How AMOLED contributes to the reduction of digital eye strain?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED and Eye Strain: Background and Objectives
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has emerged as a significant advancement in display technology, particularly in the context of digital eye strain reduction. The evolution of display technologies has been driven by the increasing prevalence of digital devices in our daily lives, from smartphones and tablets to computer monitors and televisions. As screen time has dramatically increased, so too has the incidence of digital eye strain, a condition characterized by symptoms such as eye fatigue, dryness, and discomfort.
The primary objective of AMOLED technology in relation to eye strain is to mitigate these adverse effects by addressing the fundamental causes of visual discomfort associated with prolonged screen use. AMOLED displays aim to provide a more natural viewing experience by emulating the properties of natural light and reducing the harsh blue light emissions commonly associated with traditional LCD screens.
The development of AMOLED technology can be traced back to the late 1980s, with significant advancements occurring in the 2000s. The technology has since progressed rapidly, driven by the demand for improved display quality and energy efficiency in mobile devices. As research into the effects of digital screens on eye health has expanded, AMOLED has been increasingly recognized for its potential to reduce eye strain.
Key technological goals in the development of AMOLED displays include achieving higher contrast ratios, wider color gamuts, and more precise control over individual pixel illumination. These features contribute to reduced eye strain by providing more natural-looking images with less glare and flicker. Additionally, AMOLED technology aims to optimize power consumption, allowing for the implementation of eye-friendly features without significantly impacting device battery life.
The broader context of AMOLED's role in eye strain reduction encompasses the growing awareness of digital wellness and the importance of ergonomic design in technology products. As consumers become more health-conscious, there is an increasing demand for devices that not only perform well but also prioritize user well-being. This shift in consumer priorities has accelerated research and development efforts in display technologies that can mitigate the negative effects of prolonged screen exposure.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of AMOLED technology in relation to eye strain reduction is likely to focus on further refinements in color accuracy, brightness control, and the integration of adaptive technologies that can adjust display properties based on ambient lighting conditions and individual user needs. The ultimate goal is to create displays that can be used for extended periods without causing significant visual discomfort or long-term eye health issues.
The primary objective of AMOLED technology in relation to eye strain is to mitigate these adverse effects by addressing the fundamental causes of visual discomfort associated with prolonged screen use. AMOLED displays aim to provide a more natural viewing experience by emulating the properties of natural light and reducing the harsh blue light emissions commonly associated with traditional LCD screens.
The development of AMOLED technology can be traced back to the late 1980s, with significant advancements occurring in the 2000s. The technology has since progressed rapidly, driven by the demand for improved display quality and energy efficiency in mobile devices. As research into the effects of digital screens on eye health has expanded, AMOLED has been increasingly recognized for its potential to reduce eye strain.
Key technological goals in the development of AMOLED displays include achieving higher contrast ratios, wider color gamuts, and more precise control over individual pixel illumination. These features contribute to reduced eye strain by providing more natural-looking images with less glare and flicker. Additionally, AMOLED technology aims to optimize power consumption, allowing for the implementation of eye-friendly features without significantly impacting device battery life.
The broader context of AMOLED's role in eye strain reduction encompasses the growing awareness of digital wellness and the importance of ergonomic design in technology products. As consumers become more health-conscious, there is an increasing demand for devices that not only perform well but also prioritize user well-being. This shift in consumer priorities has accelerated research and development efforts in display technologies that can mitigate the negative effects of prolonged screen exposure.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of AMOLED technology in relation to eye strain reduction is likely to focus on further refinements in color accuracy, brightness control, and the integration of adaptive technologies that can adjust display properties based on ambient lighting conditions and individual user needs. The ultimate goal is to create displays that can be used for extended periods without causing significant visual discomfort or long-term eye health issues.
Market Demand for Eye-Friendly Displays
The market demand for eye-friendly displays has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing awareness of digital eye strain and its impact on overall health and productivity. As people spend more time interacting with digital devices, the need for displays that reduce eye fatigue and discomfort has become paramount.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have recognized this trend and are actively developing and marketing products with eye-friendly features. Smartphones, tablets, laptops, and monitors are now frequently advertised with blue light reduction capabilities and flicker-free technologies. This shift in product positioning reflects the rising consumer demand for devices that prioritize eye health.
The workplace environment has also contributed significantly to the market demand for eye-friendly displays. With the increase in remote work and digital-centric office spaces, employers are investing in ergonomic solutions, including displays that reduce eye strain. This trend is driven by the desire to improve employee well-being and maintain productivity over extended periods of screen use.
In the education sector, there is a growing emphasis on digital learning tools and platforms. Schools and institutions are increasingly adopting devices with eye-friendly displays to protect students' vision during long study sessions. This has created a new market segment for manufacturers to target with specialized educational devices featuring advanced display technologies.
The healthcare industry has also played a role in driving demand for eye-friendly displays. Ophthalmologists and optometrists are recommending devices with reduced blue light emission and improved refresh rates to their patients, particularly those suffering from digital eye strain symptoms. This medical endorsement has further legitimized the need for eye-friendly display technologies in the consumer market.
Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay a premium for devices that offer enhanced eye protection features. This willingness has encouraged manufacturers to invest in research and development of advanced display technologies, such as AMOLED, which can contribute to reducing digital eye strain.
The aging population in many developed countries has also contributed to the demand for eye-friendly displays. Older adults, who may be more susceptible to eye strain and related vision problems, are seeking devices that offer comfortable viewing experiences for extended periods.
As awareness of the long-term effects of prolonged screen exposure continues to grow, the market for eye-friendly displays is expected to expand further. This trend is likely to drive innovation in display technologies and lead to the development of new standards for eye protection in digital devices across various industries and applications.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have recognized this trend and are actively developing and marketing products with eye-friendly features. Smartphones, tablets, laptops, and monitors are now frequently advertised with blue light reduction capabilities and flicker-free technologies. This shift in product positioning reflects the rising consumer demand for devices that prioritize eye health.
The workplace environment has also contributed significantly to the market demand for eye-friendly displays. With the increase in remote work and digital-centric office spaces, employers are investing in ergonomic solutions, including displays that reduce eye strain. This trend is driven by the desire to improve employee well-being and maintain productivity over extended periods of screen use.
In the education sector, there is a growing emphasis on digital learning tools and platforms. Schools and institutions are increasingly adopting devices with eye-friendly displays to protect students' vision during long study sessions. This has created a new market segment for manufacturers to target with specialized educational devices featuring advanced display technologies.
The healthcare industry has also played a role in driving demand for eye-friendly displays. Ophthalmologists and optometrists are recommending devices with reduced blue light emission and improved refresh rates to their patients, particularly those suffering from digital eye strain symptoms. This medical endorsement has further legitimized the need for eye-friendly display technologies in the consumer market.
Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay a premium for devices that offer enhanced eye protection features. This willingness has encouraged manufacturers to invest in research and development of advanced display technologies, such as AMOLED, which can contribute to reducing digital eye strain.
The aging population in many developed countries has also contributed to the demand for eye-friendly displays. Older adults, who may be more susceptible to eye strain and related vision problems, are seeking devices that offer comfortable viewing experiences for extended periods.
As awareness of the long-term effects of prolonged screen exposure continues to grow, the market for eye-friendly displays is expected to expand further. This trend is likely to drive innovation in display technologies and lead to the development of new standards for eye protection in digital devices across various industries and applications.
AMOLED Technology: Current State and Challenges
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has made significant strides in recent years, revolutionizing display technology across various devices. However, it still faces several challenges in its current state of development. One of the primary advantages of AMOLED displays is their ability to produce deep blacks and vibrant colors, which contributes to reduced eye strain compared to traditional LCD screens.
The current state of AMOLED technology showcases impressive advancements in display quality, energy efficiency, and form factor flexibility. AMOLED screens can achieve higher contrast ratios and wider color gamuts than their LCD counterparts, resulting in more visually appealing and potentially less fatiguing viewing experiences. Additionally, AMOLED displays can be manufactured on flexible substrates, enabling the creation of curved and foldable devices.
Despite these achievements, AMOLED technology faces several challenges that need to be addressed for further improvement and widespread adoption. One significant issue is the potential for screen burn-in, where static images can leave permanent marks on the display if shown for extended periods. This problem is particularly concerning for devices with long usage times, such as smartphones and televisions.
Another challenge is the relatively higher production cost of AMOLED displays compared to LCD technology. While prices have decreased over time, the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens remains more complex and expensive, limiting its adoption in budget-friendly devices.
AMOLED displays also struggle with brightness levels, especially in outdoor environments. Although improvements have been made, they still lag behind some high-end LCD displays in terms of peak brightness, which can affect visibility in bright sunlight.
Lifespan and degradation of organic materials used in AMOLED displays present another hurdle. The organic compounds in these displays can degrade over time, leading to color shifts and reduced overall display quality. Researchers are actively working on developing more stable materials to extend the lifespan of AMOLED screens.
In the context of digital eye strain reduction, AMOLED technology offers several advantages. The ability to produce true blacks by turning off individual pixels not only enhances contrast but also reduces the overall light emission from the screen. This feature, combined with the technology's capacity for more accurate color reproduction, can potentially lead to reduced eye fatigue during prolonged use.
However, the challenge lies in optimizing AMOLED displays specifically for eye comfort without compromising on other performance aspects. This includes developing more sophisticated brightness and color temperature adjustment algorithms that can adapt to various ambient lighting conditions and user preferences.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, addressing these challenges will be crucial for its wider adoption and effectiveness in reducing digital eye strain. Future developments may focus on enhancing brightness capabilities, improving longevity, and refining color accuracy while maintaining the technology's inherent advantages in contrast and energy efficiency.
The current state of AMOLED technology showcases impressive advancements in display quality, energy efficiency, and form factor flexibility. AMOLED screens can achieve higher contrast ratios and wider color gamuts than their LCD counterparts, resulting in more visually appealing and potentially less fatiguing viewing experiences. Additionally, AMOLED displays can be manufactured on flexible substrates, enabling the creation of curved and foldable devices.
Despite these achievements, AMOLED technology faces several challenges that need to be addressed for further improvement and widespread adoption. One significant issue is the potential for screen burn-in, where static images can leave permanent marks on the display if shown for extended periods. This problem is particularly concerning for devices with long usage times, such as smartphones and televisions.
Another challenge is the relatively higher production cost of AMOLED displays compared to LCD technology. While prices have decreased over time, the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens remains more complex and expensive, limiting its adoption in budget-friendly devices.
AMOLED displays also struggle with brightness levels, especially in outdoor environments. Although improvements have been made, they still lag behind some high-end LCD displays in terms of peak brightness, which can affect visibility in bright sunlight.
Lifespan and degradation of organic materials used in AMOLED displays present another hurdle. The organic compounds in these displays can degrade over time, leading to color shifts and reduced overall display quality. Researchers are actively working on developing more stable materials to extend the lifespan of AMOLED screens.
In the context of digital eye strain reduction, AMOLED technology offers several advantages. The ability to produce true blacks by turning off individual pixels not only enhances contrast but also reduces the overall light emission from the screen. This feature, combined with the technology's capacity for more accurate color reproduction, can potentially lead to reduced eye fatigue during prolonged use.
However, the challenge lies in optimizing AMOLED displays specifically for eye comfort without compromising on other performance aspects. This includes developing more sophisticated brightness and color temperature adjustment algorithms that can adapt to various ambient lighting conditions and user preferences.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, addressing these challenges will be crucial for its wider adoption and effectiveness in reducing digital eye strain. Future developments may focus on enhancing brightness capabilities, improving longevity, and refining color accuracy while maintaining the technology's inherent advantages in contrast and energy efficiency.
AMOLED Solutions for Reducing Digital Eye Strain
01 AMOLED display brightness adjustment
Techniques for adjusting the brightness of AMOLED displays to reduce eye strain. This includes methods for dynamically controlling pixel luminance based on ambient light conditions and user preferences, as well as implementing adaptive brightness algorithms to optimize visual comfort.- Display brightness adjustment: Techniques for adjusting the brightness of AMOLED displays to reduce eye strain. This includes automatic brightness control based on ambient light conditions, user preferences, and time of day. Some methods involve gradual brightness transitions to minimize discomfort.
- Color temperature and blue light reduction: Methods for modifying the color temperature and reducing blue light emission from AMOLED displays. These techniques often involve adjusting the color balance, implementing blue light filters, or using specialized pixel structures to minimize harmful light wavelengths that contribute to eye strain.
- Flicker reduction and refresh rate optimization: Strategies to minimize screen flicker and optimize refresh rates in AMOLED displays. This includes implementing high refresh rates, adaptive refresh rate technologies, and pulse-width modulation (PWM) dimming alternatives to reduce eye fatigue during extended viewing periods.
- Ergonomic display design: Innovations in AMOLED display design focusing on ergonomics to reduce eye strain. This encompasses curved displays, anti-glare coatings, and optimized pixel layouts that enhance visual comfort and reduce the need for eye accommodation.
- Eye-tracking and adaptive content display: Integration of eye-tracking technology with AMOLED displays to create adaptive content presentation. This includes adjusting display parameters based on viewing distance, gaze direction, and eye movement patterns to minimize eye strain and optimize visual comfort.
02 Color temperature and blue light reduction
Methods for modifying the color temperature and reducing blue light emission from AMOLED displays to minimize digital eye strain. This involves adjusting the color gamut, implementing night mode features, and using specialized filters to decrease harmful blue light exposure during extended viewing periods.Expand Specific Solutions03 Flicker reduction and refresh rate optimization
Techniques to minimize screen flicker and optimize refresh rates in AMOLED displays. This includes implementing variable refresh rate technologies, pulse-width modulation improvements, and other methods to reduce eye fatigue caused by rapid screen updates and imperceptible flickering.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ergonomic display design and user interface
Innovations in AMOLED display design and user interface to enhance visual comfort. This encompasses ergonomic screen curvatures, anti-glare coatings, and intuitive UI elements that reduce eye strain during prolonged use, such as dark mode implementations and customizable text sizes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Eye-tracking and gaze-based display optimization
Integration of eye-tracking technologies and gaze-based optimizations for AMOLED displays. These systems adjust display parameters based on user's eye movements and viewing patterns, dynamically optimizing content presentation to reduce eye strain and improve visual comfort.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in AMOLED Display Industry
The AMOLED technology market for reducing digital eye strain is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by rising awareness of eye health. The market size is expanding as more device manufacturers adopt AMOLED displays. Technologically, AMOLED is maturing but still evolving, with companies like Samsung Electronics, LG Display, and BOE Technology leading innovation. These firms are developing advanced AMOLED panels with features specifically designed to reduce eye strain, such as flicker-free technology and blue light filters. Other players like OPPO and Huawei are integrating these displays into their devices, further driving market growth and technological refinement.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has made significant strides in AMOLED technology to address digital eye strain. Their flexible AMOLED displays incorporate a blue light filtering layer that can reduce harmful blue light emissions by up to 40%[7]. BOE has also developed an intelligent brightness adjustment system that optimizes screen luminance based on ambient light and viewing content, reducing eye fatigue during extended use[8]. Additionally, BOE's AMOLED panels feature high refresh rates (up to 120Hz), which contribute to smoother motion and reduced eye strain, particularly when viewing fast-moving content or scrolling[9].
Strengths: Rapidly growing AMOLED production capacity, innovative flexible display technology, and comprehensive eye protection features. Weaknesses: Still catching up to market leaders in terms of overall AMOLED market share and brand recognition.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed AMOLED displays with advanced eye care technologies to reduce digital eye strain. Their AMOLED screens utilize a blue light filter that can reduce harmful blue light emissions by up to 42% compared to conventional LCD displays[1]. Additionally, Samsung has implemented adaptive brightness control, which automatically adjusts screen brightness based on ambient light conditions, reducing eye fatigue during prolonged use[2]. The company has also introduced a "Dark Mode" feature across its AMOLED devices, which not only saves battery life but also reduces eye strain in low-light environments by minimizing the contrast between the screen and surroundings[3].
Strengths: Industry-leading AMOLED technology, comprehensive eye care features, and wide implementation across various devices. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to LCD, potential for screen burn-in over extended periods.
Core Innovations in AMOLED for Eye Health
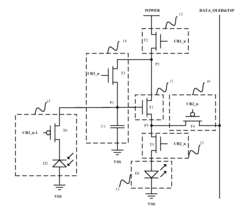
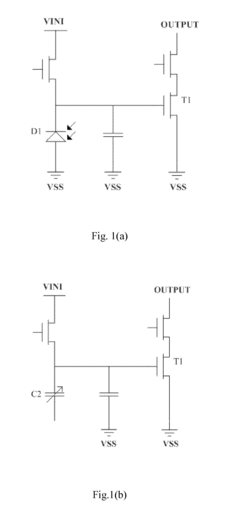
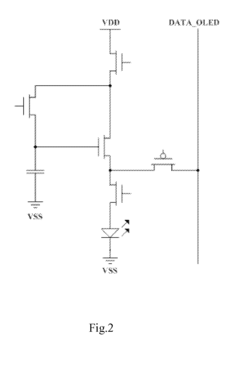
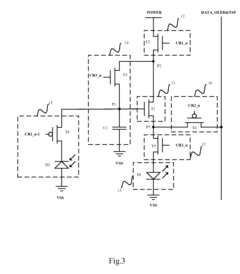
Active matrix organic light emitting diode pixel unit circuit, display panel and electronic product
PatentActiveUS9459721B2
Innovation
- The AMOLED pixel unit circuit is redesigned to include a light emitting module, a driving module, a threshold compensating module, a light emission controlling module, a touch sensing module, and an induction signal outputting module, which utilize existing data lines and control signals to integrate the TSP in Cell circuit, sharing circuit elements and control signals to minimize additional components.
Array substrate, display device, and method for manufacturing array substrate
PatentActiveUS20170148862A1
Innovation
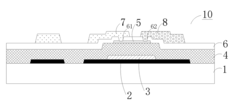
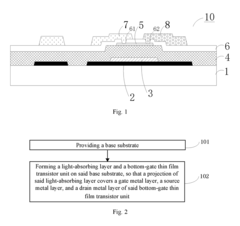
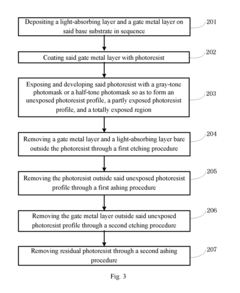
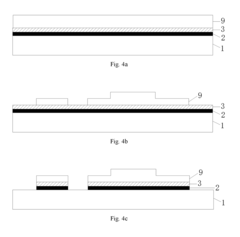
- An array substrate with a light-absorbing layer covering the gate, source, and drain metal layers of a bottom-gate thin film transistor unit, preventing ambient light irradiation while allowing useful light to pass through.
Health Regulations for Display Technologies
The regulatory landscape for display technologies has evolved significantly in response to growing concerns about digital eye strain and other health issues associated with prolonged screen use. Governments and health organizations worldwide have implemented various regulations and guidelines to ensure that display technologies, including AMOLED screens, meet specific health and safety standards.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established guidelines for computer workstations, which include recommendations for display quality and ergonomics. These guidelines, while not specifically addressing AMOLED technology, set the foundation for healthy viewing practices in professional environments.
The European Union has taken a more proactive approach with its Display Screen Equipment (DSE) regulations. These rules require employers to assess and mitigate risks associated with display screen use, including those related to eye strain. While not explicitly mentioning AMOLED, the regulations encompass all display technologies and emphasize the importance of screen quality in reducing visual fatigue.
In Asia, countries like South Korea and Japan, which are at the forefront of AMOLED development, have implemented stringent quality control measures for display manufacturers. These measures indirectly contribute to eye health by ensuring high-quality, flicker-free displays that are less likely to cause eye strain.
The International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) has issued guidelines on exposure to visible and infrared radiation from electronic displays. These guidelines, while not legally binding, are widely respected and often form the basis for national regulations. They address concerns about blue light emission, which is particularly relevant to AMOLED displays due to their ability to produce vibrant colors.
Several countries have also introduced certifications for low blue light emissions, such as TÜV Rheinland's Low Blue Light certification. These certifications, while voluntary, provide a benchmark for manufacturers and consumers to assess the potential impact of displays on eye health.
As AMOLED technology continues to gain prominence, regulators are likely to develop more specific guidelines addressing its unique characteristics. Future regulations may focus on aspects such as color accuracy, contrast ratios, and refresh rates, all of which contribute to AMOLED's potential in reducing digital eye strain.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established guidelines for computer workstations, which include recommendations for display quality and ergonomics. These guidelines, while not specifically addressing AMOLED technology, set the foundation for healthy viewing practices in professional environments.
The European Union has taken a more proactive approach with its Display Screen Equipment (DSE) regulations. These rules require employers to assess and mitigate risks associated with display screen use, including those related to eye strain. While not explicitly mentioning AMOLED, the regulations encompass all display technologies and emphasize the importance of screen quality in reducing visual fatigue.
In Asia, countries like South Korea and Japan, which are at the forefront of AMOLED development, have implemented stringent quality control measures for display manufacturers. These measures indirectly contribute to eye health by ensuring high-quality, flicker-free displays that are less likely to cause eye strain.
The International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) has issued guidelines on exposure to visible and infrared radiation from electronic displays. These guidelines, while not legally binding, are widely respected and often form the basis for national regulations. They address concerns about blue light emission, which is particularly relevant to AMOLED displays due to their ability to produce vibrant colors.
Several countries have also introduced certifications for low blue light emissions, such as TÜV Rheinland's Low Blue Light certification. These certifications, while voluntary, provide a benchmark for manufacturers and consumers to assess the potential impact of displays on eye health.
As AMOLED technology continues to gain prominence, regulators are likely to develop more specific guidelines addressing its unique characteristics. Future regulations may focus on aspects such as color accuracy, contrast ratios, and refresh rates, all of which contribute to AMOLED's potential in reducing digital eye strain.
User Experience and Adoption of AMOLED Displays
The adoption of AMOLED displays has significantly impacted user experience, particularly in the realm of digital eye strain reduction. As consumers become increasingly aware of the potential health risks associated with prolonged screen time, the demand for eye-friendly display technologies has grown substantially. AMOLED technology has emerged as a frontrunner in addressing these concerns, offering several key advantages that contribute to improved visual comfort and reduced eye fatigue.
One of the primary benefits of AMOLED displays is their ability to produce true blacks by completely turning off individual pixels. This feature not only enhances contrast ratios but also reduces the overall light emission from the screen, potentially decreasing eye strain during extended viewing sessions. The reduced blue light emission from AMOLED displays, compared to traditional LCD screens, has been particularly well-received by users who are sensitive to blue light exposure, especially during nighttime use.
The superior color reproduction capabilities of AMOLED displays have also contributed to their popularity among users. The technology's ability to render more vibrant and accurate colors has led to increased visual satisfaction, particularly in applications such as photo editing, gaming, and video streaming. This enhanced color performance not only improves the overall viewing experience but may also reduce eye strain by providing more natural and less harsh color representations.
AMOLED's faster response times and reduced motion blur have been particularly appreciated by users engaged in fast-paced activities such as gaming or watching action-packed content. The reduction in ghosting and smearing effects has led to a smoother visual experience, potentially decreasing eye fatigue associated with tracking rapid on-screen movements.
The adoption of AMOLED technology in mobile devices has been particularly noteworthy. Smartphones and tablets equipped with AMOLED displays have gained favor among consumers who prioritize visual comfort during prolonged use. The technology's energy efficiency, which allows for features like always-on displays without significant battery drain, has further enhanced user experience by providing convenient access to information without the need to constantly activate the full screen.
As awareness of digital eye strain continues to grow, manufacturers have increasingly marketed AMOLED displays as a key feature in their products, emphasizing the technology's potential benefits for eye health. This has led to a shift in consumer preferences, with many users actively seeking out devices equipped with AMOLED screens. The technology's adoption has expanded beyond mobile devices to larger displays, including televisions and computer monitors, further solidifying its position in the market.
One of the primary benefits of AMOLED displays is their ability to produce true blacks by completely turning off individual pixels. This feature not only enhances contrast ratios but also reduces the overall light emission from the screen, potentially decreasing eye strain during extended viewing sessions. The reduced blue light emission from AMOLED displays, compared to traditional LCD screens, has been particularly well-received by users who are sensitive to blue light exposure, especially during nighttime use.
The superior color reproduction capabilities of AMOLED displays have also contributed to their popularity among users. The technology's ability to render more vibrant and accurate colors has led to increased visual satisfaction, particularly in applications such as photo editing, gaming, and video streaming. This enhanced color performance not only improves the overall viewing experience but may also reduce eye strain by providing more natural and less harsh color representations.
AMOLED's faster response times and reduced motion blur have been particularly appreciated by users engaged in fast-paced activities such as gaming or watching action-packed content. The reduction in ghosting and smearing effects has led to a smoother visual experience, potentially decreasing eye fatigue associated with tracking rapid on-screen movements.
The adoption of AMOLED technology in mobile devices has been particularly noteworthy. Smartphones and tablets equipped with AMOLED displays have gained favor among consumers who prioritize visual comfort during prolonged use. The technology's energy efficiency, which allows for features like always-on displays without significant battery drain, has further enhanced user experience by providing convenient access to information without the need to constantly activate the full screen.
As awareness of digital eye strain continues to grow, manufacturers have increasingly marketed AMOLED displays as a key feature in their products, emphasizing the technology's potential benefits for eye health. This has led to a shift in consumer preferences, with many users actively seeking out devices equipped with AMOLED screens. The technology's adoption has expanded beyond mobile devices to larger displays, including televisions and computer monitors, further solidifying its position in the market.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!