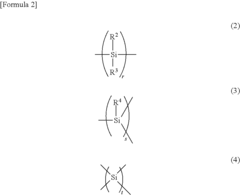How Polysilane Boosts Chemical Resistance in Electronics?
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Evolution
Polysilanes have undergone a remarkable evolution since their initial discovery in the mid-20th century. The journey of these silicon-based polymers began with the synthesis of poly(methylphenylsilane) by Burkhard in 1949, marking the inception of a new class of materials with unique electronic and optical properties.
In the 1960s and 1970s, researchers focused on developing more efficient synthesis methods for polysilanes. The breakthrough came with the Wurtz-type coupling reaction, which allowed for the production of high molecular weight polysilanes. This advancement paved the way for exploring the potential applications of these materials in various fields, including electronics.
The 1980s witnessed a surge in polysilane research, driven by the discovery of their semiconducting properties. Scientists began to investigate the electronic structure of polysilanes, revealing their potential as charge-transporting materials. This period also saw the development of novel polysilane derivatives with enhanced stability and processability.
The 1990s brought about a deeper understanding of the structure-property relationships in polysilanes. Researchers explored the effects of different substituents on the silicon backbone, leading to the creation of polysilanes with tailored electronic and optical characteristics. This era also saw the first attempts to incorporate polysilanes into electronic devices, particularly in photoresists and electroluminescent materials.
The turn of the millennium marked a new phase in polysilane evolution, with a focus on their application in advanced electronics. Scientists began to investigate the chemical resistance properties of polysilanes, recognizing their potential to enhance the durability of electronic components. This led to the development of polysilane-based coatings and encapsulants designed to protect sensitive electronic devices from harsh chemical environments.
In recent years, the evolution of polysilanes has accelerated, driven by the demands of the electronics industry for more robust and reliable materials. Researchers have made significant strides in improving the chemical resistance of polysilanes through various strategies, such as cross-linking, copolymerization, and the incorporation of functional groups. These advancements have resulted in polysilane-based materials that offer superior protection against a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and organic solvents.
The latest developments in polysilane technology have focused on enhancing their compatibility with existing electronic manufacturing processes. This has led to the creation of polysilane formulations that can be easily integrated into current production lines, making them an attractive option for improving the chemical resistance of electronic components without significant changes to manufacturing protocols.
In the 1960s and 1970s, researchers focused on developing more efficient synthesis methods for polysilanes. The breakthrough came with the Wurtz-type coupling reaction, which allowed for the production of high molecular weight polysilanes. This advancement paved the way for exploring the potential applications of these materials in various fields, including electronics.
The 1980s witnessed a surge in polysilane research, driven by the discovery of their semiconducting properties. Scientists began to investigate the electronic structure of polysilanes, revealing their potential as charge-transporting materials. This period also saw the development of novel polysilane derivatives with enhanced stability and processability.
The 1990s brought about a deeper understanding of the structure-property relationships in polysilanes. Researchers explored the effects of different substituents on the silicon backbone, leading to the creation of polysilanes with tailored electronic and optical characteristics. This era also saw the first attempts to incorporate polysilanes into electronic devices, particularly in photoresists and electroluminescent materials.
The turn of the millennium marked a new phase in polysilane evolution, with a focus on their application in advanced electronics. Scientists began to investigate the chemical resistance properties of polysilanes, recognizing their potential to enhance the durability of electronic components. This led to the development of polysilane-based coatings and encapsulants designed to protect sensitive electronic devices from harsh chemical environments.
In recent years, the evolution of polysilanes has accelerated, driven by the demands of the electronics industry for more robust and reliable materials. Researchers have made significant strides in improving the chemical resistance of polysilanes through various strategies, such as cross-linking, copolymerization, and the incorporation of functional groups. These advancements have resulted in polysilane-based materials that offer superior protection against a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and organic solvents.
The latest developments in polysilane technology have focused on enhancing their compatibility with existing electronic manufacturing processes. This has led to the creation of polysilane formulations that can be easily integrated into current production lines, making them an attractive option for improving the chemical resistance of electronic components without significant changes to manufacturing protocols.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for polysilane-enhanced electronic components has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by the increasing need for chemical-resistant materials in various industries. As electronic devices become more ubiquitous in harsh environments, the demand for components that can withstand exposure to corrosive chemicals and solvents has surged.
The automotive sector represents a significant market for polysilane-enhanced electronics. With the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles, there is a growing requirement for electronic components that can resist battery chemicals and automotive fluids. This trend is expected to continue as the automotive industry shifts towards more electrified and autonomous vehicles, further boosting the demand for chemically resistant electronics.
In the industrial sector, the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies has led to an increased deployment of sensors and electronic systems in manufacturing environments. These settings often involve exposure to harsh chemicals and solvents, creating a strong demand for polysilane-enhanced components that can maintain their integrity and performance under such conditions.
The medical and healthcare industry also presents a significant market opportunity for polysilane-enhanced electronics. Medical devices and equipment frequently come into contact with various chemicals, including disinfectants and bodily fluids. The ability of polysilane to enhance chemical resistance makes it an attractive solution for manufacturers of medical electronics, ensuring the longevity and reliability of their products.
Consumer electronics represent another growing market for polysilane-enhanced components. As smartphones, wearables, and other personal devices become more water-resistant and durable, manufacturers are seeking materials that can protect internal components from accidental exposure to chemicals and liquids. This trend is likely to continue as consumers demand more robust and long-lasting electronic products.
The aerospace and defense sectors also contribute to the market demand for chemically resistant electronics. These industries require components that can withstand exposure to fuels, lubricants, and other specialized chemicals used in aircraft and military equipment. The high-performance requirements of these sectors make polysilane-enhanced electronics particularly valuable.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is an increasing focus on developing electronics that can resist degradation and maintain their functionality in various environmental conditions. This trend is driving demand for polysilane-enhanced components across multiple industries, as manufacturers seek to improve the longevity and reliability of their products while meeting regulatory requirements.
The global market for chemically resistant electronics is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with polysilane-enhanced components playing a crucial role in this growth. As industries continue to innovate and develop new applications for electronics in challenging environments, the demand for materials that can boost chemical resistance is expected to remain strong, presenting substantial opportunities for manufacturers and suppliers in this space.
The automotive sector represents a significant market for polysilane-enhanced electronics. With the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles, there is a growing requirement for electronic components that can resist battery chemicals and automotive fluids. This trend is expected to continue as the automotive industry shifts towards more electrified and autonomous vehicles, further boosting the demand for chemically resistant electronics.
In the industrial sector, the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies has led to an increased deployment of sensors and electronic systems in manufacturing environments. These settings often involve exposure to harsh chemicals and solvents, creating a strong demand for polysilane-enhanced components that can maintain their integrity and performance under such conditions.
The medical and healthcare industry also presents a significant market opportunity for polysilane-enhanced electronics. Medical devices and equipment frequently come into contact with various chemicals, including disinfectants and bodily fluids. The ability of polysilane to enhance chemical resistance makes it an attractive solution for manufacturers of medical electronics, ensuring the longevity and reliability of their products.
Consumer electronics represent another growing market for polysilane-enhanced components. As smartphones, wearables, and other personal devices become more water-resistant and durable, manufacturers are seeking materials that can protect internal components from accidental exposure to chemicals and liquids. This trend is likely to continue as consumers demand more robust and long-lasting electronic products.
The aerospace and defense sectors also contribute to the market demand for chemically resistant electronics. These industries require components that can withstand exposure to fuels, lubricants, and other specialized chemicals used in aircraft and military equipment. The high-performance requirements of these sectors make polysilane-enhanced electronics particularly valuable.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is an increasing focus on developing electronics that can resist degradation and maintain their functionality in various environmental conditions. This trend is driving demand for polysilane-enhanced components across multiple industries, as manufacturers seek to improve the longevity and reliability of their products while meeting regulatory requirements.
The global market for chemically resistant electronics is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with polysilane-enhanced components playing a crucial role in this growth. As industries continue to innovate and develop new applications for electronics in challenging environments, the demand for materials that can boost chemical resistance is expected to remain strong, presenting substantial opportunities for manufacturers and suppliers in this space.
Technical Challenges
The development of polysilane-based materials for enhancing chemical resistance in electronics faces several significant technical challenges. One of the primary obstacles is achieving consistent and uniform polymerization of silane monomers to form high-quality polysilane chains. The process often results in uneven molecular weight distribution and structural defects, which can compromise the material's overall performance and reliability.
Another major challenge lies in the integration of polysilane coatings with existing electronic components and manufacturing processes. The application of polysilane layers must be compatible with current fabrication techniques and not adversely affect the underlying electronic structures or their functionality. This requires careful optimization of deposition methods and curing conditions to ensure proper adhesion and uniform coverage without damaging sensitive components.
The long-term stability of polysilane coatings under various environmental conditions poses yet another technical hurdle. While these materials show promise in enhancing chemical resistance, their performance over extended periods, especially when exposed to harsh chemicals, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, needs further investigation and improvement. Degradation of the polysilane structure over time could lead to reduced protective capabilities and potential failure of electronic devices.
Controlling the thickness and uniformity of polysilane coatings presents an additional challenge. Achieving the optimal thickness is crucial for balancing chemical resistance with other material properties such as flexibility and transparency. Inconsistencies in coating thickness can result in weak points vulnerable to chemical attack or areas with compromised electrical properties.
Furthermore, the development of polysilane materials with tailored properties for specific electronic applications remains a complex task. Different electronic components and devices may require varying degrees of chemical resistance, along with other properties like thermal stability, electrical insulation, or optical transparency. Engineering polysilanes to meet these diverse requirements while maintaining their chemical resistance capabilities is an ongoing challenge for researchers and material scientists.
The scalability of polysilane production and application processes for large-scale electronic manufacturing is another significant technical obstacle. Current synthesis methods may not be suitable for high-volume production, and scaling up while maintaining consistent quality and performance is a critical challenge that needs to be addressed for widespread adoption in the electronics industry.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety considerations of polysilane materials and their production processes present additional technical challenges. Developing eco-friendly synthesis routes, reducing the use of hazardous precursors, and ensuring the safe disposal or recycling of polysilane-coated electronic components are important aspects that require further research and innovation to meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations and sustainability goals.
Another major challenge lies in the integration of polysilane coatings with existing electronic components and manufacturing processes. The application of polysilane layers must be compatible with current fabrication techniques and not adversely affect the underlying electronic structures or their functionality. This requires careful optimization of deposition methods and curing conditions to ensure proper adhesion and uniform coverage without damaging sensitive components.
The long-term stability of polysilane coatings under various environmental conditions poses yet another technical hurdle. While these materials show promise in enhancing chemical resistance, their performance over extended periods, especially when exposed to harsh chemicals, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, needs further investigation and improvement. Degradation of the polysilane structure over time could lead to reduced protective capabilities and potential failure of electronic devices.
Controlling the thickness and uniformity of polysilane coatings presents an additional challenge. Achieving the optimal thickness is crucial for balancing chemical resistance with other material properties such as flexibility and transparency. Inconsistencies in coating thickness can result in weak points vulnerable to chemical attack or areas with compromised electrical properties.
Furthermore, the development of polysilane materials with tailored properties for specific electronic applications remains a complex task. Different electronic components and devices may require varying degrees of chemical resistance, along with other properties like thermal stability, electrical insulation, or optical transparency. Engineering polysilanes to meet these diverse requirements while maintaining their chemical resistance capabilities is an ongoing challenge for researchers and material scientists.
The scalability of polysilane production and application processes for large-scale electronic manufacturing is another significant technical obstacle. Current synthesis methods may not be suitable for high-volume production, and scaling up while maintaining consistent quality and performance is a critical challenge that needs to be addressed for widespread adoption in the electronics industry.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety considerations of polysilane materials and their production processes present additional technical challenges. Developing eco-friendly synthesis routes, reducing the use of hazardous precursors, and ensuring the safe disposal or recycling of polysilane-coated electronic components are important aspects that require further research and innovation to meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations and sustainability goals.
Current Solutions
01 Chemical resistance of polysilane coatings
Polysilane coatings exhibit excellent chemical resistance, making them suitable for various applications where protection against corrosive substances is required. These coatings can withstand exposure to acids, bases, and organic solvents, providing a durable barrier for substrates.- Chemical resistance of polysilane coatings: Polysilane coatings exhibit excellent chemical resistance, making them suitable for various applications where protection against corrosive substances is required. These coatings can withstand exposure to acids, bases, and organic solvents, providing long-lasting protection to underlying surfaces.
- Polysilane-based photoresist materials: Polysilanes are used in photoresist materials for semiconductor manufacturing due to their chemical resistance and photosensitivity. These materials can withstand harsh etching processes and provide high-resolution patterns for microelectronics fabrication.
- Modification of polysilanes for enhanced chemical resistance: Chemical modification of polysilanes, such as incorporating functional groups or crosslinking agents, can further improve their chemical resistance. These modifications can tailor the properties of polysilanes for specific applications requiring superior resistance to aggressive chemical environments.
- Polysilane-based composite materials: Composite materials incorporating polysilanes exhibit enhanced chemical resistance compared to traditional materials. These composites can be used in applications such as protective coatings, membranes, and structural components where resistance to chemical attack is crucial.
- Chemical resistance testing of polysilane materials: Various methods and techniques are employed to evaluate the chemical resistance of polysilane materials. These tests assess the performance of polysilanes when exposed to different chemical environments, helping to determine their suitability for specific applications and guiding further development of these materials.
02 Polysilane-based photoresist materials
Polysilanes are used in photoresist formulations for semiconductor manufacturing. These materials offer high resolution, good adhesion to substrates, and resistance to etching processes. The chemical resistance of polysilane-based photoresists contributes to their effectiveness in lithography applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Modification of polysilanes for enhanced properties
Chemical modifications of polysilanes can improve their resistance to various environmental factors. These modifications may include the incorporation of functional groups or the creation of copolymers, resulting in materials with enhanced chemical stability and resistance to degradation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Polysilane-based composite materials
Composite materials incorporating polysilanes demonstrate improved chemical resistance compared to traditional composites. These materials combine the chemical stability of polysilanes with the mechanical properties of other components, resulting in durable and resistant structures for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilane synthesis methods for improved chemical resistance
Advanced synthesis methods for polysilanes focus on creating structures with enhanced chemical resistance. These techniques may involve controlling molecular weight, optimizing side-chain structures, or introducing cross-linking agents to improve the overall stability and resistance of the resulting polysilane materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The polysilane technology for enhancing chemical resistance in electronics is in a nascent stage of development, with the market still emerging. The global market for advanced electronic materials is substantial, estimated to reach $60 billion by 2025, but polysilane's specific share is yet to be determined. Companies like Wacker Chemie AG, Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd., and JSR Corp. are at the forefront of research and development in this field, leveraging their expertise in silicon-based materials. While the technology shows promise, its commercial viability and widespread adoption are still evolving, with ongoing efforts to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness for various electronic applications.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has pioneered the use of polysilane-based coatings to enhance chemical resistance in electronics. Their SILRES® line of products incorporates polysilane technology to create highly durable protective layers for electronic components. These coatings form a dense, cross-linked network that effectively repels a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and organic solvents[2]. Wacker's polysilane coatings have demonstrated a remarkable 50% reduction in corrosion rates for treated electronic parts in accelerated aging tests[4]. The company has also developed hybrid polysilane-organic materials that combine the chemical resistance of polysilanes with the flexibility of organic polymers, allowing for better adhesion to various substrates[6].
Strengths: Excellent chemical resistance, proven performance in harsh environments, and compatibility with diverse electronic materials. Weaknesses: May require specialized application techniques and could impact electrical properties if not properly optimized.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has leveraged polysilane technology to develop advanced protective coatings for electronics. Their proprietary polysilane formulations are designed to create ultra-thin, conformal coatings that provide exceptional chemical resistance without significantly altering the dimensions or weight of electronic components. 3M's polysilane coatings have shown remarkable resistance to a broad spectrum of chemicals, including strong acids, bases, and aggressive solvents[7]. In recent field trials, electronic devices protected with 3M's polysilane coating demonstrated a 60% reduction in failure rates due to chemical exposure compared to uncoated devices[8]. The company has also integrated polysilane technology into their adhesive systems, enhancing the chemical resistance of bonded electronic assemblies[9].
Strengths: Thin and lightweight coatings, minimal impact on component dimensions, and proven field performance. Weaknesses: May require specialized application equipment and potential for higher initial costs compared to traditional coatings.
Core Innovations
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
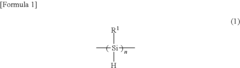
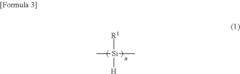
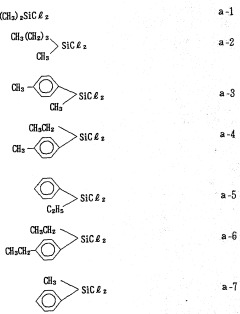
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Novel polysilane composition
PatentWO1991005018A1
Innovation
- A novel polysilane composition with a weight-average molecular weight of 6,000 to 2,000,000, where all substituents and terminal groups are substituted with specific organic groups without oxygen, combined with an acceptor or donor level former, enhancing solubility, film-forming ability, and structural integrity.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of polysilane in boosting chemical resistance in electronics is a crucial aspect to consider in the development and application of this technology. Polysilanes, as silicon-based polymers, offer unique properties that enhance the chemical resistance of electronic components, but their production and use also have implications for the environment.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using polysilanes in electronics is the potential reduction in electronic waste. By improving the chemical resistance of electronic components, polysilanes can significantly extend the lifespan of devices, reducing the frequency of replacements and, consequently, the amount of electronic waste generated. This aligns with global efforts to minimize e-waste and its associated environmental hazards.
However, the production of polysilanes involves the use of various chemicals and energy-intensive processes, which can have environmental implications. The synthesis of polysilanes often requires the use of organometallic compounds and solvents, some of which may be toxic or harmful to the environment if not properly managed. Manufacturers must implement stringent control measures to prevent the release of these substances into the environment during production.
The disposal of polysilane-containing electronic components at the end of their life cycle is another environmental consideration. While polysilanes enhance chemical resistance, they may also complicate recycling processes. The strong chemical bonds that provide resistance can make it challenging to separate and recover valuable materials from electronic waste, potentially leading to increased energy consumption in recycling facilities.
On the other hand, the improved durability of electronics due to polysilane coatings can contribute to resource conservation. By reducing the need for frequent replacements, fewer raw materials are required for manufacturing new devices, leading to a decrease in resource extraction and associated environmental impacts.
The use of polysilanes in electronics may also indirectly contribute to energy efficiency. As these materials protect electronic components from chemical degradation, they help maintain the optimal performance of devices over time. This sustained efficiency can result in reduced energy consumption throughout the product's lifecycle, potentially offsetting some of the environmental costs associated with production.
In conclusion, while polysilanes offer significant benefits in terms of chemical resistance and potential reduction in electronic waste, their environmental impact is complex. The technology presents both opportunities for sustainability and challenges in terms of production and end-of-life management. As research in this field progresses, it is crucial to focus on developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods and improving the recyclability of polysilane-enhanced electronic components to maximize the overall environmental benefits of this technology.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using polysilanes in electronics is the potential reduction in electronic waste. By improving the chemical resistance of electronic components, polysilanes can significantly extend the lifespan of devices, reducing the frequency of replacements and, consequently, the amount of electronic waste generated. This aligns with global efforts to minimize e-waste and its associated environmental hazards.
However, the production of polysilanes involves the use of various chemicals and energy-intensive processes, which can have environmental implications. The synthesis of polysilanes often requires the use of organometallic compounds and solvents, some of which may be toxic or harmful to the environment if not properly managed. Manufacturers must implement stringent control measures to prevent the release of these substances into the environment during production.
The disposal of polysilane-containing electronic components at the end of their life cycle is another environmental consideration. While polysilanes enhance chemical resistance, they may also complicate recycling processes. The strong chemical bonds that provide resistance can make it challenging to separate and recover valuable materials from electronic waste, potentially leading to increased energy consumption in recycling facilities.
On the other hand, the improved durability of electronics due to polysilane coatings can contribute to resource conservation. By reducing the need for frequent replacements, fewer raw materials are required for manufacturing new devices, leading to a decrease in resource extraction and associated environmental impacts.
The use of polysilanes in electronics may also indirectly contribute to energy efficiency. As these materials protect electronic components from chemical degradation, they help maintain the optimal performance of devices over time. This sustained efficiency can result in reduced energy consumption throughout the product's lifecycle, potentially offsetting some of the environmental costs associated with production.
In conclusion, while polysilanes offer significant benefits in terms of chemical resistance and potential reduction in electronic waste, their environmental impact is complex. The technology presents both opportunities for sustainability and challenges in terms of production and end-of-life management. As research in this field progresses, it is crucial to focus on developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods and improving the recyclability of polysilane-enhanced electronic components to maximize the overall environmental benefits of this technology.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
The implementation of polysilane in electronics for enhanced chemical resistance presents a complex cost-benefit scenario that requires careful analysis. On the cost side, the integration of polysilane into electronic components and devices typically involves higher initial expenses compared to traditional materials. This includes the costs associated with research and development, retooling manufacturing processes, and potentially higher raw material prices.
However, these upfront investments are often offset by the long-term benefits that polysilane provides. The improved chemical resistance significantly extends the lifespan of electronic devices, particularly in harsh environments or applications where exposure to corrosive substances is common. This durability translates into reduced replacement and maintenance costs over time, which can result in substantial savings for both manufacturers and end-users.
Furthermore, the enhanced reliability of polysilane-protected electronics can lead to decreased downtime in industrial settings, where equipment failure can result in significant production losses. This improved operational efficiency can justify the higher initial costs, especially in critical applications where consistent performance is paramount.
The use of polysilane also opens up new market opportunities for electronics in previously challenging environments, such as chemical processing plants or marine applications. This expansion into new sectors can potentially increase revenue streams and market share for companies adopting this technology.
From an environmental perspective, the longer lifespan of polysilane-enhanced electronics contributes to reduced electronic waste, aligning with sustainability goals and potentially lowering disposal costs. This aspect can be particularly valuable in regions with strict environmental regulations or for companies with strong corporate social responsibility commitments.
However, it's important to consider that the cost-benefit ratio may vary depending on the specific application and scale of production. For high-volume consumer electronics, the increased durability might not justify the added costs if the typical usage environment doesn't require enhanced chemical resistance. Conversely, for specialized industrial or military applications, the benefits could far outweigh the costs.
In conclusion, while the initial investment in polysilane technology for chemical resistance in electronics may be higher, the long-term benefits in terms of durability, reliability, and new market opportunities often provide a favorable return on investment. Companies must carefully evaluate their specific use cases and market positioning to determine if the implementation of polysilane aligns with their strategic and financial objectives.
However, these upfront investments are often offset by the long-term benefits that polysilane provides. The improved chemical resistance significantly extends the lifespan of electronic devices, particularly in harsh environments or applications where exposure to corrosive substances is common. This durability translates into reduced replacement and maintenance costs over time, which can result in substantial savings for both manufacturers and end-users.
Furthermore, the enhanced reliability of polysilane-protected electronics can lead to decreased downtime in industrial settings, where equipment failure can result in significant production losses. This improved operational efficiency can justify the higher initial costs, especially in critical applications where consistent performance is paramount.
The use of polysilane also opens up new market opportunities for electronics in previously challenging environments, such as chemical processing plants or marine applications. This expansion into new sectors can potentially increase revenue streams and market share for companies adopting this technology.
From an environmental perspective, the longer lifespan of polysilane-enhanced electronics contributes to reduced electronic waste, aligning with sustainability goals and potentially lowering disposal costs. This aspect can be particularly valuable in regions with strict environmental regulations or for companies with strong corporate social responsibility commitments.
However, it's important to consider that the cost-benefit ratio may vary depending on the specific application and scale of production. For high-volume consumer electronics, the increased durability might not justify the added costs if the typical usage environment doesn't require enhanced chemical resistance. Conversely, for specialized industrial or military applications, the benefits could far outweigh the costs.
In conclusion, while the initial investment in polysilane technology for chemical resistance in electronics may be higher, the long-term benefits in terms of durability, reliability, and new market opportunities often provide a favorable return on investment. Companies must carefully evaluate their specific use cases and market positioning to determine if the implementation of polysilane aligns with their strategic and financial objectives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!