How Isocyanates Innovate Beyond Traditional Boundaries?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Evolution
Isocyanates have undergone a remarkable evolution since their discovery in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for polyurethane production, these versatile compounds have continuously expanded their applications across various industries. The timeline of isocyanate evolution showcases significant milestones that have shaped their current status and future potential.
In the 1930s, Otto Bayer's groundbreaking work led to the synthesis of polyurethanes using isocyanates, marking the beginning of a new era in polymer chemistry. This discovery paved the way for the widespread use of isocyanates in foam production, coatings, and adhesives. The 1950s and 1960s saw rapid advancements in isocyanate chemistry, with the development of new formulations and production techniques that enhanced their performance and versatility.
The 1970s brought about a focus on safety and environmental concerns, leading to the development of less volatile and more environmentally friendly isocyanate variants. This period also saw the expansion of isocyanates into new applications, such as automotive parts and construction materials. The 1980s and 1990s witnessed further refinements in isocyanate technology, with improvements in catalysts and processing methods that allowed for more efficient and controlled reactions.
The turn of the millennium marked a new phase in isocyanate evolution, characterized by a push towards sustainability and bio-based alternatives. Researchers began exploring the use of renewable resources to produce isocyanates, aiming to reduce dependence on petrochemical feedstocks. This era also saw the development of novel isocyanate-free technologies that mimicked the properties of traditional isocyanate-based systems.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards smart and functional materials. Isocyanates have been incorporated into self-healing polymers, shape-memory materials, and stimuli-responsive coatings. These innovations have opened up new possibilities in fields such as biomedicine, aerospace, and advanced manufacturing.
The evolution of isocyanates has been marked by continuous improvements in performance, safety, and sustainability. From their humble beginnings in polyurethane production to their current status as key components in cutting-edge materials, isocyanates have demonstrated remarkable adaptability and potential for innovation. As research continues to push the boundaries of isocyanate chemistry, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications and technologies emerge in the coming years.
In the 1930s, Otto Bayer's groundbreaking work led to the synthesis of polyurethanes using isocyanates, marking the beginning of a new era in polymer chemistry. This discovery paved the way for the widespread use of isocyanates in foam production, coatings, and adhesives. The 1950s and 1960s saw rapid advancements in isocyanate chemistry, with the development of new formulations and production techniques that enhanced their performance and versatility.
The 1970s brought about a focus on safety and environmental concerns, leading to the development of less volatile and more environmentally friendly isocyanate variants. This period also saw the expansion of isocyanates into new applications, such as automotive parts and construction materials. The 1980s and 1990s witnessed further refinements in isocyanate technology, with improvements in catalysts and processing methods that allowed for more efficient and controlled reactions.
The turn of the millennium marked a new phase in isocyanate evolution, characterized by a push towards sustainability and bio-based alternatives. Researchers began exploring the use of renewable resources to produce isocyanates, aiming to reduce dependence on petrochemical feedstocks. This era also saw the development of novel isocyanate-free technologies that mimicked the properties of traditional isocyanate-based systems.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards smart and functional materials. Isocyanates have been incorporated into self-healing polymers, shape-memory materials, and stimuli-responsive coatings. These innovations have opened up new possibilities in fields such as biomedicine, aerospace, and advanced manufacturing.
The evolution of isocyanates has been marked by continuous improvements in performance, safety, and sustainability. From their humble beginnings in polyurethane production to their current status as key components in cutting-edge materials, isocyanates have demonstrated remarkable adaptability and potential for innovation. As research continues to push the boundaries of isocyanate chemistry, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications and technologies emerge in the coming years.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for isocyanates continues to evolve beyond traditional applications, driven by innovative uses across various industries. Historically, isocyanates have been primarily utilized in polyurethane production for foam insulation, coatings, and adhesives. However, recent market trends indicate a significant expansion into new sectors, creating diverse opportunities for growth and technological advancement.
In the automotive industry, there is a growing demand for lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Isocyanate-based composites and structural adhesives are increasingly replacing traditional metal components, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios. This shift is expected to drive substantial market growth in the coming years as automakers strive to meet stringent environmental regulations.
The construction sector presents another area of expanding demand for isocyanates. With the global focus on energy efficiency and sustainable building practices, there is a rising need for high-performance insulation materials. Spray polyurethane foam, which relies heavily on isocyanates, is gaining popularity due to its excellent insulating properties and ability to seal air leaks effectively.
In the medical field, isocyanates are finding novel applications in the development of advanced wound dressings and biomedical devices. The unique properties of isocyanate-based materials, such as controlled biodegradability and customizable mechanical characteristics, make them ideal for tissue engineering and drug delivery systems. This emerging market segment shows promising growth potential as healthcare providers seek innovative solutions for patient care.
The electronics industry is another sector where isocyanates are making significant inroads. With the miniaturization of electronic devices and the increasing demand for flexible displays, isocyanate-based materials are being used to create thin, durable coatings and encapsulants. These applications protect sensitive components from environmental factors while maintaining the flexibility required for cutting-edge device designs.
Market analysis suggests that the Asia-Pacific region will be a key driver of growth in the isocyanate market. Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in countries like China and India are fueling demand across multiple sectors. Additionally, the shift of manufacturing bases to these regions is expected to further boost consumption of isocyanate-based products.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges related to environmental and health concerns associated with certain isocyanates. This has led to increased research and development efforts focused on creating safer, more sustainable alternatives. Bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources are gaining attention as potential substitutes, aligning with the global trend towards eco-friendly materials.
In the automotive industry, there is a growing demand for lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Isocyanate-based composites and structural adhesives are increasingly replacing traditional metal components, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios. This shift is expected to drive substantial market growth in the coming years as automakers strive to meet stringent environmental regulations.
The construction sector presents another area of expanding demand for isocyanates. With the global focus on energy efficiency and sustainable building practices, there is a rising need for high-performance insulation materials. Spray polyurethane foam, which relies heavily on isocyanates, is gaining popularity due to its excellent insulating properties and ability to seal air leaks effectively.
In the medical field, isocyanates are finding novel applications in the development of advanced wound dressings and biomedical devices. The unique properties of isocyanate-based materials, such as controlled biodegradability and customizable mechanical characteristics, make them ideal for tissue engineering and drug delivery systems. This emerging market segment shows promising growth potential as healthcare providers seek innovative solutions for patient care.
The electronics industry is another sector where isocyanates are making significant inroads. With the miniaturization of electronic devices and the increasing demand for flexible displays, isocyanate-based materials are being used to create thin, durable coatings and encapsulants. These applications protect sensitive components from environmental factors while maintaining the flexibility required for cutting-edge device designs.
Market analysis suggests that the Asia-Pacific region will be a key driver of growth in the isocyanate market. Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in countries like China and India are fueling demand across multiple sectors. Additionally, the shift of manufacturing bases to these regions is expected to further boost consumption of isocyanate-based products.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges related to environmental and health concerns associated with certain isocyanates. This has led to increased research and development efforts focused on creating safer, more sustainable alternatives. Bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources are gaining attention as potential substitutes, aligning with the global trend towards eco-friendly materials.
Technical Challenges
Isocyanates, while versatile and widely used in various industries, face significant technical challenges that limit their innovation potential beyond traditional boundaries. One of the primary obstacles is their high reactivity with water, which can lead to undesired side reactions and reduced product quality. This sensitivity to moisture necessitates stringent handling and storage conditions, increasing production costs and complexity.
Another major challenge is the toxicity of isocyanates, particularly their potential to cause respiratory sensitization and occupational asthma. This health concern has led to increased regulatory scrutiny and the need for enhanced safety measures in manufacturing and application processes. The development of safer alternatives or improved handling techniques remains a critical area for innovation.
The environmental impact of isocyanates also presents a significant hurdle. Many isocyanate-based products, such as polyurethane foams, are difficult to recycle or dispose of in an environmentally friendly manner. This challenge is particularly pressing in light of growing global emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles.
Furthermore, the dependence of isocyanate production on fossil fuel-derived raw materials poses long-term sustainability concerns. As the world moves towards renewable resources, finding bio-based alternatives or developing more sustainable production methods for isocyanates becomes increasingly important.
The limited shelf life of some isocyanate products, due to their reactivity, also presents challenges in storage, transportation, and application. This instability can lead to quality issues and increased waste, necessitating the development of more stable formulations or improved stabilization techniques.
In the realm of performance, while isocyanates offer excellent properties in many applications, there is a constant demand for materials with enhanced characteristics. Improving properties such as heat resistance, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength without compromising other beneficial attributes remains a significant technical challenge.
Lastly, the complexity of isocyanate chemistry poses challenges in precise control and customization of reactions, particularly in advanced applications such as 3D printing or smart materials. Developing methods for finer control over reaction kinetics and product properties could open up new avenues for innovation beyond traditional boundaries.
Another major challenge is the toxicity of isocyanates, particularly their potential to cause respiratory sensitization and occupational asthma. This health concern has led to increased regulatory scrutiny and the need for enhanced safety measures in manufacturing and application processes. The development of safer alternatives or improved handling techniques remains a critical area for innovation.
The environmental impact of isocyanates also presents a significant hurdle. Many isocyanate-based products, such as polyurethane foams, are difficult to recycle or dispose of in an environmentally friendly manner. This challenge is particularly pressing in light of growing global emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles.
Furthermore, the dependence of isocyanate production on fossil fuel-derived raw materials poses long-term sustainability concerns. As the world moves towards renewable resources, finding bio-based alternatives or developing more sustainable production methods for isocyanates becomes increasingly important.
The limited shelf life of some isocyanate products, due to their reactivity, also presents challenges in storage, transportation, and application. This instability can lead to quality issues and increased waste, necessitating the development of more stable formulations or improved stabilization techniques.
In the realm of performance, while isocyanates offer excellent properties in many applications, there is a constant demand for materials with enhanced characteristics. Improving properties such as heat resistance, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength without compromising other beneficial attributes remains a significant technical challenge.
Lastly, the complexity of isocyanate chemistry poses challenges in precise control and customization of reactions, particularly in advanced applications such as 3D printing or smart materials. Developing methods for finer control over reaction kinetics and product properties could open up new avenues for innovation beyond traditional boundaries.
Current Applications
01 Synthesis and production of isocyanates
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel reaction pathways, catalysts, and production techniques to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate manufacturing.- Synthesis and production of isocyanates: Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel catalysts, reaction conditions, and precursor materials to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate production.
- Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry: Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents describe various applications, including coatings, adhesives, foams, and elastomers, as well as novel formulations and processing techniques.
- Isocyanate-based catalysts and additives: Several patents focus on the development of isocyanate-based catalysts and additives for various chemical processes. These include novel compounds and formulations that enhance reaction rates, selectivity, or product properties in different applications.
- Safety and handling of isocyanates: Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, patents in this category address safety concerns and improved handling methods. This includes storage techniques, exposure prevention, and the development of less hazardous isocyanate derivatives or alternatives.
- Isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes: Some patents focus on developing alternatives to traditional isocyanates, addressing environmental and health concerns. These include novel chemistries, bio-based materials, and modified production processes that aim to reduce or eliminate the use of conventional isocyanates.
02 Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry
Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents discuss various applications, including coatings, adhesives, foams, and elastomers, as well as novel formulations and processing techniques.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate-based catalysts and reaction modifiers
Several patents focus on the development of isocyanate-based catalysts and reaction modifiers. These compounds are used to enhance chemical reactions, improve product properties, or facilitate specific industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety and handling of isocyanates
Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, patents in this category address safety concerns and handling procedures. This includes methods for reducing toxicity, improving storage stability, and developing safer formulations for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes
Some patents explore alternatives to traditional isocyanates, aiming to develop more environmentally friendly or less hazardous options. This includes novel compounds, formulations, or processes that can replace isocyanates in certain applications while maintaining desired properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The isocyanates market is in a mature growth phase, characterized by steady demand and established applications across various industries. The global market size is estimated to be in the billions of dollars, driven by increasing use in polyurethane production for automotive, construction, and furniture sectors. Technologically, isocyanates are well-developed, with major players like BASF, Wanhua Chemical, and Covestro leading innovation. These companies are focusing on developing more sustainable and eco-friendly isocyanate products to address environmental concerns. Emerging players such as Econic Technologies are exploring novel catalysts to incorporate CO2 into polymer production, potentially revolutionizing the industry. The competitive landscape is intense, with established chemical giants competing on scale, efficiency, and product diversification.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed innovative isocyanate-based solutions that extend beyond traditional applications. Their approach includes the creation of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels[1]. They have also pioneered water-borne polyurethane dispersions using novel isocyanate chemistry, enabling low-VOC coatings with enhanced performance[2]. BASF's research has led to the development of isocyanate-functional nanoparticles, which offer unique properties for advanced materials and coatings[3]. Additionally, they have made strides in isocyanate-free polyurethane technologies, addressing health and environmental concerns while maintaining performance characteristics[4].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, diverse product portfolio, and focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges and market competition in eco-friendly alternatives.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
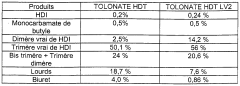
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has made significant advancements in isocyanate technology, particularly in the field of methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) production. They have developed a proprietary gas-phase phosgenation process that improves efficiency and reduces environmental impact[5]. Wanhua has also innovated in the area of aliphatic isocyanates, creating high-performance coatings with improved weatherability and UV resistance[6]. Their research extends to novel isocyanate-terminated prepolymers for specialized adhesives and sealants, offering enhanced flexibility and durability[7]. Furthermore, Wanhua has explored the use of isocyanates in the production of high-performance thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPUs) for emerging applications in 3D printing and wearable technologies[8].
Strengths: Leading MDI producer, innovative production processes, and expanding product range. Weaknesses: Heavy reliance on MDI market, potential overcapacity issues in the industry.
Breakthrough Patents
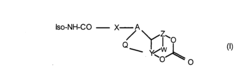
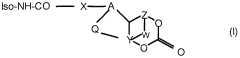
Modified isocyanates
PatentInactiveEP1382626A1
Innovation
- Development of modified isocyanate derivatives with a crosslinking functional group that remains stable at low temperatures and only reacts at high temperatures, allowing for controlled crosslinking reactions without the need for masking agents, using cyclic carbonates to form stable polyisocyanates that can react with nucleophilic compounds to form coatings and polymers.
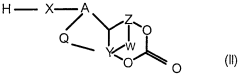
Modified isocyanates
PatentWO2000020477A1
Innovation
- Development of modified isocyanate derivatives with a crosslinking functional group that remains stable and reacts only under specific conditions, allowing for controlled crosslinking reactions without releasing isocyanate functions prematurely, using cyclic carbonates to form stable polyisocyanates that can react with nucleophilic compounds to create coatings and foams.
Environmental Impact
Isocyanates, widely used in the production of polyurethanes, have long been associated with environmental concerns due to their potential toxicity and reactivity. However, recent innovations are pushing isocyanates beyond traditional boundaries, particularly in terms of their environmental impact. These advancements are addressing key issues such as volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, energy consumption, and waste reduction.
One significant area of innovation is the development of water-based isocyanate systems. These formulations drastically reduce VOC emissions compared to traditional solvent-based systems, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. The shift towards water-based technologies not only minimizes air pollution but also enhances workplace safety by reducing exposure risks for workers in manufacturing settings.
Another breakthrough in isocyanate technology is the creation of bio-based alternatives. Researchers are exploring the use of renewable resources, such as plant-based oils and agricultural waste, to synthesize isocyanates. This approach not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also contributes to a more circular economy by utilizing waste materials. Bio-based isocyanates have shown promising results in terms of performance and environmental footprint, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional petrochemical-derived products.
Energy efficiency is another frontier where isocyanates are making strides. Advanced catalysts and process optimizations are enabling lower reaction temperatures and shorter curing times, significantly reducing energy consumption in polyurethane production. These improvements not only decrease the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes but also lead to cost savings for producers.
Recycling and end-of-life considerations are also driving innovation in isocyanate chemistry. New technologies are emerging that allow for the efficient breakdown and recovery of polyurethane materials, enabling the reuse of isocyanate components. This closed-loop approach minimizes waste and reduces the environmental impact associated with disposal of polyurethane products.
Furthermore, the development of non-toxic and low-hazard isocyanate alternatives is gaining momentum. These novel compounds aim to maintain the desirable properties of traditional isocyanates while eliminating or reducing health and environmental risks. Such innovations are particularly crucial for applications in sensitive environments or consumer products where safety concerns are paramount.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of isocyanates is being transformed through a combination of chemical innovations, process improvements, and sustainable sourcing strategies. These advancements are not only addressing historical environmental concerns but are also opening new possibilities for the use of isocyanates in environmentally conscious applications, demonstrating the potential for this versatile class of compounds to contribute to a more sustainable future.
One significant area of innovation is the development of water-based isocyanate systems. These formulations drastically reduce VOC emissions compared to traditional solvent-based systems, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. The shift towards water-based technologies not only minimizes air pollution but also enhances workplace safety by reducing exposure risks for workers in manufacturing settings.
Another breakthrough in isocyanate technology is the creation of bio-based alternatives. Researchers are exploring the use of renewable resources, such as plant-based oils and agricultural waste, to synthesize isocyanates. This approach not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also contributes to a more circular economy by utilizing waste materials. Bio-based isocyanates have shown promising results in terms of performance and environmental footprint, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional petrochemical-derived products.
Energy efficiency is another frontier where isocyanates are making strides. Advanced catalysts and process optimizations are enabling lower reaction temperatures and shorter curing times, significantly reducing energy consumption in polyurethane production. These improvements not only decrease the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes but also lead to cost savings for producers.
Recycling and end-of-life considerations are also driving innovation in isocyanate chemistry. New technologies are emerging that allow for the efficient breakdown and recovery of polyurethane materials, enabling the reuse of isocyanate components. This closed-loop approach minimizes waste and reduces the environmental impact associated with disposal of polyurethane products.
Furthermore, the development of non-toxic and low-hazard isocyanate alternatives is gaining momentum. These novel compounds aim to maintain the desirable properties of traditional isocyanates while eliminating or reducing health and environmental risks. Such innovations are particularly crucial for applications in sensitive environments or consumer products where safety concerns are paramount.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of isocyanates is being transformed through a combination of chemical innovations, process improvements, and sustainable sourcing strategies. These advancements are not only addressing historical environmental concerns but are also opening new possibilities for the use of isocyanates in environmentally conscious applications, demonstrating the potential for this versatile class of compounds to contribute to a more sustainable future.
Cross-Industry Potential
Isocyanates, traditionally known for their role in polyurethane production, are now breaking boundaries and finding innovative applications across diverse industries. This cross-industry potential is driving new research and development efforts, opening up exciting possibilities for material science and product innovation.
In the automotive sector, isocyanates are revolutionizing lightweight materials. Advanced composites incorporating isocyanate-based resins offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, enhancing fuel efficiency and performance. These materials are also being explored for electric vehicle battery enclosures, providing both structural integrity and thermal management properties.
The construction industry is leveraging isocyanates to develop high-performance insulation materials. Spray polyurethane foam, derived from isocyanates, is gaining popularity for its excellent thermal insulation properties and ability to seal buildings effectively. This technology is contributing to energy-efficient building designs and sustainable construction practices.
In the medical field, isocyanates are finding novel applications in biocompatible materials. Researchers are developing isocyanate-based hydrogels for drug delivery systems and tissue engineering scaffolds. These materials offer tunable properties, allowing for controlled release of medications and support for cell growth in regenerative medicine.
The aerospace industry is exploring isocyanate-based composites for next-generation aircraft components. These materials offer a combination of lightweight properties, high strength, and resistance to extreme temperatures, making them ideal for use in aircraft structures and interiors.
In the electronics sector, isocyanates are contributing to the development of flexible and durable coatings for electronic devices. These coatings provide protection against moisture, dust, and mechanical stress, extending the lifespan of electronic products and enabling new form factors in wearable technology.
The textile industry is incorporating isocyanate-based materials to create smart fabrics with enhanced properties. These include water-repellent finishes, breathable membranes, and self-healing textiles, opening up new possibilities in sportswear, protective clothing, and technical textiles.
As isocyanates continue to innovate beyond their traditional boundaries, interdisciplinary collaboration is becoming increasingly important. Materials scientists, chemists, and engineers from various fields are working together to unlock the full potential of isocyanates across industries. This cross-pollination of ideas is driving rapid advancements and creating new opportunities for sustainable and high-performance materials in diverse applications.
In the automotive sector, isocyanates are revolutionizing lightweight materials. Advanced composites incorporating isocyanate-based resins offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, enhancing fuel efficiency and performance. These materials are also being explored for electric vehicle battery enclosures, providing both structural integrity and thermal management properties.
The construction industry is leveraging isocyanates to develop high-performance insulation materials. Spray polyurethane foam, derived from isocyanates, is gaining popularity for its excellent thermal insulation properties and ability to seal buildings effectively. This technology is contributing to energy-efficient building designs and sustainable construction practices.
In the medical field, isocyanates are finding novel applications in biocompatible materials. Researchers are developing isocyanate-based hydrogels for drug delivery systems and tissue engineering scaffolds. These materials offer tunable properties, allowing for controlled release of medications and support for cell growth in regenerative medicine.
The aerospace industry is exploring isocyanate-based composites for next-generation aircraft components. These materials offer a combination of lightweight properties, high strength, and resistance to extreme temperatures, making them ideal for use in aircraft structures and interiors.
In the electronics sector, isocyanates are contributing to the development of flexible and durable coatings for electronic devices. These coatings provide protection against moisture, dust, and mechanical stress, extending the lifespan of electronic products and enabling new form factors in wearable technology.
The textile industry is incorporating isocyanate-based materials to create smart fabrics with enhanced properties. These include water-repellent finishes, breathable membranes, and self-healing textiles, opening up new possibilities in sportswear, protective clothing, and technical textiles.
As isocyanates continue to innovate beyond their traditional boundaries, interdisciplinary collaboration is becoming increasingly important. Materials scientists, chemists, and engineers from various fields are working together to unlock the full potential of isocyanates across industries. This cross-pollination of ideas is driving rapid advancements and creating new opportunities for sustainable and high-performance materials in diverse applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!