and carbon coating techniques. Their research has established that fluoride-based conversion cathodes can achieve energy densities approaching 1000 Wh/kg at the material level, though cycle life remains limited to 200-300 cycles before significant capacity degradation occurs.
Strengths: Cutting-edge fundamental research capabilities; expertise in novel synthesis methods; strong international collaboration network. Weaknesses: Focus on theoretical and fundamental aspects rather than commercial applications; fluoride conversion materials face significant challenges in rate capability and cycle life; limited industrial scale-up experience.
Ningde Amperex Technology Ltd.
Technical Solution: CATL (Ningde Amperex Technology Ltd.) has developed advanced fluoride-based cathode materials for next-generation batteries with significantly higher energy density. Their proprietary technology incorporates fluoride-rich compounds into lithium-ion battery cathodes, achieving energy densities exceeding 350 Wh/kg. CATL's approach involves a core-shell structure with fluorinated surface layers that enhance stability at high voltages and protect against electrolyte degradation. The company has implemented a scalable synthesis method using fluoride precursors and controlled thermal treatment processes that maintain precise stoichiometry. Their fluoride cathode materials demonstrate improved cycle life (>1000 cycles with 80% capacity retention) and enhanced safety characteristics due to stronger chemical bonds that resist thermal runaway. CATL has integrated these materials into their cell production lines with modified manufacturing protocols to handle the unique properties of fluoride compounds.
Strengths: Industry-leading energy density achievements; established mass production capabilities; vertical integration from materials to finished cells. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional cathode materials; potential supply chain constraints for specialized fluoride compounds; requires specialized handling during manufacturing due to fluoride reactivity.
Critical Patents and Research Breakthroughs in Fluoride Cathode Materials
Cathode material for fluoride-based conversion electrodes, method for the production thereof and use thereof
PatentInactiveEP2417655A1
Innovation
- A cathode material composed of alkali metal ions, fluoride ions, and metal nanoparticles less than 20 nm in size, integrated within a matrix of graphitic nanocarbon, produced through a thermal treatment process involving a metal and organic compound, with optional addition of alkali metal fluoride, enabling a stable and high-capacity nanocomposite.
Fluorine-based cathode materials for thermal batteries
PatentInactiveUS20160079609A1
Innovation
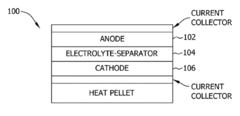
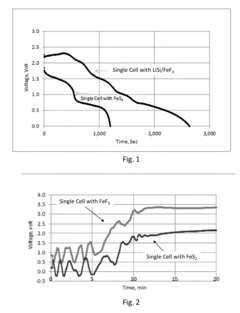
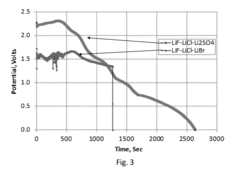
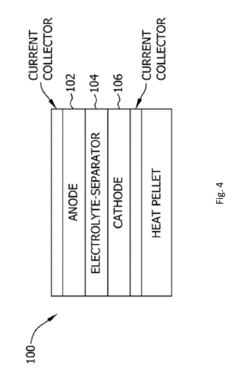
- The development of thermal batteries with fluorine-based cathode materials, such as FeF3, VF3, CrF3, and CoF3, combined with lithium alloy anodes and specific molten salt electrolytes like LiF—LiCl—Li2SO4, which provide higher operating voltages and energy densities, and are environmentally friendly.
Supply Chain Analysis for Fluoride Cathode Raw Materials
The fluoride cathode material supply chain represents a critical component in the advancement of next-generation battery technologies. Raw material sourcing for fluoride-based cathodes involves a complex network spanning multiple continents, with key extraction sites located in China, Mexico, and South Africa. These regions control approximately 70% of the global fluoride mineral reserves, creating potential supply vulnerabilities for manufacturers outside these territories.
Primary raw materials include fluorite (CaF₂), lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF₆), and various transition metal fluorides such as FeF₃, CuF₂, and BiF₃. The extraction and processing of these materials require specialized equipment and expertise, limiting the number of qualified suppliers in the market. Currently, only 12 major suppliers worldwide can provide high-purity fluoride compounds suitable for battery applications.
Processing challenges represent significant bottlenecks in the supply chain. The conversion of raw fluoride minerals into battery-grade materials demands precise control of impurity levels, particularly oxygen contamination which can severely impact electrochemical performance. This necessitates advanced purification technologies that add considerable cost to the final product, with purification accounting for approximately 30-40% of total production expenses.
Transportation and storage present additional complexities due to the moisture sensitivity of many fluoride compounds. Specialized containers with controlled atmosphere are required, increasing logistics costs by an estimated 15-25% compared to conventional cathode materials. This sensitivity also impacts inventory management strategies, with manufacturers typically maintaining smaller inventories to reduce degradation risks.
Vertical integration trends are emerging among leading battery manufacturers, with companies like CATL and Samsung SDI investing in securing their own fluoride material processing capabilities. This strategy aims to mitigate supply risks and reduce dependency on third-party suppliers, though it requires substantial capital investment that smaller players cannot match.
Regulatory considerations further complicate the supply landscape, with increasing scrutiny on environmental impacts of fluoride mining and processing. The European Union's recent classification of certain fluoride compounds under REACH regulations has imposed additional compliance requirements, potentially restricting material flows and increasing documentation burdens throughout the supply chain.
Price volatility remains a significant concern, with fluoride raw material costs fluctuating by up to 35% in the past three years. This volatility is primarily driven by limited supplier diversity and growing demand from competing industries, including semiconductor manufacturing and specialized metallurgy applications.
Primary raw materials include fluorite (CaF₂), lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF₆), and various transition metal fluorides such as FeF₃, CuF₂, and BiF₃. The extraction and processing of these materials require specialized equipment and expertise, limiting the number of qualified suppliers in the market. Currently, only 12 major suppliers worldwide can provide high-purity fluoride compounds suitable for battery applications.
Processing challenges represent significant bottlenecks in the supply chain. The conversion of raw fluoride minerals into battery-grade materials demands precise control of impurity levels, particularly oxygen contamination which can severely impact electrochemical performance. This necessitates advanced purification technologies that add considerable cost to the final product, with purification accounting for approximately 30-40% of total production expenses.
Transportation and storage present additional complexities due to the moisture sensitivity of many fluoride compounds. Specialized containers with controlled atmosphere are required, increasing logistics costs by an estimated 15-25% compared to conventional cathode materials. This sensitivity also impacts inventory management strategies, with manufacturers typically maintaining smaller inventories to reduce degradation risks.
Vertical integration trends are emerging among leading battery manufacturers, with companies like CATL and Samsung SDI investing in securing their own fluoride material processing capabilities. This strategy aims to mitigate supply risks and reduce dependency on third-party suppliers, though it requires substantial capital investment that smaller players cannot match.
Regulatory considerations further complicate the supply landscape, with increasing scrutiny on environmental impacts of fluoride mining and processing. The European Union's recent classification of certain fluoride compounds under REACH regulations has imposed additional compliance requirements, potentially restricting material flows and increasing documentation burdens throughout the supply chain.
Price volatility remains a significant concern, with fluoride raw material costs fluctuating by up to 35% in the past three years. This volatility is primarily driven by limited supplier diversity and growing demand from competing industries, including semiconductor manufacturing and specialized metallurgy applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Fluoride Cathode Materials
The environmental footprint of fluoride cathode materials represents a critical consideration in their market adoption trajectory. These materials, while promising superior energy density for next-generation batteries, present distinct sustainability challenges throughout their lifecycle. The extraction processes for fluoride compounds often involve energy-intensive mining operations and chemical processing that generate significant carbon emissions and potential groundwater contamination risks.
Manufacturing fluoride cathode materials typically requires high-temperature synthesis methods consuming substantial energy, with some processes operating at temperatures exceeding 800°C. This energy demand translates to increased carbon footprints unless powered by renewable energy sources. Additionally, the production often involves hazardous fluorinating agents such as hydrogen fluoride (HF), presenting occupational safety concerns and requiring specialized containment systems to prevent environmental releases.
Toxicity considerations remain paramount, as many fluoride compounds exhibit varying degrees of environmental persistence. Copper fluoride and iron fluoride cathodes generally demonstrate lower environmental toxicity compared to cobalt-based alternatives, potentially offering a sustainability advantage. However, comprehensive leaching studies under various environmental conditions remain limited in the scientific literature.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities. The recycling infrastructure for fluoride-based battery materials remains underdeveloped compared to established lithium-ion recycling pathways. Current recycling processes struggle with efficient separation of fluoride compounds from other battery components, though hydrometallurgical approaches show promise for selective recovery of valuable metals while managing fluoride content.
Several manufacturers have begun implementing closed-loop production systems that capture and reuse fluoride compounds during manufacturing, significantly reducing waste streams. These circular economy approaches, while currently limited to larger production facilities, demonstrate pathways toward improved sustainability profiles. Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that the environmental benefits of fluoride cathodes' extended cycle life and higher energy density may offset their production impacts when evaluated on a full-lifecycle basis.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly addressing fluoride-containing materials, with the European Union's Battery Directive revisions specifically targeting sustainable sourcing and end-of-life management requirements that will impact fluoride cathode adoption. Companies investing in these materials must navigate evolving compliance landscapes while developing environmentally responsible supply chains.
Manufacturing fluoride cathode materials typically requires high-temperature synthesis methods consuming substantial energy, with some processes operating at temperatures exceeding 800°C. This energy demand translates to increased carbon footprints unless powered by renewable energy sources. Additionally, the production often involves hazardous fluorinating agents such as hydrogen fluoride (HF), presenting occupational safety concerns and requiring specialized containment systems to prevent environmental releases.
Toxicity considerations remain paramount, as many fluoride compounds exhibit varying degrees of environmental persistence. Copper fluoride and iron fluoride cathodes generally demonstrate lower environmental toxicity compared to cobalt-based alternatives, potentially offering a sustainability advantage. However, comprehensive leaching studies under various environmental conditions remain limited in the scientific literature.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities. The recycling infrastructure for fluoride-based battery materials remains underdeveloped compared to established lithium-ion recycling pathways. Current recycling processes struggle with efficient separation of fluoride compounds from other battery components, though hydrometallurgical approaches show promise for selective recovery of valuable metals while managing fluoride content.
Several manufacturers have begun implementing closed-loop production systems that capture and reuse fluoride compounds during manufacturing, significantly reducing waste streams. These circular economy approaches, while currently limited to larger production facilities, demonstrate pathways toward improved sustainability profiles. Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that the environmental benefits of fluoride cathodes' extended cycle life and higher energy density may offset their production impacts when evaluated on a full-lifecycle basis.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly addressing fluoride-containing materials, with the European Union's Battery Directive revisions specifically targeting sustainable sourcing and end-of-life management requirements that will impact fluoride cathode adoption. Companies investing in these materials must navigate evolving compliance landscapes while developing environmentally responsible supply chains.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!