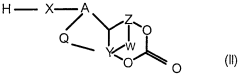
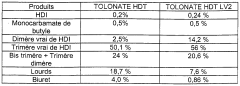
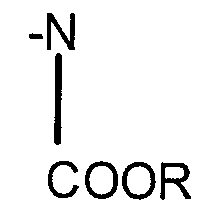How Isocyanates Stimulate Sustainable Business Growth?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Technology Evolution and Objectives
Isocyanates have played a pivotal role in the chemical industry since their discovery in the early 20th century. The evolution of isocyanate technology has been marked by continuous innovation and adaptation to meet changing market demands and environmental concerns. Initially developed for their reactivity with various compounds, isocyanates quickly found applications in the production of polyurethanes, a versatile class of materials that revolutionized multiple industries.
The technological trajectory of isocyanates has been driven by the pursuit of enhanced performance, cost-effectiveness, and increasingly, sustainability. Early developments focused on improving the synthesis and purification processes of isocyanates, leading to more efficient production methods and higher-quality end products. As the potential of isocyanates became apparent, research efforts expanded to explore new molecular structures and formulations, resulting in a diverse range of isocyanate-based materials with tailored properties.
In recent decades, the objectives of isocyanate technology have shifted significantly towards addressing environmental and health concerns. This has led to the development of low-emission and zero-emission isocyanates, as well as bio-based alternatives that reduce reliance on fossil fuels. The industry has also made strides in improving the safety profile of isocyanates, both in production and end-use applications, through advanced handling techniques and protective measures.
The current technological landscape of isocyanates is characterized by a focus on sustainable growth and circular economy principles. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring ways to incorporate recycled materials into isocyanate production, develop more efficient catalysts for polymerization, and create products that are easier to recycle or biodegrade at the end of their lifecycle. These efforts align with global sustainability goals and position isocyanates as a key enabler of green technologies in various sectors.
Looking forward, the objectives of isocyanate technology are multifaceted. There is a strong emphasis on developing 'smart' isocyanate-based materials that can respond to environmental stimuli, self-heal, or change properties on demand. Additionally, the integration of isocyanates with emerging technologies such as 3D printing and nanotechnology is opening new avenues for innovation and application. The industry is also investing in digital technologies to optimize production processes, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency in the isocyanate value chain.
As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, the isocyanate industry is poised to play a crucial role in enabling this transition. The technology's evolution is now guided by the principles of green chemistry, with objectives centered on minimizing environmental impact while maximizing economic value. This includes the development of isocyanates that can contribute to energy-efficient buildings, lightweight vehicles, and advanced medical devices, all of which are essential for sustainable business growth in the 21st century.
The technological trajectory of isocyanates has been driven by the pursuit of enhanced performance, cost-effectiveness, and increasingly, sustainability. Early developments focused on improving the synthesis and purification processes of isocyanates, leading to more efficient production methods and higher-quality end products. As the potential of isocyanates became apparent, research efforts expanded to explore new molecular structures and formulations, resulting in a diverse range of isocyanate-based materials with tailored properties.
In recent decades, the objectives of isocyanate technology have shifted significantly towards addressing environmental and health concerns. This has led to the development of low-emission and zero-emission isocyanates, as well as bio-based alternatives that reduce reliance on fossil fuels. The industry has also made strides in improving the safety profile of isocyanates, both in production and end-use applications, through advanced handling techniques and protective measures.
The current technological landscape of isocyanates is characterized by a focus on sustainable growth and circular economy principles. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring ways to incorporate recycled materials into isocyanate production, develop more efficient catalysts for polymerization, and create products that are easier to recycle or biodegrade at the end of their lifecycle. These efforts align with global sustainability goals and position isocyanates as a key enabler of green technologies in various sectors.
Looking forward, the objectives of isocyanate technology are multifaceted. There is a strong emphasis on developing 'smart' isocyanate-based materials that can respond to environmental stimuli, self-heal, or change properties on demand. Additionally, the integration of isocyanates with emerging technologies such as 3D printing and nanotechnology is opening new avenues for innovation and application. The industry is also investing in digital technologies to optimize production processes, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency in the isocyanate value chain.
As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, the isocyanate industry is poised to play a crucial role in enabling this transition. The technology's evolution is now guided by the principles of green chemistry, with objectives centered on minimizing environmental impact while maximizing economic value. This includes the development of isocyanates that can contribute to energy-efficient buildings, lightweight vehicles, and advanced medical devices, all of which are essential for sustainable business growth in the 21st century.
Market Demand for Sustainable Isocyanate Products
The market demand for sustainable isocyanate products has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness and stringent regulations. Isocyanates, widely used in the production of polyurethanes, have traditionally been associated with environmental and health concerns. However, the shift towards sustainability has created new opportunities for eco-friendly isocyanate-based products.
In the construction sector, there is a rising demand for sustainable insulation materials. Isocyanate-based rigid foams offer excellent thermal insulation properties while contributing to energy efficiency in buildings. The market for these products is expected to expand as governments worldwide implement stricter energy conservation standards for new and existing structures.
The automotive industry is another key driver of sustainable isocyanate product demand. Lightweight materials are crucial for improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Isocyanate-based composites and foams play a significant role in vehicle weight reduction without compromising safety or performance. As electric vehicles gain popularity, the demand for these materials is likely to increase further.
Furniture and bedding manufacturers are also turning to sustainable isocyanate products. Bio-based polyols derived from renewable sources, when combined with isocyanates, produce more environmentally friendly foams for mattresses and upholstery. Consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for products with reduced environmental impact, driving market growth in this sector.
The packaging industry is exploring sustainable isocyanate-based adhesives and coatings. These products offer improved recyclability and biodegradability compared to traditional alternatives. As companies face pressure to reduce plastic waste and improve packaging sustainability, the demand for these innovative solutions is expected to rise.
In the textile industry, waterproof and breathable fabrics made with sustainable isocyanate-based coatings are gaining traction. These materials find applications in outdoor apparel, sportswear, and protective clothing. The market for such products is expanding as consumers seek high-performance, eco-friendly clothing options.
The medical sector presents another growth area for sustainable isocyanate products. Biocompatible polyurethanes are used in various medical devices and implants. As the healthcare industry focuses on reducing its environmental footprint, the demand for sustainable alternatives in this field is likely to increase.
While the market for sustainable isocyanate products shows promising growth, challenges remain. The higher cost of production compared to conventional isocyanates can be a barrier to widespread adoption. However, as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, this gap is expected to narrow, further stimulating market demand across various industries.
In the construction sector, there is a rising demand for sustainable insulation materials. Isocyanate-based rigid foams offer excellent thermal insulation properties while contributing to energy efficiency in buildings. The market for these products is expected to expand as governments worldwide implement stricter energy conservation standards for new and existing structures.
The automotive industry is another key driver of sustainable isocyanate product demand. Lightweight materials are crucial for improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Isocyanate-based composites and foams play a significant role in vehicle weight reduction without compromising safety or performance. As electric vehicles gain popularity, the demand for these materials is likely to increase further.
Furniture and bedding manufacturers are also turning to sustainable isocyanate products. Bio-based polyols derived from renewable sources, when combined with isocyanates, produce more environmentally friendly foams for mattresses and upholstery. Consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for products with reduced environmental impact, driving market growth in this sector.
The packaging industry is exploring sustainable isocyanate-based adhesives and coatings. These products offer improved recyclability and biodegradability compared to traditional alternatives. As companies face pressure to reduce plastic waste and improve packaging sustainability, the demand for these innovative solutions is expected to rise.
In the textile industry, waterproof and breathable fabrics made with sustainable isocyanate-based coatings are gaining traction. These materials find applications in outdoor apparel, sportswear, and protective clothing. The market for such products is expanding as consumers seek high-performance, eco-friendly clothing options.
The medical sector presents another growth area for sustainable isocyanate products. Biocompatible polyurethanes are used in various medical devices and implants. As the healthcare industry focuses on reducing its environmental footprint, the demand for sustainable alternatives in this field is likely to increase.
While the market for sustainable isocyanate products shows promising growth, challenges remain. The higher cost of production compared to conventional isocyanates can be a barrier to widespread adoption. However, as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, this gap is expected to narrow, further stimulating market demand across various industries.
Current Challenges in Isocyanate Sustainability
The isocyanate industry faces significant challenges in achieving sustainability, primarily due to environmental and health concerns associated with these chemicals. One of the main issues is the toxicity of isocyanates, which can cause respiratory problems and skin irritation upon exposure. This has led to increased regulatory scrutiny and pressure to develop safer alternatives or improved handling methods.
Another major challenge is the environmental impact of isocyanate production and use. The manufacturing process often involves the use of fossil fuel-based raw materials, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. Additionally, the disposal of isocyanate-containing products at the end of their lifecycle can lead to pollution if not managed properly.
The industry is also grappling with the need to reduce its carbon footprint and energy consumption. Traditional isocyanate production methods are energy-intensive, and there is a growing demand for more efficient, sustainable processes. This includes exploring renewable feedstocks and developing bio-based isocyanates to decrease reliance on petrochemicals.
Waste reduction and circular economy principles present another set of challenges. The current linear model of production, use, and disposal is increasingly seen as unsustainable. Companies are now tasked with finding ways to recycle or repurpose isocyanate-based products, which can be technically challenging due to the complex chemical structures involved.
Supply chain sustainability is an emerging concern, with stakeholders demanding greater transparency and traceability. Ensuring responsible sourcing of raw materials and ethical production practices throughout the supply chain is becoming crucial for maintaining consumer trust and meeting regulatory requirements.
Water usage and management in isocyanate production also pose sustainability challenges. The industry needs to address water consumption, treatment of wastewater, and prevention of water pollution to align with sustainable development goals.
Lastly, the industry faces the challenge of balancing sustainability efforts with economic viability. Implementing more sustainable practices often requires significant investment in research, technology, and infrastructure. Companies must find ways to innovate while maintaining competitiveness in a market that still largely prioritizes cost-effectiveness over environmental considerations.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving technological innovation, policy changes, and industry-wide collaboration. As the demand for sustainable solutions grows, the isocyanate industry must adapt to ensure its long-term viability and contribute positively to global sustainability efforts.
Another major challenge is the environmental impact of isocyanate production and use. The manufacturing process often involves the use of fossil fuel-based raw materials, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. Additionally, the disposal of isocyanate-containing products at the end of their lifecycle can lead to pollution if not managed properly.
The industry is also grappling with the need to reduce its carbon footprint and energy consumption. Traditional isocyanate production methods are energy-intensive, and there is a growing demand for more efficient, sustainable processes. This includes exploring renewable feedstocks and developing bio-based isocyanates to decrease reliance on petrochemicals.
Waste reduction and circular economy principles present another set of challenges. The current linear model of production, use, and disposal is increasingly seen as unsustainable. Companies are now tasked with finding ways to recycle or repurpose isocyanate-based products, which can be technically challenging due to the complex chemical structures involved.
Supply chain sustainability is an emerging concern, with stakeholders demanding greater transparency and traceability. Ensuring responsible sourcing of raw materials and ethical production practices throughout the supply chain is becoming crucial for maintaining consumer trust and meeting regulatory requirements.
Water usage and management in isocyanate production also pose sustainability challenges. The industry needs to address water consumption, treatment of wastewater, and prevention of water pollution to align with sustainable development goals.
Lastly, the industry faces the challenge of balancing sustainability efforts with economic viability. Implementing more sustainable practices often requires significant investment in research, technology, and infrastructure. Companies must find ways to innovate while maintaining competitiveness in a market that still largely prioritizes cost-effectiveness over environmental considerations.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving technological innovation, policy changes, and industry-wide collaboration. As the demand for sustainable solutions grows, the isocyanate industry must adapt to ensure its long-term viability and contribute positively to global sustainability efforts.
Existing Sustainable Isocyanate Solutions
01 Market analysis and forecasting for isocyanates
Utilizing data analytics and market research to analyze trends, forecast demand, and identify growth opportunities in the isocyanates industry. This approach helps businesses make informed decisions about production, pricing, and expansion strategies.- Market analysis and forecasting for isocyanates: Utilizing data analytics and market research to analyze trends, forecast demand, and identify growth opportunities in the isocyanates industry. This approach helps businesses make informed decisions about production, investment, and expansion strategies.
- Innovation in isocyanate production processes: Developing and implementing new technologies and processes to improve the efficiency and sustainability of isocyanate production. This includes optimizing reaction conditions, exploring alternative raw materials, and reducing environmental impact to drive business growth.
- Expanding applications of isocyanates: Exploring and developing new applications for isocyanates in various industries such as automotive, construction, and electronics. This diversification strategy helps to create new market opportunities and drive business growth in the isocyanates sector.
- Strategic partnerships and collaborations: Forming strategic alliances with suppliers, customers, and research institutions to enhance product development, improve supply chain efficiency, and expand market reach. These partnerships can lead to synergies that drive growth in the isocyanates business.
- Sustainable and eco-friendly isocyanate solutions: Developing and promoting environmentally friendly isocyanate products and production methods to meet growing demand for sustainable solutions. This approach addresses regulatory requirements and consumer preferences, potentially opening new markets and driving business growth.
02 Innovation in isocyanate production processes
Developing and implementing new technologies and methods to improve the efficiency and sustainability of isocyanate production. This includes optimizing reaction conditions, reducing waste, and exploring alternative raw materials to enhance competitiveness and meet growing market demands.Expand Specific Solutions03 Expansion of isocyanate applications
Exploring and developing new applications for isocyanates in various industries, such as construction, automotive, and electronics. This strategy focuses on diversifying product offerings and entering new markets to drive business growth.Expand Specific Solutions04 Strategic partnerships and collaborations
Forming alliances with other companies, research institutions, and industry stakeholders to leverage complementary strengths, share resources, and accelerate innovation in the isocyanates sector. This approach can lead to new product developments and market expansion opportunities.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sustainable and eco-friendly isocyanate solutions
Developing environmentally friendly isocyanate products and production processes to meet growing consumer demand for sustainable materials. This includes reducing carbon footprint, minimizing harmful emissions, and exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional isocyanates.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Isocyanate Production
The isocyanates market is in a mature growth phase, characterized by steady demand and established applications across various industries. The global market size for isocyanates is projected to reach significant figures, driven by increasing use in polyurethane production for automotive, construction, and furniture sectors. Technologically, isocyanates are well-developed, with major players like Wanhua Chemical Group, BASF, and Covestro leading innovation. These companies are focusing on sustainable isocyanate production methods and bio-based alternatives to address environmental concerns. Emerging players such as Mitsui Chemicals and Asahi Kasei are also contributing to technological advancements, particularly in specialty isocyanates for high-performance applications. The competitive landscape is intensifying as companies invest in R&D to develop eco-friendly solutions and expand their product portfolios.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has developed innovative isocyanate-based solutions for sustainable business growth. Their approach includes the production of bio-based polyurethanes using isocyanates derived from renewable resources[1]. They have also implemented a closed-loop recycling system for polyurethane materials, reducing waste and improving resource efficiency[2]. Additionally, Wanhua has invested in energy-efficient production processes, reducing the carbon footprint of isocyanate manufacturing by up to 30% compared to traditional methods[3]. The company has also developed water-based polyurethane dispersions, which offer lower VOC emissions and improved environmental performance in various applications[4].
Strengths: Strong focus on sustainability, innovative bio-based solutions, and efficient production processes. Weaknesses: Potential dependency on specific raw materials and market fluctuations in the renewable resources sector.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a comprehensive strategy for sustainable isocyanate production and utilization. They have introduced a novel catalytic process that reduces energy consumption in isocyanate synthesis by up to 40%[5]. BASF has also pioneered the use of CO2 as a raw material in polyurethane production, effectively reducing the carbon footprint of their isocyanate-based products[6]. The company has implemented a circular economy approach, developing technologies for chemical recycling of polyurethane waste back into isocyanates[7]. Furthermore, BASF has created bio-based isocyanates derived from castor oil, offering a renewable alternative to traditional petrochemical-based products[8].
Strengths: Diverse portfolio of sustainable solutions, strong R&D capabilities, and established market presence. Weaknesses: High investment costs for new technologies and potential challenges in scaling up novel processes.
Innovative Approaches in Green Isocyanate Chemistry
Sustainable preparation of organic amino compounds for the production of organic isocyanates
PatentWO2024017890A2
Innovation
- A process using green hydrogen and green ammonia to produce organic amino compounds, which are then used to synthesize isocyanates, incorporating renewable energy sources and reducing waste through closed-loop recycling of materials.
Modified isocyanates
PatentWO2000020477A1
Innovation
- Development of modified isocyanate derivatives with a crosslinking functional group that remains stable and reacts only under specific conditions, allowing for controlled crosslinking reactions without releasing isocyanate functions prematurely, using cyclic carbonates to form stable polyisocyanates that can react with nucleophilic compounds to create coatings and foams.
Environmental Regulations Impact on Isocyanates
Environmental regulations have significantly impacted the isocyanates industry, driving sustainable business growth through innovation and adaptation. Stringent regulations, particularly in developed countries, have forced manufacturers to invest in cleaner production processes and develop more environmentally friendly products.
The implementation of the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the European Union has been a major catalyst for change. This comprehensive regulatory framework has required isocyanate producers to thoroughly assess and document the environmental and health impacts of their products. As a result, companies have invested heavily in research and development to create safer alternatives and improve existing formulations.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has also tightened regulations on isocyanates, particularly concerning air quality and worker safety. These regulations have prompted manufacturers to adopt advanced emission control technologies and implement more robust safety protocols in their production facilities. This has not only improved environmental performance but also enhanced worker safety and productivity.
The increasing focus on sustainability has led to the development of bio-based isocyanates, derived from renewable resources such as vegetable oils. These innovative products offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based isocyanates, opening up new market opportunities and positioning companies at the forefront of sustainable chemistry.
Regulatory pressure has also driven improvements in product design and application techniques. For instance, the development of low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations has enabled isocyanate-based products to comply with increasingly strict air quality regulations. This has allowed manufacturers to maintain their market presence in sectors such as construction and automotive, where environmental standards are becoming more stringent.
The circular economy concept has gained traction in the isocyanates industry, partly due to regulatory incentives. Companies are exploring ways to recycle and reuse isocyanate-based products, reducing waste and improving resource efficiency. This approach not only helps meet regulatory requirements but also creates new business models and revenue streams.
As regulations continue to evolve, isocyanate manufacturers are increasingly adopting a proactive approach to compliance. Many companies are going beyond minimum requirements, anticipating future regulatory trends and positioning themselves as industry leaders in sustainability. This forward-thinking strategy has led to increased investment in green chemistry initiatives and the development of more sustainable production processes.
The implementation of the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the European Union has been a major catalyst for change. This comprehensive regulatory framework has required isocyanate producers to thoroughly assess and document the environmental and health impacts of their products. As a result, companies have invested heavily in research and development to create safer alternatives and improve existing formulations.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has also tightened regulations on isocyanates, particularly concerning air quality and worker safety. These regulations have prompted manufacturers to adopt advanced emission control technologies and implement more robust safety protocols in their production facilities. This has not only improved environmental performance but also enhanced worker safety and productivity.
The increasing focus on sustainability has led to the development of bio-based isocyanates, derived from renewable resources such as vegetable oils. These innovative products offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based isocyanates, opening up new market opportunities and positioning companies at the forefront of sustainable chemistry.
Regulatory pressure has also driven improvements in product design and application techniques. For instance, the development of low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations has enabled isocyanate-based products to comply with increasingly strict air quality regulations. This has allowed manufacturers to maintain their market presence in sectors such as construction and automotive, where environmental standards are becoming more stringent.
The circular economy concept has gained traction in the isocyanates industry, partly due to regulatory incentives. Companies are exploring ways to recycle and reuse isocyanate-based products, reducing waste and improving resource efficiency. This approach not only helps meet regulatory requirements but also creates new business models and revenue streams.
As regulations continue to evolve, isocyanate manufacturers are increasingly adopting a proactive approach to compliance. Many companies are going beyond minimum requirements, anticipating future regulatory trends and positioning themselves as industry leaders in sustainability. This forward-thinking strategy has led to increased investment in green chemistry initiatives and the development of more sustainable production processes.
Life Cycle Assessment of Isocyanate Products
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of isocyanate products is a crucial tool for evaluating their environmental impact and sustainability throughout their entire lifecycle. This comprehensive analysis encompasses raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, product use, and end-of-life disposal or recycling.
The production of isocyanates typically begins with the synthesis of aniline from benzene, followed by its reaction with phosgene to form isocyanates. This process involves energy-intensive steps and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. LCA studies have shown that the production phase often accounts for the majority of environmental impacts associated with isocyanate products.
During the use phase, isocyanate-based products, such as polyurethane foams and coatings, often demonstrate superior performance and longevity compared to alternatives. This extended lifespan can offset initial production impacts by reducing the need for frequent replacements. Additionally, the insulating properties of polyurethane foams contribute to energy savings in buildings, potentially lowering overall environmental impact during the use phase.
End-of-life considerations for isocyanate products vary depending on the specific application. While some products can be mechanically recycled, others may require chemical recycling or energy recovery through incineration. The development of more efficient recycling technologies for isocyanate-based materials is an ongoing area of research aimed at improving their overall lifecycle performance.
Recent advancements in green chemistry have led to the exploration of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources. These alternatives aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the carbon footprint of isocyanate production. However, comprehensive LCA studies are needed to ensure that these bio-based options truly offer environmental benefits across their entire lifecycle.
Water-based and solvent-free formulations have also emerged as more environmentally friendly alternatives in certain applications. These formulations can reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during application and curing, contributing to improved air quality and worker safety.
To further enhance the sustainability of isocyanate products, manufacturers are focusing on optimizing production processes to minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and improve resource efficiency. This includes the implementation of closed-loop systems, heat recovery technologies, and the use of catalysts to increase reaction efficiency and selectivity.
The production of isocyanates typically begins with the synthesis of aniline from benzene, followed by its reaction with phosgene to form isocyanates. This process involves energy-intensive steps and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. LCA studies have shown that the production phase often accounts for the majority of environmental impacts associated with isocyanate products.
During the use phase, isocyanate-based products, such as polyurethane foams and coatings, often demonstrate superior performance and longevity compared to alternatives. This extended lifespan can offset initial production impacts by reducing the need for frequent replacements. Additionally, the insulating properties of polyurethane foams contribute to energy savings in buildings, potentially lowering overall environmental impact during the use phase.
End-of-life considerations for isocyanate products vary depending on the specific application. While some products can be mechanically recycled, others may require chemical recycling or energy recovery through incineration. The development of more efficient recycling technologies for isocyanate-based materials is an ongoing area of research aimed at improving their overall lifecycle performance.
Recent advancements in green chemistry have led to the exploration of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources. These alternatives aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the carbon footprint of isocyanate production. However, comprehensive LCA studies are needed to ensure that these bio-based options truly offer environmental benefits across their entire lifecycle.
Water-based and solvent-free formulations have also emerged as more environmentally friendly alternatives in certain applications. These formulations can reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during application and curing, contributing to improved air quality and worker safety.
To further enhance the sustainability of isocyanate products, manufacturers are focusing on optimizing production processes to minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and improve resource efficiency. This includes the implementation of closed-loop systems, heat recovery technologies, and the use of catalysts to increase reaction efficiency and selectivity.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!