How Public Awareness Campaigns Address Carbon Tetrachloride Hazards
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
CCl4 Hazards Background
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a synthetic chemical compound that has been widely used in various industrial and consumer applications since the early 20th century. Initially hailed for its effectiveness as a cleaning agent, fire extinguishing medium, and refrigerant, CCl4 was extensively employed in dry cleaning, metal degreasing, and the production of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). However, as scientific understanding of its environmental and health impacts grew, the perception of CCl4 shifted dramatically.
The hazards associated with CCl4 became increasingly apparent in the latter half of the 20th century. Research revealed its significant ozone-depleting potential, contributing to the thinning of the Earth's protective ozone layer. This discovery led to its inclusion in the Montreal Protocol, an international treaty designed to phase out substances that deplete the ozone layer. Consequently, the production and use of CCl4 for dispersive applications were largely discontinued in developed countries by the mid-1990s.
From a health perspective, CCl4 poses serious risks to human well-being. Exposure can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact, with the liver and kidneys being particularly vulnerable to its toxic effects. Acute exposure may lead to symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and nausea, while chronic exposure has been linked to liver and kidney damage, and potentially, cancer. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has classified CCl4 as possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B).
Despite regulatory efforts to curtail its use, CCl4 remains a persistent environmental contaminant due to its long atmospheric lifetime and historical widespread use. It can be found in soil, groundwater, and air, particularly in areas with a history of industrial activity. The compound's ability to bioaccumulate in aquatic organisms further complicates its environmental impact, potentially affecting entire food chains.
The recognition of CCl4 hazards has spurred significant changes in industrial practices and consumer behavior. Alternative substances and technologies have been developed to replace CCl4 in many of its former applications. However, the legacy of its past use continues to pose challenges for environmental remediation and public health protection. This background underscores the importance of ongoing public awareness campaigns to educate communities about the risks associated with CCl4 and the necessary precautions to minimize exposure.
The hazards associated with CCl4 became increasingly apparent in the latter half of the 20th century. Research revealed its significant ozone-depleting potential, contributing to the thinning of the Earth's protective ozone layer. This discovery led to its inclusion in the Montreal Protocol, an international treaty designed to phase out substances that deplete the ozone layer. Consequently, the production and use of CCl4 for dispersive applications were largely discontinued in developed countries by the mid-1990s.
From a health perspective, CCl4 poses serious risks to human well-being. Exposure can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact, with the liver and kidneys being particularly vulnerable to its toxic effects. Acute exposure may lead to symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and nausea, while chronic exposure has been linked to liver and kidney damage, and potentially, cancer. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has classified CCl4 as possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B).
Despite regulatory efforts to curtail its use, CCl4 remains a persistent environmental contaminant due to its long atmospheric lifetime and historical widespread use. It can be found in soil, groundwater, and air, particularly in areas with a history of industrial activity. The compound's ability to bioaccumulate in aquatic organisms further complicates its environmental impact, potentially affecting entire food chains.
The recognition of CCl4 hazards has spurred significant changes in industrial practices and consumer behavior. Alternative substances and technologies have been developed to replace CCl4 in many of its former applications. However, the legacy of its past use continues to pose challenges for environmental remediation and public health protection. This background underscores the importance of ongoing public awareness campaigns to educate communities about the risks associated with CCl4 and the necessary precautions to minimize exposure.
Public Awareness Needs
Public awareness campaigns addressing carbon tetrachloride hazards face significant challenges due to the complex nature of this chemical and its widespread historical use. The primary need is to educate the general public about the potential health risks associated with carbon tetrachloride exposure, particularly in indoor environments where it may linger due to its past use in cleaning products and fire extinguishers.
A critical aspect of these campaigns is to highlight the long-term effects of carbon tetrachloride on human health and the environment. This includes emphasizing its potential to cause liver and kidney damage, as well as its contribution to ozone depletion. Awareness efforts must also focus on identifying common sources of carbon tetrachloride in everyday life, such as old cleaning supplies, industrial solvents, and contaminated soil or groundwater near former manufacturing sites.
Another key need is to provide clear, actionable information on how to reduce exposure risks. This involves educating the public on proper disposal methods for products that may contain carbon tetrachloride, as well as guidance on what to do if exposure is suspected. Campaigns should also address the importance of proper ventilation in areas where the chemical might be present and promote the use of safer alternatives in industrial and household applications.
Public awareness initiatives must also target specific high-risk groups, such as workers in industries where carbon tetrachloride may still be used or encountered. This includes providing specialized training and information on personal protective equipment and safe handling procedures. Additionally, campaigns should focus on communities near former manufacturing sites or areas with known contamination, offering resources for environmental testing and remediation.
Effective communication strategies are essential to overcome potential barriers to public engagement. This includes using plain language to explain complex scientific concepts, leveraging various media channels to reach diverse audiences, and partnering with community organizations to build trust and credibility. Visual aids, interactive tools, and real-life case studies can help make the information more relatable and memorable.
Lastly, there is a need for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of public awareness efforts. This involves assessing changes in public knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors related to carbon tetrachloride over time. Such assessments can help refine campaign strategies and ensure that resources are being used effectively to address the most pressing awareness gaps and misconceptions about this hazardous substance.
A critical aspect of these campaigns is to highlight the long-term effects of carbon tetrachloride on human health and the environment. This includes emphasizing its potential to cause liver and kidney damage, as well as its contribution to ozone depletion. Awareness efforts must also focus on identifying common sources of carbon tetrachloride in everyday life, such as old cleaning supplies, industrial solvents, and contaminated soil or groundwater near former manufacturing sites.
Another key need is to provide clear, actionable information on how to reduce exposure risks. This involves educating the public on proper disposal methods for products that may contain carbon tetrachloride, as well as guidance on what to do if exposure is suspected. Campaigns should also address the importance of proper ventilation in areas where the chemical might be present and promote the use of safer alternatives in industrial and household applications.
Public awareness initiatives must also target specific high-risk groups, such as workers in industries where carbon tetrachloride may still be used or encountered. This includes providing specialized training and information on personal protective equipment and safe handling procedures. Additionally, campaigns should focus on communities near former manufacturing sites or areas with known contamination, offering resources for environmental testing and remediation.
Effective communication strategies are essential to overcome potential barriers to public engagement. This includes using plain language to explain complex scientific concepts, leveraging various media channels to reach diverse audiences, and partnering with community organizations to build trust and credibility. Visual aids, interactive tools, and real-life case studies can help make the information more relatable and memorable.
Lastly, there is a need for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of public awareness efforts. This involves assessing changes in public knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors related to carbon tetrachloride over time. Such assessments can help refine campaign strategies and ensure that resources are being used effectively to address the most pressing awareness gaps and misconceptions about this hazardous substance.
Current Challenges
Public awareness campaigns addressing carbon tetrachloride hazards face several significant challenges in effectively communicating the risks and promoting preventive measures. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of general knowledge about carbon tetrachloride among the public. Many individuals are unaware of its existence, properties, and potential dangers, making it difficult to engage them in meaningful discussions about its hazards.
The complexity of the subject matter poses another challenge. Carbon tetrachloride's chemical properties, environmental impacts, and health effects can be intricate and difficult to explain in simple terms. This complexity often leads to oversimplification in awareness campaigns, potentially resulting in incomplete or inaccurate information being disseminated to the public.
Limited resources and funding for public awareness campaigns present ongoing challenges. Comprehensive campaigns require substantial financial investment for research, content creation, and widespread distribution. Without adequate funding, campaigns may struggle to reach a broad audience or maintain long-term engagement, reducing their overall effectiveness.
The diverse nature of target audiences adds another layer of complexity to awareness campaigns. Different demographic groups may have varying levels of scientific literacy, risk perception, and information-seeking behaviors. Tailoring messages to resonate with diverse audiences while maintaining scientific accuracy is a delicate balance that campaigns must strike.
Competing environmental and health concerns can overshadow carbon tetrachloride hazards in public discourse. With numerous environmental issues vying for attention, such as climate change and plastic pollution, campaigns focused on carbon tetrachloride may struggle to gain traction and maintain public interest over time.
Misinformation and conflicting information present significant hurdles for awareness campaigns. The internet and social media platforms can rapidly spread inaccurate or outdated information about carbon tetrachloride, making it challenging for campaigns to counter misconceptions and establish credible sources of information.
Behavioral change resistance is another critical challenge. Even when individuals are aware of the hazards associated with carbon tetrachloride, translating that knowledge into actionable changes in behavior or policy support can be difficult. Overcoming ingrained habits and societal norms requires persistent effort and innovative approaches to communication and engagement.
Measuring the impact and effectiveness of awareness campaigns poses ongoing challenges. Establishing clear metrics for success and conducting long-term evaluations of campaign outcomes can be complex and resource-intensive. Without robust assessment methods, it becomes difficult to refine strategies and demonstrate the value of continued investment in awareness efforts.
The complexity of the subject matter poses another challenge. Carbon tetrachloride's chemical properties, environmental impacts, and health effects can be intricate and difficult to explain in simple terms. This complexity often leads to oversimplification in awareness campaigns, potentially resulting in incomplete or inaccurate information being disseminated to the public.
Limited resources and funding for public awareness campaigns present ongoing challenges. Comprehensive campaigns require substantial financial investment for research, content creation, and widespread distribution. Without adequate funding, campaigns may struggle to reach a broad audience or maintain long-term engagement, reducing their overall effectiveness.
The diverse nature of target audiences adds another layer of complexity to awareness campaigns. Different demographic groups may have varying levels of scientific literacy, risk perception, and information-seeking behaviors. Tailoring messages to resonate with diverse audiences while maintaining scientific accuracy is a delicate balance that campaigns must strike.
Competing environmental and health concerns can overshadow carbon tetrachloride hazards in public discourse. With numerous environmental issues vying for attention, such as climate change and plastic pollution, campaigns focused on carbon tetrachloride may struggle to gain traction and maintain public interest over time.
Misinformation and conflicting information present significant hurdles for awareness campaigns. The internet and social media platforms can rapidly spread inaccurate or outdated information about carbon tetrachloride, making it challenging for campaigns to counter misconceptions and establish credible sources of information.
Behavioral change resistance is another critical challenge. Even when individuals are aware of the hazards associated with carbon tetrachloride, translating that knowledge into actionable changes in behavior or policy support can be difficult. Overcoming ingrained habits and societal norms requires persistent effort and innovative approaches to communication and engagement.
Measuring the impact and effectiveness of awareness campaigns poses ongoing challenges. Establishing clear metrics for success and conducting long-term evaluations of campaign outcomes can be complex and resource-intensive. Without robust assessment methods, it becomes difficult to refine strategies and demonstrate the value of continued investment in awareness efforts.
Existing Strategies
01 Digital platforms for public awareness campaigns
Utilizing digital platforms and social media for public awareness campaigns. These platforms allow for widespread dissemination of information, interactive engagement with the public, and real-time updates on various issues. They can be used to create targeted campaigns, share educational content, and gather feedback from the audience.- Digital platforms for public awareness campaigns: Utilizing digital platforms and social media for public awareness campaigns. These platforms allow for widespread dissemination of information, interactive engagement with the public, and real-time updates on important issues. They can be used to create targeted campaigns, share educational content, and gather feedback from the community.
- Mobile applications for awareness and education: Developing mobile applications specifically designed for public awareness and education. These apps can provide easy access to information, send push notifications for important updates, and offer interactive features to engage users. They can be tailored to specific awareness campaigns and allow for personalized content delivery.
- Gamification in awareness campaigns: Incorporating gamification elements into public awareness campaigns to increase engagement and retention of information. This approach uses game-like features such as points, rewards, and challenges to motivate participation and learning. It can make complex or serious topics more approachable and memorable for the target audience.
- IoT and sensor-based awareness systems: Leveraging Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors to collect and disseminate real-time data for public awareness. These systems can provide up-to-date information on environmental conditions, traffic, public health, and other relevant factors. The data can be used to trigger alerts and inform the public about immediate concerns or long-term trends.
- AI-powered personalized awareness content: Using artificial intelligence to create and deliver personalized awareness content to individuals. AI algorithms can analyze user data and behavior to tailor information and messages for maximum impact. This approach can improve the relevance and effectiveness of awareness campaigns by addressing specific interests and concerns of different audience segments.
02 Mobile applications for awareness and education
Developing mobile applications specifically designed for public awareness and education. These apps can provide personalized information, push notifications for important updates, and interactive learning modules. They can be used to reach a wider audience and provide easy access to information on various topics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Wearable technology for health awareness
Incorporating wearable technology into public health awareness campaigns. These devices can track personal health data, provide real-time health information, and send alerts for health-related issues. They can be used to increase individual awareness of health conditions and promote preventive measures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Virtual and augmented reality for immersive awareness experiences
Using virtual and augmented reality technologies to create immersive awareness experiences. These technologies can simulate real-life scenarios, provide interactive educational content, and enhance engagement with awareness campaigns. They can be particularly effective in demonstrating complex concepts or potential outcomes of certain behaviors.Expand Specific Solutions05 Data analytics for targeted awareness campaigns
Employing data analytics and artificial intelligence to create more targeted and effective public awareness campaigns. By analyzing user data and behavior patterns, campaigns can be tailored to specific demographics or regions. This approach can improve the relevance and impact of awareness messages, leading to better outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Stakeholders
The competitive landscape for addressing carbon tetrachloride hazards through public awareness campaigns is in a developing stage, with growing market potential as environmental concerns increase globally. The technology maturity varies across different approaches, from established educational methods to emerging digital platforms. Key players like the Georgia Tech Research Corp. and the University of Massachusetts are leveraging their research capabilities to develop innovative awareness strategies. Companies such as Caterpillar Inc. and Bayer AG are also engaging in this space, potentially integrating awareness campaigns into their corporate social responsibility initiatives. The involvement of diverse entities, including academic institutions, research organizations, and corporations, indicates a multifaceted approach to tackling this environmental challenge.
Bayer AG
Technical Solution: Bayer AG, as a global pharmaceutical and life sciences company, has implemented a corporate social responsibility initiative focused on addressing carbon tetrachloride hazards. Their public awareness campaign combines scientific expertise with global reach. Bayer has developed a series of educational videos and infographics explaining the sources, health risks, and environmental impacts of carbon tetrachloride, which are distributed through their social media channels and website[1]. The company has also created a mobile app that provides real-time air quality information, including carbon tetrachloride levels, for various locations worldwide[2]. Bayer collaborates with environmental NGOs to conduct community outreach programs in areas where carbon tetrachloride contamination is a significant concern. These programs include free health screenings and distribution of informational materials in multiple languages[3]. Additionally, Bayer funds research grants for universities studying innovative methods to detect and remediate carbon tetrachloride in the environment.
Strengths: Global reach and multilingual approach ensure wide accessibility. Combination of digital tools and on-the-ground initiatives. Collaboration with NGOs enhances credibility and local relevance. Weaknesses: As a chemical manufacturer, Bayer may face skepticism from some audiences regarding their motivations. The campaign may be perceived as a public relations effort rather than a genuine environmental initiative.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Technical Solution: MIT has developed a multifaceted public awareness campaign addressing carbon tetrachloride hazards, leveraging its research expertise and technological innovations. The institute has created an open-access online course on the MIT OpenCourseWare platform, detailing the chemistry, environmental impact, and health risks associated with carbon tetrachloride[1]. This course includes interactive simulations demonstrating the compound's behavior in different environments. MIT researchers have also developed a low-cost, portable sensor for detecting carbon tetrachloride in air and water, which is being distributed to communities at risk[2]. The institute organizes public lectures and webinars featuring leading experts in environmental toxicology and chemical engineering to discuss the latest findings on carbon tetrachloride hazards and mitigation strategies[3]. Additionally, MIT's Media Lab has created a series of data visualizations and infographics that effectively communicate complex information about carbon tetrachloride to the general public.
Strengths: Leverages MIT's scientific expertise and technological resources. Open-access approach ensures wide availability of information. Innovative sensor technology provides practical tools for at-risk communities. Weaknesses: May be perceived as too academic for some audiences. The technical nature of some content could be challenging for general public comprehension.
Effective Messaging
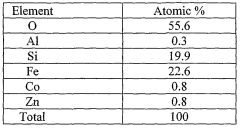
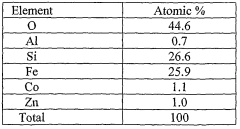
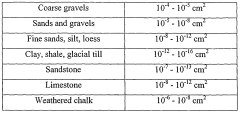
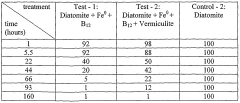
Zero valent metal composite for catalyticaly treating contaminated water
PatentWO2006072944A2
Innovation
- A zero valent metal composite is developed, comprising a powdered diatomite matrix with incorporated zero valent metal particles and an electron transfer mediator, which catalytically treats contaminated water by reducing contaminants under anaerobic conditions, effectively degrading halogenated organic compounds and other inorganic species.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) hazards and public awareness campaigns is complex and multifaceted. At the international level, the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, established in 1987, has been instrumental in phasing out the production and consumption of CCl4. This treaty has been ratified by 198 countries, making it one of the most widely adopted environmental agreements.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating CCl4 under various statutes. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) grants the EPA authority to restrict the manufacture, processing, and distribution of CCl4. Additionally, the Clean Air Act classifies CCl4 as a hazardous air pollutant, subjecting it to stringent emission controls.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits for CCl4 in workplace settings. These regulations require employers to implement engineering controls, work practices, and personal protective equipment to minimize worker exposure.
At the state level, many jurisdictions have enacted their own regulations to address CCl4 hazards. For example, California's Proposition 65 requires businesses to provide warnings about significant exposures to chemicals that cause cancer or reproductive harm, including CCl4.
Public awareness campaigns addressing CCl4 hazards must navigate this regulatory landscape to ensure compliance and effectiveness. These campaigns often collaborate with regulatory agencies to disseminate accurate information about legal requirements and safety standards. For instance, the EPA's Risk Management Program mandates that facilities handling large quantities of CCl4 develop and implement risk management plans, which include public communication strategies.
International organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), provide guidelines and best practices for public awareness campaigns addressing chemical hazards. These resources often inform national and local initiatives, ensuring a consistent global approach to CCl4 risk communication.
The regulatory framework also influences the content and delivery methods of public awareness campaigns. For example, labeling requirements for products containing CCl4 are often incorporated into educational materials. Similarly, workplace safety regulations shape the development of training programs and informational resources for employees in industries where CCl4 exposure is a concern.
As regulations evolve in response to new scientific evidence and changing environmental priorities, public awareness campaigns must adapt accordingly. This dynamic relationship between regulatory frameworks and public education efforts is crucial for effectively addressing CCl4 hazards and protecting public health and the environment.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating CCl4 under various statutes. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) grants the EPA authority to restrict the manufacture, processing, and distribution of CCl4. Additionally, the Clean Air Act classifies CCl4 as a hazardous air pollutant, subjecting it to stringent emission controls.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits for CCl4 in workplace settings. These regulations require employers to implement engineering controls, work practices, and personal protective equipment to minimize worker exposure.
At the state level, many jurisdictions have enacted their own regulations to address CCl4 hazards. For example, California's Proposition 65 requires businesses to provide warnings about significant exposures to chemicals that cause cancer or reproductive harm, including CCl4.
Public awareness campaigns addressing CCl4 hazards must navigate this regulatory landscape to ensure compliance and effectiveness. These campaigns often collaborate with regulatory agencies to disseminate accurate information about legal requirements and safety standards. For instance, the EPA's Risk Management Program mandates that facilities handling large quantities of CCl4 develop and implement risk management plans, which include public communication strategies.
International organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), provide guidelines and best practices for public awareness campaigns addressing chemical hazards. These resources often inform national and local initiatives, ensuring a consistent global approach to CCl4 risk communication.
The regulatory framework also influences the content and delivery methods of public awareness campaigns. For example, labeling requirements for products containing CCl4 are often incorporated into educational materials. Similarly, workplace safety regulations shape the development of training programs and informational resources for employees in industries where CCl4 exposure is a concern.
As regulations evolve in response to new scientific evidence and changing environmental priorities, public awareness campaigns must adapt accordingly. This dynamic relationship between regulatory frameworks and public education efforts is crucial for effectively addressing CCl4 hazards and protecting public health and the environment.
Environmental Impact
Carbon tetrachloride, a potent ozone-depleting substance and greenhouse gas, poses significant environmental risks when released into the atmosphere. Public awareness campaigns addressing carbon tetrachloride hazards play a crucial role in mitigating its environmental impact. These campaigns aim to educate the public about the detrimental effects of carbon tetrachloride on the ozone layer and global climate system.
The release of carbon tetrachloride into the atmosphere contributes to the depletion of the ozone layer, which protects Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation. As public awareness campaigns highlight this issue, they help reduce the use and improper disposal of products containing carbon tetrachloride, thereby minimizing its release into the environment. This reduction in emissions directly correlates with a decrease in ozone depletion, ultimately preserving the protective ozone layer.
Furthermore, carbon tetrachloride is a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential significantly higher than carbon dioxide. Public awareness campaigns emphasize this fact, encouraging individuals and industries to adopt alternative substances and practices that have less impact on climate change. By promoting the use of environmentally friendly alternatives, these campaigns contribute to reducing the overall carbon footprint associated with carbon tetrachloride.
Awareness campaigns also focus on the long-term persistence of carbon tetrachloride in the environment. With an atmospheric lifetime of several decades, the compound can continue to impact ecosystems long after its release. By educating the public about this persistence, campaigns motivate individuals and organizations to take immediate action to prevent further environmental damage.
The impact of these campaigns extends to aquatic ecosystems as well. Carbon tetrachloride can contaminate water sources through industrial runoff and improper disposal. Public awareness initiatives highlight the risks to aquatic life and water quality, promoting responsible handling and disposal practices to protect these vital ecosystems.
Moreover, these campaigns often emphasize the interconnectedness of environmental systems, demonstrating how the release of carbon tetrachloride in one area can have far-reaching consequences globally. This holistic approach helps foster a sense of global environmental responsibility among the public, encouraging collective action to address the challenges posed by carbon tetrachloride and similar substances.
By raising awareness about the environmental impact of carbon tetrachloride, public campaigns contribute to policy changes and stricter regulations on its use and disposal. This, in turn, leads to improved environmental monitoring and enforcement, further reducing the compound's impact on the environment. The cumulative effect of these efforts results in a more sustainable approach to chemical use and management, benefiting the global environment in the long term.
The release of carbon tetrachloride into the atmosphere contributes to the depletion of the ozone layer, which protects Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation. As public awareness campaigns highlight this issue, they help reduce the use and improper disposal of products containing carbon tetrachloride, thereby minimizing its release into the environment. This reduction in emissions directly correlates with a decrease in ozone depletion, ultimately preserving the protective ozone layer.
Furthermore, carbon tetrachloride is a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential significantly higher than carbon dioxide. Public awareness campaigns emphasize this fact, encouraging individuals and industries to adopt alternative substances and practices that have less impact on climate change. By promoting the use of environmentally friendly alternatives, these campaigns contribute to reducing the overall carbon footprint associated with carbon tetrachloride.
Awareness campaigns also focus on the long-term persistence of carbon tetrachloride in the environment. With an atmospheric lifetime of several decades, the compound can continue to impact ecosystems long after its release. By educating the public about this persistence, campaigns motivate individuals and organizations to take immediate action to prevent further environmental damage.
The impact of these campaigns extends to aquatic ecosystems as well. Carbon tetrachloride can contaminate water sources through industrial runoff and improper disposal. Public awareness initiatives highlight the risks to aquatic life and water quality, promoting responsible handling and disposal practices to protect these vital ecosystems.
Moreover, these campaigns often emphasize the interconnectedness of environmental systems, demonstrating how the release of carbon tetrachloride in one area can have far-reaching consequences globally. This holistic approach helps foster a sense of global environmental responsibility among the public, encouraging collective action to address the challenges posed by carbon tetrachloride and similar substances.
By raising awareness about the environmental impact of carbon tetrachloride, public campaigns contribute to policy changes and stricter regulations on its use and disposal. This, in turn, leads to improved environmental monitoring and enforcement, further reducing the compound's impact on the environment. The cumulative effect of these efforts results in a more sustainable approach to chemical use and management, benefiting the global environment in the long term.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!