How AMOLED enhances foldable display technology?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED in Foldables: Background and Objectives
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of display technologies, particularly in the context of foldable devices. The evolution of AMOLED displays has been closely intertwined with the development of flexible and foldable screens, marking a significant milestone in the history of mobile devices and wearable technology.
The journey of AMOLED in foldable displays began with the recognition of its inherent advantages over traditional LCD screens. AMOLED's ability to produce vibrant colors, deep blacks, and high contrast ratios made it an ideal candidate for next-generation display solutions. Moreover, its self-emissive nature eliminated the need for a backlight, allowing for thinner and more flexible panel designs – a crucial factor in the development of foldable devices.
As the demand for more innovative and versatile mobile devices grew, manufacturers began exploring ways to create screens that could bend and fold without compromising on display quality. AMOLED's flexibility and durability under repeated bending stress positioned it as the frontrunner in this technological race. The goal was clear: to create a seamless, high-quality display that could withstand thousands of folding cycles while maintaining its visual integrity and functionality.
The integration of AMOLED into foldable displays presented several technical challenges that needed to be overcome. These included developing flexible substrates, creating bendable encapsulation layers to protect the organic materials, and designing circuitry that could withstand repeated folding and unfolding. Researchers and engineers focused on enhancing the mechanical properties of AMOLED panels while preserving their superior visual characteristics.
As the technology progressed, the objectives for AMOLED in foldable displays expanded. Beyond just enabling the folding mechanism, the focus shifted to improving durability, increasing brightness and color accuracy, reducing power consumption, and minimizing the visibility of the fold crease. These goals drove continuous innovation in materials science, manufacturing processes, and display architectures.
The potential applications of AMOLED-based foldable displays extended far beyond smartphones. The technology promised to revolutionize various sectors, including wearable devices, automotive displays, and even foldable laptops and tablets. This broad applicability fueled further research and development, aiming to push the boundaries of what was possible with flexible display technology.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of AMOLED in foldable display technology represent a convergence of cutting-edge materials science, innovative engineering, and market-driven demand for more versatile and immersive display solutions. As the technology continues to evolve, it promises to reshape our interaction with digital devices, opening up new possibilities in design and functionality across multiple industries.
The journey of AMOLED in foldable displays began with the recognition of its inherent advantages over traditional LCD screens. AMOLED's ability to produce vibrant colors, deep blacks, and high contrast ratios made it an ideal candidate for next-generation display solutions. Moreover, its self-emissive nature eliminated the need for a backlight, allowing for thinner and more flexible panel designs – a crucial factor in the development of foldable devices.
As the demand for more innovative and versatile mobile devices grew, manufacturers began exploring ways to create screens that could bend and fold without compromising on display quality. AMOLED's flexibility and durability under repeated bending stress positioned it as the frontrunner in this technological race. The goal was clear: to create a seamless, high-quality display that could withstand thousands of folding cycles while maintaining its visual integrity and functionality.
The integration of AMOLED into foldable displays presented several technical challenges that needed to be overcome. These included developing flexible substrates, creating bendable encapsulation layers to protect the organic materials, and designing circuitry that could withstand repeated folding and unfolding. Researchers and engineers focused on enhancing the mechanical properties of AMOLED panels while preserving their superior visual characteristics.
As the technology progressed, the objectives for AMOLED in foldable displays expanded. Beyond just enabling the folding mechanism, the focus shifted to improving durability, increasing brightness and color accuracy, reducing power consumption, and minimizing the visibility of the fold crease. These goals drove continuous innovation in materials science, manufacturing processes, and display architectures.
The potential applications of AMOLED-based foldable displays extended far beyond smartphones. The technology promised to revolutionize various sectors, including wearable devices, automotive displays, and even foldable laptops and tablets. This broad applicability fueled further research and development, aiming to push the boundaries of what was possible with flexible display technology.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of AMOLED in foldable display technology represent a convergence of cutting-edge materials science, innovative engineering, and market-driven demand for more versatile and immersive display solutions. As the technology continues to evolve, it promises to reshape our interaction with digital devices, opening up new possibilities in design and functionality across multiple industries.
Market Analysis for Foldable AMOLED Displays
The foldable AMOLED display market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for innovative and versatile mobile devices. As smartphones and tablets continue to evolve, foldable displays have emerged as a key differentiator in the premium segment, offering users expanded screen real estate without compromising portability.
Market research indicates that the global foldable display market is poised for substantial expansion, with AMOLED technology playing a crucial role in this growth. The unique properties of AMOLED, such as flexibility, thinness, and vibrant color reproduction, make it particularly well-suited for foldable devices. This synergy between AMOLED and foldable form factors has created a new category of high-end mobile devices that command premium pricing and offer enhanced user experiences.
Consumer adoption of foldable AMOLED devices has been steadily increasing, with major smartphone manufacturers introducing flagship models featuring this technology. The market has seen a diversification of form factors, including inward-folding, outward-folding, and even multi-fold designs, each catering to different user preferences and use cases.
The automotive industry has also shown interest in foldable AMOLED displays, exploring applications in dashboard interfaces and entertainment systems. This expansion beyond mobile devices suggests a broader market potential for the technology across various sectors.
Despite the growing enthusiasm, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of foldable AMOLED displays. High production costs and technical complexities associated with ensuring durability and longevity of folding mechanisms have limited market penetration to premium device segments. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues, potentially paving the way for more affordable options in the future.
The competitive landscape is dominated by a few key players with advanced AMOLED manufacturing capabilities. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve folding technologies, increase production yields, and reduce costs. As the technology matures, we can expect to see increased competition and innovation in the foldable AMOLED display market.
Looking ahead, the market for foldable AMOLED displays is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Factors such as 5G adoption, increasing demand for larger screens in compact form factors, and advancements in flexible battery technology are likely to drive further growth and innovation in this sector.
Market research indicates that the global foldable display market is poised for substantial expansion, with AMOLED technology playing a crucial role in this growth. The unique properties of AMOLED, such as flexibility, thinness, and vibrant color reproduction, make it particularly well-suited for foldable devices. This synergy between AMOLED and foldable form factors has created a new category of high-end mobile devices that command premium pricing and offer enhanced user experiences.
Consumer adoption of foldable AMOLED devices has been steadily increasing, with major smartphone manufacturers introducing flagship models featuring this technology. The market has seen a diversification of form factors, including inward-folding, outward-folding, and even multi-fold designs, each catering to different user preferences and use cases.
The automotive industry has also shown interest in foldable AMOLED displays, exploring applications in dashboard interfaces and entertainment systems. This expansion beyond mobile devices suggests a broader market potential for the technology across various sectors.
Despite the growing enthusiasm, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of foldable AMOLED displays. High production costs and technical complexities associated with ensuring durability and longevity of folding mechanisms have limited market penetration to premium device segments. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues, potentially paving the way for more affordable options in the future.
The competitive landscape is dominated by a few key players with advanced AMOLED manufacturing capabilities. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve folding technologies, increase production yields, and reduce costs. As the technology matures, we can expect to see increased competition and innovation in the foldable AMOLED display market.
Looking ahead, the market for foldable AMOLED displays is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Factors such as 5G adoption, increasing demand for larger screens in compact form factors, and advancements in flexible battery technology are likely to drive further growth and innovation in this sector.
Current AMOLED Foldable Display Challenges
AMOLED technology has significantly enhanced foldable display capabilities, but it still faces several challenges in its current implementation. One of the primary issues is the durability of the flexible OLED panels. The repeated folding and unfolding actions put considerable stress on the display materials, potentially leading to creases, pixel degradation, and even display failure over time. Manufacturers are continually working to improve the flexibility and resilience of AMOLED panels to withstand thousands of folding cycles without compromising display quality.
Another challenge lies in the power consumption of AMOLED displays in foldable devices. While AMOLED technology is generally more energy-efficient than traditional LCD displays, the larger screen sizes and complex folding mechanisms of foldable devices can lead to increased power draw. Balancing the need for vibrant, high-resolution displays with energy efficiency remains a key focus area for developers.
Color accuracy and consistency across the folding area present another hurdle. The bending of the display can cause slight variations in color reproduction and brightness, particularly along the fold line. Ensuring uniform color performance across the entire screen, regardless of its folded or unfolded state, is crucial for delivering a seamless user experience.
The integration of touch sensitivity with AMOLED foldable displays also poses challenges. Maintaining accurate touch response across the folding area, especially when the device is partially folded, requires sophisticated hardware and software solutions. Additionally, the incorporation of features like in-display fingerprint sensors becomes more complex in foldable form factors.
Manufacturing complexities and yield rates are significant obstacles in the mass production of AMOLED foldable displays. The intricate layering of flexible materials and the need for precise alignment in the folding mechanism contribute to higher production costs and lower yield rates compared to traditional flat displays. Improving manufacturing processes to increase yield and reduce costs is essential for wider adoption of foldable AMOLED devices.
Lastly, the development of protective layers for AMOLED foldable displays remains challenging. These displays require ultra-thin, flexible cover materials that can protect against scratches and impacts while maintaining clarity and touch sensitivity. Current solutions often involve compromises between durability and flexibility, and finding the optimal balance is an ongoing area of research and development in the industry.
Another challenge lies in the power consumption of AMOLED displays in foldable devices. While AMOLED technology is generally more energy-efficient than traditional LCD displays, the larger screen sizes and complex folding mechanisms of foldable devices can lead to increased power draw. Balancing the need for vibrant, high-resolution displays with energy efficiency remains a key focus area for developers.
Color accuracy and consistency across the folding area present another hurdle. The bending of the display can cause slight variations in color reproduction and brightness, particularly along the fold line. Ensuring uniform color performance across the entire screen, regardless of its folded or unfolded state, is crucial for delivering a seamless user experience.
The integration of touch sensitivity with AMOLED foldable displays also poses challenges. Maintaining accurate touch response across the folding area, especially when the device is partially folded, requires sophisticated hardware and software solutions. Additionally, the incorporation of features like in-display fingerprint sensors becomes more complex in foldable form factors.
Manufacturing complexities and yield rates are significant obstacles in the mass production of AMOLED foldable displays. The intricate layering of flexible materials and the need for precise alignment in the folding mechanism contribute to higher production costs and lower yield rates compared to traditional flat displays. Improving manufacturing processes to increase yield and reduce costs is essential for wider adoption of foldable AMOLED devices.
Lastly, the development of protective layers for AMOLED foldable displays remains challenging. These displays require ultra-thin, flexible cover materials that can protect against scratches and impacts while maintaining clarity and touch sensitivity. Current solutions often involve compromises between durability and flexibility, and finding the optimal balance is an ongoing area of research and development in the industry.
Existing AMOLED Solutions for Foldable Displays
01 Pixel structure and arrangement
AMOLED display quality is significantly influenced by the pixel structure and arrangement. This includes the design of sub-pixels, their layout, and the overall pixel density. Optimizing these factors can lead to improved color accuracy, resolution, and overall image quality.- Pixel structure and arrangement: AMOLED display quality is significantly influenced by the pixel structure and arrangement. This includes the design of sub-pixels, their layout, and the overall pixel density. Optimizing these factors can lead to improved color accuracy, resolution, and overall image quality.
- Driving method and circuitry: The driving method and circuitry of AMOLED displays play a crucial role in display quality. This involves the design of thin-film transistors (TFTs), capacitors, and other electronic components that control each pixel. Advanced driving techniques can enhance brightness, contrast, and power efficiency.
- Color management and calibration: Effective color management and calibration techniques are essential for maintaining high AMOLED display quality. This includes methods for accurate color reproduction, gamma correction, and white point adjustment. Advanced algorithms and hardware solutions can significantly improve color accuracy and consistency across the display.
- OLED materials and fabrication: The quality of AMOLED displays is heavily dependent on the OLED materials used and the fabrication processes. This includes the development of new organic compounds, electrode materials, and encapsulation techniques. Improvements in these areas can lead to better efficiency, longer lifespan, and enhanced color performance.
- Display panel design and integration: The overall design and integration of the AMOLED display panel contribute significantly to its quality. This encompasses aspects such as bezel design, touch integration, and flexible display technologies. Innovations in these areas can lead to improved form factors, durability, and user experience.
02 Driving method and circuit design
The driving method and circuit design play a crucial role in AMOLED display quality. This involves the development of efficient driving schemes, compensation circuits, and timing controllers to enhance display performance, reduce power consumption, and improve image uniformity.Expand Specific Solutions03 OLED material and stack structure
The choice of OLED materials and the design of the stack structure significantly impact display quality. This includes the selection of emissive materials, transport layers, and electrode materials to optimize efficiency, color gamut, and lifetime of the AMOLED display.Expand Specific Solutions04 Color management and calibration
Implementing advanced color management techniques and calibration methods is essential for achieving high AMOLED display quality. This involves color gamut mapping, gamma correction, and white point adjustment to ensure accurate and consistent color reproduction across the display.Expand Specific Solutions05 Touch integration and display flexibility
Integrating touch functionality and incorporating flexible display technologies can enhance the overall quality and user experience of AMOLED displays. This includes developing in-cell touch sensors, flexible substrates, and foldable display structures to improve display performance and versatility.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in AMOLED Foldable Display Industry
The AMOLED technology for foldable displays is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and advancing technological maturity. Major players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and TCL China Star Optoelectronics are driving innovation in this field. The market is expanding rapidly as consumer demand for flexible, high-quality displays grows. Technological advancements focus on improving durability, color accuracy, and energy efficiency of AMOLED panels. Companies are investing heavily in R&D to overcome challenges such as crease visibility and longevity of folding mechanisms. As the technology matures, we're seeing wider adoption in smartphones, tablets, and emerging form factors, indicating a promising future for AMOLED in foldable display applications.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has made significant strides in AMOLED technology for foldable displays. They've developed a 12.3-inch rollable AMOLED display with a bending radius of just 5mm[5]. BOE's foldable AMOLED panels utilize a multi-layer stack structure to enhance flexibility and durability. Their displays feature a resolution of up to 2480x2200 pixels and can withstand over 200,000 folds[6]. BOE has also introduced an innovative "3D Free Form" AMOLED technology, allowing for various folding designs beyond the typical inward and outward folds[7].
Strengths: Innovative folding designs, high resolution, and durability. Weaknesses: Less market presence compared to Samsung, potentially higher costs due to newer technology.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has pioneered AMOLED technology for foldable displays, utilizing their flexible OLED panels. Their Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG) technology enhances durability while maintaining flexibility[1]. The company's latest foldable devices feature a 120Hz refresh rate and improved brightness, reaching up to 1,750 nits[2]. Samsung's AMOLED displays for foldables incorporate a specialized pixel structure that reduces stress on the folding area, minimizing the visible crease[3]. They've also developed an advanced touch layer that improves responsiveness in folded and unfolded states[4].
Strengths: Market leader in foldable AMOLED technology, advanced UTG for durability, high refresh rates, and brightness. Weaknesses: Higher production costs, potential for screen burn-in over time.
Core AMOLED Innovations for Foldable Screens
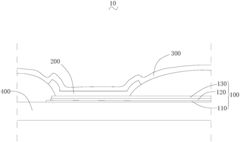
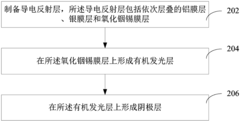
Organic luminescence display device, organic electroluminescent device and preparation method thereof
PatentActiveCN108232032A
Innovation
- The aluminum film layer, silver film layer and indium tin oxide film layer are etched using a dry etching process, and through the high reflectivity and conductivity of the aluminum film layer, combined with the transparency and protective effect of the indium tin oxide film layer, Form a conductive reflective layer to improve the reflectivity and adhesion of the device.
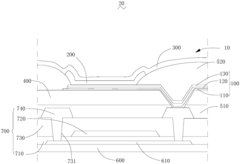
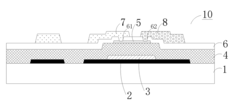
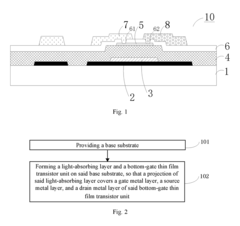
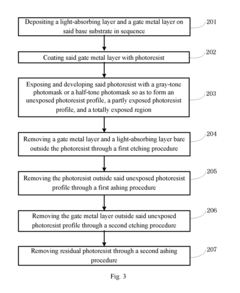
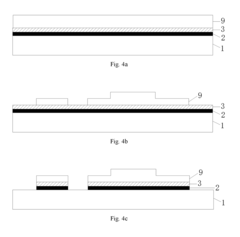
Array substrate, display device, and method for manufacturing array substrate
PatentActiveUS20170148862A1
Innovation
- An array substrate with a light-absorbing layer covering the gate, source, and drain metal layers of a bottom-gate thin film transistor unit, preventing ambient light irradiation while allowing useful light to pass through.
Supply Chain Analysis for AMOLED Foldable Displays
The supply chain for AMOLED foldable displays is a complex network involving multiple key components and processes. At the core of this chain are the AMOLED panel manufacturers, who play a crucial role in producing the flexible displays that enable foldable devices. These manufacturers, such as Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE, have invested heavily in research and development to perfect the technology.
Raw material suppliers form the foundation of the supply chain, providing essential components like flexible substrates, organic light-emitting materials, and thin-film transistors. The quality and availability of these materials significantly impact the performance and cost of the final product. Specialized equipment manufacturers also play a vital role, developing and producing the machinery needed for the precise fabrication of AMOLED panels.
The assembly process involves integrating the AMOLED display with other components, including the folding mechanism, touch sensors, and protective layers. This stage requires close collaboration between display manufacturers and device makers to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance.
Testing and quality control are critical aspects of the supply chain, given the complexity and novelty of foldable display technology. Rigorous testing procedures are implemented at various stages to ensure durability, color accuracy, and folding reliability.
The supply chain also extends to software developers who create applications and user interfaces optimized for foldable displays. Their work is essential in maximizing the potential of this innovative form factor.
Distribution channels for AMOLED foldable displays are primarily B2B, with panel manufacturers supplying to device makers. However, as the technology matures, we may see more diverse distribution models emerge, potentially including direct-to-consumer options for customized or replacement displays.
The global nature of this supply chain introduces both opportunities and challenges. While it allows for specialization and cost optimization, it also exposes the industry to geopolitical risks and supply disruptions, as seen in recent years with chip shortages and trade tensions.
Innovation in the supply chain is ongoing, with efforts focused on improving yield rates, reducing costs, and enhancing the durability of foldable displays. Advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes are continually being pursued to address these challenges and drive the technology forward.
Raw material suppliers form the foundation of the supply chain, providing essential components like flexible substrates, organic light-emitting materials, and thin-film transistors. The quality and availability of these materials significantly impact the performance and cost of the final product. Specialized equipment manufacturers also play a vital role, developing and producing the machinery needed for the precise fabrication of AMOLED panels.
The assembly process involves integrating the AMOLED display with other components, including the folding mechanism, touch sensors, and protective layers. This stage requires close collaboration between display manufacturers and device makers to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance.
Testing and quality control are critical aspects of the supply chain, given the complexity and novelty of foldable display technology. Rigorous testing procedures are implemented at various stages to ensure durability, color accuracy, and folding reliability.
The supply chain also extends to software developers who create applications and user interfaces optimized for foldable displays. Their work is essential in maximizing the potential of this innovative form factor.
Distribution channels for AMOLED foldable displays are primarily B2B, with panel manufacturers supplying to device makers. However, as the technology matures, we may see more diverse distribution models emerge, potentially including direct-to-consumer options for customized or replacement displays.
The global nature of this supply chain introduces both opportunities and challenges. While it allows for specialization and cost optimization, it also exposes the industry to geopolitical risks and supply disruptions, as seen in recent years with chip shortages and trade tensions.
Innovation in the supply chain is ongoing, with efforts focused on improving yield rates, reducing costs, and enhancing the durability of foldable displays. Advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes are continually being pursued to address these challenges and drive the technology forward.
Environmental Impact of AMOLED Foldable Displays
The environmental impact of AMOLED foldable displays is a crucial consideration as this technology becomes increasingly prevalent in the consumer electronics market. These displays offer significant advantages in terms of energy efficiency and device versatility, but their production and disposal processes raise important environmental concerns.
AMOLED technology inherently consumes less power than traditional LCD displays, particularly when displaying darker content. This energy efficiency translates to longer battery life in devices, potentially reducing the frequency of charging cycles and, by extension, overall energy consumption. For foldable devices, this efficiency is particularly beneficial as it helps mitigate the increased power demands of larger screen areas.
However, the manufacturing process of AMOLED displays involves the use of rare earth elements and other precious metals, which can have significant environmental implications. The extraction and processing of these materials often involve energy-intensive and potentially polluting activities. Additionally, the complex layered structure of AMOLED displays makes them challenging to recycle, potentially contributing to electronic waste issues.
The foldable nature of these displays introduces further environmental considerations. While the ability to fold the device may extend its lifespan by reducing the risk of screen damage, the mechanical stress on the folding components could lead to earlier failure of the entire device. This could potentially increase the rate of device replacement and electronic waste generation.
On the positive side, the versatility of foldable AMOLED displays could lead to the consolidation of multiple devices into one, potentially reducing overall electronic waste. For instance, a foldable smartphone could replace both a phone and a tablet, reducing the total number of devices a consumer needs to purchase and eventually dispose of.
The production of AMOLED foldable displays also raises concerns about chemical usage and emissions. The fabrication process involves various volatile organic compounds and other potentially harmful chemicals. Proper management and disposal of these substances are critical to minimizing environmental impact.
As the technology matures, there is a growing focus on developing more sustainable production methods and materials for AMOLED displays. Research into bio-based materials and more efficient manufacturing processes could help mitigate some of the environmental concerns associated with this technology. Additionally, efforts to improve the recyclability of AMOLED displays and establish effective e-waste management systems are crucial for reducing the long-term environmental impact of these devices.
AMOLED technology inherently consumes less power than traditional LCD displays, particularly when displaying darker content. This energy efficiency translates to longer battery life in devices, potentially reducing the frequency of charging cycles and, by extension, overall energy consumption. For foldable devices, this efficiency is particularly beneficial as it helps mitigate the increased power demands of larger screen areas.
However, the manufacturing process of AMOLED displays involves the use of rare earth elements and other precious metals, which can have significant environmental implications. The extraction and processing of these materials often involve energy-intensive and potentially polluting activities. Additionally, the complex layered structure of AMOLED displays makes them challenging to recycle, potentially contributing to electronic waste issues.
The foldable nature of these displays introduces further environmental considerations. While the ability to fold the device may extend its lifespan by reducing the risk of screen damage, the mechanical stress on the folding components could lead to earlier failure of the entire device. This could potentially increase the rate of device replacement and electronic waste generation.
On the positive side, the versatility of foldable AMOLED displays could lead to the consolidation of multiple devices into one, potentially reducing overall electronic waste. For instance, a foldable smartphone could replace both a phone and a tablet, reducing the total number of devices a consumer needs to purchase and eventually dispose of.
The production of AMOLED foldable displays also raises concerns about chemical usage and emissions. The fabrication process involves various volatile organic compounds and other potentially harmful chemicals. Proper management and disposal of these substances are critical to minimizing environmental impact.
As the technology matures, there is a growing focus on developing more sustainable production methods and materials for AMOLED displays. Research into bio-based materials and more efficient manufacturing processes could help mitigate some of the environmental concerns associated with this technology. Additionally, efforts to improve the recyclability of AMOLED displays and establish effective e-waste management systems are crucial for reducing the long-term environmental impact of these devices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!