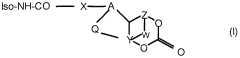
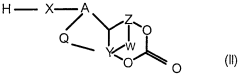
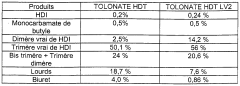
How Isocyanates Align with Futuristic Retail Needs?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Technology Evolution and Objectives
Isocyanates have been a cornerstone in various industries for decades, with their versatile chemical properties making them indispensable in the production of polyurethanes. The evolution of isocyanate technology has been driven by the need for more efficient, sustainable, and versatile materials that can meet the ever-changing demands of modern retail environments.
The journey of isocyanates began in the 1930s with their initial synthesis, but it wasn't until the 1950s that their potential in polyurethane production was fully realized. Since then, the technology has undergone significant advancements, focusing on improving performance, reducing environmental impact, and expanding application possibilities.
In the context of futuristic retail needs, isocyanate technology has evolved to address several key objectives. One primary goal has been the development of more environmentally friendly formulations. This includes the creation of water-based systems and the reduction of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainability in retail spaces.
Another crucial objective has been enhancing the durability and longevity of isocyanate-based products. This is particularly relevant in retail environments where materials are subjected to high foot traffic, frequent cleaning, and varying environmental conditions. Advanced isocyanate formulations now offer improved resistance to wear, chemicals, and UV radiation, ensuring that retail fixtures and flooring maintain their appearance and functionality for longer periods.
Flexibility and customization have also been at the forefront of isocyanate technology evolution. The retail sector demands materials that can be easily molded, colored, and textured to create unique and engaging shopping experiences. Modern isocyanate systems allow for greater design freedom, enabling retailers to create distinctive brand identities through innovative store layouts and product displays.
Energy efficiency is another key objective that has shaped the development of isocyanate technology. Improved insulation properties of polyurethane foams, derived from advanced isocyanate formulations, contribute to better temperature regulation in retail spaces. This not only enhances customer comfort but also aligns with the increasing focus on energy conservation and reduced operational costs in the retail sector.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for isocyanate technology in retail applications continue to evolve. There is a growing emphasis on developing bio-based isocyanates, which could significantly reduce the carbon footprint of retail materials. Additionally, research is ongoing to improve the recyclability and end-of-life management of isocyanate-based products, addressing the circular economy principles that are becoming increasingly important in retail strategy.
The journey of isocyanates began in the 1930s with their initial synthesis, but it wasn't until the 1950s that their potential in polyurethane production was fully realized. Since then, the technology has undergone significant advancements, focusing on improving performance, reducing environmental impact, and expanding application possibilities.
In the context of futuristic retail needs, isocyanate technology has evolved to address several key objectives. One primary goal has been the development of more environmentally friendly formulations. This includes the creation of water-based systems and the reduction of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainability in retail spaces.
Another crucial objective has been enhancing the durability and longevity of isocyanate-based products. This is particularly relevant in retail environments where materials are subjected to high foot traffic, frequent cleaning, and varying environmental conditions. Advanced isocyanate formulations now offer improved resistance to wear, chemicals, and UV radiation, ensuring that retail fixtures and flooring maintain their appearance and functionality for longer periods.
Flexibility and customization have also been at the forefront of isocyanate technology evolution. The retail sector demands materials that can be easily molded, colored, and textured to create unique and engaging shopping experiences. Modern isocyanate systems allow for greater design freedom, enabling retailers to create distinctive brand identities through innovative store layouts and product displays.
Energy efficiency is another key objective that has shaped the development of isocyanate technology. Improved insulation properties of polyurethane foams, derived from advanced isocyanate formulations, contribute to better temperature regulation in retail spaces. This not only enhances customer comfort but also aligns with the increasing focus on energy conservation and reduced operational costs in the retail sector.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for isocyanate technology in retail applications continue to evolve. There is a growing emphasis on developing bio-based isocyanates, which could significantly reduce the carbon footprint of retail materials. Additionally, research is ongoing to improve the recyclability and end-of-life management of isocyanate-based products, addressing the circular economy principles that are becoming increasingly important in retail strategy.
Retail Market Demand for Isocyanate-Based Products
The retail market demand for isocyanate-based products has been steadily growing, driven by the unique properties and versatile applications of these materials. Isocyanates, particularly in the form of polyurethanes, have found extensive use in various retail sectors, including furniture, bedding, automotive, footwear, and consumer electronics.
In the furniture industry, isocyanate-based foams are highly sought after for their comfort, durability, and customizable properties. Consumers increasingly demand ergonomic and long-lasting furniture, which has led to a surge in the use of polyurethane foams in sofas, chairs, and mattresses. The bedding sector has also seen a significant uptick in demand for memory foam mattresses and pillows, which rely heavily on isocyanate chemistry.
The automotive retail market has been another major driver of isocyanate demand. Polyurethane components are used extensively in car interiors, including seats, dashboards, and headliners, due to their lightweight nature and ability to enhance fuel efficiency. As consumers prioritize comfort and sustainability in their vehicle choices, the demand for isocyanate-based products in this sector continues to rise.
In the footwear industry, polyurethane soles have gained popularity for their flexibility, durability, and shock-absorbing properties. This trend is particularly evident in the athletic and comfort shoe segments, where consumers are willing to pay a premium for high-performance materials.
The consumer electronics sector has also embraced isocyanate-based products, particularly in the form of protective cases and coatings. As smartphones and tablets become increasingly ubiquitous, the demand for durable, impact-resistant accessories has grown substantially.
Emerging trends in retail, such as the growing emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly products, are shaping the future of isocyanate-based materials. Manufacturers are responding by developing bio-based isocyanates and improving recycling technologies for polyurethane products. This shift aligns with consumer preferences for environmentally responsible purchasing decisions.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further influenced market demand, with increased focus on hygiene and cleanliness driving interest in antimicrobial coatings and easily sanitized surfaces, many of which incorporate isocyanate-based technologies.
As retail continues to evolve, the demand for customization and personalization is expected to fuel further innovation in isocyanate-based products. From made-to-order furniture to bespoke footwear, the versatility of these materials positions them well to meet future retail needs.
In the furniture industry, isocyanate-based foams are highly sought after for their comfort, durability, and customizable properties. Consumers increasingly demand ergonomic and long-lasting furniture, which has led to a surge in the use of polyurethane foams in sofas, chairs, and mattresses. The bedding sector has also seen a significant uptick in demand for memory foam mattresses and pillows, which rely heavily on isocyanate chemistry.
The automotive retail market has been another major driver of isocyanate demand. Polyurethane components are used extensively in car interiors, including seats, dashboards, and headliners, due to their lightweight nature and ability to enhance fuel efficiency. As consumers prioritize comfort and sustainability in their vehicle choices, the demand for isocyanate-based products in this sector continues to rise.
In the footwear industry, polyurethane soles have gained popularity for their flexibility, durability, and shock-absorbing properties. This trend is particularly evident in the athletic and comfort shoe segments, where consumers are willing to pay a premium for high-performance materials.
The consumer electronics sector has also embraced isocyanate-based products, particularly in the form of protective cases and coatings. As smartphones and tablets become increasingly ubiquitous, the demand for durable, impact-resistant accessories has grown substantially.
Emerging trends in retail, such as the growing emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly products, are shaping the future of isocyanate-based materials. Manufacturers are responding by developing bio-based isocyanates and improving recycling technologies for polyurethane products. This shift aligns with consumer preferences for environmentally responsible purchasing decisions.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further influenced market demand, with increased focus on hygiene and cleanliness driving interest in antimicrobial coatings and easily sanitized surfaces, many of which incorporate isocyanate-based technologies.
As retail continues to evolve, the demand for customization and personalization is expected to fuel further innovation in isocyanate-based products. From made-to-order furniture to bespoke footwear, the versatility of these materials positions them well to meet future retail needs.
Current Challenges in Isocyanate Applications
Isocyanates, while versatile and widely used in various industries, face several challenges in their applications, particularly in the context of futuristic retail needs. One of the primary concerns is the potential health hazards associated with exposure to isocyanates. These compounds are known respiratory sensitizers and can cause severe allergic reactions, asthma, and other respiratory issues. This poses significant risks for workers in manufacturing and retail environments, necessitating stringent safety measures and protective equipment.
Environmental concerns also present a major challenge for isocyanate applications. The production and use of isocyanates can lead to the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants, contributing to air and water pollution. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in retail and consumer products, finding eco-friendly alternatives or developing cleaner production methods for isocyanates is crucial.
The complexity of handling and storing isocyanates presents another significant challenge. These compounds are highly reactive and sensitive to moisture, requiring careful storage and handling procedures. This complexity can lead to increased costs and logistical challenges in retail supply chains, particularly for smaller businesses or those operating in humid environments.
Regulatory compliance is an ongoing challenge for isocyanate applications. As health and environmental regulations become more stringent globally, manufacturers and retailers must constantly adapt their processes and products to meet new standards. This can result in increased costs and potential limitations on the use of isocyanates in certain applications or markets.
The performance limitations of current isocyanate-based products also pose challenges in meeting evolving retail needs. While isocyanates offer excellent properties in many applications, there is a growing demand for materials with enhanced durability, flexibility, and customization options. Meeting these demands while maintaining the beneficial properties of isocyanates requires ongoing research and development efforts.
Lastly, the public perception of isocyanates presents a challenge for their continued use in retail applications. As consumers become more aware of potential health and environmental impacts, there is increasing pressure on retailers and manufacturers to provide safer, more sustainable alternatives. Addressing these concerns through improved communication, transparency, and product innovation is essential for the future of isocyanate applications in retail.
Environmental concerns also present a major challenge for isocyanate applications. The production and use of isocyanates can lead to the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants, contributing to air and water pollution. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in retail and consumer products, finding eco-friendly alternatives or developing cleaner production methods for isocyanates is crucial.
The complexity of handling and storing isocyanates presents another significant challenge. These compounds are highly reactive and sensitive to moisture, requiring careful storage and handling procedures. This complexity can lead to increased costs and logistical challenges in retail supply chains, particularly for smaller businesses or those operating in humid environments.
Regulatory compliance is an ongoing challenge for isocyanate applications. As health and environmental regulations become more stringent globally, manufacturers and retailers must constantly adapt their processes and products to meet new standards. This can result in increased costs and potential limitations on the use of isocyanates in certain applications or markets.
The performance limitations of current isocyanate-based products also pose challenges in meeting evolving retail needs. While isocyanates offer excellent properties in many applications, there is a growing demand for materials with enhanced durability, flexibility, and customization options. Meeting these demands while maintaining the beneficial properties of isocyanates requires ongoing research and development efforts.
Lastly, the public perception of isocyanates presents a challenge for their continued use in retail applications. As consumers become more aware of potential health and environmental impacts, there is increasing pressure on retailers and manufacturers to provide safer, more sustainable alternatives. Addressing these concerns through improved communication, transparency, and product innovation is essential for the future of isocyanate applications in retail.
Innovative Isocyanate Formulations for Retail
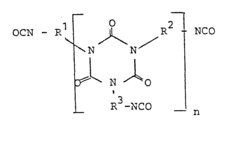
01 Synthesis and production of isocyanates
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel catalysts, reaction conditions, and precursor materials to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate production.- Synthesis and production of isocyanates: Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel reaction pathways, catalysts, and production techniques to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate manufacturing.
- Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry: Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents discuss various applications, including coatings, adhesives, foams, and elastomers, as well as novel formulations and processing techniques.
- Isocyanate-based catalysts and reaction modifiers: Several patents focus on the development of isocyanate-based catalysts and reaction modifiers. These compounds are used to enhance chemical reactions, improve product properties, or facilitate specific industrial processes.
- Safety and handling of isocyanates: Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, patents in this category address safety concerns and handling procedures. This includes methods for reducing toxicity, improving storage stability, and developing safer alternatives or formulations.
- Isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes: Some patents explore alternatives to traditional isocyanates or methods to reduce or eliminate their use in certain applications. This includes the development of new chemistries, bio-based substitutes, or modified production processes that achieve similar end-product properties without relying on isocyanates.
02 Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry
Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents discuss different formulations, curing methods, and applications of isocyanate-based polymers in various industries such as coatings, adhesives, and foams.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes
Research into isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes is presented, addressing environmental and health concerns associated with traditional isocyanates. These alternatives aim to provide similar performance characteristics while reducing potential hazards.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modification and functionalization of isocyanates
Techniques for modifying and functionalizing isocyanates to enhance their properties or create new derivatives are described. These modifications can lead to improved reactivity, stability, or specific performance characteristics for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and handling of isocyanates
Patents addressing safety concerns and proper handling procedures for isocyanates are included. These cover storage methods, protective equipment, exposure prevention, and risk mitigation strategies for working with these potentially hazardous compounds.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Isocyanate Manufacturers and Suppliers
The isocyanates market for futuristic retail needs is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for polyurethane-based products in various applications. The global market size is projected to expand significantly, with key players like BASF, Covestro, and Wanhua Chemical Group leading the way. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to develop innovative, sustainable isocyanate solutions. The technology is relatively mature but evolving, with a focus on eco-friendly alternatives and improved performance characteristics. Emerging players such as Vencorex and Asahi Kasei are also making strides in specialized applications, contributing to the competitive landscape and driving technological advancements in the sector.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed innovative isocyanate-based solutions for futuristic retail needs. Their approach includes the creation of high-performance polyurethane materials for retail applications. These materials offer enhanced durability, flexibility, and customization options for store fixtures, displays, and packaging[1]. BASF's isocyanate-based products also contribute to energy efficiency in retail spaces through improved insulation properties[2]. The company has focused on developing bio-based and recyclable isocyanates to align with sustainability trends in the retail sector[3]. Additionally, BASF has introduced smart coatings using isocyanate chemistry that can change color or texture in response to environmental stimuli, providing interactive and dynamic retail experiences[4].
Strengths: Wide range of applications, sustainability focus, innovative smart materials. Weaknesses: Potential health and environmental concerns associated with isocyanates, regulatory challenges in some markets.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has developed a comprehensive isocyanate portfolio tailored for future retail applications. Their approach focuses on creating lightweight, durable materials for store fixtures and displays using advanced MDI (methylene diphenyl diisocyanate) formulations[1]. Wanhua has also introduced water-based polyurethane dispersions for eco-friendly coatings and adhesives in retail packaging[2]. The company's research has yielded isocyanate-based foam systems with superior insulation properties, contributing to energy-efficient retail spaces[3]. Furthermore, Wanhua has developed specialized isocyanate prepolymers for 3D printing applications, enabling rapid prototyping and customization of retail products and displays[4].
Strengths: Diverse product range, focus on energy efficiency, advanced manufacturing capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns, dependency on petrochemical feedstocks.
Breakthrough Patents in Isocyanate Technology
Modified isocyanates
PatentWO2000020477A1
Innovation
- Development of modified isocyanate derivatives with a crosslinking functional group that remains stable and reacts only under specific conditions, allowing for controlled crosslinking reactions without releasing isocyanate functions prematurely, using cyclic carbonates to form stable polyisocyanates that can react with nucleophilic compounds to create coatings and foams.
Isocyanato-isocyanurates, process for their preparation and their use in polyurethane lacquers as isocyanate component
PatentInactiveEP0039864A1
Innovation
- Development of new isocyanato-isocyanurates with high melting points and improved solvent compatibility through the catalytic trimerization of diisocyanates, specifically using bis-(isocyanatomethyl)-tricyclo[5,2,1,0,2,6]-decane, with quaternary ammonium hydroxides as catalysts, and optionally blocking isocyanate groups for enhanced reactivity and stability.
Environmental Impact of Isocyanates in Retail
The environmental impact of isocyanates in retail is a critical consideration as the industry moves towards more sustainable practices. Isocyanates, widely used in the production of polyurethane foams, coatings, and adhesives, have significant implications for both the environment and human health throughout their lifecycle.
In the manufacturing process, isocyanates can contribute to air pollution if not properly controlled. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted during production can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. This not only affects local air quality but also contributes to broader environmental issues such as climate change.
Water pollution is another concern, particularly if isocyanate-containing waste is not disposed of properly. Runoff from manufacturing sites or improper disposal can contaminate water sources, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and posing risks to human health through contaminated drinking water.
The use of isocyanates in retail products also raises concerns about indoor air quality. Off-gassing from furniture, carpets, and other items containing polyurethane foam can release trace amounts of isocyanates into the air, potentially affecting both retail employees and customers. This is particularly relevant in enclosed retail spaces with limited ventilation.
End-of-life disposal of isocyanate-containing products presents additional environmental challenges. Many polyurethane products are not easily recyclable, contributing to landfill waste. When incinerated, these materials can release toxic fumes, including hydrogen cyanide and other harmful substances.
However, the retail industry is increasingly recognizing these environmental impacts and taking steps to mitigate them. Some retailers are exploring alternative materials with lower environmental footprints, such as bio-based polyurethanes or recycled content foams. Others are implementing stricter supplier guidelines to ensure more environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
Improved waste management strategies are also being developed, including chemical recycling technologies that can break down polyurethane products into their constituent components for reuse. This circular economy approach has the potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of isocyanate-based products in retail.
As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, retailers are under increasing pressure to address the environmental impact of their products and operations. This is driving innovation in product design, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life management strategies for isocyanate-containing goods. The future of retail will likely see a continued shift towards more sustainable alternatives and improved lifecycle management of isocyanate-based products.
In the manufacturing process, isocyanates can contribute to air pollution if not properly controlled. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted during production can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. This not only affects local air quality but also contributes to broader environmental issues such as climate change.
Water pollution is another concern, particularly if isocyanate-containing waste is not disposed of properly. Runoff from manufacturing sites or improper disposal can contaminate water sources, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and posing risks to human health through contaminated drinking water.
The use of isocyanates in retail products also raises concerns about indoor air quality. Off-gassing from furniture, carpets, and other items containing polyurethane foam can release trace amounts of isocyanates into the air, potentially affecting both retail employees and customers. This is particularly relevant in enclosed retail spaces with limited ventilation.
End-of-life disposal of isocyanate-containing products presents additional environmental challenges. Many polyurethane products are not easily recyclable, contributing to landfill waste. When incinerated, these materials can release toxic fumes, including hydrogen cyanide and other harmful substances.
However, the retail industry is increasingly recognizing these environmental impacts and taking steps to mitigate them. Some retailers are exploring alternative materials with lower environmental footprints, such as bio-based polyurethanes or recycled content foams. Others are implementing stricter supplier guidelines to ensure more environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
Improved waste management strategies are also being developed, including chemical recycling technologies that can break down polyurethane products into their constituent components for reuse. This circular economy approach has the potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of isocyanate-based products in retail.
As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, retailers are under increasing pressure to address the environmental impact of their products and operations. This is driving innovation in product design, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life management strategies for isocyanate-containing goods. The future of retail will likely see a continued shift towards more sustainable alternatives and improved lifecycle management of isocyanate-based products.
Safety Regulations for Isocyanate Use in Consumer Products
The use of isocyanates in consumer products has been subject to increasingly stringent safety regulations due to their potential health hazards. These regulations aim to protect consumers, workers, and the environment from exposure to these reactive chemicals. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits for various isocyanates in workplace settings. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has also recommended exposure limits and safety practices for handling isocyanates.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which includes specific provisions for isocyanates. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers must register isocyanates and provide safety data. The EU has also restricted the use of certain isocyanates in consumer products, particularly in spray applications where inhalation exposure is a concern.
In the retail sector, safety regulations for isocyanate-containing products often focus on labeling requirements and restrictions on volatile organic compound (VOC) content. Many jurisdictions require clear hazard warnings and handling instructions on product packaging. Some regions have banned or severely restricted the sale of certain isocyanate-containing products to the general public, limiting their availability to professional users only.
Product-specific regulations have been implemented for items such as furniture, mattresses, and building materials that may contain isocyanates. These regulations often mandate fire safety standards and emissions testing to ensure that products do not release harmful levels of isocyanates during use. In the automotive industry, regulations govern the use of isocyanates in paints, adhesives, and sealants, with a focus on worker protection during manufacturing and repair processes.
As the retail landscape evolves, there is a growing trend towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly products. This has led to the development of alternative materials and formulations that aim to reduce or eliminate the use of isocyanates in consumer goods. Regulatory bodies are increasingly encouraging the adoption of these safer alternatives through incentives and stricter controls on traditional isocyanate-based products.
The future of isocyanate regulations in retail is likely to see further tightening of exposure limits and expanded restrictions on their use in consumer products. There is also a push for more comprehensive lifecycle assessments of isocyanate-containing products, considering their environmental impact from production to disposal. As scientific understanding of the long-term effects of isocyanate exposure grows, regulations are expected to adapt, potentially leading to the phasing out of certain isocyanates in favor of safer substitutes.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which includes specific provisions for isocyanates. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers must register isocyanates and provide safety data. The EU has also restricted the use of certain isocyanates in consumer products, particularly in spray applications where inhalation exposure is a concern.
In the retail sector, safety regulations for isocyanate-containing products often focus on labeling requirements and restrictions on volatile organic compound (VOC) content. Many jurisdictions require clear hazard warnings and handling instructions on product packaging. Some regions have banned or severely restricted the sale of certain isocyanate-containing products to the general public, limiting their availability to professional users only.
Product-specific regulations have been implemented for items such as furniture, mattresses, and building materials that may contain isocyanates. These regulations often mandate fire safety standards and emissions testing to ensure that products do not release harmful levels of isocyanates during use. In the automotive industry, regulations govern the use of isocyanates in paints, adhesives, and sealants, with a focus on worker protection during manufacturing and repair processes.
As the retail landscape evolves, there is a growing trend towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly products. This has led to the development of alternative materials and formulations that aim to reduce or eliminate the use of isocyanates in consumer goods. Regulatory bodies are increasingly encouraging the adoption of these safer alternatives through incentives and stricter controls on traditional isocyanate-based products.
The future of isocyanate regulations in retail is likely to see further tightening of exposure limits and expanded restrictions on their use in consumer products. There is also a push for more comprehensive lifecycle assessments of isocyanate-containing products, considering their environmental impact from production to disposal. As scientific understanding of the long-term effects of isocyanate exposure grows, regulations are expected to adapt, potentially leading to the phasing out of certain isocyanates in favor of safer substitutes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!