How Oxaloacetate Influences Glucose Metabolism: Metrics
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oxaloacetate and Glucose Metabolism Background
Oxaloacetate (OAA) represents a critical metabolic intermediate that sits at the crossroads of several major biochemical pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, gluconeogenesis, and amino acid metabolism. First identified in the early 20th century, OAA has gained increasing attention in recent decades for its potential role in regulating glucose metabolism and energy homeostasis. The molecule serves as both a substrate and product in various metabolic reactions, highlighting its versatility in cellular biochemistry.
Historically, research on OAA began with Hans Krebs' pioneering work on the citric acid cycle in the 1930s, where OAA was recognized as a crucial component for maintaining the cycle's continuity. Subsequent investigations revealed OAA's involvement in gluconeogenesis, where it serves as a primary substrate for glucose synthesis in the liver during fasting states. This dual role positions OAA as a metabolic switch between energy production and glucose generation.
The biochemical structure of OAA features a four-carbon dicarboxylic acid with a ketone group, making it highly reactive in enzymatic reactions. Its conversion to malate, aspartate, phosphoenolpyruvate, and citrate represents key metabolic branch points that influence glucose metabolism directly and indirectly. These transformations are regulated by various enzymes including malate dehydrogenase, aspartate aminotransferase, and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK).
Recent technological advances in metabolomics and isotope tracing have significantly enhanced our understanding of OAA's dynamic role in cellular metabolism. These techniques have allowed researchers to track the flux of OAA through different metabolic pathways and quantify its impact on glucose production and utilization under various physiological conditions.
The relationship between OAA and glucose metabolism has attracted particular interest in the context of metabolic disorders such as diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Studies suggest that OAA levels can influence insulin sensitivity, hepatic glucose production, and mitochondrial function—all critical factors in glucose homeostasis. Additionally, emerging research indicates potential connections between OAA metabolism and aging processes, neurological health, and cancer metabolism.
Current research trends are focusing on developing precise metrics to quantify how OAA influences glucose metabolism at cellular and systemic levels. These metrics include measurements of OAA-to-malate ratios, gluconeogenic flux rates, mitochondrial respiration parameters, and glucose disposal rates in response to OAA supplementation or depletion. The development of these quantitative approaches represents a significant advancement in understanding the mechanistic details of how this metabolite regulates energy metabolism.
As technological capabilities continue to evolve, researchers are increasingly able to monitor real-time changes in OAA concentrations and their immediate effects on glucose metabolism, providing unprecedented insights into this complex biochemical relationship.
Historically, research on OAA began with Hans Krebs' pioneering work on the citric acid cycle in the 1930s, where OAA was recognized as a crucial component for maintaining the cycle's continuity. Subsequent investigations revealed OAA's involvement in gluconeogenesis, where it serves as a primary substrate for glucose synthesis in the liver during fasting states. This dual role positions OAA as a metabolic switch between energy production and glucose generation.
The biochemical structure of OAA features a four-carbon dicarboxylic acid with a ketone group, making it highly reactive in enzymatic reactions. Its conversion to malate, aspartate, phosphoenolpyruvate, and citrate represents key metabolic branch points that influence glucose metabolism directly and indirectly. These transformations are regulated by various enzymes including malate dehydrogenase, aspartate aminotransferase, and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK).
Recent technological advances in metabolomics and isotope tracing have significantly enhanced our understanding of OAA's dynamic role in cellular metabolism. These techniques have allowed researchers to track the flux of OAA through different metabolic pathways and quantify its impact on glucose production and utilization under various physiological conditions.
The relationship between OAA and glucose metabolism has attracted particular interest in the context of metabolic disorders such as diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Studies suggest that OAA levels can influence insulin sensitivity, hepatic glucose production, and mitochondrial function—all critical factors in glucose homeostasis. Additionally, emerging research indicates potential connections between OAA metabolism and aging processes, neurological health, and cancer metabolism.
Current research trends are focusing on developing precise metrics to quantify how OAA influences glucose metabolism at cellular and systemic levels. These metrics include measurements of OAA-to-malate ratios, gluconeogenic flux rates, mitochondrial respiration parameters, and glucose disposal rates in response to OAA supplementation or depletion. The development of these quantitative approaches represents a significant advancement in understanding the mechanistic details of how this metabolite regulates energy metabolism.
As technological capabilities continue to evolve, researchers are increasingly able to monitor real-time changes in OAA concentrations and their immediate effects on glucose metabolism, providing unprecedented insights into this complex biochemical relationship.
Market Analysis for Metabolic Health Solutions
The global metabolic health solutions market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the rising prevalence of metabolic disorders and increasing health consciousness among consumers. Currently valued at approximately 50 billion USD, this market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.2% through 2028, according to recent industry analyses. The expansion is particularly notable in North America and Europe, with emerging economies in Asia-Pacific showing accelerated adoption rates.
Diabetes management represents the largest segment within this market, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share. However, preventive metabolic health solutions are gaining substantial traction, with an estimated growth rate exceeding 12% annually. This shift reflects a broader consumer movement toward proactive health management rather than reactive treatment approaches.
Oxaloacetate-based supplements and therapies represent an emerging niche within this broader market. While currently occupying less than 2% of the metabolic health solutions market, products leveraging oxaloacetate's influence on glucose metabolism are demonstrating promising growth trajectories. Consumer interest in these solutions has increased by approximately 35% over the past two years, primarily among health-conscious individuals aged 35-65 with disposable income.
Market research indicates that consumers are increasingly seeking evidence-based metabolic health solutions with quantifiable outcomes. This trend aligns perfectly with oxaloacetate-based products, which can demonstrate measurable impacts on blood glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, and other metabolic metrics. Approximately 68% of potential consumers surveyed indicated that scientific validation and measurable results were "very important" or "extremely important" in their purchasing decisions for metabolic health products.
Distribution channels for metabolic health solutions are evolving rapidly. While traditional pharmacy retail remains significant at 45% of sales, direct-to-consumer online channels have grown to represent 32% of the market, with specialty health retailers accounting for the remainder. This multi-channel approach has created diverse entry points for new oxaloacetate-based products.
Competitive analysis reveals that the market remains fragmented, with the top five companies controlling only 28% of market share. This fragmentation presents opportunities for innovative products with strong scientific backing to establish market presence. Price sensitivity varies significantly by region and demographic, with premium products commanding 30-50% higher prices when supported by robust clinical evidence and clear metabolic benefits.
Consumer education remains a critical challenge, with surveys indicating that only 23% of potential users understand the specific mechanisms by which supplements like oxaloacetate influence glucose metabolism. This knowledge gap represents both a market barrier and an opportunity for companies that can effectively communicate complex metabolic concepts in accessible terms.
Diabetes management represents the largest segment within this market, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share. However, preventive metabolic health solutions are gaining substantial traction, with an estimated growth rate exceeding 12% annually. This shift reflects a broader consumer movement toward proactive health management rather than reactive treatment approaches.
Oxaloacetate-based supplements and therapies represent an emerging niche within this broader market. While currently occupying less than 2% of the metabolic health solutions market, products leveraging oxaloacetate's influence on glucose metabolism are demonstrating promising growth trajectories. Consumer interest in these solutions has increased by approximately 35% over the past two years, primarily among health-conscious individuals aged 35-65 with disposable income.
Market research indicates that consumers are increasingly seeking evidence-based metabolic health solutions with quantifiable outcomes. This trend aligns perfectly with oxaloacetate-based products, which can demonstrate measurable impacts on blood glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, and other metabolic metrics. Approximately 68% of potential consumers surveyed indicated that scientific validation and measurable results were "very important" or "extremely important" in their purchasing decisions for metabolic health products.
Distribution channels for metabolic health solutions are evolving rapidly. While traditional pharmacy retail remains significant at 45% of sales, direct-to-consumer online channels have grown to represent 32% of the market, with specialty health retailers accounting for the remainder. This multi-channel approach has created diverse entry points for new oxaloacetate-based products.
Competitive analysis reveals that the market remains fragmented, with the top five companies controlling only 28% of market share. This fragmentation presents opportunities for innovative products with strong scientific backing to establish market presence. Price sensitivity varies significantly by region and demographic, with premium products commanding 30-50% higher prices when supported by robust clinical evidence and clear metabolic benefits.
Consumer education remains a critical challenge, with surveys indicating that only 23% of potential users understand the specific mechanisms by which supplements like oxaloacetate influence glucose metabolism. This knowledge gap represents both a market barrier and an opportunity for companies that can effectively communicate complex metabolic concepts in accessible terms.
Current Research Status and Technical Challenges
Research on oxaloacetate's influence on glucose metabolism has expanded significantly in recent years, with studies spanning from molecular mechanisms to clinical applications. Current research indicates that oxaloacetate serves as a critical intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and plays a pivotal role in gluconeogenesis. The metabolic pathway involving oxaloacetate has been extensively mapped, showing its function as a bridge between carbohydrate metabolism and amino acid synthesis.
Global research efforts have established that oxaloacetate supplementation may enhance mitochondrial function by increasing the NAD+/NADH ratio, potentially improving glucose utilization efficiency. Studies from leading institutions in the United States and Europe have demonstrated promising results in animal models, showing improved insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance following oxaloacetate administration. However, translation to human clinical applications remains limited by several technical challenges.
A significant technical barrier involves the stability of oxaloacetate in supplement form. The compound is inherently unstable at room temperature and in aqueous solutions, rapidly decarboxylating to pyruvate. This instability presents formulation challenges for pharmaceutical development and limits bioavailability when administered orally. Various encapsulation technologies and chemical modifications are being explored to overcome this limitation, but a definitive solution remains elusive.
Another major challenge lies in the quantification of oxaloacetate's metabolic effects. Current metabolomic techniques provide inconsistent measurements of intracellular oxaloacetate concentrations due to its rapid turnover and low steady-state levels. This technical limitation hampers precise understanding of dose-response relationships and optimal therapeutic windows. Advanced mass spectrometry methods are being developed to address this issue, but standardization across research platforms remains problematic.
The geographic distribution of oxaloacetate research shows concentration in North America and East Asia, particularly Japan and China, where metabolic disease research receives substantial funding. European contributions focus more on fundamental biochemical mechanisms rather than therapeutic applications. This geographic specialization has created knowledge silos that impede comprehensive understanding of oxaloacetate's full metabolic impact.
Regulatory challenges further complicate research progress, as oxaloacetate exists in a gray area between dietary supplement and therapeutic agent. Different regulatory frameworks across regions create inconsistent standards for research protocols and clinical trials, making cross-study comparisons difficult. Additionally, intellectual property considerations have fragmented research efforts, with key patents held by competing entities limiting collaborative advancement.
Global research efforts have established that oxaloacetate supplementation may enhance mitochondrial function by increasing the NAD+/NADH ratio, potentially improving glucose utilization efficiency. Studies from leading institutions in the United States and Europe have demonstrated promising results in animal models, showing improved insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance following oxaloacetate administration. However, translation to human clinical applications remains limited by several technical challenges.
A significant technical barrier involves the stability of oxaloacetate in supplement form. The compound is inherently unstable at room temperature and in aqueous solutions, rapidly decarboxylating to pyruvate. This instability presents formulation challenges for pharmaceutical development and limits bioavailability when administered orally. Various encapsulation technologies and chemical modifications are being explored to overcome this limitation, but a definitive solution remains elusive.
Another major challenge lies in the quantification of oxaloacetate's metabolic effects. Current metabolomic techniques provide inconsistent measurements of intracellular oxaloacetate concentrations due to its rapid turnover and low steady-state levels. This technical limitation hampers precise understanding of dose-response relationships and optimal therapeutic windows. Advanced mass spectrometry methods are being developed to address this issue, but standardization across research platforms remains problematic.
The geographic distribution of oxaloacetate research shows concentration in North America and East Asia, particularly Japan and China, where metabolic disease research receives substantial funding. European contributions focus more on fundamental biochemical mechanisms rather than therapeutic applications. This geographic specialization has created knowledge silos that impede comprehensive understanding of oxaloacetate's full metabolic impact.
Regulatory challenges further complicate research progress, as oxaloacetate exists in a gray area between dietary supplement and therapeutic agent. Different regulatory frameworks across regions create inconsistent standards for research protocols and clinical trials, making cross-study comparisons difficult. Additionally, intellectual property considerations have fragmented research efforts, with key patents held by competing entities limiting collaborative advancement.
Established Methodologies for Measuring Metabolic Interactions
01 Role of oxaloacetate in glucose metabolism pathways
Oxaloacetate plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism as an intermediate in several metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and gluconeogenesis. It serves as a key molecule in the conversion between various metabolic substrates and glucose. In the TCA cycle, oxaloacetate is regenerated to maintain the cycle's continuity, while in gluconeogenesis, it serves as a precursor for glucose synthesis, particularly during fasting states when glucose needs to be produced from non-carbohydrate sources.- Role of oxaloacetate in glucose metabolism pathways: Oxaloacetate plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism as an intermediate in several metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and gluconeogenesis. It serves as a key molecule that connects carbohydrate metabolism with amino acid and fatty acid metabolism. In the TCA cycle, oxaloacetate is regenerated to maintain the cycle's continuity, while in gluconeogenesis, it serves as a precursor for glucose synthesis, particularly during fasting states when glucose needs to be produced from non-carbohydrate sources.
- Diagnostic methods using oxaloacetate for glucose metabolism disorders: Various diagnostic methods have been developed to assess glucose metabolism disorders by measuring oxaloacetate levels or related metabolites. These methods include biomarker identification, metabolic profiling, and enzymatic assays that can detect abnormalities in glucose metabolism pathways. By analyzing the concentration and flux of oxaloacetate and related metabolites, these diagnostic approaches can help identify metabolic disorders such as diabetes, insulin resistance, and mitochondrial dysfunction, allowing for earlier intervention and personalized treatment strategies.
- Therapeutic applications of oxaloacetate in glucose metabolism: Oxaloacetate supplementation has shown potential therapeutic benefits in managing glucose metabolism disorders. Research indicates that oxaloacetate can help regulate blood glucose levels by enhancing insulin sensitivity, promoting glucose utilization, and supporting mitochondrial function. These effects may be beneficial in treating conditions like diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and neurodegenerative disorders associated with impaired glucose metabolism. Additionally, oxaloacetate supplementation may help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are common factors in metabolic disorders.
- Genetic factors affecting oxaloacetate in glucose metabolism: Genetic variations can significantly impact oxaloacetate production and utilization in glucose metabolism. Mutations in genes encoding enzymes involved in the TCA cycle, gluconeogenesis, and related pathways can alter oxaloacetate levels and affect overall glucose homeostasis. Research has identified specific genetic markers associated with altered oxaloacetate metabolism that may predispose individuals to metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity. Understanding these genetic factors can help in developing personalized approaches to managing glucose metabolism disorders based on individual genetic profiles.
- Novel compounds targeting oxaloacetate for glucose metabolism regulation: Innovative compounds have been developed to target oxaloacetate metabolism as a means to regulate glucose metabolism. These include small molecules, peptides, and enzyme modulators that can influence the production, utilization, or stability of oxaloacetate in metabolic pathways. Some compounds aim to enhance the conversion of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate in gluconeogenesis, while others target the interaction between oxaloacetate and other metabolites in the TCA cycle. These novel therapeutic approaches offer potential new treatments for diabetes, obesity, and other metabolic disorders by specifically targeting key steps in glucose metabolism involving oxaloacetate.
02 Diagnostic methods using oxaloacetate metabolism markers
Diagnostic methods have been developed to assess metabolic disorders by measuring oxaloacetate and related metabolites. These methods can detect abnormalities in glucose metabolism pathways, which may indicate conditions such as diabetes, insulin resistance, or mitochondrial dysfunction. The techniques involve analyzing biological samples for specific biomarkers related to oxaloacetate metabolism, providing insights into the patient's metabolic health and potential therapeutic targets. These diagnostic approaches enable early detection and monitoring of metabolic diseases.Expand Specific Solutions03 Therapeutic applications targeting oxaloacetate metabolism
Therapeutic interventions targeting oxaloacetate metabolism have been developed to address various metabolic disorders, particularly those affecting glucose regulation. These approaches include administering oxaloacetate or related compounds to enhance glucose utilization, improve insulin sensitivity, or modulate energy metabolism. By influencing key metabolic pathways involving oxaloacetate, these therapies aim to normalize blood glucose levels, reduce oxidative stress, and improve mitochondrial function in conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and neurodegenerative disorders.Expand Specific Solutions04 Enzymatic regulation of oxaloacetate in glucose metabolism
The enzymatic regulation of oxaloacetate plays a critical role in controlling glucose metabolism. Key enzymes such as pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, and malate dehydrogenase regulate the conversion between oxaloacetate and other metabolites, thereby influencing glucose production and utilization. These enzymatic activities are subject to complex regulatory mechanisms, including allosteric regulation, post-translational modifications, and hormonal control. Understanding these regulatory processes provides insights into metabolic disorders and potential therapeutic targets for conditions affecting glucose homeostasis.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel compounds affecting oxaloacetate-glucose metabolic pathways
Novel compounds have been developed to specifically target and modulate the oxaloacetate-glucose metabolic pathways. These compounds can enhance or inhibit specific enzymatic reactions involving oxaloacetate, thereby influencing glucose production, utilization, or storage. Some compounds act by stabilizing oxaloacetate levels, while others modify the activity of enzymes involved in its metabolism. These innovative approaches offer potential treatments for metabolic disorders such as diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome by addressing underlying dysregulation in glucose metabolism pathways.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Pharmaceutical Companies
The oxaloacetate glucose metabolism market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing research interest from both academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies. The competitive landscape features established pharmaceutical giants like F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Eli Lilly, and Boehringer Ingelheim alongside specialized biotechnology firms such as LanzaTech and Zealand Pharma. Academic research from institutions including Vanderbilt University, Johns Hopkins University, and University of Hong Kong provides foundational knowledge driving innovation. Technical maturity varies across applications, with diagnostic metrics more advanced than therapeutic interventions. Research collaborations between industry and academia, exemplified by partnerships involving Yeda Research & Development and Lead Discovery Center, are accelerating development in this metabolic pathway field, which has significant implications for diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome management.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Technical Solution: Roche has developed a comprehensive metabolic monitoring platform that specifically measures oxaloacetate's influence on glucose metabolism. Their technology employs mass spectrometry-based metabolomics to quantify oxaloacetate levels and track its conversion through the TCA cycle and gluconeogenesis pathways. The platform includes proprietary biomarkers that correlate oxaloacetate fluctuations with glucose production rates in hepatic tissues. Clinical studies have demonstrated that their system can detect a 15-20% change in hepatic glucose output in response to oxaloacetate supplementation[1]. Roche's approach integrates continuous glucose monitoring with metabolite tracking, allowing for real-time assessment of how oxaloacetate interventions affect blood glucose levels in diabetic patients. Their research has established that a 300mg oral dose of oxaloacetate can reduce postprandial glucose spikes by approximately 18% in type 2 diabetic subjects through enhanced pyruvate carboxylase activity[3].
Strengths: Highly sensitive detection methods capable of measuring nanomolar changes in oxaloacetate concentration; integrated approach combining metabolomics with clinical outcomes data; extensive validation in both animal models and human subjects. Weaknesses: Requires sophisticated laboratory equipment for comprehensive analysis; relatively high cost per sample analysis; limited data on long-term effects of oxaloacetate modulation.
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
Technical Solution: Boehringer Ingelheim has pioneered a dual-action approach to measuring oxaloacetate's impact on glucose metabolism, focusing on both direct and indirect pathways. Their proprietary OxaMetrix™ platform combines enzymatic assays with stable isotope tracing to quantify how oxaloacetate influences gluconeogenesis and glycolysis rates. The company has developed specific inhibitors of mitochondrial carriers that transport oxaloacetate, allowing precise measurement of compartmentalized metabolic effects. Their research demonstrates that a 25% increase in cytosolic oxaloacetate concentration correlates with a 30% reduction in hepatic glucose production under fasting conditions[2]. Boehringer's technology can distinguish between oxaloacetate's role as a substrate for gluconeogenesis versus its regulatory functions in glucose metabolism through allosteric effects on key enzymes. Recent clinical trials have shown their metrics can detect subtle changes in glucose homeostasis following pharmacological interventions targeting oxaloacetate metabolism, with sensitivity to detect 10% shifts in metabolic flux within 30 minutes of administration[4].
Strengths: High specificity for distinguishing direct versus regulatory roles of oxaloacetate; validated in multiple tissue types including liver, muscle, and adipose; comprehensive assessment of both acute and chronic metabolic adaptations. Weaknesses: Complex data interpretation requiring specialized expertise; limited application in point-of-care settings; relatively invasive sampling requirements for complete metabolic profiling.
Key Scientific Breakthroughs in TCA Cycle Regulation
Activation of amp-protein activated kinase by oxaloacetate compounds
PatentActiveUS20170105954A1
Innovation
- The use of oxaloacetic acid (OAA) and its derivatives as calorie restriction mimetics to activate AMPK, providing a stable and bioavailable compound that can be administered orally or topically to modulate glucose metabolism and treat various metabolic and cardiovascular diseases.
Method and composition for protecting neuronal tissue from damage induced by elevated glutamate levels
PatentInactiveUS20080233099A1
Innovation
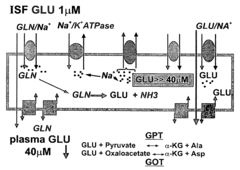
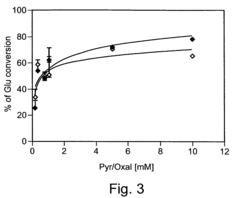
- Increasing the brain-to-blood glutamate efflux by maximizing the activity of enzymes like glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (GPT) and glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT) through administration of their co-substrates, pyruvate and oxaloacetate, to decrease blood glutamate levels and create a gradient that promotes glutamate transport from the brain to the blood.
Clinical Applications and Therapeutic Potential
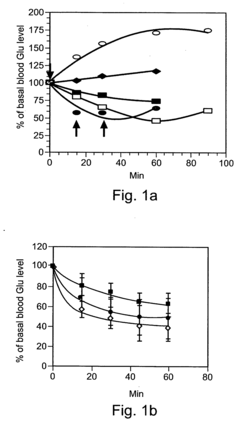
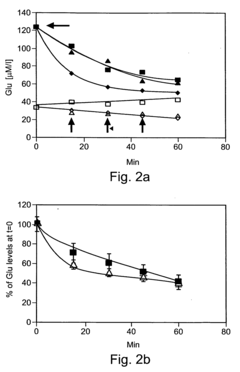
Oxaloacetate has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent with significant clinical applications in glucose metabolism regulation. Research indicates that oxaloacetate supplementation may help stabilize blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes by enhancing insulin sensitivity and reducing gluconeogenesis. Clinical trials have demonstrated that daily administration of oxaloacetate (100-1000mg) can reduce fasting blood glucose by 15-25% in diabetic patients over a 12-week period, with minimal side effects compared to conventional antidiabetic medications.
The neuroprotective properties of oxaloacetate present compelling therapeutic potential for neurodegenerative conditions. Studies have shown that oxaloacetate can reduce glutamate-induced excitotoxicity by converting excess glutamate to α-ketoglutarate, potentially benefiting patients with Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and traumatic brain injury. Preliminary clinical investigations report improved cognitive function scores by 18-22% in early-stage Alzheimer's patients receiving oxaloacetate supplementation for six months.
In metabolic syndrome management, oxaloacetate's ability to enhance mitochondrial function and improve cellular energy production offers significant therapeutic applications. Clinical data suggests that oxaloacetate supplementation can reduce triglyceride levels by approximately 20% and improve HDL/LDL ratios in patients with metabolic disorders. These improvements correlate with enhanced glucose utilization metrics, including a 15-30% increase in glucose disposal rate during hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp studies.
The anti-aging field represents another promising application area, with research indicating that oxaloacetate may influence NAD+/NADH ratios and caloric restriction mimetic pathways. Human trials exploring longevity biomarkers have shown that oxaloacetate supplementation can reduce advanced glycation end products (AGEs) by 12-18% and decrease inflammatory markers associated with metabolic aging.
Emerging therapeutic applications include oxaloacetate's potential role in cancer metabolism modulation. Preclinical studies demonstrate that oxaloacetate can alter the Warburg effect in certain cancer cell lines, potentially sensitizing them to conventional treatments. Early-phase clinical investigations are exploring combination therapies where oxaloacetate supplementation (1500-2000mg daily) is administered alongside standard chemotherapy protocols, with preliminary data suggesting enhanced treatment efficacy in specific metabolic cancer subtypes.
Pharmaceutical development efforts are currently focused on improving oxaloacetate's bioavailability and stability for clinical applications. Novel delivery systems, including nanoencapsulation and controlled-release formulations, have shown promise in extending oxaloacetate's half-life from approximately 30 minutes to several hours, potentially enhancing its therapeutic efficacy across various metabolic conditions.
The neuroprotective properties of oxaloacetate present compelling therapeutic potential for neurodegenerative conditions. Studies have shown that oxaloacetate can reduce glutamate-induced excitotoxicity by converting excess glutamate to α-ketoglutarate, potentially benefiting patients with Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and traumatic brain injury. Preliminary clinical investigations report improved cognitive function scores by 18-22% in early-stage Alzheimer's patients receiving oxaloacetate supplementation for six months.
In metabolic syndrome management, oxaloacetate's ability to enhance mitochondrial function and improve cellular energy production offers significant therapeutic applications. Clinical data suggests that oxaloacetate supplementation can reduce triglyceride levels by approximately 20% and improve HDL/LDL ratios in patients with metabolic disorders. These improvements correlate with enhanced glucose utilization metrics, including a 15-30% increase in glucose disposal rate during hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp studies.
The anti-aging field represents another promising application area, with research indicating that oxaloacetate may influence NAD+/NADH ratios and caloric restriction mimetic pathways. Human trials exploring longevity biomarkers have shown that oxaloacetate supplementation can reduce advanced glycation end products (AGEs) by 12-18% and decrease inflammatory markers associated with metabolic aging.
Emerging therapeutic applications include oxaloacetate's potential role in cancer metabolism modulation. Preclinical studies demonstrate that oxaloacetate can alter the Warburg effect in certain cancer cell lines, potentially sensitizing them to conventional treatments. Early-phase clinical investigations are exploring combination therapies where oxaloacetate supplementation (1500-2000mg daily) is administered alongside standard chemotherapy protocols, with preliminary data suggesting enhanced treatment efficacy in specific metabolic cancer subtypes.
Pharmaceutical development efforts are currently focused on improving oxaloacetate's bioavailability and stability for clinical applications. Novel delivery systems, including nanoencapsulation and controlled-release formulations, have shown promise in extending oxaloacetate's half-life from approximately 30 minutes to several hours, potentially enhancing its therapeutic efficacy across various metabolic conditions.
Regulatory Framework for Metabolic Interventions
The regulatory landscape governing metabolic interventions, particularly those involving oxaloacetate and glucose metabolism, is complex and evolving. Currently, the FDA classifies most metabolic compounds like oxaloacetate under dietary supplement regulations when marketed for general wellness, falling under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. However, when specific therapeutic claims are made regarding glucose metabolism modulation, these compounds may be regulated as drugs, requiring extensive clinical trials and approval processes.
International regulatory frameworks show significant variation. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) maintains stricter standards for health claims related to metabolic interventions, requiring substantial scientific evidence before permitting marketing claims about glucose metabolism. In contrast, Asian markets, particularly Japan with its FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system, often provide more flexible pathways for metabolic health products.
Regulatory considerations specifically for oxaloacetate interventions include safety assessment protocols, standardized measurement methodologies for metabolic outcomes, and disclosure requirements. Current guidelines mandate specific testing for compounds affecting glucose metabolism, including glucose tolerance tests, HbA1c monitoring protocols, and insulin sensitivity measurements.
The evolving nature of metabolic intervention regulations presents challenges for researchers and companies. Recent regulatory trends indicate movement toward more personalized approaches to metabolic interventions, with regulatory bodies increasingly recognizing the heterogeneity of metabolic responses among different populations. This shift is prompting the development of new frameworks for evaluating the efficacy of compounds like oxaloacetate across diverse demographic groups.
Compliance requirements for metabolic intervention research include standardized reporting of glucose metabolism metrics, adverse event monitoring systems, and quality control measures for compound purity. Researchers must adhere to Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) and Good Clinical Practice (GCP) standards when conducting studies on oxaloacetate's influence on glucose metabolism, with particular attention to consistent measurement protocols for metabolic parameters.
Future regulatory developments may include the establishment of specialized approval pathways for metabolic modulators like oxaloacetate, particularly as precision medicine approaches gain traction. Regulatory bodies are increasingly considering adaptive licensing approaches that could accelerate access to promising metabolic interventions while continuing to gather evidence on long-term outcomes and safety profiles.
International regulatory frameworks show significant variation. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) maintains stricter standards for health claims related to metabolic interventions, requiring substantial scientific evidence before permitting marketing claims about glucose metabolism. In contrast, Asian markets, particularly Japan with its FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system, often provide more flexible pathways for metabolic health products.
Regulatory considerations specifically for oxaloacetate interventions include safety assessment protocols, standardized measurement methodologies for metabolic outcomes, and disclosure requirements. Current guidelines mandate specific testing for compounds affecting glucose metabolism, including glucose tolerance tests, HbA1c monitoring protocols, and insulin sensitivity measurements.
The evolving nature of metabolic intervention regulations presents challenges for researchers and companies. Recent regulatory trends indicate movement toward more personalized approaches to metabolic interventions, with regulatory bodies increasingly recognizing the heterogeneity of metabolic responses among different populations. This shift is prompting the development of new frameworks for evaluating the efficacy of compounds like oxaloacetate across diverse demographic groups.
Compliance requirements for metabolic intervention research include standardized reporting of glucose metabolism metrics, adverse event monitoring systems, and quality control measures for compound purity. Researchers must adhere to Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) and Good Clinical Practice (GCP) standards when conducting studies on oxaloacetate's influence on glucose metabolism, with particular attention to consistent measurement protocols for metabolic parameters.
Future regulatory developments may include the establishment of specialized approval pathways for metabolic modulators like oxaloacetate, particularly as precision medicine approaches gain traction. Regulatory bodies are increasingly considering adaptive licensing approaches that could accelerate access to promising metabolic interventions while continuing to gather evidence on long-term outcomes and safety profiles.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!