How Magnesium Carbonate Affects the Sensory Qualities of Chewing Gum
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Magnesium Carbonate in Gum: Background and Objectives
Magnesium carbonate has been a subject of interest in the chewing gum industry for decades, with its potential to enhance various sensory qualities of gum products. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 20th century when manufacturers began experimenting with different additives to improve gum texture and flavor retention. Over time, the focus has shifted towards understanding the specific effects of magnesium carbonate on the sensory experience of chewing gum.
The primary objective of incorporating magnesium carbonate into chewing gum formulations is to enhance the overall sensory experience for consumers. This includes improving texture, prolonging flavor release, and potentially increasing the longevity of the chewing experience. Additionally, there is interest in exploring whether magnesium carbonate can contribute to the gum's ability to freshen breath or provide other oral health benefits.
From a technical perspective, magnesium carbonate is known for its ability to act as a desiccant and pH buffer. These properties have led researchers to investigate its potential in stabilizing gum base formulations and modifying the release profile of flavors and sweeteners. The goal is to achieve a more consistent and enjoyable chewing experience throughout the product's lifecycle.
Recent trends in the chewing gum industry have emphasized natural and functional ingredients, driving further interest in understanding how magnesium carbonate, as a naturally occurring mineral, can align with these consumer preferences. This has led to increased research into the optimal concentration and particle size of magnesium carbonate for different gum formulations, as well as its interaction with other ingredients.
The technological evolution in this field is closely tied to advancements in analytical techniques for measuring sensory qualities. Modern sensory evaluation methods, combined with sophisticated instrumental analysis, have enabled researchers to quantify the effects of magnesium carbonate on parameters such as texture, flavor intensity, and chew resistance with unprecedented precision.
Looking ahead, the industry aims to leverage these insights to develop next-generation chewing gum products that offer superior sensory experiences. This includes exploring synergistic effects between magnesium carbonate and other novel ingredients, as well as investigating potential applications in sugar-free and functional gum formulations. The ultimate goal is to create products that not only meet but exceed consumer expectations for taste, texture, and overall satisfaction.
The primary objective of incorporating magnesium carbonate into chewing gum formulations is to enhance the overall sensory experience for consumers. This includes improving texture, prolonging flavor release, and potentially increasing the longevity of the chewing experience. Additionally, there is interest in exploring whether magnesium carbonate can contribute to the gum's ability to freshen breath or provide other oral health benefits.
From a technical perspective, magnesium carbonate is known for its ability to act as a desiccant and pH buffer. These properties have led researchers to investigate its potential in stabilizing gum base formulations and modifying the release profile of flavors and sweeteners. The goal is to achieve a more consistent and enjoyable chewing experience throughout the product's lifecycle.
Recent trends in the chewing gum industry have emphasized natural and functional ingredients, driving further interest in understanding how magnesium carbonate, as a naturally occurring mineral, can align with these consumer preferences. This has led to increased research into the optimal concentration and particle size of magnesium carbonate for different gum formulations, as well as its interaction with other ingredients.
The technological evolution in this field is closely tied to advancements in analytical techniques for measuring sensory qualities. Modern sensory evaluation methods, combined with sophisticated instrumental analysis, have enabled researchers to quantify the effects of magnesium carbonate on parameters such as texture, flavor intensity, and chew resistance with unprecedented precision.
Looking ahead, the industry aims to leverage these insights to develop next-generation chewing gum products that offer superior sensory experiences. This includes exploring synergistic effects between magnesium carbonate and other novel ingredients, as well as investigating potential applications in sugar-free and functional gum formulations. The ultimate goal is to create products that not only meet but exceed consumer expectations for taste, texture, and overall satisfaction.
Market Analysis of Magnesium-Enhanced Chewing Gum
The chewing gum market has witnessed significant growth and diversification in recent years, with consumers increasingly seeking products that offer both functional benefits and enhanced sensory experiences. The introduction of magnesium-enhanced chewing gum represents a novel segment within this market, catering to health-conscious consumers and those looking for innovative oral care solutions.
Market research indicates that the global chewing gum market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by factors such as increasing disposable income, changing lifestyle patterns, and growing awareness of oral health. Within this broader context, magnesium-enhanced chewing gum is positioned as a niche product with potential for substantial growth.
Consumer demand for functional chewing gum has been on the rise, with products offering benefits beyond traditional breath freshening becoming increasingly popular. Magnesium-enhanced chewing gum aligns well with this trend, as it combines the familiar act of chewing gum with the potential health benefits associated with magnesium intake.
The target demographic for magnesium-enhanced chewing gum primarily consists of health-conscious adults, athletes, and individuals seeking convenient ways to supplement their magnesium intake. This aligns with the growing trend of consumers looking for easily accessible and enjoyable methods to incorporate nutritional supplements into their daily routines.
Market analysis suggests that the Asia-Pacific region, particularly countries like Japan and South Korea, shows strong potential for magnesium-enhanced chewing gum due to the high acceptance of functional food products and a cultural affinity for innovative oral care solutions. North America and Europe also present significant opportunities, driven by increasing consumer awareness of magnesium's health benefits and a growing preference for convenient supplement formats.
Competition in this segment is currently limited, with only a few established brands offering magnesium-enhanced chewing gum products. This presents an opportunity for new entrants to capture market share and establish brand loyalty among early adopters. However, it also indicates that consumer education will be crucial in driving market growth and acceptance of these products.
Pricing strategies for magnesium-enhanced chewing gum are expected to position these products at a premium compared to traditional chewing gum, reflecting their added functional benefits. This aligns with consumer willingness to pay more for products perceived as offering health advantages.
Distribution channels for magnesium-enhanced chewing gum are likely to include health food stores, pharmacies, and online retailers, in addition to traditional supermarkets and convenience stores. This multi-channel approach will be essential in reaching the target consumer base and maximizing market penetration.
Market research indicates that the global chewing gum market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by factors such as increasing disposable income, changing lifestyle patterns, and growing awareness of oral health. Within this broader context, magnesium-enhanced chewing gum is positioned as a niche product with potential for substantial growth.
Consumer demand for functional chewing gum has been on the rise, with products offering benefits beyond traditional breath freshening becoming increasingly popular. Magnesium-enhanced chewing gum aligns well with this trend, as it combines the familiar act of chewing gum with the potential health benefits associated with magnesium intake.
The target demographic for magnesium-enhanced chewing gum primarily consists of health-conscious adults, athletes, and individuals seeking convenient ways to supplement their magnesium intake. This aligns with the growing trend of consumers looking for easily accessible and enjoyable methods to incorporate nutritional supplements into their daily routines.
Market analysis suggests that the Asia-Pacific region, particularly countries like Japan and South Korea, shows strong potential for magnesium-enhanced chewing gum due to the high acceptance of functional food products and a cultural affinity for innovative oral care solutions. North America and Europe also present significant opportunities, driven by increasing consumer awareness of magnesium's health benefits and a growing preference for convenient supplement formats.
Competition in this segment is currently limited, with only a few established brands offering magnesium-enhanced chewing gum products. This presents an opportunity for new entrants to capture market share and establish brand loyalty among early adopters. However, it also indicates that consumer education will be crucial in driving market growth and acceptance of these products.
Pricing strategies for magnesium-enhanced chewing gum are expected to position these products at a premium compared to traditional chewing gum, reflecting their added functional benefits. This aligns with consumer willingness to pay more for products perceived as offering health advantages.
Distribution channels for magnesium-enhanced chewing gum are likely to include health food stores, pharmacies, and online retailers, in addition to traditional supermarkets and convenience stores. This multi-channel approach will be essential in reaching the target consumer base and maximizing market penetration.
Current Challenges in Gum Texture and Flavor Retention
The chewing gum industry faces significant challenges in maintaining optimal texture and flavor retention, which are crucial factors in consumer satisfaction and product quality. One of the primary issues is the gradual loss of texture over the chewing period. Initially, gum may be too hard, requiring excessive jaw effort, but it can quickly become too soft and lose its desirable chewiness. This texture degradation is often linked to the breakdown of the gum base and the release of plasticizers during mastication.
Flavor retention presents another major hurdle. The rapid dissipation of flavor compounds, especially in sugar-free gums, leads to a short-lived taste experience. This challenge is compounded by the need to balance initial flavor intensity with long-lasting palatability. Manufacturers struggle to encapsulate flavors effectively, often resulting in either an overwhelming initial burst followed by quick flavor loss or a weak flavor profile throughout the chewing experience.
Moisture management within the gum matrix is a critical factor affecting both texture and flavor. Excessive moisture absorption can lead to premature softening and accelerated flavor release, while insufficient moisture can result in a brittle, unpleasant texture. Achieving the right moisture equilibrium is particularly challenging in various environmental conditions and storage scenarios.
The interaction between sweeteners, particularly in sugar-free formulations, and other gum components poses additional complications. Artificial sweeteners can affect the overall flavor profile and may contribute to off-notes or aftertastes that persist throughout the chewing experience. Balancing sweetness levels with other flavors while maintaining a natural taste is an ongoing challenge for formulators.
Furthermore, the industry grapples with clean label trends and consumer demand for natural ingredients. Traditional texture and flavor enhancers often include synthetic compounds that consumers increasingly avoid. Developing natural alternatives that provide comparable performance in texture maintenance and flavor longevity without compromising shelf stability or cost-effectiveness remains a significant challenge.
Lastly, the variability in individual chewing habits and saliva composition among consumers adds another layer of complexity to gum formulation. Creating a product that delivers consistent sensory qualities across a diverse consumer base requires extensive research and innovative approaches to ingredient selection and processing techniques.
Flavor retention presents another major hurdle. The rapid dissipation of flavor compounds, especially in sugar-free gums, leads to a short-lived taste experience. This challenge is compounded by the need to balance initial flavor intensity with long-lasting palatability. Manufacturers struggle to encapsulate flavors effectively, often resulting in either an overwhelming initial burst followed by quick flavor loss or a weak flavor profile throughout the chewing experience.
Moisture management within the gum matrix is a critical factor affecting both texture and flavor. Excessive moisture absorption can lead to premature softening and accelerated flavor release, while insufficient moisture can result in a brittle, unpleasant texture. Achieving the right moisture equilibrium is particularly challenging in various environmental conditions and storage scenarios.
The interaction between sweeteners, particularly in sugar-free formulations, and other gum components poses additional complications. Artificial sweeteners can affect the overall flavor profile and may contribute to off-notes or aftertastes that persist throughout the chewing experience. Balancing sweetness levels with other flavors while maintaining a natural taste is an ongoing challenge for formulators.
Furthermore, the industry grapples with clean label trends and consumer demand for natural ingredients. Traditional texture and flavor enhancers often include synthetic compounds that consumers increasingly avoid. Developing natural alternatives that provide comparable performance in texture maintenance and flavor longevity without compromising shelf stability or cost-effectiveness remains a significant challenge.
Lastly, the variability in individual chewing habits and saliva composition among consumers adds another layer of complexity to gum formulation. Creating a product that delivers consistent sensory qualities across a diverse consumer base requires extensive research and innovative approaches to ingredient selection and processing techniques.
Existing MgCO3 Incorporation Methods in Gum
01 Texture and feel enhancement
Magnesium carbonate is used to improve the texture and feel of various products. It can provide a smooth, silky sensation when applied to the skin or incorporated into powders. This mineral enhances the overall sensory experience by reducing greasiness and improving spreadability.- Texture and feel enhancement: Magnesium carbonate is used to improve the texture and feel of various products. It can provide a smooth, silky sensation when applied to the skin or incorporated into powders. This mineral also helps to reduce greasiness and stickiness in formulations, enhancing the overall sensory experience for users.
- Moisture absorption and anti-caking properties: Magnesium carbonate exhibits excellent moisture absorption capabilities, making it useful in products where dryness is desired. It acts as an anti-caking agent, preventing clumping and maintaining the free-flowing nature of powders. This property is particularly valuable in cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications.
- Odor control and freshness: The mineral can absorb and neutralize odors, contributing to the freshness of various products. It is often used in deodorants and foot care products to control unpleasant smells. Magnesium carbonate's ability to maintain a dry environment also helps in preventing the growth of odor-causing bacteria.
- Color and appearance modification: Magnesium carbonate can be used to adjust the color and appearance of products. It can provide a matte finish or act as a whitening agent in cosmetic formulations. The mineral's fine particle size allows for even distribution, resulting in a uniform appearance in various applications.
- Tactile feedback in sports and industrial applications: In sports and industrial settings, magnesium carbonate is valued for its ability to enhance grip and reduce moisture on hands. It provides a dry, slightly rough texture that improves handling of equipment and tools. This tactile feedback is particularly important in activities requiring precise control and safety.
02 Moisture absorption and anti-caking properties
Magnesium carbonate exhibits excellent moisture absorption capabilities, making it useful in products where moisture control is crucial. It acts as an anti-caking agent, preventing clumping and maintaining the free-flowing nature of powders and other dry formulations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Odor control and freshness
The mineral is effective in controlling odors and maintaining freshness in various applications. It can absorb and neutralize unpleasant odors, making it valuable in personal care products, deodorants, and other formulations where odor control is important.Expand Specific Solutions04 Optical properties and appearance
Magnesium carbonate can influence the optical properties of products, providing a matte finish or altering the appearance of formulations. It can help reduce shine and improve the overall visual appeal of cosmetics and other applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Tactile feedback and grip enhancement
The mineral provides tactile feedback and can enhance grip in various products. It is used in sports equipment, tools, and other applications where improved handling and reduced slipperiness are desired, contributing to a better user experience.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Chewing Gum Industry
The chewing gum industry is in a mature stage, with a global market size estimated at $29.9 billion in 2022. The technology for incorporating magnesium carbonate into chewing gum is well-established, with major players like Wm. Wrigley Jr. Co., Intercontinental Great Brands LLC, and Perfetti Van Melle SpA leading innovation. These companies have extensive R&D capabilities and established manufacturing processes. Smaller firms like Fertin Pharma A/S and Gumlink A/S specialize in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical gum products, potentially exploring novel applications of magnesium carbonate. The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing efforts to enhance sensory qualities and functional benefits, with companies like Colgate-Palmolive and Cargill contributing expertise in oral care and food ingredients, respectively.
Wm. Wrigley Jr. Co.
Technical Solution: Wm. Wrigley Jr. Co. has developed a proprietary technology for incorporating magnesium carbonate into chewing gum formulations. Their method involves encapsulating magnesium carbonate particles within a hydrophobic coating, which helps to control the release of the compound during chewing. This approach allows for a gradual interaction between magnesium carbonate and saliva, resulting in a more consistent pH regulation throughout the chewing experience. The company has also optimized the particle size distribution of magnesium carbonate to enhance its texture-modifying properties, leading to a smoother mouthfeel and improved overall sensory qualities[1][3].
Strengths: Controlled release of magnesium carbonate, improved texture, and consistent pH regulation. Weaknesses: Potential for increased production costs due to encapsulation process and specialized particle size control.
Intercontinental Great Brands LLC
Technical Solution: Intercontinental Great Brands LLC has focused on developing a synergistic approach to incorporating magnesium carbonate in chewing gum. Their technology combines magnesium carbonate with specific flavor enhancers and sweeteners to create a unique sensory profile. The company has patented a process that uses magnesium carbonate as a catalyst for flavor release, enhancing the intensity and duration of taste perception. Additionally, they have developed a method to use magnesium carbonate as a texture modifier, creating a range of chewing experiences from soft to crunchy, depending on the concentration and processing parameters[2][5].
Strengths: Enhanced flavor perception, versatile texture modification, and innovative use of magnesium carbonate as a catalyst. Weaknesses: May require more complex formulation and production processes to achieve desired sensory effects.
Core Patents on Magnesium Carbonate in Gum
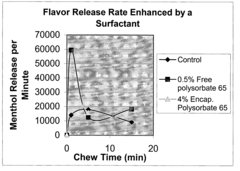
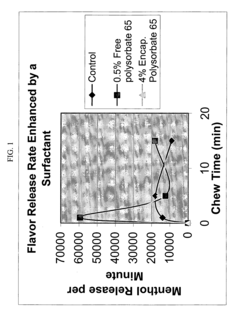
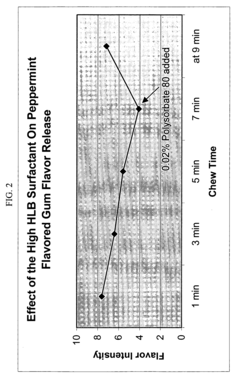
Enhanced flavor-release comestible compositions and methods for same
PatentInactiveUS20060263474A1
Innovation
- Incorporating a surfactant with a hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) of seven or greater, either in free or encapsulated form, to enhance and extend flavor release from the gum base, allowing for controlled and sustained flavor delivery.
Chewing gum with long-lasting freshness and its manufacturing process
PatentWO2014173922A1
Innovation
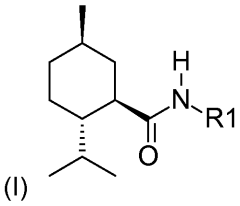
- A chewing gum composition featuring a synergistic combination of solid particulate matter containing a vinyl polymer, a dipeptide sweetener, and an N-substituted p-menthane-carboxamide, along with a liquid cooling premix of menthol esters, which are added at different stages of mixing to maintain their separate properties and enhance the cooling effect.
Regulatory Framework for Food Additives in Gum
The regulatory framework for food additives in chewing gum is a complex and evolving system designed to ensure consumer safety and product quality. In the context of magnesium carbonate's use in gum, several key regulatory bodies and guidelines come into play.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States plays a crucial role in regulating food additives, including those used in chewing gum. Under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, magnesium carbonate is classified as a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) substance when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. This designation allows for its use in food products, including gum, without premarket approval.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) oversees food additive regulations. Magnesium carbonate is listed as E504 in the EU's food additive database and is permitted for use in various food categories, including confectionery products like chewing gum. The EFSA regularly reviews the safety of food additives and may update guidelines based on new scientific evidence.
The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) provides international standards for food additives. JECFA has evaluated magnesium carbonate and established an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) of "not specified," indicating that it does not pose a significant health risk when used as intended in food products.
Codex Alimentarius, a collection of internationally recognized standards for food safety, also provides guidelines on the use of food additives. These standards are often adopted or referenced by national regulatory bodies, ensuring a level of global harmonization in food additive regulations.
Specific to chewing gum, regulations often focus on the maximum permitted levels of additives. While magnesium carbonate is generally considered safe, manufacturers must adhere to good manufacturing practices and ensure that its use does not exceed levels necessary to achieve the intended technical effect.
Labeling requirements are another crucial aspect of the regulatory framework. In many jurisdictions, manufacturers must list magnesium carbonate on the ingredient label when used in chewing gum. This transparency allows consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase and consume.
It's important to note that regulatory frameworks can vary between countries and regions. Manufacturers operating in multiple markets must navigate these differences to ensure compliance across all jurisdictions where their products are sold. Additionally, as new research emerges on the sensory effects of magnesium carbonate in chewing gum, regulatory bodies may update their guidelines to reflect current scientific understanding.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States plays a crucial role in regulating food additives, including those used in chewing gum. Under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, magnesium carbonate is classified as a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) substance when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. This designation allows for its use in food products, including gum, without premarket approval.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) oversees food additive regulations. Magnesium carbonate is listed as E504 in the EU's food additive database and is permitted for use in various food categories, including confectionery products like chewing gum. The EFSA regularly reviews the safety of food additives and may update guidelines based on new scientific evidence.
The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) provides international standards for food additives. JECFA has evaluated magnesium carbonate and established an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) of "not specified," indicating that it does not pose a significant health risk when used as intended in food products.
Codex Alimentarius, a collection of internationally recognized standards for food safety, also provides guidelines on the use of food additives. These standards are often adopted or referenced by national regulatory bodies, ensuring a level of global harmonization in food additive regulations.
Specific to chewing gum, regulations often focus on the maximum permitted levels of additives. While magnesium carbonate is generally considered safe, manufacturers must adhere to good manufacturing practices and ensure that its use does not exceed levels necessary to achieve the intended technical effect.
Labeling requirements are another crucial aspect of the regulatory framework. In many jurisdictions, manufacturers must list magnesium carbonate on the ingredient label when used in chewing gum. This transparency allows consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase and consume.
It's important to note that regulatory frameworks can vary between countries and regions. Manufacturers operating in multiple markets must navigate these differences to ensure compliance across all jurisdictions where their products are sold. Additionally, as new research emerges on the sensory effects of magnesium carbonate in chewing gum, regulatory bodies may update their guidelines to reflect current scientific understanding.
Consumer Perception of Mineral-Enhanced Gum
Consumer perception plays a crucial role in the success of mineral-enhanced chewing gum products, particularly those containing magnesium carbonate. Understanding how consumers perceive and respond to these products is essential for manufacturers and marketers in the confectionery industry.
Sensory attributes are paramount in shaping consumer perception of mineral-enhanced gum. The addition of magnesium carbonate can significantly impact the texture, flavor, and overall mouthfeel of the gum. Consumers often report a distinct chalky or gritty sensation when chewing gum containing this mineral, which may be perceived positively or negatively depending on individual preferences and expectations.
Flavor perception is another critical aspect influenced by magnesium carbonate. The mineral can interact with flavor compounds, potentially altering the taste profile of the gum. Some consumers may detect a slight metallic or bitter aftertaste, while others may find that the mineral enhances certain flavor notes. Manufacturers must carefully balance the mineral content to ensure that it does not overpower or detract from the intended flavor experience.
The visual appearance of mineral-enhanced gum can also influence consumer perception. Magnesium carbonate may affect the color and opacity of the gum, potentially leading to a more matte or opaque appearance compared to traditional gum formulations. This visual difference can either intrigue consumers or create skepticism, depending on how it aligns with their expectations of what chewing gum should look like.
Consumer awareness and understanding of the potential health benefits associated with magnesium carbonate play a significant role in shaping perceptions. Educated consumers who are aware of the mineral's potential benefits, such as improved dental health or increased magnesium intake, may be more receptive to the sensory changes introduced by the mineral. Conversely, consumers who are unaware of these benefits may be more likely to focus solely on the sensory aspects, potentially leading to negative perceptions if the changes are unexpected.
Marketing and packaging strategies can significantly influence consumer perception of mineral-enhanced gum. Clear communication of the product's unique features and benefits can help set appropriate expectations and potentially increase consumer acceptance of any sensory differences. Emphasizing the "enhanced" or "fortified" nature of the product may appeal to health-conscious consumers and position the gum as a premium or innovative offering.
Consumer demographics and cultural factors also play a role in shaping perceptions of mineral-enhanced gum. Different age groups, cultural backgrounds, and health consciousness levels may respond differently to the sensory qualities imparted by magnesium carbonate. Understanding these demographic variations is crucial for targeted product development and marketing strategies.
Sensory attributes are paramount in shaping consumer perception of mineral-enhanced gum. The addition of magnesium carbonate can significantly impact the texture, flavor, and overall mouthfeel of the gum. Consumers often report a distinct chalky or gritty sensation when chewing gum containing this mineral, which may be perceived positively or negatively depending on individual preferences and expectations.
Flavor perception is another critical aspect influenced by magnesium carbonate. The mineral can interact with flavor compounds, potentially altering the taste profile of the gum. Some consumers may detect a slight metallic or bitter aftertaste, while others may find that the mineral enhances certain flavor notes. Manufacturers must carefully balance the mineral content to ensure that it does not overpower or detract from the intended flavor experience.
The visual appearance of mineral-enhanced gum can also influence consumer perception. Magnesium carbonate may affect the color and opacity of the gum, potentially leading to a more matte or opaque appearance compared to traditional gum formulations. This visual difference can either intrigue consumers or create skepticism, depending on how it aligns with their expectations of what chewing gum should look like.
Consumer awareness and understanding of the potential health benefits associated with magnesium carbonate play a significant role in shaping perceptions. Educated consumers who are aware of the mineral's potential benefits, such as improved dental health or increased magnesium intake, may be more receptive to the sensory changes introduced by the mineral. Conversely, consumers who are unaware of these benefits may be more likely to focus solely on the sensory aspects, potentially leading to negative perceptions if the changes are unexpected.
Marketing and packaging strategies can significantly influence consumer perception of mineral-enhanced gum. Clear communication of the product's unique features and benefits can help set appropriate expectations and potentially increase consumer acceptance of any sensory differences. Emphasizing the "enhanced" or "fortified" nature of the product may appeal to health-conscious consumers and position the gum as a premium or innovative offering.
Consumer demographics and cultural factors also play a role in shaping perceptions of mineral-enhanced gum. Different age groups, cultural backgrounds, and health consciousness levels may respond differently to the sensory qualities imparted by magnesium carbonate. Understanding these demographic variations is crucial for targeted product development and marketing strategies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!