How to Achieve Cost Reduction in Isocyanate Production?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Production Overview and Cost Reduction Goals
Isocyanates are crucial chemical compounds widely used in the production of polyurethanes, a versatile class of materials with applications ranging from flexible foams to rigid insulation and coatings. The global isocyanate market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand in construction, automotive, and furniture industries. However, the production of isocyanates faces significant challenges, particularly in terms of cost-effectiveness and environmental impact.
The isocyanate production process typically involves the reaction of amines with phosgene, a highly toxic and corrosive gas. This traditional method, while effective, is associated with high production costs due to the expensive raw materials, energy-intensive processes, and stringent safety measures required. Additionally, the use of phosgene raises environmental and safety concerns, prompting the industry to seek alternative production methods.
Cost reduction in isocyanate production has become a primary goal for manufacturers to maintain competitiveness in the global market. The main objectives include optimizing raw material utilization, improving energy efficiency, enhancing process yields, and exploring alternative synthesis routes. Achieving these goals would not only reduce production costs but also potentially mitigate environmental impacts and improve overall sustainability.
One of the key areas for cost reduction is the development of non-phosgene routes for isocyanate synthesis. These alternative methods aim to eliminate the need for phosgene, thereby reducing raw material costs and simplifying safety protocols. Research efforts are focused on catalytic carbonylation of nitro compounds and the use of carbon dioxide as a raw material, which could potentially lead to more economical and environmentally friendly production processes.
Energy efficiency improvements represent another significant opportunity for cost reduction. Isocyanate production is energy-intensive, particularly in the distillation and purification stages. Implementing advanced heat integration systems, optimizing reaction conditions, and exploring novel separation technologies could substantially reduce energy consumption and associated costs.
Process intensification and continuous manufacturing techniques are also being explored to enhance production efficiency and reduce operational costs. These approaches aim to minimize reactor volumes, improve heat and mass transfer, and increase overall process yields. By adopting such advanced manufacturing strategies, producers can potentially achieve higher throughput with reduced capital and operational expenditures.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is a growing emphasis on developing bio-based isocyanates. This approach not only addresses cost concerns but also aligns with the increasing demand for eco-friendly products. Research into renewable feedstocks and green chemistry principles could lead to innovative production methods that are both economically viable and environmentally responsible.
The isocyanate production process typically involves the reaction of amines with phosgene, a highly toxic and corrosive gas. This traditional method, while effective, is associated with high production costs due to the expensive raw materials, energy-intensive processes, and stringent safety measures required. Additionally, the use of phosgene raises environmental and safety concerns, prompting the industry to seek alternative production methods.
Cost reduction in isocyanate production has become a primary goal for manufacturers to maintain competitiveness in the global market. The main objectives include optimizing raw material utilization, improving energy efficiency, enhancing process yields, and exploring alternative synthesis routes. Achieving these goals would not only reduce production costs but also potentially mitigate environmental impacts and improve overall sustainability.
One of the key areas for cost reduction is the development of non-phosgene routes for isocyanate synthesis. These alternative methods aim to eliminate the need for phosgene, thereby reducing raw material costs and simplifying safety protocols. Research efforts are focused on catalytic carbonylation of nitro compounds and the use of carbon dioxide as a raw material, which could potentially lead to more economical and environmentally friendly production processes.
Energy efficiency improvements represent another significant opportunity for cost reduction. Isocyanate production is energy-intensive, particularly in the distillation and purification stages. Implementing advanced heat integration systems, optimizing reaction conditions, and exploring novel separation technologies could substantially reduce energy consumption and associated costs.
Process intensification and continuous manufacturing techniques are also being explored to enhance production efficiency and reduce operational costs. These approaches aim to minimize reactor volumes, improve heat and mass transfer, and increase overall process yields. By adopting such advanced manufacturing strategies, producers can potentially achieve higher throughput with reduced capital and operational expenditures.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is a growing emphasis on developing bio-based isocyanates. This approach not only addresses cost concerns but also aligns with the increasing demand for eco-friendly products. Research into renewable feedstocks and green chemistry principles could lead to innovative production methods that are both economically viable and environmentally responsible.
Market Demand Analysis for Isocyanates
The global isocyanate market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand from various end-use industries such as automotive, construction, furniture, and electronics. Isocyanates, particularly methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI), are crucial components in the production of polyurethanes, which find extensive applications in insulation materials, coatings, adhesives, and elastomers.
The construction industry remains a significant driver of isocyanate demand, with polyurethane foams being widely used for thermal insulation in buildings. The growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainable construction practices has further boosted the adoption of polyurethane-based materials. Additionally, the automotive sector's shift towards lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency has increased the use of polyurethane components, thereby driving isocyanate consumption.
In the Asia-Pacific region, rapid industrialization and urbanization, particularly in China and India, have led to a surge in isocyanate demand. The region has emerged as a major consumer and producer of isocyanates, with China accounting for a substantial share of global production capacity. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and specialty applications.
The market for bio-based isocyanates is gaining traction, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations. This trend presents both challenges and opportunities for isocyanate producers, as they need to invest in research and development to create sustainable alternatives while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the isocyanate market faces challenges related to raw material price volatility and environmental regulations. The production of isocyanates is heavily dependent on crude oil derivatives, making it susceptible to fluctuations in oil prices. This volatility underscores the importance of cost reduction strategies in isocyanate production to maintain profitability and competitiveness.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily disrupted the isocyanate market, causing supply chain issues and reduced demand from end-use industries. However, the market has shown resilience and is expected to recover, driven by the resumption of construction activities and the automotive sector's rebound. The pandemic has also highlighted the importance of diversifying supply chains and optimizing production processes to enhance resilience against future disruptions.
The construction industry remains a significant driver of isocyanate demand, with polyurethane foams being widely used for thermal insulation in buildings. The growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainable construction practices has further boosted the adoption of polyurethane-based materials. Additionally, the automotive sector's shift towards lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency has increased the use of polyurethane components, thereby driving isocyanate consumption.
In the Asia-Pacific region, rapid industrialization and urbanization, particularly in China and India, have led to a surge in isocyanate demand. The region has emerged as a major consumer and producer of isocyanates, with China accounting for a substantial share of global production capacity. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and specialty applications.
The market for bio-based isocyanates is gaining traction, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations. This trend presents both challenges and opportunities for isocyanate producers, as they need to invest in research and development to create sustainable alternatives while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the isocyanate market faces challenges related to raw material price volatility and environmental regulations. The production of isocyanates is heavily dependent on crude oil derivatives, making it susceptible to fluctuations in oil prices. This volatility underscores the importance of cost reduction strategies in isocyanate production to maintain profitability and competitiveness.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily disrupted the isocyanate market, causing supply chain issues and reduced demand from end-use industries. However, the market has shown resilience and is expected to recover, driven by the resumption of construction activities and the automotive sector's rebound. The pandemic has also highlighted the importance of diversifying supply chains and optimizing production processes to enhance resilience against future disruptions.
Current Challenges in Isocyanate Manufacturing
The isocyanate manufacturing industry faces several significant challenges that impact production costs and efficiency. One of the primary issues is the high energy consumption required for the production process. Isocyanate synthesis typically involves multiple reaction steps and separation processes, each demanding substantial thermal energy. This energy-intensive nature of production contributes significantly to overall manufacturing costs.
Raw material costs pose another major challenge. Isocyanates are derived from petrochemical feedstocks, which are subject to price volatility in the global market. Fluctuations in oil prices directly affect the cost of key precursors, such as toluene and aniline, leading to unpredictable production expenses. Additionally, the limited availability of certain raw materials can create supply chain bottlenecks, further driving up costs.
Environmental and safety regulations present ongoing challenges for isocyanate manufacturers. Stringent emission control requirements necessitate substantial investments in pollution abatement technologies and monitoring systems. The handling and storage of hazardous materials, including phosgene, a common intermediate in isocyanate production, require sophisticated safety measures and specialized equipment, adding to operational costs.
Process inefficiencies and yield losses remain persistent issues in isocyanate manufacturing. Side reactions, incomplete conversions, and the formation of by-products reduce overall yield and increase the need for purification steps. These inefficiencies not only result in higher raw material consumption but also necessitate additional processing, contributing to increased energy use and operational costs.
The complexity of isocyanate chemistry presents challenges in process control and optimization. Maintaining precise reaction conditions and managing heat transfer in large-scale reactors can be difficult, leading to quality inconsistencies and potential batch-to-batch variations. This complexity often requires advanced process control systems and highly skilled operators, adding to labor and technology costs.
Maintenance and equipment reliability are critical concerns in isocyanate production facilities. The corrosive nature of some reactants and intermediates can lead to equipment degradation, necessitating frequent maintenance and replacement of critical components. Unplanned downtime due to equipment failures can result in significant production losses and increased operational costs.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in innovation and technology adoption. Developing new, more efficient catalysts or alternative production routes often requires substantial research and development investments. The implementation of novel technologies or process improvements can be hindered by high capital costs and the risks associated with scaling up new processes in an established production environment.
Raw material costs pose another major challenge. Isocyanates are derived from petrochemical feedstocks, which are subject to price volatility in the global market. Fluctuations in oil prices directly affect the cost of key precursors, such as toluene and aniline, leading to unpredictable production expenses. Additionally, the limited availability of certain raw materials can create supply chain bottlenecks, further driving up costs.
Environmental and safety regulations present ongoing challenges for isocyanate manufacturers. Stringent emission control requirements necessitate substantial investments in pollution abatement technologies and monitoring systems. The handling and storage of hazardous materials, including phosgene, a common intermediate in isocyanate production, require sophisticated safety measures and specialized equipment, adding to operational costs.
Process inefficiencies and yield losses remain persistent issues in isocyanate manufacturing. Side reactions, incomplete conversions, and the formation of by-products reduce overall yield and increase the need for purification steps. These inefficiencies not only result in higher raw material consumption but also necessitate additional processing, contributing to increased energy use and operational costs.
The complexity of isocyanate chemistry presents challenges in process control and optimization. Maintaining precise reaction conditions and managing heat transfer in large-scale reactors can be difficult, leading to quality inconsistencies and potential batch-to-batch variations. This complexity often requires advanced process control systems and highly skilled operators, adding to labor and technology costs.
Maintenance and equipment reliability are critical concerns in isocyanate production facilities. The corrosive nature of some reactants and intermediates can lead to equipment degradation, necessitating frequent maintenance and replacement of critical components. Unplanned downtime due to equipment failures can result in significant production losses and increased operational costs.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in innovation and technology adoption. Developing new, more efficient catalysts or alternative production routes often requires substantial research and development investments. The implementation of novel technologies or process improvements can be hindered by high capital costs and the risks associated with scaling up new processes in an established production environment.
Existing Cost Reduction Techniques in Isocyanate Synthesis
01 Production methods affecting isocyanate cost
Various production methods can significantly impact the cost of isocyanates. These include optimizing reaction conditions, improving catalysts, and developing more efficient synthesis routes. Advancements in these areas can lead to reduced production costs and increased yield, ultimately affecting the market price of isocyanates.- Production cost factors for isocyanates: The cost of isocyanates is influenced by various factors including raw material prices, manufacturing processes, and energy consumption. Efficient production methods and optimized reaction conditions can help reduce overall costs. Additionally, the scale of production and market demand play significant roles in determining the final cost of isocyanates.
- Recycling and recovery of isocyanates: Implementing recycling and recovery processes for isocyanates can significantly reduce production costs. This involves the development of efficient separation and purification techniques to reclaim unreacted isocyanates from waste streams. Such methods can improve overall process efficiency and minimize raw material expenses.
- Alternative raw materials for isocyanate production: Exploring alternative, cost-effective raw materials for isocyanate production can help reduce overall costs. This may include the use of bio-based feedstocks or waste products from other industrial processes. Developing new synthetic routes that utilize these alternative materials can lead to more economical isocyanate production.
- Process optimization and energy efficiency: Optimizing production processes and improving energy efficiency can significantly impact isocyanate costs. This involves developing catalysts that enable lower reaction temperatures, implementing heat recovery systems, and utilizing more efficient reactor designs. Such improvements can reduce energy consumption and increase production yields.
- Market dynamics and supply chain management: Understanding market dynamics and implementing effective supply chain management strategies can help control isocyanate costs. This includes forecasting demand, optimizing inventory levels, and establishing long-term supplier relationships. Additionally, exploring vertical integration opportunities can provide better control over raw material costs and production efficiency.
02 Raw material sourcing and pricing
The cost of isocyanates is heavily influenced by the availability and pricing of raw materials. Fluctuations in the prices of key precursors, such as aniline and phosgene, can have a significant impact on the overall production cost. Strategies for securing stable and cost-effective raw material supplies are crucial for managing isocyanate costs.Expand Specific Solutions03 Energy efficiency in isocyanate production
Improving energy efficiency in the production process can lead to significant cost reductions for isocyanates. This includes optimizing reactor designs, implementing heat recovery systems, and utilizing more efficient separation and purification techniques. Energy-saving measures can help offset production costs and improve overall economic viability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and waste reduction strategies
Implementing effective recycling and waste reduction strategies can contribute to lowering isocyanate costs. This involves recovering and reusing unreacted materials, minimizing by-product formation, and developing closed-loop production systems. Such approaches can improve resource utilization and reduce overall production expenses.Expand Specific Solutions05 Market dynamics and demand fluctuations
The cost of isocyanates is influenced by market dynamics and demand fluctuations in various industries, such as automotive, construction, and furniture. Understanding these factors and developing strategies to adapt to changing market conditions can help manage production costs and pricing strategies for isocyanates.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isocyanate Production
The isocyanate production market is in a mature stage, with established players and technologies dominating the industry. The global market size for isocyanates is substantial, estimated to be over $30 billion annually. Technologically, the production process is well-developed, but companies are continuously seeking cost reduction and efficiency improvements. Key players like Wanhua Chemical, BASF, Covestro, and Mitsui Chemicals have advanced capabilities in isocyanate production. These firms are investing in research and development to optimize processes, reduce energy consumption, and explore alternative raw materials. The focus is on incremental innovations rather than disruptive technologies, given the maturity of the industry.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has developed an innovative gas-phase process for isocyanate production, which significantly reduces energy consumption and production costs. This process utilizes a novel catalyst system that allows for higher conversion rates and selectivity[1]. The company has also implemented advanced process control systems and heat integration techniques to optimize energy efficiency. Additionally, Wanhua has invested in large-scale production facilities, enabling economies of scale and further cost reductions[2]. Their continuous improvement efforts focus on raw material efficiency and by-product utilization, contributing to overall cost reduction in isocyanate production.
Strengths: Advanced technology, economies of scale, and integrated production. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs and potential dependency on specific raw materials.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a proprietary gas-phase technology for isocyanate production, which offers significant cost advantages over traditional liquid-phase processes. This technology, known as the Gas Phase Technology (GPT), reduces energy consumption by up to 60% compared to conventional methods[3]. BASF's approach also includes the use of highly efficient catalysts and optimized reactor designs, resulting in improved yield and product quality. The company has implemented advanced process control systems and digital technologies to further enhance operational efficiency. BASF's commitment to circular economy principles has led to the development of recycling technologies for isocyanate by-products, contributing to overall cost reduction and sustainability[4].
Strengths: Highly efficient process, significant energy savings, and focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Complex technology implementation and potential high initial investment.
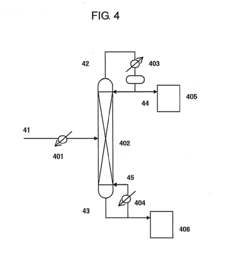
Innovative Catalysts and Process Optimizations
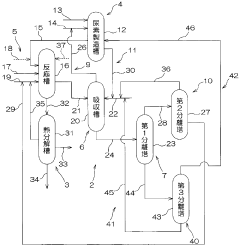
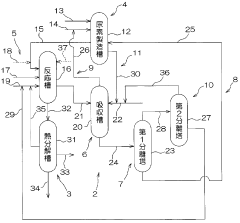
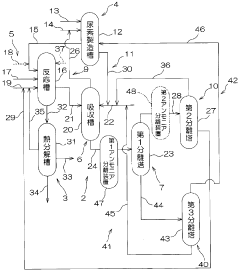
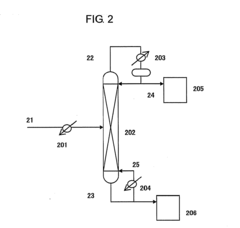
Carbamate production method, isocyanate production method, carbamate production device and isocyanate production device
PatentWO2011158598A1
Innovation
- A method and apparatus for producing isocyanate through a carbamate reaction involving ammonia, urea, and alcohol, where the by-products are efficiently recovered and recycled by absorbing gases with water in the presence of carbonate, allowing for the separation and reuse of ammonia and carbon dioxide, thereby reducing waste and costs.
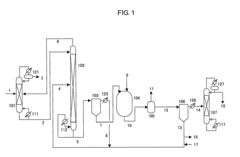
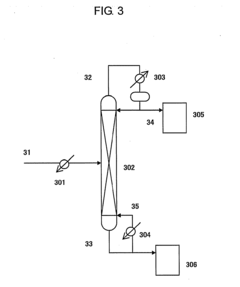
Process for producing isocyanate using diaryl carbonate
PatentInactiveEP2275405A1
Innovation
- A process involving the reaction of diaryl carbonates with amine compounds to form aryl carbamates, followed by transferring the reaction mixture to a thermal decomposition vessel where the aryl carbamates undergo thermal decomposition to produce isocyanates, with specific conditions and solvents used to enhance yield and purity, including the use of aromatic hydroxy compounds as solvents and acid cleaning to remove high-boiling point by-products.
Environmental Regulations Impact on Production Costs
Environmental regulations have a significant impact on the production costs of isocyanates, a key component in the manufacture of polyurethanes and other industrial products. These regulations, aimed at protecting human health and the environment, impose stringent requirements on isocyanate producers, often leading to increased operational expenses.
One of the primary areas affected by environmental regulations is emissions control. Isocyanate production processes generate various air pollutants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). To comply with air quality standards, manufacturers must invest in advanced emission control technologies such as thermal oxidizers, scrubbers, and catalytic converters. These systems require substantial capital investment and ongoing maintenance, contributing to higher production costs.
Water treatment is another critical aspect influenced by environmental regulations. Isocyanate production involves the use of large volumes of water, which can become contaminated with various chemicals. Stringent wastewater discharge limits necessitate the implementation of sophisticated water treatment systems, including biological treatment, advanced oxidation processes, and membrane filtration technologies. These systems not only require significant upfront investment but also incur ongoing operational and maintenance costs.
Waste management regulations also play a crucial role in shaping production costs. The disposal of hazardous waste generated during isocyanate production is subject to strict guidelines. Producers must invest in proper storage, handling, and disposal methods, often involving specialized equipment and facilities. Additionally, the costs associated with waste transportation and disposal at authorized treatment facilities can be substantial.
Environmental monitoring and reporting requirements further add to the overall production costs. Isocyanate manufacturers are typically required to conduct regular environmental assessments, maintain detailed records of emissions and waste generation, and submit periodic reports to regulatory authorities. These activities necessitate dedicated personnel and sophisticated monitoring equipment, contributing to increased operational expenses.
The implementation of best available techniques (BAT) and best environmental practices (BEP) as mandated by many environmental regulations can also lead to significant cost implications. These requirements often involve upgrading existing production processes or adopting new technologies to minimize environmental impact. While such improvements may result in long-term efficiency gains, they often require substantial initial investments and can temporarily disrupt production.
Furthermore, the evolving nature of environmental regulations poses additional challenges for isocyanate producers. As regulations become more stringent over time, manufacturers must continually adapt their processes and invest in new technologies to maintain compliance. This ongoing need for adaptation and improvement can result in recurring costs and potential production disruptions.
One of the primary areas affected by environmental regulations is emissions control. Isocyanate production processes generate various air pollutants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). To comply with air quality standards, manufacturers must invest in advanced emission control technologies such as thermal oxidizers, scrubbers, and catalytic converters. These systems require substantial capital investment and ongoing maintenance, contributing to higher production costs.
Water treatment is another critical aspect influenced by environmental regulations. Isocyanate production involves the use of large volumes of water, which can become contaminated with various chemicals. Stringent wastewater discharge limits necessitate the implementation of sophisticated water treatment systems, including biological treatment, advanced oxidation processes, and membrane filtration technologies. These systems not only require significant upfront investment but also incur ongoing operational and maintenance costs.
Waste management regulations also play a crucial role in shaping production costs. The disposal of hazardous waste generated during isocyanate production is subject to strict guidelines. Producers must invest in proper storage, handling, and disposal methods, often involving specialized equipment and facilities. Additionally, the costs associated with waste transportation and disposal at authorized treatment facilities can be substantial.
Environmental monitoring and reporting requirements further add to the overall production costs. Isocyanate manufacturers are typically required to conduct regular environmental assessments, maintain detailed records of emissions and waste generation, and submit periodic reports to regulatory authorities. These activities necessitate dedicated personnel and sophisticated monitoring equipment, contributing to increased operational expenses.
The implementation of best available techniques (BAT) and best environmental practices (BEP) as mandated by many environmental regulations can also lead to significant cost implications. These requirements often involve upgrading existing production processes or adopting new technologies to minimize environmental impact. While such improvements may result in long-term efficiency gains, they often require substantial initial investments and can temporarily disrupt production.
Furthermore, the evolving nature of environmental regulations poses additional challenges for isocyanate producers. As regulations become more stringent over time, manufacturers must continually adapt their processes and invest in new technologies to maintain compliance. This ongoing need for adaptation and improvement can result in recurring costs and potential production disruptions.
Supply Chain Optimization for Cost Efficiency
Supply chain optimization plays a crucial role in achieving cost reduction in isocyanate production. By streamlining the entire supply chain process, from raw material procurement to final product delivery, manufacturers can significantly lower production costs and improve overall efficiency.
One key aspect of supply chain optimization is the strategic sourcing of raw materials. Isocyanate production relies heavily on petrochemical feedstocks, which are subject to price volatility. Implementing a diversified supplier base and negotiating long-term contracts can help mitigate price fluctuations and ensure a stable supply of raw materials at competitive prices.
Inventory management is another critical area for cost reduction. Adopting just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices can minimize storage costs and reduce the risk of obsolescence. Advanced forecasting techniques and real-time inventory tracking systems enable manufacturers to maintain optimal stock levels, balancing the need for production continuity with the goal of minimizing working capital tied up in inventory.
Transportation and logistics optimization can yield substantial cost savings. Consolidating shipments, optimizing routes, and leveraging intermodal transportation options can reduce freight costs and improve delivery times. Implementing a centralized logistics management system allows for better coordination and visibility across the supply chain, leading to more efficient resource allocation and reduced transportation expenses.
Collaborative planning with suppliers and customers is essential for aligning production schedules with demand forecasts. This synchronization helps minimize overproduction and underproduction, reducing waste and associated costs. Implementing vendor-managed inventory (VMI) programs with key suppliers can further streamline the replenishment process and reduce administrative overhead.
Leveraging technology and data analytics can drive significant improvements in supply chain efficiency. Advanced planning and scheduling (APS) systems can optimize production schedules, while predictive maintenance algorithms can minimize unplanned downtime. Blockchain technology can enhance traceability and transparency across the supply chain, reducing the risk of disruptions and improving overall reliability.
Continuous improvement initiatives, such as Six Sigma and Lean manufacturing principles, should be applied throughout the supply chain. These methodologies can identify and eliminate inefficiencies, reduce waste, and improve overall productivity. Regular performance monitoring and benchmarking against industry standards can help identify areas for further optimization and cost reduction.
By implementing these supply chain optimization strategies, isocyanate producers can achieve significant cost reductions, improve operational efficiency, and enhance their competitive position in the market. The resulting savings can be reinvested in research and development, further driving innovation and long-term sustainability in isocyanate production.
One key aspect of supply chain optimization is the strategic sourcing of raw materials. Isocyanate production relies heavily on petrochemical feedstocks, which are subject to price volatility. Implementing a diversified supplier base and negotiating long-term contracts can help mitigate price fluctuations and ensure a stable supply of raw materials at competitive prices.
Inventory management is another critical area for cost reduction. Adopting just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices can minimize storage costs and reduce the risk of obsolescence. Advanced forecasting techniques and real-time inventory tracking systems enable manufacturers to maintain optimal stock levels, balancing the need for production continuity with the goal of minimizing working capital tied up in inventory.
Transportation and logistics optimization can yield substantial cost savings. Consolidating shipments, optimizing routes, and leveraging intermodal transportation options can reduce freight costs and improve delivery times. Implementing a centralized logistics management system allows for better coordination and visibility across the supply chain, leading to more efficient resource allocation and reduced transportation expenses.
Collaborative planning with suppliers and customers is essential for aligning production schedules with demand forecasts. This synchronization helps minimize overproduction and underproduction, reducing waste and associated costs. Implementing vendor-managed inventory (VMI) programs with key suppliers can further streamline the replenishment process and reduce administrative overhead.
Leveraging technology and data analytics can drive significant improvements in supply chain efficiency. Advanced planning and scheduling (APS) systems can optimize production schedules, while predictive maintenance algorithms can minimize unplanned downtime. Blockchain technology can enhance traceability and transparency across the supply chain, reducing the risk of disruptions and improving overall reliability.
Continuous improvement initiatives, such as Six Sigma and Lean manufacturing principles, should be applied throughout the supply chain. These methodologies can identify and eliminate inefficiencies, reduce waste, and improve overall productivity. Regular performance monitoring and benchmarking against industry standards can help identify areas for further optimization and cost reduction.
By implementing these supply chain optimization strategies, isocyanate producers can achieve significant cost reductions, improve operational efficiency, and enhance their competitive position in the market. The resulting savings can be reinvested in research and development, further driving innovation and long-term sustainability in isocyanate production.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!