How Isocyanate Technologies Contribute to Energy Efficiency?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Tech Evolution
Isocyanate technologies have undergone significant evolution since their inception in the early 20th century. The timeline of this evolution can be traced through several key stages, each marked by important technological advancements and applications that have contributed to energy efficiency.
In the 1930s, Otto Bayer and his team at IG Farben in Germany pioneered the development of polyurethanes, which are formed by the reaction of isocyanates with polyols. This breakthrough laid the foundation for the widespread use of isocyanates in various industries. The initial applications were primarily focused on fibers and coatings, with limited consideration for energy efficiency.
The 1950s and 1960s saw a rapid expansion in the use of isocyanate-based materials, particularly in the form of flexible and rigid foams. This period marked the beginning of isocyanates' contribution to energy efficiency, as rigid polyurethane foams began to be used as insulation materials in buildings and refrigeration systems. The excellent thermal insulation properties of these foams significantly reduced energy consumption in heating and cooling applications.
During the 1970s and 1980s, environmental concerns and energy crises drove further innovation in isocyanate technologies. Researchers focused on developing more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient production processes for isocyanates. This era also saw the introduction of new types of isocyanates, such as methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), which offered improved performance and versatility compared to earlier compounds.
The 1990s and early 2000s brought about a shift towards sustainable and energy-efficient solutions. Isocyanate technologies played a crucial role in this trend, with the development of high-performance insulation materials for buildings and appliances. Advanced spray foam insulation systems, utilizing isocyanate-based formulations, became increasingly popular for their superior insulating properties and ability to create airtight building envelopes.
In recent years, the focus has been on enhancing the energy efficiency of isocyanate production processes themselves. Innovations in catalysis and process engineering have led to more efficient manufacturing methods, reducing the energy required to produce these versatile chemicals. Additionally, research into bio-based isocyanates and renewable feedstocks has gained momentum, aiming to further improve the sustainability and energy efficiency of isocyanate technologies.
The evolution of isocyanate technologies has been closely tied to advancements in polymer science, chemical engineering, and materials science. Each stage of development has brought new opportunities for energy efficiency, from improved insulation materials to more sustainable production processes. As we look to the future, ongoing research in areas such as nanotechnology and smart materials promises to unlock even greater potential for isocyanates in contributing to energy efficiency across various sectors.
In the 1930s, Otto Bayer and his team at IG Farben in Germany pioneered the development of polyurethanes, which are formed by the reaction of isocyanates with polyols. This breakthrough laid the foundation for the widespread use of isocyanates in various industries. The initial applications were primarily focused on fibers and coatings, with limited consideration for energy efficiency.
The 1950s and 1960s saw a rapid expansion in the use of isocyanate-based materials, particularly in the form of flexible and rigid foams. This period marked the beginning of isocyanates' contribution to energy efficiency, as rigid polyurethane foams began to be used as insulation materials in buildings and refrigeration systems. The excellent thermal insulation properties of these foams significantly reduced energy consumption in heating and cooling applications.
During the 1970s and 1980s, environmental concerns and energy crises drove further innovation in isocyanate technologies. Researchers focused on developing more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient production processes for isocyanates. This era also saw the introduction of new types of isocyanates, such as methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), which offered improved performance and versatility compared to earlier compounds.
The 1990s and early 2000s brought about a shift towards sustainable and energy-efficient solutions. Isocyanate technologies played a crucial role in this trend, with the development of high-performance insulation materials for buildings and appliances. Advanced spray foam insulation systems, utilizing isocyanate-based formulations, became increasingly popular for their superior insulating properties and ability to create airtight building envelopes.
In recent years, the focus has been on enhancing the energy efficiency of isocyanate production processes themselves. Innovations in catalysis and process engineering have led to more efficient manufacturing methods, reducing the energy required to produce these versatile chemicals. Additionally, research into bio-based isocyanates and renewable feedstocks has gained momentum, aiming to further improve the sustainability and energy efficiency of isocyanate technologies.
The evolution of isocyanate technologies has been closely tied to advancements in polymer science, chemical engineering, and materials science. Each stage of development has brought new opportunities for energy efficiency, from improved insulation materials to more sustainable production processes. As we look to the future, ongoing research in areas such as nanotechnology and smart materials promises to unlock even greater potential for isocyanates in contributing to energy efficiency across various sectors.
Energy Efficiency Market
The energy efficiency market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing global awareness of climate change and the need for sustainable energy solutions. This market encompasses a wide range of technologies, products, and services aimed at reducing energy consumption and improving overall energy performance across various sectors, including buildings, industry, and transportation.
In the building sector, which accounts for a substantial portion of global energy consumption, there is a growing demand for energy-efficient materials and technologies. This includes advanced insulation solutions, smart building management systems, and energy-efficient lighting and appliances. The industrial sector also presents significant opportunities for energy efficiency improvements, with a focus on optimizing manufacturing processes, implementing energy recovery systems, and adopting more efficient equipment.
The transportation sector is another key area driving the energy efficiency market, with a shift towards electric vehicles, improved fuel efficiency in conventional vehicles, and the development of alternative fuels. Additionally, the rise of smart grid technologies and energy management systems is contributing to the overall growth of the energy efficiency market.
Government regulations and incentives play a crucial role in shaping the energy efficiency market. Many countries have implemented stringent energy efficiency standards and building codes, while offering tax incentives and rebates for energy-efficient upgrades. These policies have been instrumental in driving market growth and encouraging innovation in energy-efficient technologies.
The global energy efficiency market is characterized by a diverse range of players, including large multinational corporations, specialized technology providers, and innovative startups. Competition in this market is intense, with companies constantly striving to develop more advanced and cost-effective solutions to meet the growing demand for energy-efficient products and services.
Looking ahead, the energy efficiency market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by factors such as increasing energy costs, stricter environmental regulations, and growing consumer awareness of the benefits of energy-efficient solutions. Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, are likely to play a significant role in further advancing energy efficiency capabilities and opening up new market opportunities.
In this context, isocyanate technologies have the potential to make substantial contributions to the energy efficiency market, particularly in the areas of insulation and lightweight materials. By enhancing thermal insulation properties and reducing overall weight in various applications, isocyanate-based products can help improve energy efficiency across multiple sectors, aligning with the market's growing demand for innovative and effective energy-saving solutions.
In the building sector, which accounts for a substantial portion of global energy consumption, there is a growing demand for energy-efficient materials and technologies. This includes advanced insulation solutions, smart building management systems, and energy-efficient lighting and appliances. The industrial sector also presents significant opportunities for energy efficiency improvements, with a focus on optimizing manufacturing processes, implementing energy recovery systems, and adopting more efficient equipment.
The transportation sector is another key area driving the energy efficiency market, with a shift towards electric vehicles, improved fuel efficiency in conventional vehicles, and the development of alternative fuels. Additionally, the rise of smart grid technologies and energy management systems is contributing to the overall growth of the energy efficiency market.
Government regulations and incentives play a crucial role in shaping the energy efficiency market. Many countries have implemented stringent energy efficiency standards and building codes, while offering tax incentives and rebates for energy-efficient upgrades. These policies have been instrumental in driving market growth and encouraging innovation in energy-efficient technologies.
The global energy efficiency market is characterized by a diverse range of players, including large multinational corporations, specialized technology providers, and innovative startups. Competition in this market is intense, with companies constantly striving to develop more advanced and cost-effective solutions to meet the growing demand for energy-efficient products and services.
Looking ahead, the energy efficiency market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by factors such as increasing energy costs, stricter environmental regulations, and growing consumer awareness of the benefits of energy-efficient solutions. Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, are likely to play a significant role in further advancing energy efficiency capabilities and opening up new market opportunities.
In this context, isocyanate technologies have the potential to make substantial contributions to the energy efficiency market, particularly in the areas of insulation and lightweight materials. By enhancing thermal insulation properties and reducing overall weight in various applications, isocyanate-based products can help improve energy efficiency across multiple sectors, aligning with the market's growing demand for innovative and effective energy-saving solutions.
Isocyanate Challenges
Despite the significant contributions of isocyanate technologies to energy efficiency, several challenges persist in their development and application. One of the primary concerns is the toxicity of isocyanates, particularly during the manufacturing process. Exposure to isocyanates can cause respiratory issues and skin irritation, necessitating stringent safety measures and protective equipment for workers. This not only increases production costs but also raises environmental and health concerns.
Another challenge lies in the environmental impact of isocyanate production. The process often involves the use of fossil fuel-based raw materials, which contributes to carbon emissions and resource depletion. As global efforts to reduce carbon footprints intensify, the isocyanate industry faces pressure to develop more sustainable production methods and explore bio-based alternatives.
The volatility of raw material prices, especially for key components like toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), poses a significant challenge to manufacturers. Price fluctuations can impact profit margins and make long-term planning difficult, potentially hindering investment in research and development for more energy-efficient applications.
Regulatory compliance presents another hurdle for isocyanate technologies. Stringent regulations regarding the use and disposal of isocyanates vary across regions, making it challenging for companies to maintain consistent global operations. Adapting to evolving environmental and safety standards requires continuous investment in technology upgrades and process improvements.
The complexity of isocyanate chemistry also presents technical challenges in achieving optimal energy efficiency. Balancing reactivity, cure times, and final product properties requires precise formulation and process control. This complexity can lead to increased energy consumption during production and limit the potential for energy savings in certain applications.
Recycling and end-of-life management of isocyanate-based products, particularly polyurethanes, remain significant challenges. The cross-linked structure of many polyurethane products makes them difficult to recycle, leading to increased waste and reduced overall energy efficiency across the product lifecycle. Developing effective recycling technologies for these materials is crucial for improving their sustainability profile.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in public perception and acceptance of isocyanate technologies. Concerns about health and environmental impacts can lead to resistance in adopting isocyanate-based solutions, even when they offer superior energy efficiency. Overcoming these perceptions requires extensive education and transparent communication about the benefits and safety measures associated with isocyanate technologies.
Another challenge lies in the environmental impact of isocyanate production. The process often involves the use of fossil fuel-based raw materials, which contributes to carbon emissions and resource depletion. As global efforts to reduce carbon footprints intensify, the isocyanate industry faces pressure to develop more sustainable production methods and explore bio-based alternatives.
The volatility of raw material prices, especially for key components like toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), poses a significant challenge to manufacturers. Price fluctuations can impact profit margins and make long-term planning difficult, potentially hindering investment in research and development for more energy-efficient applications.
Regulatory compliance presents another hurdle for isocyanate technologies. Stringent regulations regarding the use and disposal of isocyanates vary across regions, making it challenging for companies to maintain consistent global operations. Adapting to evolving environmental and safety standards requires continuous investment in technology upgrades and process improvements.
The complexity of isocyanate chemistry also presents technical challenges in achieving optimal energy efficiency. Balancing reactivity, cure times, and final product properties requires precise formulation and process control. This complexity can lead to increased energy consumption during production and limit the potential for energy savings in certain applications.
Recycling and end-of-life management of isocyanate-based products, particularly polyurethanes, remain significant challenges. The cross-linked structure of many polyurethane products makes them difficult to recycle, leading to increased waste and reduced overall energy efficiency across the product lifecycle. Developing effective recycling technologies for these materials is crucial for improving their sustainability profile.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in public perception and acceptance of isocyanate technologies. Concerns about health and environmental impacts can lead to resistance in adopting isocyanate-based solutions, even when they offer superior energy efficiency. Overcoming these perceptions requires extensive education and transparent communication about the benefits and safety measures associated with isocyanate technologies.
Current Isocyanate Solutions
01 Energy-efficient isocyanate production processes
Advanced technologies for producing isocyanates with improved energy efficiency, including optimized reaction conditions, catalysts, and process integration. These methods aim to reduce energy consumption and increase yield in isocyanate manufacturing.- Energy-efficient isocyanate production processes: Advanced technologies for producing isocyanates with improved energy efficiency, including optimized reaction conditions, catalysts, and process integration. These methods aim to reduce energy consumption and increase yield in isocyanate manufacturing.
- Isocyanate-based insulation materials for energy conservation: Development of high-performance insulation materials using isocyanate-based foams or composites. These materials offer superior thermal insulation properties, contributing to energy efficiency in buildings and industrial applications.
- Energy-efficient curing systems for isocyanate coatings: Innovative curing technologies for isocyanate-based coatings that require less energy input. These systems may include UV-curable formulations, low-temperature curing agents, or catalysts that accelerate the curing process at ambient conditions.
- Isocyanate-based energy storage materials: Utilization of isocyanate chemistry in the development of advanced energy storage materials, such as electrolytes or electrode components for batteries. These materials aim to improve energy density, charge-discharge efficiency, or overall battery performance.
- Energy-efficient recycling and recovery of isocyanates: Technologies for recycling or recovering isocyanates from waste streams or end-of-life products. These processes aim to reduce energy consumption in isocyanate production by reusing materials and minimizing waste generation.
02 Isocyanate-based insulation materials for energy conservation
Development of high-performance insulation materials using isocyanate-based foams or composites. These materials offer superior thermal insulation properties, contributing to energy efficiency in buildings and industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Energy-efficient curing systems for isocyanate coatings
Innovative curing technologies for isocyanate-based coatings that require less energy input. These systems may include UV-curing, low-temperature curing, or catalytic methods that reduce the overall energy consumption in coating applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Isocyanate-based energy storage materials
Research into novel energy storage materials incorporating isocyanate chemistry. This includes the development of advanced battery components, supercapacitors, or thermal energy storage systems that utilize isocyanate-derived materials for improved energy efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy-efficient recycling and upcycling of isocyanate-based products
Technologies focused on the efficient recycling or upcycling of isocyanate-containing materials, such as polyurethanes. These processes aim to reduce energy consumption in waste management and promote circular economy principles in the isocyanate industry.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The isocyanate technologies market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient materials across various industries. The global market size is projected to expand significantly, fueled by applications in construction, automotive, and consumer goods sectors. Technologically, isocyanate solutions are advancing rapidly, with major players like Covestro, Wanhua Chemical, and BASF leading innovation. These companies are developing more sustainable and high-performance isocyanate products, focusing on improving energy efficiency in end-use applications. The technology's maturity varies across different isocyanate types, with established players continuously refining processes and newer entrants bringing novel approaches to enhance energy-saving properties.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro has developed innovative isocyanate technologies that significantly contribute to energy efficiency. Their cardyon® technology uses CO2 as a raw material to produce polyols, which are then combined with isocyanates to create energy-efficient polyurethane foams[1]. These foams are used in insulation applications, reducing energy consumption in buildings. Covestro has also introduced low-emission PMDI (polymeric methylene diphenyl diisocyanate) products that improve the thermal insulation properties of polyurethane rigid foams, leading to enhanced energy efficiency in refrigerators and buildings[2]. Additionally, their aliphatic isocyanates are used in the production of high-performance coatings for wind turbine blades, improving their durability and efficiency[3].
Strengths: Innovative CO2 utilization, improved insulation properties, and versatile applications. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs and reliance on specialized manufacturing processes.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has developed advanced isocyanate technologies that contribute significantly to energy efficiency. Their WANNATE® PM series of polymeric MDI products are used in the production of high-performance polyurethane insulation materials, which greatly reduce energy consumption in buildings and refrigeration systems[1]. Wanhua has also introduced eco-friendly water-blown technologies for spray polyurethane foam (SPF) insulation, eliminating the need for harmful blowing agents while maintaining excellent thermal insulation properties[2]. Furthermore, their innovative isocyanate-based composites are used in lightweight automotive parts, contributing to improved fuel efficiency in vehicles[3]. Wanhua's continuous investment in R&D has led to the development of low-free-monomer technology, reducing VOC emissions and improving the overall environmental profile of their isocyanate products[4].
Strengths: Wide range of energy-efficient applications, eco-friendly technologies, and strong R&D capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges in some markets and competition from alternative materials.
Innovative Isocyanate Tech
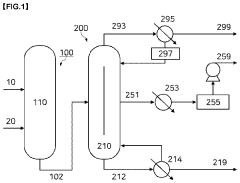
Isocyanate production system, isocyanate composition, polymerizable composition, resin, and molded article
PatentPendingUS20240343684A1
Innovation
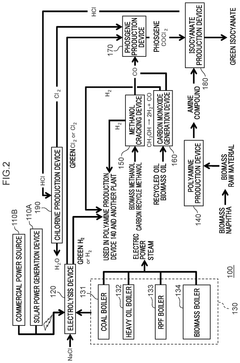
- An isocyanate production system incorporating biomass boilers, carbon monoxide and hydrogen production from biomass or recycled methanol, and polyamine compounds derived from biomass raw materials, along with a control device that optimizes energy use and selects production methods to minimize environmental load, thereby reducing carbon dioxide emissions.
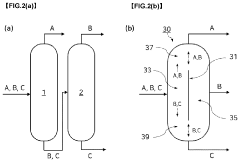
Method for preparing isocyanate compound
PatentPendingUS20240067601A1
Innovation
- A method involving a reaction step where a salt of an amine compound is reacted with phosgene in the presence of a solvent, followed by distillation in a dividing-wall distillation column to separate unreacted phosgene, the isocyanate compound, and the solvent, maintaining a temperature of 165° C. or less at the bottom of the column.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the development and application of isocyanate technologies in the context of energy efficiency. These regulations have been instrumental in driving innovation and promoting sustainable practices within the industry.
In recent years, governments worldwide have implemented stringent environmental policies to address climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These regulations have had a significant impact on the isocyanate industry, particularly in the areas of production, application, and disposal of isocyanate-based products.
One of the key regulatory frameworks affecting isocyanate technologies is the Montreal Protocol, which aims to phase out substances that deplete the ozone layer. This agreement has led to the development of alternative blowing agents for polyurethane foams, a major application of isocyanates in energy-efficient insulation materials.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation has also influenced the isocyanate industry. It requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with chemicals, including isocyanates, and to provide safety information to users.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established regulations under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) that govern the production and use of isocyanates. These regulations focus on worker safety, emissions control, and proper handling and disposal of isocyanate-containing materials.
The increasing focus on energy efficiency in buildings has led to the development of more stringent building codes and standards. These regulations often specify minimum insulation requirements, which has driven the demand for high-performance polyurethane insulation materials made with isocyanates.
Environmental regulations have also spurred research and development efforts to create more environmentally friendly isocyanate-based products. This includes the development of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, as well as improved recycling and recovery processes for polyurethane materials.
The automotive industry, a major consumer of isocyanate-based products, has been subject to increasingly strict fuel efficiency standards. This has led to the adoption of lightweight materials, including polyurethane composites, to improve vehicle energy efficiency.
As environmental regulations continue to evolve, the isocyanate industry is likely to face both challenges and opportunities. Compliance with these regulations may require significant investments in new technologies and processes. However, it also presents opportunities for innovation and the development of more sustainable and energy-efficient products.
In recent years, governments worldwide have implemented stringent environmental policies to address climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These regulations have had a significant impact on the isocyanate industry, particularly in the areas of production, application, and disposal of isocyanate-based products.
One of the key regulatory frameworks affecting isocyanate technologies is the Montreal Protocol, which aims to phase out substances that deplete the ozone layer. This agreement has led to the development of alternative blowing agents for polyurethane foams, a major application of isocyanates in energy-efficient insulation materials.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation has also influenced the isocyanate industry. It requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with chemicals, including isocyanates, and to provide safety information to users.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established regulations under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) that govern the production and use of isocyanates. These regulations focus on worker safety, emissions control, and proper handling and disposal of isocyanate-containing materials.
The increasing focus on energy efficiency in buildings has led to the development of more stringent building codes and standards. These regulations often specify minimum insulation requirements, which has driven the demand for high-performance polyurethane insulation materials made with isocyanates.
Environmental regulations have also spurred research and development efforts to create more environmentally friendly isocyanate-based products. This includes the development of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, as well as improved recycling and recovery processes for polyurethane materials.
The automotive industry, a major consumer of isocyanate-based products, has been subject to increasingly strict fuel efficiency standards. This has led to the adoption of lightweight materials, including polyurethane composites, to improve vehicle energy efficiency.
As environmental regulations continue to evolve, the isocyanate industry is likely to face both challenges and opportunities. Compliance with these regulations may require significant investments in new technologies and processes. However, it also presents opportunities for innovation and the development of more sustainable and energy-efficient products.
Lifecycle Assessment
Lifecycle assessment (LCA) plays a crucial role in evaluating the environmental impact and energy efficiency of isocyanate technologies throughout their entire lifecycle. This comprehensive approach considers all stages, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, providing valuable insights into the overall sustainability of these technologies.
In the production phase, isocyanates contribute to energy efficiency through their versatile chemical properties. The reactive nature of isocyanates allows for efficient polymerization processes, reducing energy consumption during manufacturing. Advanced production techniques, such as continuous flow reactors and process intensification, further enhance energy efficiency by optimizing reaction conditions and minimizing waste.
During the use phase, isocyanate-based products significantly contribute to energy efficiency in various applications. In the construction industry, polyurethane insulation materials derived from isocyanates offer superior thermal insulation properties, reducing heating and cooling energy demands in buildings. The lightweight nature of polyurethane foams also contributes to fuel efficiency in transportation applications, such as automotive and aerospace industries.
End-of-life considerations for isocyanate-based products present both challenges and opportunities for energy efficiency. While some polyurethane products can be mechanically recycled, chemical recycling methods are emerging as promising alternatives. These processes aim to break down polyurethanes into their original components, potentially recovering valuable raw materials and reducing the overall energy footprint of the lifecycle.
The durability and longevity of isocyanate-based products also contribute to energy efficiency from a lifecycle perspective. Extended product lifespans reduce the need for frequent replacements, thereby conserving energy and resources associated with manufacturing and disposal processes. This aspect is particularly relevant in applications such as durable coatings, adhesives, and structural materials.
However, it is essential to consider the potential environmental and health impacts associated with isocyanate production and use. Proper handling, exposure control, and waste management practices are crucial to mitigate risks and ensure the overall sustainability of these technologies. Ongoing research and development efforts focus on developing bio-based isocyanates and improving end-of-life recycling options to further enhance the lifecycle energy efficiency of isocyanate technologies.
In the production phase, isocyanates contribute to energy efficiency through their versatile chemical properties. The reactive nature of isocyanates allows for efficient polymerization processes, reducing energy consumption during manufacturing. Advanced production techniques, such as continuous flow reactors and process intensification, further enhance energy efficiency by optimizing reaction conditions and minimizing waste.
During the use phase, isocyanate-based products significantly contribute to energy efficiency in various applications. In the construction industry, polyurethane insulation materials derived from isocyanates offer superior thermal insulation properties, reducing heating and cooling energy demands in buildings. The lightweight nature of polyurethane foams also contributes to fuel efficiency in transportation applications, such as automotive and aerospace industries.
End-of-life considerations for isocyanate-based products present both challenges and opportunities for energy efficiency. While some polyurethane products can be mechanically recycled, chemical recycling methods are emerging as promising alternatives. These processes aim to break down polyurethanes into their original components, potentially recovering valuable raw materials and reducing the overall energy footprint of the lifecycle.
The durability and longevity of isocyanate-based products also contribute to energy efficiency from a lifecycle perspective. Extended product lifespans reduce the need for frequent replacements, thereby conserving energy and resources associated with manufacturing and disposal processes. This aspect is particularly relevant in applications such as durable coatings, adhesives, and structural materials.
However, it is essential to consider the potential environmental and health impacts associated with isocyanate production and use. Proper handling, exposure control, and waste management practices are crucial to mitigate risks and ensure the overall sustainability of these technologies. Ongoing research and development efforts focus on developing bio-based isocyanates and improving end-of-life recycling options to further enhance the lifecycle energy efficiency of isocyanate technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!