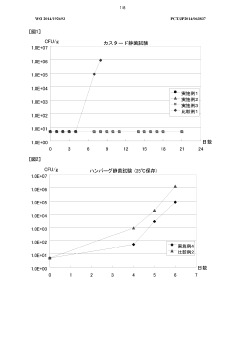
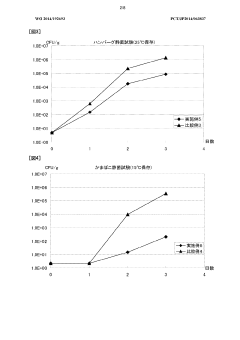
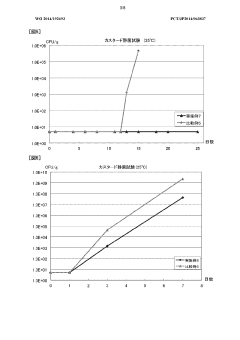
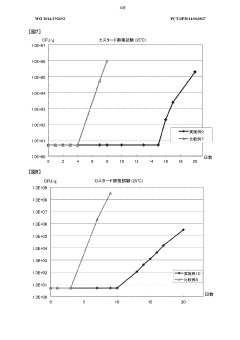
How Ammonium Hydroxide Affects the Longevity of Food Preservation
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ammonium Hydroxide in Food Preservation: Background and Objectives
Ammonium hydroxide has been utilized in food preservation for decades, playing a significant role in extending the shelf life of various food products. This compound, also known as ammonia solution or ammonia water, is a mixture of ammonia and water that has been recognized for its antimicrobial properties and pH-altering capabilities. The use of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation dates back to the early 20th century when food manufacturers began exploring chemical methods to enhance food safety and longevity.
The primary objective of employing ammonium hydroxide in food preservation is to inhibit microbial growth and reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses. By raising the pH of food products, ammonium hydroxide creates an environment that is less favorable for the proliferation of harmful bacteria, yeasts, and molds. This alkaline environment not only suppresses microbial activity but also helps maintain the color and texture of certain foods, particularly in meat products.
Over the years, the application of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation has evolved, with advancements in food science and technology leading to more refined and targeted uses. Initially, it was primarily used as a direct additive, but modern applications often involve its use in processing aids or as part of complex preservation systems. The food industry has continually sought to optimize the balance between effective preservation and minimal alteration of food quality and taste.
The technological trajectory of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation has been influenced by changing consumer preferences, regulatory frameworks, and scientific understanding of food safety. As concerns about chemical additives have grown, there has been a push towards more natural preservation methods. However, ammonium hydroxide continues to play a role in certain food preservation applications due to its efficacy and cost-effectiveness.
Current research in this field aims to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which ammonium hydroxide affects food longevity at a molecular level. Scientists are investigating its interactions with various food components, its impact on microbial cell structures, and potential synergies with other preservation techniques. The goal is to develop more targeted and efficient preservation strategies that maximize food safety while minimizing the use of chemical additives.
As we look towards the future of food preservation, the role of ammonium hydroxide is likely to be reevaluated in light of emerging technologies and changing consumer demands. The challenge lies in balancing the proven efficacy of this compound with the growing preference for clean label products and natural preservation methods. This technological landscape sets the stage for innovative approaches that may combine traditional chemical preservatives with novel, bio-based solutions to achieve optimal food longevity and safety.
The primary objective of employing ammonium hydroxide in food preservation is to inhibit microbial growth and reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses. By raising the pH of food products, ammonium hydroxide creates an environment that is less favorable for the proliferation of harmful bacteria, yeasts, and molds. This alkaline environment not only suppresses microbial activity but also helps maintain the color and texture of certain foods, particularly in meat products.
Over the years, the application of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation has evolved, with advancements in food science and technology leading to more refined and targeted uses. Initially, it was primarily used as a direct additive, but modern applications often involve its use in processing aids or as part of complex preservation systems. The food industry has continually sought to optimize the balance between effective preservation and minimal alteration of food quality and taste.
The technological trajectory of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation has been influenced by changing consumer preferences, regulatory frameworks, and scientific understanding of food safety. As concerns about chemical additives have grown, there has been a push towards more natural preservation methods. However, ammonium hydroxide continues to play a role in certain food preservation applications due to its efficacy and cost-effectiveness.
Current research in this field aims to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which ammonium hydroxide affects food longevity at a molecular level. Scientists are investigating its interactions with various food components, its impact on microbial cell structures, and potential synergies with other preservation techniques. The goal is to develop more targeted and efficient preservation strategies that maximize food safety while minimizing the use of chemical additives.
As we look towards the future of food preservation, the role of ammonium hydroxide is likely to be reevaluated in light of emerging technologies and changing consumer demands. The challenge lies in balancing the proven efficacy of this compound with the growing preference for clean label products and natural preservation methods. This technological landscape sets the stage for innovative approaches that may combine traditional chemical preservatives with novel, bio-based solutions to achieve optimal food longevity and safety.
Market Analysis of Extended Shelf-Life Food Products
The market for extended shelf-life food products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by changing consumer lifestyles, increasing urbanization, and the demand for convenience. This segment of the food industry encompasses a wide range of products, from ready-to-eat meals to packaged fruits and vegetables, all designed to maintain quality and safety for longer periods.
Consumer preferences have shifted towards products that offer both convenience and perceived freshness, leading to a surge in demand for extended shelf-life foods. This trend is particularly pronounced in urban areas, where busy lifestyles necessitate quick meal solutions without compromising on nutritional value. As a result, manufacturers have been investing heavily in technologies and processes that can extend the shelf life of food products while maintaining their organoleptic properties.
The global extended shelf-life food market is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is fueled by advancements in food preservation techniques, packaging innovations, and the expansion of cold chain logistics in emerging markets.
Key market segments within the extended shelf-life food category include dairy products, bakery items, meat and poultry, and fruits and vegetables. Among these, dairy products have shown particularly robust growth, with technologies like ultra-high temperature (UHT) processing enabling milk and other dairy items to remain shelf-stable for months without refrigeration.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for extended shelf-life foods, owing to well-established retail networks and consumer acceptance of such products. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing disposable incomes, changing food habits, and improvements in distribution infrastructure.
The competitive landscape of the extended shelf-life food market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and innovative start-ups. Major players are focusing on research and development to introduce new preservation methods and improve existing ones, with a particular emphasis on natural and clean-label solutions to meet consumer demands for healthier options.
Market challenges include stringent regulations regarding food additives and preservation methods, as well as consumer skepticism towards highly processed foods. To address these concerns, companies are increasingly adopting transparent labeling practices and investing in consumer education about the safety and benefits of extended shelf-life products.
Consumer preferences have shifted towards products that offer both convenience and perceived freshness, leading to a surge in demand for extended shelf-life foods. This trend is particularly pronounced in urban areas, where busy lifestyles necessitate quick meal solutions without compromising on nutritional value. As a result, manufacturers have been investing heavily in technologies and processes that can extend the shelf life of food products while maintaining their organoleptic properties.
The global extended shelf-life food market is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is fueled by advancements in food preservation techniques, packaging innovations, and the expansion of cold chain logistics in emerging markets.
Key market segments within the extended shelf-life food category include dairy products, bakery items, meat and poultry, and fruits and vegetables. Among these, dairy products have shown particularly robust growth, with technologies like ultra-high temperature (UHT) processing enabling milk and other dairy items to remain shelf-stable for months without refrigeration.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for extended shelf-life foods, owing to well-established retail networks and consumer acceptance of such products. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing disposable incomes, changing food habits, and improvements in distribution infrastructure.
The competitive landscape of the extended shelf-life food market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and innovative start-ups. Major players are focusing on research and development to introduce new preservation methods and improve existing ones, with a particular emphasis on natural and clean-label solutions to meet consumer demands for healthier options.
Market challenges include stringent regulations regarding food additives and preservation methods, as well as consumer skepticism towards highly processed foods. To address these concerns, companies are increasingly adopting transparent labeling practices and investing in consumer education about the safety and benefits of extended shelf-life products.
Current Applications and Challenges in Ammonium Hydroxide Usage
Ammonium hydroxide, a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen in water, has found widespread use in the food industry as a preservative and pH regulator. Its primary applications include meat processing, where it is used to control microbial growth and enhance food safety. In dairy products, it serves as a neutralizing agent and helps maintain product stability. The baking industry utilizes ammonium hydroxide as a leavening agent, contributing to the texture and volume of baked goods.
Despite its effectiveness, the use of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation faces several challenges. One of the main concerns is the potential formation of carcinogenic compounds when ammonium hydroxide reacts with certain food components at high temperatures. This has led to increased scrutiny and calls for alternative preservation methods in some sectors of the food industry.
Another challenge is the public perception of ammonium hydroxide as an "artificial" additive. As consumers increasingly demand "clean label" products, food manufacturers are under pressure to find natural alternatives or reduce the use of chemical preservatives. This shift in consumer preferences has prompted research into plant-based antimicrobials and other novel preservation techniques.
Regulatory compliance presents an ongoing challenge for food producers using ammonium hydroxide. While it is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA, its use is subject to strict guidelines and concentration limits. Ensuring compliance across different jurisdictions, especially for exported products, can be complex and costly for food manufacturers.
The environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide production and use is another area of concern. The manufacturing process can be energy-intensive and may contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, improper handling or disposal of ammonium hydroxide can lead to water pollution, affecting aquatic ecosystems.
In response to these challenges, the food industry is exploring innovative approaches to extend food preservation while minimizing the use of ammonium hydroxide. These include the development of intelligent packaging systems that can monitor food quality in real-time, the use of high-pressure processing technologies, and the application of natural antimicrobial compounds derived from plants and microorganisms.
Research is also ongoing to optimize the use of ammonium hydroxide in existing applications. This includes investigating synergistic effects with other preservatives to reduce overall chemical usage, as well as developing more precise application methods to enhance efficacy while minimizing potential negative impacts.
Despite its effectiveness, the use of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation faces several challenges. One of the main concerns is the potential formation of carcinogenic compounds when ammonium hydroxide reacts with certain food components at high temperatures. This has led to increased scrutiny and calls for alternative preservation methods in some sectors of the food industry.
Another challenge is the public perception of ammonium hydroxide as an "artificial" additive. As consumers increasingly demand "clean label" products, food manufacturers are under pressure to find natural alternatives or reduce the use of chemical preservatives. This shift in consumer preferences has prompted research into plant-based antimicrobials and other novel preservation techniques.
Regulatory compliance presents an ongoing challenge for food producers using ammonium hydroxide. While it is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA, its use is subject to strict guidelines and concentration limits. Ensuring compliance across different jurisdictions, especially for exported products, can be complex and costly for food manufacturers.
The environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide production and use is another area of concern. The manufacturing process can be energy-intensive and may contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, improper handling or disposal of ammonium hydroxide can lead to water pollution, affecting aquatic ecosystems.
In response to these challenges, the food industry is exploring innovative approaches to extend food preservation while minimizing the use of ammonium hydroxide. These include the development of intelligent packaging systems that can monitor food quality in real-time, the use of high-pressure processing technologies, and the application of natural antimicrobial compounds derived from plants and microorganisms.
Research is also ongoing to optimize the use of ammonium hydroxide in existing applications. This includes investigating synergistic effects with other preservatives to reduce overall chemical usage, as well as developing more precise application methods to enhance efficacy while minimizing potential negative impacts.
Ammonium Hydroxide-Based Preservation Methods
01 Stabilization of ammonium hydroxide solutions
Various methods are employed to stabilize ammonium hydroxide solutions, increasing their longevity. These methods may include the use of additives, pH control, or specific storage conditions to prevent degradation and maintain the solution's effectiveness over time.- Stabilization of ammonium hydroxide solutions: Various methods are employed to stabilize ammonium hydroxide solutions, thereby increasing their longevity. These methods may include the use of additives, pH control, or specific storage conditions to prevent degradation and maintain the solution's effectiveness over time.
- Ammonium hydroxide in industrial processes: Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in various industrial processes, where its longevity is crucial for maintaining process efficiency. Applications may include chemical manufacturing, wastewater treatment, and cleaning operations. Techniques are developed to extend its useful life in these processes.
- Storage and handling of ammonium hydroxide: Proper storage and handling techniques are essential for extending the longevity of ammonium hydroxide. This includes using appropriate containers, controlling temperature and humidity, and implementing safety measures to prevent contamination or degradation of the solution.
- Ammonium hydroxide in agricultural applications: In agricultural settings, the longevity of ammonium hydroxide is important for fertilizer applications and soil treatment. Methods are developed to enhance its stability and effectiveness in soil, ensuring prolonged nutrient availability for plants.
- Recycling and regeneration of ammonium hydroxide: To improve the overall longevity and sustainability of ammonium hydroxide use, techniques for recycling and regenerating spent solutions are developed. These methods aim to extend the useful life of the compound and reduce waste in various applications.
02 Ammonium hydroxide in industrial processes
Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in various industrial processes where its longevity is crucial. These applications may include chemical manufacturing, water treatment, and cleaning processes. Techniques are developed to extend the shelf life and maintain the efficacy of ammonium hydroxide in these industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental impact and safety considerations
Research focuses on improving the environmental impact and safety of ammonium hydroxide use. This includes developing methods to reduce emissions, enhance storage safety, and minimize potential hazards associated with long-term storage and use of ammonium hydroxide solutions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ammonium hydroxide in agricultural applications
The use of ammonium hydroxide in agriculture, particularly as a fertilizer, requires consideration of its longevity in soil and its interaction with plants over time. Research in this area aims to optimize the application and persistence of ammonium hydroxide for improved crop yields and soil health.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical methods for ammonium hydroxide stability
Development of analytical techniques to assess the stability and longevity of ammonium hydroxide solutions. These methods may include spectroscopic analysis, chemical assays, or monitoring of physical properties to determine the degradation rate and shelf life of ammonium hydroxide under various conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Food Preservation Technologies
The competitive landscape for ammonium hydroxide in food preservation is evolving, with the market in a growth phase. The global food preservatives market is projected to reach significant size, driven by increasing demand for processed foods and extended shelf life. Technologically, the use of ammonium hydroxide is mature but faces scrutiny due to health concerns. Key players like Chr. Hansen A/S, Arla Foods AmbA, and Kraft Foods Group Brands LLC are investing in research to develop safer, more natural preservation methods. Companies such as Purac Biochem BV and Galactic SA/NV are focusing on alternative preservatives, while LANXESS Deutschland GmbH and Chemische Fabrik Budenheim KG are exploring innovative applications of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation.
Chr. Hansen A/S
Technical Solution: Chr. Hansen has developed a range of natural preservation solutions that can be used as alternatives to ammonium hydroxide. Their approach focuses on using protective cultures and natural antimicrobials to extend food shelf life. They have introduced a line of bioprotective cultures called FreshQ®, which can inhibit yeast and mold growth in dairy products, potentially extending shelf life by up to 7 days[1]. These cultures work by producing specific metabolites that create an unfavorable environment for spoilage organisms, without significantly altering the product's pH or taste[2]. Additionally, Chr. Hansen has explored the use of fermentates, which are natural compounds produced by bacterial fermentation, to enhance food preservation in various applications including meat, dairy, and bakery products[3].
Strengths: Natural and clean label solution, effective against a wide range of spoilage organisms, minimal impact on product taste. Weaknesses: May require careful formulation and process adjustments, potentially higher cost compared to synthetic preservatives.
Purac Biochem BV
Technical Solution: Purac Biochem, now part of Corbion, has developed innovative solutions for food preservation that can serve as alternatives to ammonium hydroxide. Their approach centers on the use of lactic acid and its derivatives. Purac's PURASAL® portfolio includes natural antimicrobials derived from fermentation processes, which can effectively control Listeria, yeasts, and molds in various food products[1]. These solutions work by lowering the pH of the food, creating an environment inhospitable to many spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms. Purac has also introduced Verdad® Avanta™, a clean-label preservation system that combines cultured sugar and vinegar to extend shelf life in meat and poultry products[2]. This solution can increase product shelf life by up to 100% while maintaining color, flavor, and texture[3]. Furthermore, Purac has explored synergistic combinations of organic acids and their salts to enhance antimicrobial efficacy while minimizing impact on sensory properties.
Strengths: Natural and clean label solutions, broad spectrum antimicrobial activity, minimal organoleptic impact. Weaknesses: May require reformulation of existing products, potential pH limitations in certain applications.
Scientific Insights on Ammonium Hydroxide's Preservative Effects
Food-keeping-quality improver, and method for improving food keeping quality
PatentWO2014192693A1
Innovation
- A shelf life improving agent comprising one or more bacteriostatic substances such as acetate, sorbic acid, propionic acid, benzoic acid, amino acids, and nisin, in combination with inulin, which maintains the taste and color of food while effectively extending shelf life by suppressing acidity and bitterness.
Method for producing a frozen meal salad
PatentPendingEP4445738A1
Innovation
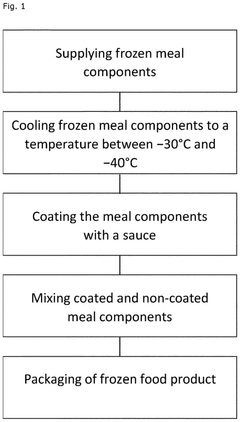
- A method involving cryogenic freezing and coating of food components with a sauce having a pH between 2.5 and 5, a salt content between 5 and 15%, and an oil content between 25 and 50%, followed by packaging, which results in a product with a pH between 4 and 6 and a water activity between 0.978 and 0.990, effectively inhibiting microbial growth and extending shelf life.
Regulatory Framework for Food Preservatives
The regulatory framework for food preservatives plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and quality of food products while addressing the use of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory body responsible for overseeing food additives, including preservatives. The FDA has established specific guidelines and regulations for the use of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation, classifying it as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices.
The European Union (EU) has its own set of regulations governing food additives, including preservatives. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety of food additives and providing scientific opinions to the European Commission. In the EU, ammonium hydroxide is approved for use as a food additive (E527) with specific limitations and conditions.
International organizations, such as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), also play a significant role in establishing global standards for food additives. JECFA provides scientific evaluations of food additives, including ammonium hydroxide, which inform the development of international food safety standards through the Codex Alimentarius Commission.
Regulatory frameworks typically include maximum permitted levels of ammonium hydroxide in various food categories, labeling requirements, and specific conditions of use. These regulations aim to balance the benefits of extended food preservation with potential health risks associated with excessive consumption of preservatives.
Many countries have adopted risk assessment approaches to evaluate the safety of food additives, including ammonium hydroxide. These assessments consider factors such as toxicological data, exposure levels, and potential long-term effects on human health. Regulatory bodies often require manufacturers to provide scientific evidence demonstrating the safety and efficacy of ammonium hydroxide as a food preservative before granting approval for its use.
Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for food manufacturers using ammonium hydroxide in their products. This includes adhering to good manufacturing practices, maintaining proper documentation, and implementing quality control measures to ensure that the use of ammonium hydroxide remains within permitted levels and does not compromise food safety.
As scientific understanding of food preservatives evolves, regulatory frameworks are subject to periodic review and updates. This ongoing process ensures that regulations remain current with the latest scientific evidence and technological advancements in food preservation techniques. Stakeholders, including food manufacturers, consumer advocacy groups, and scientific experts, often participate in the regulatory review process to provide input and shape future guidelines for the use of ammonium hydroxide and other food preservatives.
The European Union (EU) has its own set of regulations governing food additives, including preservatives. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety of food additives and providing scientific opinions to the European Commission. In the EU, ammonium hydroxide is approved for use as a food additive (E527) with specific limitations and conditions.
International organizations, such as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), also play a significant role in establishing global standards for food additives. JECFA provides scientific evaluations of food additives, including ammonium hydroxide, which inform the development of international food safety standards through the Codex Alimentarius Commission.
Regulatory frameworks typically include maximum permitted levels of ammonium hydroxide in various food categories, labeling requirements, and specific conditions of use. These regulations aim to balance the benefits of extended food preservation with potential health risks associated with excessive consumption of preservatives.
Many countries have adopted risk assessment approaches to evaluate the safety of food additives, including ammonium hydroxide. These assessments consider factors such as toxicological data, exposure levels, and potential long-term effects on human health. Regulatory bodies often require manufacturers to provide scientific evidence demonstrating the safety and efficacy of ammonium hydroxide as a food preservative before granting approval for its use.
Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for food manufacturers using ammonium hydroxide in their products. This includes adhering to good manufacturing practices, maintaining proper documentation, and implementing quality control measures to ensure that the use of ammonium hydroxide remains within permitted levels and does not compromise food safety.
As scientific understanding of food preservatives evolves, regulatory frameworks are subject to periodic review and updates. This ongoing process ensures that regulations remain current with the latest scientific evidence and technological advancements in food preservation techniques. Stakeholders, including food manufacturers, consumer advocacy groups, and scientific experts, often participate in the regulatory review process to provide input and shape future guidelines for the use of ammonium hydroxide and other food preservatives.
Environmental Impact of Ammonium Hydroxide in Food Industry
The use of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. This chemical compound, while effective in extending food shelf life, can have both direct and indirect impacts on the environment throughout its lifecycle.
In the production phase, the manufacturing of ammonium hydroxide requires substantial energy inputs and may result in emissions of greenhouse gases and other pollutants. The industrial processes involved often rely on fossil fuels, contributing to climate change and air quality degradation. Additionally, the transportation of this chemical to food processing facilities further increases its carbon footprint.
During food processing, the application of ammonium hydroxide can lead to the release of ammonia vapors into the atmosphere. These emissions, if not properly controlled, may contribute to local air pollution and potentially affect nearby ecosystems. Ammonia is known to be a precursor to particulate matter formation, which can have adverse effects on both human health and the environment.
The disposal of food products treated with ammonium hydroxide also raises environmental concerns. When these products reach landfills, the breakdown of ammonium compounds can result in the release of ammonia and nitrogen-containing compounds into soil and groundwater. This can lead to soil acidification and potential contamination of water resources, impacting local flora and fauna.
Furthermore, the widespread use of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation may indirectly contribute to food waste reduction. By extending the shelf life of various food products, it potentially decreases the amount of food discarded due to spoilage. This reduction in food waste can have positive environmental implications, such as lower methane emissions from landfills and reduced resource consumption in food production.
However, the long-term ecological effects of persistent ammonium hydroxide use in the food industry remain a subject of ongoing research. There are concerns about the potential bioaccumulation of ammonia-derived compounds in aquatic environments and their impact on biodiversity. The cumulative effects of these chemicals on ecosystems over time are not yet fully understood and require further investigation.
In response to these environmental challenges, there is a growing emphasis on developing more sustainable food preservation methods. Research into alternative natural preservatives and innovative packaging technologies aims to reduce reliance on chemical additives like ammonium hydroxide. Additionally, improved waste management practices and stricter regulations on chemical usage in the food industry are being implemented to mitigate potential environmental risks.
In the production phase, the manufacturing of ammonium hydroxide requires substantial energy inputs and may result in emissions of greenhouse gases and other pollutants. The industrial processes involved often rely on fossil fuels, contributing to climate change and air quality degradation. Additionally, the transportation of this chemical to food processing facilities further increases its carbon footprint.
During food processing, the application of ammonium hydroxide can lead to the release of ammonia vapors into the atmosphere. These emissions, if not properly controlled, may contribute to local air pollution and potentially affect nearby ecosystems. Ammonia is known to be a precursor to particulate matter formation, which can have adverse effects on both human health and the environment.
The disposal of food products treated with ammonium hydroxide also raises environmental concerns. When these products reach landfills, the breakdown of ammonium compounds can result in the release of ammonia and nitrogen-containing compounds into soil and groundwater. This can lead to soil acidification and potential contamination of water resources, impacting local flora and fauna.
Furthermore, the widespread use of ammonium hydroxide in food preservation may indirectly contribute to food waste reduction. By extending the shelf life of various food products, it potentially decreases the amount of food discarded due to spoilage. This reduction in food waste can have positive environmental implications, such as lower methane emissions from landfills and reduced resource consumption in food production.
However, the long-term ecological effects of persistent ammonium hydroxide use in the food industry remain a subject of ongoing research. There are concerns about the potential bioaccumulation of ammonia-derived compounds in aquatic environments and their impact on biodiversity. The cumulative effects of these chemicals on ecosystems over time are not yet fully understood and require further investigation.
In response to these environmental challenges, there is a growing emphasis on developing more sustainable food preservation methods. Research into alternative natural preservatives and innovative packaging technologies aims to reduce reliance on chemical additives like ammonium hydroxide. Additionally, improved waste management practices and stricter regulations on chemical usage in the food industry are being implemented to mitigate potential environmental risks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!