How Ammonium Hydroxide Impacts Electrodeposition Coatings in Automotive Manufacturing
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ammonium Hydroxide in Electrodeposition: Background and Objectives
Electrodeposition coatings have been a cornerstone in automotive manufacturing for decades, providing essential protection against corrosion and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of vehicles. The use of ammonium hydroxide in this process has emerged as a significant factor influencing the quality and efficiency of electrodeposition. This technical research report aims to explore the impact of ammonium hydroxide on electrodeposition coatings in the automotive industry.
The evolution of electrodeposition technology in automotive manufacturing can be traced back to the 1960s when it was first introduced as a method to improve corrosion resistance. Over the years, the process has undergone significant refinements, with the introduction of various chemical additives playing a crucial role in enhancing coating performance. Ammonium hydroxide, in particular, has gained attention for its potential to optimize the electrodeposition process.
The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively analyze how ammonium hydroxide affects the electrodeposition coating process, specifically in the context of automotive manufacturing. This includes examining its influence on coating adhesion, uniformity, and overall quality. Additionally, we aim to investigate the potential benefits and challenges associated with incorporating ammonium hydroxide into existing electrodeposition systems.
Understanding the role of ammonium hydroxide in electrodeposition is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it has the potential to improve the efficiency of the coating process, potentially leading to reduced production times and costs. Secondly, it may contribute to enhanced coating properties, which could result in improved corrosion resistance and durability of automotive components. Lastly, optimizing the use of ammonium hydroxide could lead to more environmentally friendly coating processes, aligning with the industry's growing focus on sustainability.
The automotive industry's continuous pursuit of innovation and quality improvement drives the need for this research. As vehicle manufacturers face increasing pressure to produce more durable, efficient, and environmentally friendly vehicles, understanding and optimizing every aspect of the production process becomes crucial. The insights gained from this study could potentially lead to advancements in electrodeposition technology, contributing to the overall progress of automotive manufacturing techniques.
This report will delve into the chemical properties of ammonium hydroxide and its interactions with other components in the electrodeposition bath. We will explore how these interactions influence the deposition process at a molecular level and how they translate to macroscopic coating properties. By examining both theoretical principles and practical applications, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of ammonium hydroxide's role in electrodeposition coatings.
The evolution of electrodeposition technology in automotive manufacturing can be traced back to the 1960s when it was first introduced as a method to improve corrosion resistance. Over the years, the process has undergone significant refinements, with the introduction of various chemical additives playing a crucial role in enhancing coating performance. Ammonium hydroxide, in particular, has gained attention for its potential to optimize the electrodeposition process.
The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively analyze how ammonium hydroxide affects the electrodeposition coating process, specifically in the context of automotive manufacturing. This includes examining its influence on coating adhesion, uniformity, and overall quality. Additionally, we aim to investigate the potential benefits and challenges associated with incorporating ammonium hydroxide into existing electrodeposition systems.
Understanding the role of ammonium hydroxide in electrodeposition is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it has the potential to improve the efficiency of the coating process, potentially leading to reduced production times and costs. Secondly, it may contribute to enhanced coating properties, which could result in improved corrosion resistance and durability of automotive components. Lastly, optimizing the use of ammonium hydroxide could lead to more environmentally friendly coating processes, aligning with the industry's growing focus on sustainability.
The automotive industry's continuous pursuit of innovation and quality improvement drives the need for this research. As vehicle manufacturers face increasing pressure to produce more durable, efficient, and environmentally friendly vehicles, understanding and optimizing every aspect of the production process becomes crucial. The insights gained from this study could potentially lead to advancements in electrodeposition technology, contributing to the overall progress of automotive manufacturing techniques.
This report will delve into the chemical properties of ammonium hydroxide and its interactions with other components in the electrodeposition bath. We will explore how these interactions influence the deposition process at a molecular level and how they translate to macroscopic coating properties. By examining both theoretical principles and practical applications, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of ammonium hydroxide's role in electrodeposition coatings.
Market Analysis of Electrodeposition Coatings in Automotive Industry
The electrodeposition coating market in the automotive industry has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for durable and corrosion-resistant coatings in vehicle manufacturing. This market segment is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2021 to 2026.
The automotive sector remains the largest consumer of electrodeposition coatings, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market share. This dominance is attributed to the coatings' ability to provide excellent protection against corrosion, chemical resistance, and improved aesthetics for vehicle bodies and components.
Key factors driving the market growth include the rising production of vehicles worldwide, stringent environmental regulations promoting the use of eco-friendly coatings, and the increasing focus on lightweight materials in automotive design. Additionally, the growing trend of electric vehicles (EVs) has created new opportunities for electrodeposition coating manufacturers, as these coatings are essential for protecting EV battery components.
The Asia-Pacific region leads the market, with China and India being the primary contributors to growth. This is due to the rapid expansion of automotive manufacturing in these countries and the increasing adoption of advanced coating technologies. North America and Europe follow closely, with steady demand driven by the presence of major automotive manufacturers and stringent quality standards.
In terms of product types, cathodic electrodeposition coatings dominate the market, accounting for over 70% of the total share. These coatings offer superior corrosion resistance and are widely used in automotive body-in-white applications. Anodic electrodeposition coatings, while less prevalent, still maintain a significant market presence, particularly in specialized automotive components.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, including PPG Industries, Axalta Coating Systems, BASF SE, and Nippon Paint Holdings. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve coating performance, reduce environmental impact, and develop innovative solutions for emerging automotive technologies.
Challenges facing the market include volatile raw material prices, particularly for resins and pigments, which can impact profit margins. Additionally, the ongoing shift towards electric vehicles may require adaptations in coating formulations to meet the specific needs of EV components.
The automotive sector remains the largest consumer of electrodeposition coatings, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market share. This dominance is attributed to the coatings' ability to provide excellent protection against corrosion, chemical resistance, and improved aesthetics for vehicle bodies and components.
Key factors driving the market growth include the rising production of vehicles worldwide, stringent environmental regulations promoting the use of eco-friendly coatings, and the increasing focus on lightweight materials in automotive design. Additionally, the growing trend of electric vehicles (EVs) has created new opportunities for electrodeposition coating manufacturers, as these coatings are essential for protecting EV battery components.
The Asia-Pacific region leads the market, with China and India being the primary contributors to growth. This is due to the rapid expansion of automotive manufacturing in these countries and the increasing adoption of advanced coating technologies. North America and Europe follow closely, with steady demand driven by the presence of major automotive manufacturers and stringent quality standards.
In terms of product types, cathodic electrodeposition coatings dominate the market, accounting for over 70% of the total share. These coatings offer superior corrosion resistance and are widely used in automotive body-in-white applications. Anodic electrodeposition coatings, while less prevalent, still maintain a significant market presence, particularly in specialized automotive components.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, including PPG Industries, Axalta Coating Systems, BASF SE, and Nippon Paint Holdings. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve coating performance, reduce environmental impact, and develop innovative solutions for emerging automotive technologies.
Challenges facing the market include volatile raw material prices, particularly for resins and pigments, which can impact profit margins. Additionally, the ongoing shift towards electric vehicles may require adaptations in coating formulations to meet the specific needs of EV components.
Current Challenges in Electrodeposition Coating Processes
Electrodeposition coating processes in automotive manufacturing face several significant challenges that impact the quality, efficiency, and environmental sustainability of the production line. One of the primary issues is achieving uniform coating thickness across complex vehicle body shapes. Irregular surfaces, recessed areas, and sharp edges often result in uneven coating distribution, leading to potential weak spots in corrosion protection.
Another major challenge is the control of coating adhesion to various substrate materials. Modern vehicles incorporate a mix of metals, alloys, and composites, each requiring specific surface preparation and coating formulations to ensure proper adhesion. Inconsistent adhesion can lead to premature coating failure and reduced vehicle longevity.
The presence of contaminants in the electrodeposition bath poses a significant hurdle. Oil, grease, and other impurities from previous manufacturing stages can interfere with the coating process, causing defects such as pinholes, blisters, and poor surface finish. Maintaining bath chemistry stability is crucial but challenging due to continuous contamination and depletion of active components.
Energy efficiency remains a concern in electrodeposition processes. The high voltages required for effective coating deposition contribute significantly to manufacturing costs and environmental impact. Optimizing energy consumption while maintaining coating quality is an ongoing challenge for automotive manufacturers.
Environmental regulations present another set of challenges. The industry is under pressure to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and eliminate hazardous materials from coating formulations. This necessitates the development of new, eco-friendly coating technologies that can match or exceed the performance of traditional systems.
Coating throw power, or the ability to coat recessed areas and interior surfaces, is a persistent challenge in automotive electrodeposition. Improving throw power without compromising other coating properties requires advanced formulation techniques and process control.
The integration of automation and real-time monitoring systems in electrodeposition processes presents both opportunities and challenges. While these technologies can enhance process control and consistency, their implementation requires significant investment and expertise to effectively manage the complex interplay of variables in the coating process.
Lastly, the impact of ammonium hydroxide on electrodeposition coatings introduces specific challenges. Ammonium hydroxide affects pH levels, which in turn influences coating deposition rates, adhesion, and final film properties. Balancing the benefits of ammonium hydroxide, such as improved throwing power and leveling, against potential drawbacks like increased porosity or reduced corrosion resistance, requires careful process optimization and control.
Another major challenge is the control of coating adhesion to various substrate materials. Modern vehicles incorporate a mix of metals, alloys, and composites, each requiring specific surface preparation and coating formulations to ensure proper adhesion. Inconsistent adhesion can lead to premature coating failure and reduced vehicle longevity.
The presence of contaminants in the electrodeposition bath poses a significant hurdle. Oil, grease, and other impurities from previous manufacturing stages can interfere with the coating process, causing defects such as pinholes, blisters, and poor surface finish. Maintaining bath chemistry stability is crucial but challenging due to continuous contamination and depletion of active components.
Energy efficiency remains a concern in electrodeposition processes. The high voltages required for effective coating deposition contribute significantly to manufacturing costs and environmental impact. Optimizing energy consumption while maintaining coating quality is an ongoing challenge for automotive manufacturers.
Environmental regulations present another set of challenges. The industry is under pressure to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and eliminate hazardous materials from coating formulations. This necessitates the development of new, eco-friendly coating technologies that can match or exceed the performance of traditional systems.
Coating throw power, or the ability to coat recessed areas and interior surfaces, is a persistent challenge in automotive electrodeposition. Improving throw power without compromising other coating properties requires advanced formulation techniques and process control.
The integration of automation and real-time monitoring systems in electrodeposition processes presents both opportunities and challenges. While these technologies can enhance process control and consistency, their implementation requires significant investment and expertise to effectively manage the complex interplay of variables in the coating process.
Lastly, the impact of ammonium hydroxide on electrodeposition coatings introduces specific challenges. Ammonium hydroxide affects pH levels, which in turn influences coating deposition rates, adhesion, and final film properties. Balancing the benefits of ammonium hydroxide, such as improved throwing power and leveling, against potential drawbacks like increased porosity or reduced corrosion resistance, requires careful process optimization and control.
Existing Solutions for Ammonium Hydroxide Integration in Electrodeposition
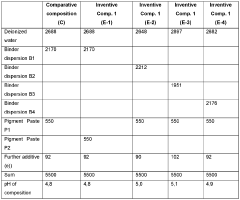
01 Electrodeposition process using ammonium hydroxide
Ammonium hydroxide is used in electrodeposition processes to control pH and improve coating quality. It can enhance the conductivity of the electrolyte solution and promote uniform deposition of metal ions onto the substrate surface.- Electrodeposition process using ammonium hydroxide: Ammonium hydroxide is used in electrodeposition processes to control pH and improve coating quality. It can enhance the conductivity of the electrolyte solution and promote uniform deposition of metal ions onto the substrate surface.
- Composition of electrodeposition baths containing ammonium hydroxide: Electrodeposition baths incorporating ammonium hydroxide often include other components such as metal salts, complexing agents, and additives. These formulations are designed to optimize coating properties and deposition efficiency.
- Application of ammonium hydroxide in specific coating materials: Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in the electrodeposition of various coating materials, including metals, alloys, and conductive polymers. It can influence the morphology, adhesion, and functional properties of the deposited coatings.
- Ammonium hydroxide as a complexing agent in electrodeposition: In some electrodeposition processes, ammonium hydroxide acts as a complexing agent, forming stable complexes with metal ions. This can help control the deposition rate and improve the uniformity of the coating.
- Environmental and safety considerations in ammonium hydroxide electrodeposition: The use of ammonium hydroxide in electrodeposition processes requires careful consideration of environmental and safety factors. Proper handling, waste management, and emission control are essential to ensure compliance with regulations and worker safety.
02 Composition of electrodeposition baths containing ammonium hydroxide
Electrodeposition baths containing ammonium hydroxide are formulated with various components to achieve desired coating properties. These may include metal salts, complexing agents, and additives to improve adhesion, hardness, and corrosion resistance of the deposited coating.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application of ammonium hydroxide in specific coating materials
Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in the electrodeposition of specific coating materials, such as zinc, copper, or nickel alloys. It can influence the microstructure and properties of the deposited coatings, leading to improved performance in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Optimization of electrodeposition parameters
The concentration of ammonium hydroxide, current density, temperature, and deposition time are crucial parameters in the electrodeposition process. Optimizing these factors can lead to improved coating quality, thickness uniformity, and adhesion to the substrate.Expand Specific Solutions05 Post-treatment of electrodeposited coatings
After electrodeposition, coatings may undergo post-treatment processes involving ammonium hydroxide to enhance their properties. These treatments can improve corrosion resistance, hardness, or surface finish of the deposited coatings.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Automotive Electrodeposition Coating Industry
The automotive electrodeposition coating market is in a mature stage, with a global market size estimated to be over $3 billion. The technology is well-established, with major players like PPG Industries, BASF Coatings, and Axalta Coating Systems dominating the field. These companies have developed advanced formulations to improve coating performance and efficiency. The impact of ammonium hydroxide on electrodeposition coatings is a key area of research, as manufacturers seek to optimize coating properties and reduce environmental impact. Toyota Motor Corp. and Honda Motor Co., Ltd. are significant end-users driving innovation in this sector, collaborating with coating suppliers to meet stringent automotive industry standards for corrosion protection and durability.
PPG Industries Ohio, Inc.
Technical Solution: PPG Industries has developed advanced electrodeposition coating technologies that utilize ammonium hydroxide to enhance coating performance in automotive manufacturing. Their e-coat process incorporates a precise balance of ammonium hydroxide to optimize pH levels, improving the uniformity and adhesion of the coating. The company's proprietary formulation includes nano-scale additives that work synergistically with ammonium hydroxide to increase corrosion resistance and durability[1]. PPG's system also employs a closed-loop control mechanism to continuously monitor and adjust ammonium hydroxide levels, ensuring consistent coating quality across large production volumes[3].
Strengths: Superior corrosion resistance, excellent adhesion properties, and consistent coating quality. Weaknesses: May require more complex process control systems and potentially higher initial implementation costs.
BASF Coatings GmbH
Technical Solution: BASF Coatings has innovated in the field of electrodeposition coatings by developing a novel approach to ammonium hydroxide utilization. Their CathoGuard® technology incorporates a specially formulated ammonium hydroxide blend that enhances the throwing power of the e-coat, allowing for better coverage of complex automotive geometries[2]. The company's process also features a unique rinsing system that optimizes the removal of excess ammonium hydroxide, reducing waste and improving environmental sustainability. BASF's coatings incorporate smart polymers that react with ammonium hydroxide to create a self-healing effect, significantly extending the lifespan of the protective layer[4].
Strengths: Excellent coverage of complex parts, improved environmental profile, and self-healing properties. Weaknesses: May be more expensive than traditional e-coat systems and require specialized application equipment.
Core Innovations in Ammonium Hydroxide-based Electrodeposition
Electrodeposition coating material compositions comprising alkoxylated polyethyleneimines
PatentWO2023237284A1
Innovation
- An aqueous cathodically depositable electrodeposition coating material composition incorporating an alkoxylated polyethyleneimine as part of the binder dispersion or pigment paste, which ensures improved film build and homogeneity on edges while maintaining corrosion resistance, achieved by immersing the substrate in a bath containing the composition and baking the coating.
Electrodepositable coating compositions comprising onium salt group-containing polymers prepared by atom transfer radical polymerization
PatentInactiveEP1112327B1
Innovation
- The use of atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) to produce active hydrogen group-containing polymers with controlled molecular weights and narrow molecular weight distributions, combined with specific polymer chain structures and a curing agent reactive with active hydrogen groups, to create a thermosetting composition for improved electrocoating.
Environmental Impact of Ammonium Hydroxide in Electrodeposition
The environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide in electrodeposition processes within automotive manufacturing is a critical consideration for sustainability and regulatory compliance. Ammonium hydroxide, commonly used as a pH regulator in electrodeposition baths, can have significant effects on both the immediate working environment and broader ecosystems if not properly managed.
In the electrodeposition process, ammonium hydroxide volatilizes readily, releasing ammonia gas into the air. This can lead to poor air quality in manufacturing facilities, potentially causing respiratory irritation and other health issues for workers. Proper ventilation systems and personal protective equipment are essential to mitigate these risks.
The release of ammonia-containing wastewater from electrodeposition processes poses a threat to aquatic environments. Excessive ammonia levels in water bodies can lead to eutrophication, causing algal blooms and depleting oxygen levels, which is detrimental to aquatic life. Treatment of wastewater to remove or neutralize ammonia before discharge is crucial to prevent ecological damage.
Ammonium hydroxide can also contribute to soil contamination if spills or improper disposal occur. This can alter soil pH and nitrogen content, affecting plant growth and soil microbial communities. Implementing robust spill prevention and containment measures is necessary to protect soil quality in and around manufacturing facilities.
The production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide for industrial use contribute to the overall carbon footprint of the electrodeposition process. Manufacturers are increasingly looking at ways to optimize chemical usage or find alternative pH regulators to reduce this indirect environmental impact.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established strict guidelines for the handling, use, and disposal of ammonium hydroxide in industrial processes. Compliance with these regulations often requires significant investment in treatment technologies and monitoring systems, driving innovation in more environmentally friendly electrodeposition processes.
As the automotive industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is growing research into alternative electrodeposition methods that reduce or eliminate the need for ammonium hydroxide. These include the development of low-temperature processes, use of less volatile alkaline agents, and exploration of entirely new coating technologies that achieve similar protective qualities without the environmental concerns associated with traditional electrodeposition.
In the electrodeposition process, ammonium hydroxide volatilizes readily, releasing ammonia gas into the air. This can lead to poor air quality in manufacturing facilities, potentially causing respiratory irritation and other health issues for workers. Proper ventilation systems and personal protective equipment are essential to mitigate these risks.
The release of ammonia-containing wastewater from electrodeposition processes poses a threat to aquatic environments. Excessive ammonia levels in water bodies can lead to eutrophication, causing algal blooms and depleting oxygen levels, which is detrimental to aquatic life. Treatment of wastewater to remove or neutralize ammonia before discharge is crucial to prevent ecological damage.
Ammonium hydroxide can also contribute to soil contamination if spills or improper disposal occur. This can alter soil pH and nitrogen content, affecting plant growth and soil microbial communities. Implementing robust spill prevention and containment measures is necessary to protect soil quality in and around manufacturing facilities.
The production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide for industrial use contribute to the overall carbon footprint of the electrodeposition process. Manufacturers are increasingly looking at ways to optimize chemical usage or find alternative pH regulators to reduce this indirect environmental impact.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established strict guidelines for the handling, use, and disposal of ammonium hydroxide in industrial processes. Compliance with these regulations often requires significant investment in treatment technologies and monitoring systems, driving innovation in more environmentally friendly electrodeposition processes.
As the automotive industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is growing research into alternative electrodeposition methods that reduce or eliminate the need for ammonium hydroxide. These include the development of low-temperature processes, use of less volatile alkaline agents, and exploration of entirely new coating technologies that achieve similar protective qualities without the environmental concerns associated with traditional electrodeposition.
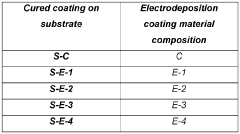
Quality Control Measures for Ammonium Hydroxide-influenced Coatings
Quality control measures for ammonium hydroxide-influenced coatings in automotive manufacturing are crucial to ensure the integrity and performance of electrodeposition coatings. These measures typically involve a combination of process monitoring, material testing, and finished product evaluation.
One key aspect of quality control is the continuous monitoring of the electrodeposition bath composition. This includes regular testing of the ammonium hydroxide concentration, pH levels, and other critical parameters such as temperature and conductivity. Automated systems with real-time sensors can be employed to maintain optimal bath conditions and alert operators to any deviations that may affect coating quality.
Material testing is another essential component of quality control. Incoming raw materials, including the ammonium hydroxide solution, must be rigorously tested for purity and consistency. This helps prevent the introduction of contaminants that could compromise the coating process or the final product's performance.
In-process testing during the electrodeposition coating application is vital. This may involve monitoring current density, voltage, and coating thickness in real-time. Advanced techniques such as impedance spectroscopy can be used to assess the coating's formation and properties as it is being deposited.
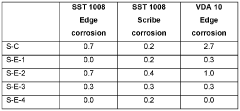
Post-application quality control measures are equally important. These include visual inspections for uniformity, adhesion tests, and corrosion resistance evaluations. Standardized tests such as salt spray exposure and cyclic corrosion testing are commonly used to assess the long-term performance of the coatings under simulated environmental conditions.
Microscopic analysis techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM), can be employed to examine the coating's microstructure and surface morphology. These methods can reveal defects or inconsistencies that may not be visible to the naked eye.
Statistical process control (SPC) methods are often implemented to track quality metrics over time and identify trends or anomalies. This data-driven approach allows for proactive adjustments to the coating process, helping to maintain consistent quality and reduce defects.
Finally, accelerated weathering tests and field trials provide valuable data on the coating's durability and performance under real-world conditions. These long-term evaluations are critical for validating the effectiveness of the quality control measures and ensuring that the ammonium hydroxide-influenced coatings meet the stringent requirements of the automotive industry.
One key aspect of quality control is the continuous monitoring of the electrodeposition bath composition. This includes regular testing of the ammonium hydroxide concentration, pH levels, and other critical parameters such as temperature and conductivity. Automated systems with real-time sensors can be employed to maintain optimal bath conditions and alert operators to any deviations that may affect coating quality.
Material testing is another essential component of quality control. Incoming raw materials, including the ammonium hydroxide solution, must be rigorously tested for purity and consistency. This helps prevent the introduction of contaminants that could compromise the coating process or the final product's performance.
In-process testing during the electrodeposition coating application is vital. This may involve monitoring current density, voltage, and coating thickness in real-time. Advanced techniques such as impedance spectroscopy can be used to assess the coating's formation and properties as it is being deposited.
Post-application quality control measures are equally important. These include visual inspections for uniformity, adhesion tests, and corrosion resistance evaluations. Standardized tests such as salt spray exposure and cyclic corrosion testing are commonly used to assess the long-term performance of the coatings under simulated environmental conditions.
Microscopic analysis techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM), can be employed to examine the coating's microstructure and surface morphology. These methods can reveal defects or inconsistencies that may not be visible to the naked eye.
Statistical process control (SPC) methods are often implemented to track quality metrics over time and identify trends or anomalies. This data-driven approach allows for proactive adjustments to the coating process, helping to maintain consistent quality and reduce defects.
Finally, accelerated weathering tests and field trials provide valuable data on the coating's durability and performance under real-world conditions. These long-term evaluations are critical for validating the effectiveness of the quality control measures and ensuring that the ammonium hydroxide-influenced coatings meet the stringent requirements of the automotive industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!