How Calorimetry Enhances Synthetic Route Development for Pharmaceuticals
AUG 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Calorimetry in Pharma Synthesis: Background and Objectives
Calorimetry has emerged as a powerful tool in the pharmaceutical industry, revolutionizing the way synthetic routes for drug development are designed and optimized. This technique, which measures heat changes during chemical reactions, has a rich history dating back to the 18th century. However, its application in pharmaceutical synthesis has gained significant momentum in recent decades due to advancements in instrumentation and data analysis capabilities.
The evolution of calorimetry in pharmaceutical synthesis can be traced through several key milestones. Initially, calorimetry was primarily used for basic thermodynamic studies. As the pharmaceutical industry grew more complex, the need for more precise and efficient synthetic routes became apparent. This led to the adaptation of calorimetric techniques for reaction monitoring and optimization in the 1980s and 1990s.
The turn of the 21st century marked a significant shift in the application of calorimetry in pharmaceutical synthesis. With the advent of high-throughput screening and combinatorial chemistry, the demand for rapid and accurate assessment of reaction parameters increased dramatically. Calorimetry, with its ability to provide real-time data on reaction kinetics and thermodynamics, became an invaluable tool in this new landscape.
Today, the objectives of using calorimetry in pharmaceutical synthesis are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to enhance the efficiency and safety of drug manufacturing processes. By providing detailed insights into reaction mechanisms, heat flow, and potential side reactions, calorimetry enables researchers to design more robust and scalable synthetic routes. This is particularly crucial in an industry where time-to-market and cost-effectiveness are paramount.
Another key objective is to improve the quality and consistency of pharmaceutical products. Calorimetric data helps in identifying optimal reaction conditions, which can lead to higher yields, improved purity, and reduced batch-to-batch variability. This aligns with the industry's increasing focus on Quality by Design (QbD) principles, where understanding and controlling the manufacturing process is essential for ensuring product quality.
Furthermore, calorimetry plays a vital role in risk assessment and process safety. By measuring the heat released or absorbed during reactions, it helps identify potential hazards associated with exothermic processes or thermal runaways. This information is crucial for designing safer processes and scaling up reactions from laboratory to industrial production.
Looking ahead, the integration of calorimetry with other analytical techniques and the advent of machine learning algorithms promise to further revolutionize synthetic route development in pharmaceuticals. The goal is to create a more holistic approach to process understanding and optimization, ultimately leading to faster, safer, and more sustainable drug manufacturing processes.
The evolution of calorimetry in pharmaceutical synthesis can be traced through several key milestones. Initially, calorimetry was primarily used for basic thermodynamic studies. As the pharmaceutical industry grew more complex, the need for more precise and efficient synthetic routes became apparent. This led to the adaptation of calorimetric techniques for reaction monitoring and optimization in the 1980s and 1990s.
The turn of the 21st century marked a significant shift in the application of calorimetry in pharmaceutical synthesis. With the advent of high-throughput screening and combinatorial chemistry, the demand for rapid and accurate assessment of reaction parameters increased dramatically. Calorimetry, with its ability to provide real-time data on reaction kinetics and thermodynamics, became an invaluable tool in this new landscape.
Today, the objectives of using calorimetry in pharmaceutical synthesis are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to enhance the efficiency and safety of drug manufacturing processes. By providing detailed insights into reaction mechanisms, heat flow, and potential side reactions, calorimetry enables researchers to design more robust and scalable synthetic routes. This is particularly crucial in an industry where time-to-market and cost-effectiveness are paramount.
Another key objective is to improve the quality and consistency of pharmaceutical products. Calorimetric data helps in identifying optimal reaction conditions, which can lead to higher yields, improved purity, and reduced batch-to-batch variability. This aligns with the industry's increasing focus on Quality by Design (QbD) principles, where understanding and controlling the manufacturing process is essential for ensuring product quality.
Furthermore, calorimetry plays a vital role in risk assessment and process safety. By measuring the heat released or absorbed during reactions, it helps identify potential hazards associated with exothermic processes or thermal runaways. This information is crucial for designing safer processes and scaling up reactions from laboratory to industrial production.
Looking ahead, the integration of calorimetry with other analytical techniques and the advent of machine learning algorithms promise to further revolutionize synthetic route development in pharmaceuticals. The goal is to create a more holistic approach to process understanding and optimization, ultimately leading to faster, safer, and more sustainable drug manufacturing processes.
Market Demand for Efficient Drug Development
The pharmaceutical industry is experiencing a growing demand for more efficient drug development processes, driven by the need to reduce time-to-market and development costs while maintaining high-quality standards. Calorimetry, as a powerful analytical technique, plays a crucial role in enhancing synthetic route development for pharmaceuticals, addressing these market demands.
The global pharmaceutical market is projected to reach $1.5 trillion by 2023, with a compound annual growth rate of 3-6%. This growth is accompanied by increasing pressure to streamline drug development processes. Traditional methods of synthetic route development often involve time-consuming and resource-intensive trial-and-error approaches, leading to extended development timelines and higher costs.
Calorimetry offers a solution to these challenges by providing real-time, quantitative data on chemical reactions. This technology enables researchers to optimize reaction conditions, improve yield, and enhance process safety. The market for calorimetry equipment in pharmaceutical applications is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2021 to 2026, reflecting the industry's recognition of its value in drug development.
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly adopting calorimetry to accelerate their drug discovery and development processes. This trend is driven by the need to reduce the average time for drug development, which currently stands at 10-15 years, and the associated costs, estimated at $2.6 billion per new drug. Calorimetry can potentially shorten development timelines by 20-30% and reduce costs by 15-25% through more efficient route selection and optimization.
The demand for calorimetry in pharmaceutical synthetic route development is also fueled by regulatory requirements for process understanding and control. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA are emphasizing the importance of Quality by Design (QbD) principles, which require a thorough understanding of the manufacturing process. Calorimetry provides valuable insights into reaction kinetics, thermodynamics, and potential scale-up issues, aligning with these regulatory expectations.
Furthermore, the increasing complexity of drug molecules and the shift towards personalized medicine are driving the need for more sophisticated synthetic routes. Calorimetry enables the development of more efficient and sustainable processes, supporting the industry's move towards green chemistry and reducing environmental impact. This aligns with the growing market demand for environmentally friendly pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, which is expected to influence 60% of drug development projects by 2025.
In conclusion, the market demand for efficient drug development is strongly driving the adoption of calorimetry in synthetic route development for pharmaceuticals. This technology addresses key industry challenges, including cost reduction, time-to-market acceleration, regulatory compliance, and sustainability, positioning it as a critical tool in modern pharmaceutical research and development.
The global pharmaceutical market is projected to reach $1.5 trillion by 2023, with a compound annual growth rate of 3-6%. This growth is accompanied by increasing pressure to streamline drug development processes. Traditional methods of synthetic route development often involve time-consuming and resource-intensive trial-and-error approaches, leading to extended development timelines and higher costs.
Calorimetry offers a solution to these challenges by providing real-time, quantitative data on chemical reactions. This technology enables researchers to optimize reaction conditions, improve yield, and enhance process safety. The market for calorimetry equipment in pharmaceutical applications is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2021 to 2026, reflecting the industry's recognition of its value in drug development.
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly adopting calorimetry to accelerate their drug discovery and development processes. This trend is driven by the need to reduce the average time for drug development, which currently stands at 10-15 years, and the associated costs, estimated at $2.6 billion per new drug. Calorimetry can potentially shorten development timelines by 20-30% and reduce costs by 15-25% through more efficient route selection and optimization.
The demand for calorimetry in pharmaceutical synthetic route development is also fueled by regulatory requirements for process understanding and control. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA are emphasizing the importance of Quality by Design (QbD) principles, which require a thorough understanding of the manufacturing process. Calorimetry provides valuable insights into reaction kinetics, thermodynamics, and potential scale-up issues, aligning with these regulatory expectations.
Furthermore, the increasing complexity of drug molecules and the shift towards personalized medicine are driving the need for more sophisticated synthetic routes. Calorimetry enables the development of more efficient and sustainable processes, supporting the industry's move towards green chemistry and reducing environmental impact. This aligns with the growing market demand for environmentally friendly pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, which is expected to influence 60% of drug development projects by 2025.
In conclusion, the market demand for efficient drug development is strongly driving the adoption of calorimetry in synthetic route development for pharmaceuticals. This technology addresses key industry challenges, including cost reduction, time-to-market acceleration, regulatory compliance, and sustainability, positioning it as a critical tool in modern pharmaceutical research and development.
Current Challenges in Pharmaceutical Synthesis
The pharmaceutical industry faces several significant challenges in synthetic route development, particularly in the context of increasing complexity and regulatory demands. One of the primary obstacles is the need for more efficient and cost-effective synthesis processes. As drug molecules become more intricate, traditional synthetic routes often require numerous steps, leading to lower yields and increased production costs. This complexity also amplifies the risk of impurities, which can compromise drug safety and efficacy.
Another critical challenge is the environmental impact of pharmaceutical synthesis. Many conventional synthetic routes rely on hazardous solvents and reagents, generating substantial waste. The industry is under pressure to develop greener processes that minimize environmental footprint while maintaining product quality. This shift towards sustainable chemistry requires innovative approaches and often necessitates a complete redesign of established synthetic pathways.
The time-to-market pressure presents another significant hurdle. With increasing competition and the need to address urgent medical needs, pharmaceutical companies must accelerate their drug development timelines. This acceleration demand often conflicts with the time required for thorough route optimization and scale-up studies, potentially compromising process robustness and product quality.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to synthetic route development. Stringent quality standards and documentation requirements necessitate extensive process characterization and control. Ensuring consistent product quality across different batches and scales remains a persistent challenge, especially when dealing with complex molecules and multi-step syntheses.
The unpredictability of scale-up processes further complicates synthetic route development. Reactions that perform well at laboratory scale may encounter unforeseen issues when scaled up to production levels. These challenges can include heat transfer problems, mixing inefficiencies, and unexpected side reactions, all of which can significantly impact yield and product purity.
Lastly, the pharmaceutical industry faces a growing need for flexible and adaptable synthetic routes. With the rise of personalized medicine and the demand for smaller batch sizes, traditional large-scale processes are becoming less suitable. Developing modular and scalable synthetic routes that can accommodate varying production volumes while maintaining consistency and quality is an ongoing challenge that requires innovative solutions and advanced process technologies.
Another critical challenge is the environmental impact of pharmaceutical synthesis. Many conventional synthetic routes rely on hazardous solvents and reagents, generating substantial waste. The industry is under pressure to develop greener processes that minimize environmental footprint while maintaining product quality. This shift towards sustainable chemistry requires innovative approaches and often necessitates a complete redesign of established synthetic pathways.
The time-to-market pressure presents another significant hurdle. With increasing competition and the need to address urgent medical needs, pharmaceutical companies must accelerate their drug development timelines. This acceleration demand often conflicts with the time required for thorough route optimization and scale-up studies, potentially compromising process robustness and product quality.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to synthetic route development. Stringent quality standards and documentation requirements necessitate extensive process characterization and control. Ensuring consistent product quality across different batches and scales remains a persistent challenge, especially when dealing with complex molecules and multi-step syntheses.
The unpredictability of scale-up processes further complicates synthetic route development. Reactions that perform well at laboratory scale may encounter unforeseen issues when scaled up to production levels. These challenges can include heat transfer problems, mixing inefficiencies, and unexpected side reactions, all of which can significantly impact yield and product purity.
Lastly, the pharmaceutical industry faces a growing need for flexible and adaptable synthetic routes. With the rise of personalized medicine and the demand for smaller batch sizes, traditional large-scale processes are becoming less suitable. Developing modular and scalable synthetic routes that can accommodate varying production volumes while maintaining consistency and quality is an ongoing challenge that requires innovative solutions and advanced process technologies.
Calorimetric Techniques in Synthetic Route Optimization
01 Calorimetric analysis for synthetic route optimization
Calorimetry is used to analyze and optimize synthetic routes in chemical processes. This method helps in understanding reaction thermodynamics, identifying potential hazards, and improving process efficiency. By measuring heat flow during reactions, researchers can determine optimal conditions and scale-up parameters for synthetic routes.- Calorimetric analysis for synthetic route optimization: Calorimetry is used to analyze and optimize synthetic routes in chemical processes. This technique measures heat flow during reactions, providing valuable data on reaction kinetics, thermodynamics, and potential safety hazards. By monitoring heat release or absorption, researchers can identify optimal reaction conditions, improve yield, and enhance process efficiency.
- Integration of calorimetry with automated synthesis platforms: Advanced calorimetric systems are integrated with automated synthesis platforms to streamline the development of synthetic routes. These integrated systems allow for real-time monitoring of reaction progress, automated data collection, and rapid screening of reaction conditions. This approach accelerates the optimization of synthetic pathways and facilitates high-throughput experimentation.
- Microfluidic calorimetry for small-scale route development: Microfluidic calorimetry devices are employed for small-scale synthetic route development. These miniaturized systems allow for precise control of reaction conditions and enable the study of fast reactions with minimal sample consumption. Microfluidic calorimetry is particularly useful for screening multiple reaction parameters and optimizing synthetic routes in the early stages of development.
- Machine learning algorithms for calorimetric data analysis: Machine learning algorithms are applied to analyze complex calorimetric data sets in synthetic route development. These algorithms can identify patterns, predict reaction outcomes, and suggest optimal reaction conditions based on historical data. By leveraging artificial intelligence, researchers can accelerate the discovery and optimization of new synthetic routes.
- Combination of calorimetry with spectroscopic techniques: Calorimetry is combined with spectroscopic techniques, such as in-situ IR or Raman spectroscopy, to provide comprehensive insights into reaction mechanisms and kinetics. This multi-modal approach allows for simultaneous monitoring of heat flow and molecular changes during synthesis, enabling a deeper understanding of reaction pathways and facilitating the development of more efficient synthetic routes.
02 Integration of calorimetry with process analytical technology
Combining calorimetry with process analytical technology (PAT) enhances the development of synthetic routes. This integration allows for real-time monitoring of reaction progress, enabling better control and optimization of chemical processes. Advanced sensors and data analysis techniques are employed to provide comprehensive insights into reaction kinetics and thermodynamics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Microfluidic calorimetry for high-throughput screening
Microfluidic calorimetry systems are utilized for high-throughput screening of synthetic routes. These miniaturized platforms allow for rapid and efficient evaluation of multiple reaction conditions with minimal sample consumption. This approach accelerates the optimization of synthetic pathways and facilitates the discovery of new chemical transformations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Machine learning-assisted calorimetric analysis
Machine learning algorithms are applied to calorimetric data to enhance synthetic route development. These computational methods can predict reaction outcomes, optimize conditions, and identify trends in complex datasets. By leveraging artificial intelligence, researchers can accelerate the discovery and optimization of novel synthetic pathways.Expand Specific Solutions05 In-situ calorimetry for continuous flow synthesis
In-situ calorimetry techniques are implemented in continuous flow reactors to monitor and control synthetic processes in real-time. This approach enables precise temperature control, rapid optimization of reaction parameters, and seamless scale-up of synthetic routes. The integration of calorimetry with flow chemistry enhances process safety and efficiency in industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Pharmaceutical Calorimetry
The field of calorimetry in pharmaceutical route development is in a mature stage, with a growing market driven by increasing demand for efficient drug discovery processes. The global pharmaceutical calorimetry market size is estimated to reach several hundred million dollars by 2025, with a steady growth rate. Technologically, calorimetry has evolved significantly, offering high-precision instruments and advanced data analysis capabilities. Key players like The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory, Northeastern University, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology are at the forefront, developing innovative calorimetric techniques and applications. Pharmaceutical giants such as BASF Corp. and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. are also investing in calorimetry research to enhance their drug development processes.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Technical Solution: MIT has developed advanced calorimetry techniques for pharmaceutical route development. They utilize high-precision isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) to study drug-target interactions and optimize synthetic pathways[1]. Their approach combines microfluidic devices with calorimetry, allowing for rapid screening of reaction conditions and real-time monitoring of heat flow during synthesis[2]. This enables researchers to identify the most efficient and cost-effective routes for drug production. MIT's calorimetry methods also incorporate machine learning algorithms to predict reaction outcomes and suggest optimal parameters, significantly reducing the time and resources required for pharmaceutical development[3].
Strengths: Cutting-edge technology integration, high precision measurements, and AI-assisted optimization. Weaknesses: Potentially high initial investment costs and complexity in implementation for smaller pharmaceutical companies.
The Regents of the University of California
Technical Solution: The University of California system has made significant contributions to calorimetry in pharmaceutical route development. They have pioneered the use of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) for studying the thermal behavior of drug compounds and excipients[4]. Their research focuses on using calorimetry to assess drug stability, polymorphism, and compatibility with other formulation components. The UC system has also developed novel calorimetric methods for investigating the kinetics of drug degradation and predicting shelf-life[5]. Additionally, they have applied reaction calorimetry to optimize synthetic routes, particularly for temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals, enabling safer and more efficient large-scale production processes[6].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach covering multiple aspects of drug development, strong focus on practical applications. Weaknesses: May require extensive collaboration between different UC campuses for full implementation.
Innovations in Reaction Calorimetry for Pharmaceuticals
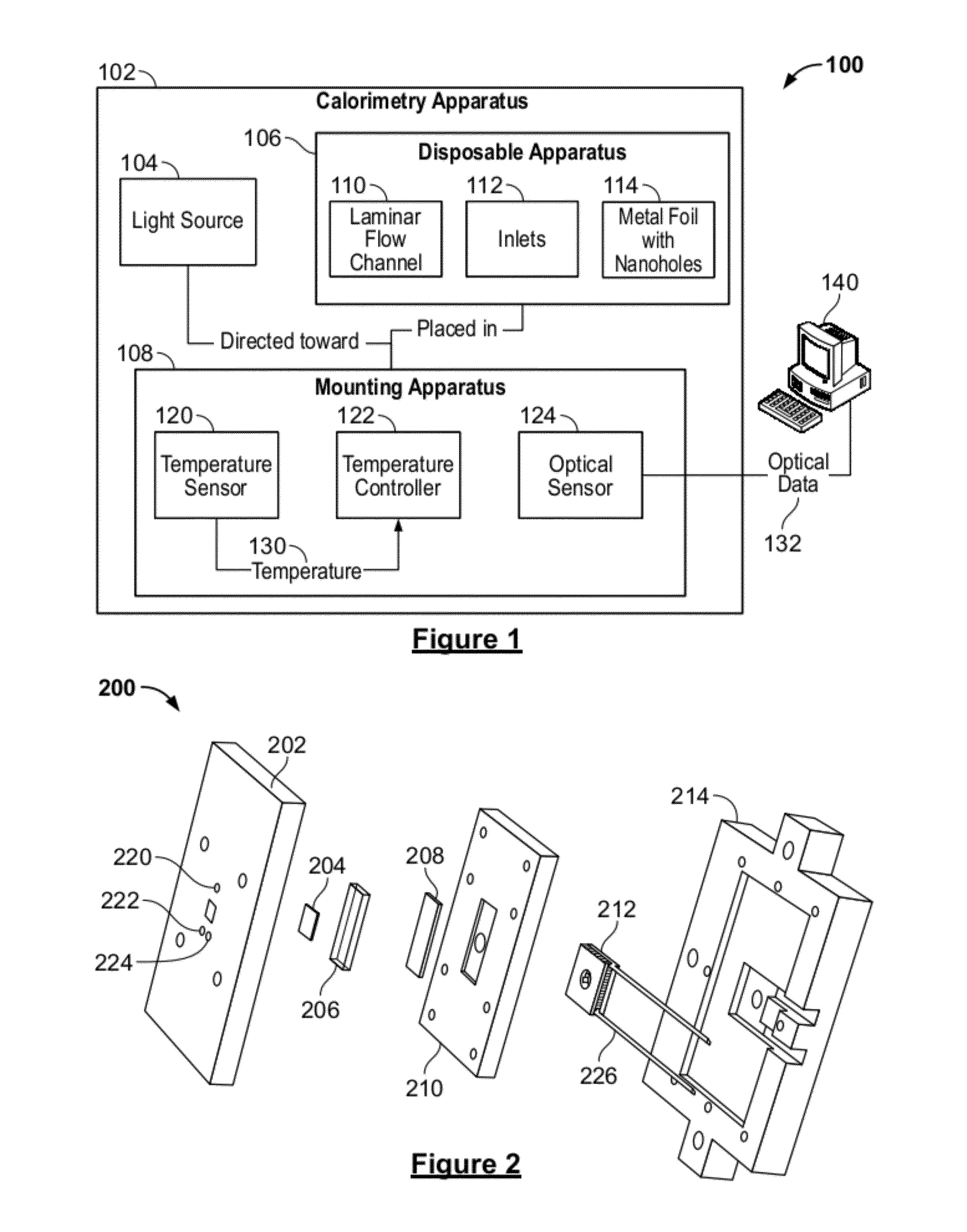
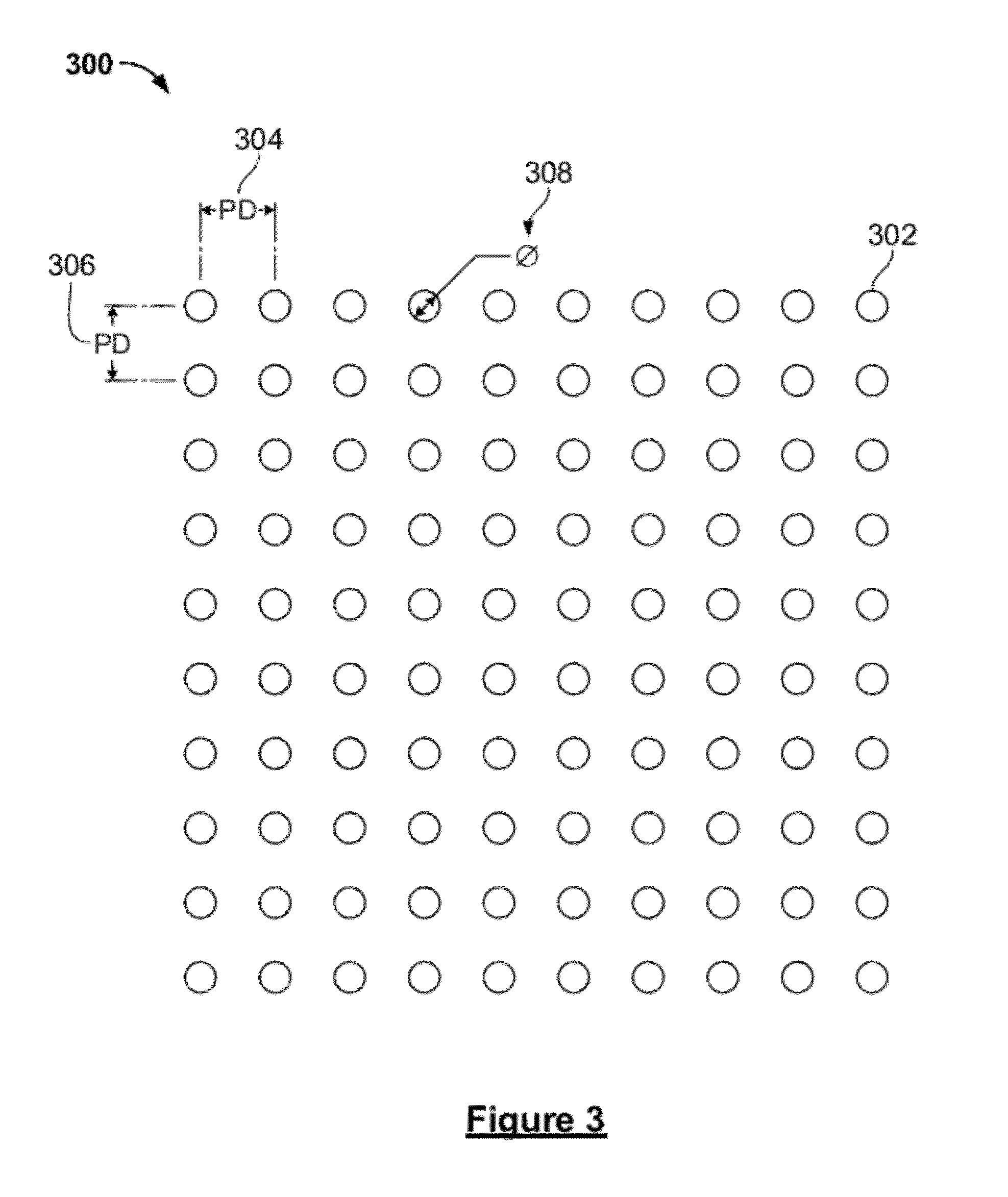
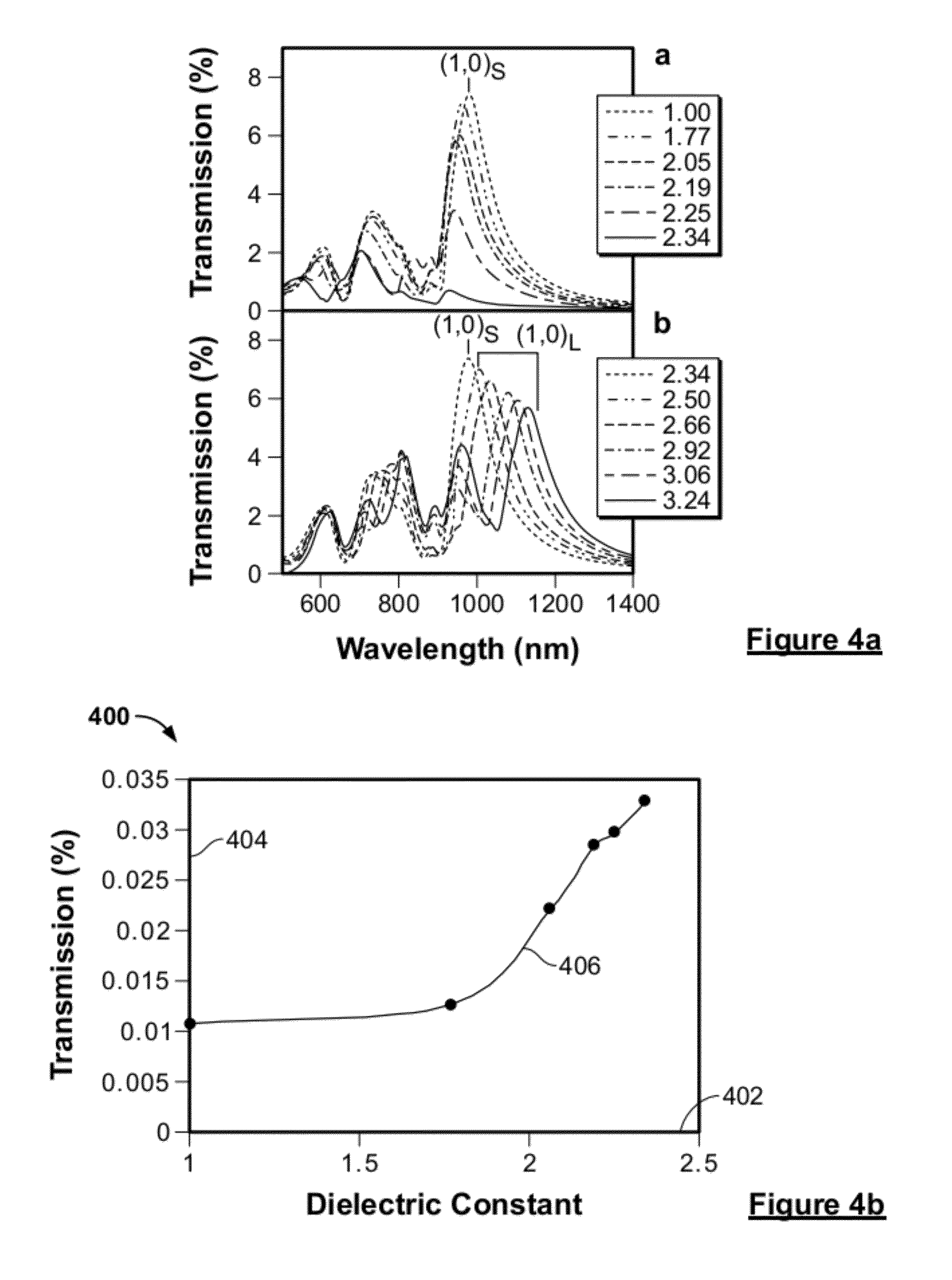
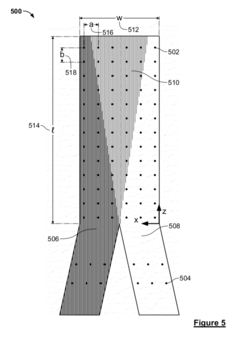
System and method for a microfluidic calorimeter
PatentWO2012097221A1
Innovation
- A microfluidic calorimeter system utilizing microscale temperature sensors and nanohole arrays in a metal film to detect temperature changes in microfluidic laminar flow, allowing for precise calorimetry measurements without requiring exact reagent volumes and enabling continuous reaction observation, which reduces noise and error by integrating data over time.
System and method for a microfluidic calorimeter
PatentActiveUS20120264224A1
Innovation
- A microfluidic calorimetry system utilizing microscale temperature sensors and nanohole arrays in a metal film to measure temperature changes in microfluidic laminar flow, allowing for precise calorimetry measurements with reduced reagent volumes and improved experimental efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance in Pharmaceutical Process Development
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of pharmaceutical process development, including the application of calorimetry in synthetic route development. The pharmaceutical industry is heavily regulated to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of drug products. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other national authorities set stringent guidelines for pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
In the context of calorimetry and synthetic route development, regulatory compliance involves adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Quality by Design (QbD) principles. Calorimetry data must be collected, analyzed, and documented in accordance with these regulatory requirements. This includes maintaining detailed records of experimental procedures, equipment calibration, and data analysis methods.
The use of calorimetry in process development aligns with regulatory expectations for thorough process understanding and control. Regulatory agencies emphasize the importance of identifying and controlling critical process parameters (CPPs) that affect critical quality attributes (CQAs) of the final product. Calorimetric studies provide valuable insights into reaction kinetics, heat transfer, and potential safety hazards, which are essential for establishing robust process control strategies.
Regulatory compliance also extends to the validation of analytical methods used in calorimetry. This includes demonstrating the accuracy, precision, and reproducibility of calorimetric measurements. Validation protocols must be established and followed to ensure the reliability of data used in process development decisions.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies require pharmaceutical companies to implement risk management strategies throughout the drug development process. Calorimetry plays a crucial role in identifying and mitigating potential risks associated with chemical reactions, such as thermal runaway or unexpected exotherms. The data generated from calorimetric studies contributes to comprehensive risk assessments and helps in developing appropriate control measures.
In the context of continuous manufacturing, which is gaining regulatory acceptance, calorimetry data is particularly valuable for process analytical technology (PAT) implementation. PAT is encouraged by regulatory agencies as a means to enhance process understanding and control. Calorimetric measurements can be integrated into PAT systems to provide real-time monitoring of reaction progress and process parameters.
Regulatory compliance also necessitates the proper documentation and reporting of calorimetry data in regulatory submissions. This includes providing detailed descriptions of experimental methods, data analysis techniques, and the rationale for process design decisions based on calorimetric studies. Clear and comprehensive documentation supports regulatory review processes and demonstrates the scientific rigor applied in synthetic route development.
In the context of calorimetry and synthetic route development, regulatory compliance involves adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Quality by Design (QbD) principles. Calorimetry data must be collected, analyzed, and documented in accordance with these regulatory requirements. This includes maintaining detailed records of experimental procedures, equipment calibration, and data analysis methods.
The use of calorimetry in process development aligns with regulatory expectations for thorough process understanding and control. Regulatory agencies emphasize the importance of identifying and controlling critical process parameters (CPPs) that affect critical quality attributes (CQAs) of the final product. Calorimetric studies provide valuable insights into reaction kinetics, heat transfer, and potential safety hazards, which are essential for establishing robust process control strategies.
Regulatory compliance also extends to the validation of analytical methods used in calorimetry. This includes demonstrating the accuracy, precision, and reproducibility of calorimetric measurements. Validation protocols must be established and followed to ensure the reliability of data used in process development decisions.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies require pharmaceutical companies to implement risk management strategies throughout the drug development process. Calorimetry plays a crucial role in identifying and mitigating potential risks associated with chemical reactions, such as thermal runaway or unexpected exotherms. The data generated from calorimetric studies contributes to comprehensive risk assessments and helps in developing appropriate control measures.
In the context of continuous manufacturing, which is gaining regulatory acceptance, calorimetry data is particularly valuable for process analytical technology (PAT) implementation. PAT is encouraged by regulatory agencies as a means to enhance process understanding and control. Calorimetric measurements can be integrated into PAT systems to provide real-time monitoring of reaction progress and process parameters.
Regulatory compliance also necessitates the proper documentation and reporting of calorimetry data in regulatory submissions. This includes providing detailed descriptions of experimental methods, data analysis techniques, and the rationale for process design decisions based on calorimetric studies. Clear and comprehensive documentation supports regulatory review processes and demonstrates the scientific rigor applied in synthetic route development.
Economic Impact of Calorimetry in Drug Manufacturing
Calorimetry has emerged as a powerful tool in the pharmaceutical industry, significantly impacting the economic landscape of drug manufacturing. By providing precise measurements of heat changes during chemical reactions, calorimetry enables more efficient and cost-effective synthetic route development for pharmaceuticals.
The implementation of calorimetry in drug manufacturing processes has led to substantial reductions in production costs. By optimizing reaction conditions and identifying the most efficient synthetic pathways, pharmaceutical companies can minimize raw material usage and energy consumption. This optimization translates directly into lower production expenses, contributing to improved profit margins and overall economic viability of drug development projects.
Furthermore, calorimetry enhances process safety by identifying potential exothermic reactions and thermal runaway scenarios. This proactive approach to risk management reduces the likelihood of costly accidents and production disruptions, thereby safeguarding investments and ensuring consistent manufacturing output. The economic benefits of improved safety protocols extend beyond immediate cost savings, encompassing reduced insurance premiums and enhanced regulatory compliance.
The application of calorimetry in drug manufacturing also accelerates time-to-market for new pharmaceutical products. By enabling rapid screening of reaction conditions and providing valuable kinetic data, calorimetry streamlines the process development phase. This reduction in development timelines allows pharmaceutical companies to bring drugs to market faster, potentially extending patent protection periods and maximizing revenue generation opportunities.
Calorimetry's impact on quality control and consistency in drug manufacturing processes cannot be overstated. By providing real-time monitoring of reaction progress and product formation, calorimetry ensures consistent product quality across batches. This consistency reduces the need for costly rework or product recalls, further contributing to economic efficiency in pharmaceutical production.
The economic benefits of calorimetry extend to resource allocation within pharmaceutical companies. By providing detailed insights into reaction mechanisms and thermodynamics, calorimetry allows for more informed decision-making in research and development efforts. This targeted approach to resource allocation optimizes R&D spending and increases the likelihood of successful drug candidates progressing through clinical trials.
In the broader context of the pharmaceutical industry, the widespread adoption of calorimetry has contributed to a more competitive landscape. Companies leveraging calorimetric techniques gain a significant advantage in terms of cost-effectiveness and product quality, driving industry-wide innovation and efficiency improvements. This competitive pressure ultimately benefits consumers through potentially lower drug prices and increased availability of novel therapeutics.
The implementation of calorimetry in drug manufacturing processes has led to substantial reductions in production costs. By optimizing reaction conditions and identifying the most efficient synthetic pathways, pharmaceutical companies can minimize raw material usage and energy consumption. This optimization translates directly into lower production expenses, contributing to improved profit margins and overall economic viability of drug development projects.
Furthermore, calorimetry enhances process safety by identifying potential exothermic reactions and thermal runaway scenarios. This proactive approach to risk management reduces the likelihood of costly accidents and production disruptions, thereby safeguarding investments and ensuring consistent manufacturing output. The economic benefits of improved safety protocols extend beyond immediate cost savings, encompassing reduced insurance premiums and enhanced regulatory compliance.
The application of calorimetry in drug manufacturing also accelerates time-to-market for new pharmaceutical products. By enabling rapid screening of reaction conditions and providing valuable kinetic data, calorimetry streamlines the process development phase. This reduction in development timelines allows pharmaceutical companies to bring drugs to market faster, potentially extending patent protection periods and maximizing revenue generation opportunities.
Calorimetry's impact on quality control and consistency in drug manufacturing processes cannot be overstated. By providing real-time monitoring of reaction progress and product formation, calorimetry ensures consistent product quality across batches. This consistency reduces the need for costly rework or product recalls, further contributing to economic efficiency in pharmaceutical production.
The economic benefits of calorimetry extend to resource allocation within pharmaceutical companies. By providing detailed insights into reaction mechanisms and thermodynamics, calorimetry allows for more informed decision-making in research and development efforts. This targeted approach to resource allocation optimizes R&D spending and increases the likelihood of successful drug candidates progressing through clinical trials.
In the broader context of the pharmaceutical industry, the widespread adoption of calorimetry has contributed to a more competitive landscape. Companies leveraging calorimetric techniques gain a significant advantage in terms of cost-effectiveness and product quality, driving industry-wide innovation and efficiency improvements. This competitive pressure ultimately benefits consumers through potentially lower drug prices and increased availability of novel therapeutics.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!